Yixin Zhu
Interactive Spatial-Frequency Fusion Mamba for Multi-Modal Image Fusion
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Multi-Modal Image Fusion (MMIF) aims to combine images from different modalities to produce fused images, retaining texture details and preserving significant information. Recently, some MMIF methods incorporate frequency domain information to enhance spatial features. However, these methods typically rely on simple serial or parallel spatial-frequency fusion without interaction. In this paper, we propose a novel Interactive Spatial-Frequency Fusion Mamba (ISFM) framework for MMIF. Specifically, we begin with a Modality-Specific Extractor (MSE) to extract features from different modalities. It models long-range dependencies across the image with linear computational complexity. To effectively leverage frequency information, we then propose a Multi-scale Frequency Fusion (MFF). It adaptively integrates low-frequency and high-frequency components across multiple scales, enabling robust representations of frequency features. More importantly, we further propose an Interactive Spatial-Frequency Fusion (ISF). It incorporates frequency features to guide spatial features across modalities, enhancing complementary representations. Extensive experiments are conducted on six MMIF datasets. The experimental results demonstrate that our ISFM can achieve better performances than other state-of-the-art methods. The source code is available at https://github.com/Namn23/ISFM.
Learning Physics-Grounded 4D Dynamics with Neural Gaussian Force Fields
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Predicting physical dynamics from raw visual data remains a major challenge in AI. While recent video generation models have achieved impressive visual quality, they still cannot consistently generate physically plausible videos due to a lack of modeling of physical laws. Recent approaches combining 3D Gaussian splatting and physics engines can produce physically plausible videos, but are hindered by high computational costs in both reconstruction and simulation, and often lack robustness in complex real-world scenarios. To address these issues, we introduce Neural Gaussian Force Field (NGFF), an end-to-end neural framework that integrates 3D Gaussian perception with physics-based dynamic modeling to generate interactive, physically realistic 4D videos from multi-view RGB inputs, achieving two orders of magnitude faster than prior Gaussian simulators. To support training, we also present GSCollision, a 4D Gaussian dataset featuring diverse materials, multi-object interactions, and complex scenes, totaling over 640k rendered physical videos (~4 TB). Evaluations on synthetic and real 3D scenarios show NGFF's strong generalization and robustness in physical reasoning, advancing video prediction towards physics-grounded world models.
Code over Words: Overcoming Semantic Inertia via Code-Grounded Reasoning
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:LLMs struggle with Semantic Inertia: the inability to inhibit pre-trained priors (e.g., "Lava is Dangerous") when dynamic, in-context rules contradict them. We probe this phenomenon using Baba Is You, where physical laws are mutable text rules, enabling precise evaluation of models' ability to override learned priors when rules change. We quantatively observe that larger models can exhibit inverse scaling: they perform worse than smaller models when natural language reasoning requires suppressing pre-trained associations (e.g., accepting "Lava is Safe"). Our analysis attributes this to natural language encoding, which entangles descriptive semantics and logical rules, leading to persistent hallucinations of familiar physics despite explicit contradictory rules. Here we show that representing dynamics as executable code, rather than descriptive text, reverses this trend and enables effective prior inhibition. We introduce Code-Grounded Vistas (LCV), which fine-tunes models on counterfactual pairs and identifies states with contradictory rules, thereby forcing attention to logical constraints rather than visual semantics. This training-time approach outperforms expensive inference-time search methods in both efficiency and accuracy. Our results demonstrate that representation fundamentally determines whether scaling improves or impairs contextual reasoning. This challenges the assumption that larger models are universally better, with implications for domains that require dynamic overriding of learned priors.
UniAct: Unified Motion Generation and Action Streaming for Humanoid Robots
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:A long-standing objective in humanoid robotics is the realization of versatile agents capable of following diverse multimodal instructions with human-level flexibility. Despite advances in humanoid control, bridging high-level multimodal perception with whole-body execution remains a significant bottleneck. Existing methods often struggle to translate heterogeneous instructions -- such as language, music, and trajectories -- into stable, real-time actions. Here we show that UniAct, a two-stage framework integrating a fine-tuned MLLM with a causal streaming pipeline, enables humanoid robots to execute multimodal instructions with sub-500 ms latency. By unifying inputs through a shared discrete codebook via FSQ, UniAct ensures cross-modal alignment while constraining motions to a physically grounded manifold. This approach yields a 19% improvement in the success rate of zero-shot tracking of imperfect reference motions. We validate UniAct on UniMoCap, our 20-hour humanoid motion benchmark, demonstrating robust generalization across diverse real-world scenarios. Our results mark a critical step toward responsive, general-purpose humanoid assistants capable of seamless interaction through unified perception and control.
Simultaneous Tactile-Visual Perception for Learning Multimodal Robot Manipulation
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Robotic manipulation requires both rich multimodal perception and effective learning frameworks to handle complex real-world tasks. See-through-skin (STS) sensors, which combine tactile and visual perception, offer promising sensing capabilities, while modern imitation learning provides powerful tools for policy acquisition. However, existing STS designs lack simultaneous multimodal perception and suffer from unreliable tactile tracking. Furthermore, integrating these rich multimodal signals into learning-based manipulation pipelines remains an open challenge. We introduce TacThru, an STS sensor enabling simultaneous visual perception and robust tactile signal extraction, and TacThru-UMI, an imitation learning framework that leverages these multimodal signals for manipulation. Our sensor features a fully transparent elastomer, persistent illumination, novel keyline markers, and efficient tracking, while our learning system integrates these signals through a Transformer-based Diffusion Policy. Experiments on five challenging real-world tasks show that TacThru-UMI achieves an average success rate of 85.5%, significantly outperforming the baselines of alternating tactile-visual (66.3%) and vision-only (55.4%). The system excels in critical scenarios, including contact detection with thin and soft objects and precision manipulation requiring multimodal coordination. This work demonstrates that combining simultaneous multimodal perception with modern learning frameworks enables more precise, adaptable robotic manipulation.
Data-driven solar forecasting enables near-optimal economic decisions
Sep 08, 2025Abstract:Solar energy adoption is critical to achieving net-zero emissions. However, it remains difficult for many industrial and commercial actors to decide on whether they should adopt distributed solar-battery systems, which is largely due to the unavailability of fast, low-cost, and high-resolution irradiance forecasts. Here, we present SunCastNet, a lightweight data-driven forecasting system that provides 0.05$^\circ$, 10-minute resolution predictions of surface solar radiation downwards (SSRD) up to 7 days ahead. SunCastNet, coupled with reinforcement learning (RL) for battery scheduling, reduces operational regret by 76--93\% compared to robust decision making (RDM). In 25-year investment backtests, it enables up to five of ten high-emitting industrial sectors per region to cross the commercial viability threshold of 12\% Internal Rate of Return (IRR). These results show that high-resolution, long-horizon solar forecasts can directly translate into measurable economic gains, supporting near-optimal energy operations and accelerating renewable deployment.
ERSR: An Ellipse-constrained pseudo-label refinement and symmetric regularization framework for semi-supervised fetal head segmentation in ultrasound images
Aug 27, 2025
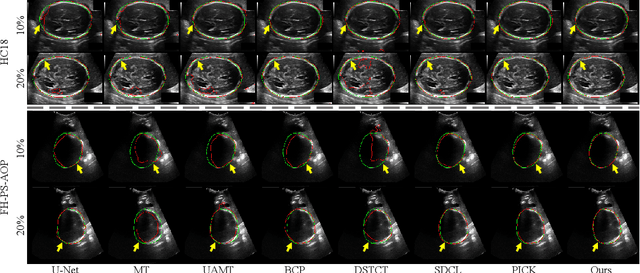

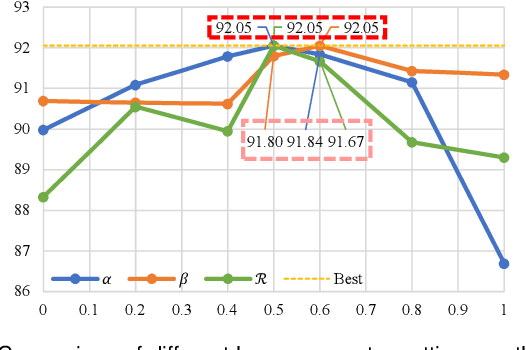
Abstract:Automated segmentation of the fetal head in ultrasound images is critical for prenatal monitoring. However, achieving robust segmentation remains challenging due to the poor quality of ultrasound images and the lack of annotated data. Semi-supervised methods alleviate the lack of annotated data but struggle with the unique characteristics of fetal head ultrasound images, making it challenging to generate reliable pseudo-labels and enforce effective consistency regularization constraints. To address this issue, we propose a novel semi-supervised framework, ERSR, for fetal head ultrasound segmentation. Our framework consists of the dual-scoring adaptive filtering strategy, the ellipse-constrained pseudo-label refinement, and the symmetry-based multiple consistency regularization. The dual-scoring adaptive filtering strategy uses boundary consistency and contour regularity criteria to evaluate and filter teacher outputs. The ellipse-constrained pseudo-label refinement refines these filtered outputs by fitting least-squares ellipses, which strengthens pixels near the center of the fitted ellipse and suppresses noise simultaneously. The symmetry-based multiple consistency regularization enforces multi-level consistency across perturbed images, symmetric regions, and between original predictions and pseudo-labels, enabling the model to capture robust and stable shape representations. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on two benchmarks. On the HC18 dataset, it reaches Dice scores of 92.05% and 95.36% with 10% and 20% labeled data, respectively. On the PSFH dataset, the scores are 91.68% and 93.70% under the same settings.
WeatherDiffusion: Weather-Guided Diffusion Model for Forward and Inverse Rendering
Aug 09, 2025Abstract:Forward and inverse rendering have emerged as key techniques for enabling understanding and reconstruction in the context of autonomous driving (AD). However, complex weather and illumination pose great challenges to this task. The emergence of large diffusion models has shown promise in achieving reasonable results through learning from 2D priors, but these models are difficult to control and lack robustness. In this paper, we introduce WeatherDiffusion, a diffusion-based framework for forward and inverse rendering on AD scenes with various weather and lighting conditions. Our method enables authentic estimation of material properties, scene geometry, and lighting, and further supports controllable weather and illumination editing through the use of predicted intrinsic maps guided by text descriptions. We observe that different intrinsic maps should correspond to different regions of the original image. Based on this observation, we propose Intrinsic map-aware attention (MAA) to enable high-quality inverse rendering. Additionally, we introduce a synthetic dataset (\ie WeatherSynthetic) and a real-world dataset (\ie WeatherReal) for forward and inverse rendering on AD scenes with diverse weather and lighting. Extensive experiments show that our WeatherDiffusion outperforms state-of-the-art methods on several benchmarks. Moreover, our method demonstrates significant value in downstream tasks for AD, enhancing the robustness of object detection and image segmentation in challenging weather scenarios.
CLONE: Closed-Loop Whole-Body Humanoid Teleoperation for Long-Horizon Tasks
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Humanoid teleoperation plays a vital role in demonstrating and collecting data for complex humanoid-scene interactions. However, current teleoperation systems face critical limitations: they decouple upper- and lower-body control to maintain stability, restricting natural coordination, and operate open-loop without real-time position feedback, leading to accumulated drift. The fundamental challenge is achieving precise, coordinated whole-body teleoperation over extended durations while maintaining accurate global positioning. Here we show that an MoE-based teleoperation system, CLONE, with closed-loop error correction enables unprecedented whole-body teleoperation fidelity, maintaining minimal positional drift over long-range trajectories using only head and hand tracking from an MR headset. Unlike previous methods that either sacrifice coordination for stability or suffer from unbounded drift, CLONE learns diverse motion skills while preventing tracking error accumulation through real-time feedback, enabling complex coordinated movements such as ``picking up objects from the ground.'' These results establish a new milestone for whole-body humanoid teleoperation for long-horizon humanoid-scene interaction tasks.
Multivariate Long-term Time Series Forecasting with Fourier Neural Filter
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Multivariate long-term time series forecasting has been suffering from the challenge of capturing both temporal dependencies within variables and spatial correlations across variables simultaneously. Current approaches predominantly repurpose backbones from natural language processing or computer vision (e.g., Transformers), which fail to adequately address the unique properties of time series (e.g., periodicity). The research community lacks a dedicated backbone with temporal-specific inductive biases, instead relying on domain-agnostic backbones supplemented with auxiliary techniques (e.g., signal decomposition). We introduce FNF as the backbone and DBD as the architecture to provide excellent learning capabilities and optimal learning pathways for spatio-temporal modeling, respectively. Our theoretical analysis proves that FNF unifies local time-domain and global frequency-domain information processing within a single backbone that extends naturally to spatial modeling, while information bottleneck theory demonstrates that DBD provides superior gradient flow and representation capacity compared to existing unified or sequential architectures. Our empirical evaluation across 11 public benchmark datasets spanning five domains (energy, meteorology, transportation, environment, and nature) confirms state-of-the-art performance with consistent hyperparameter settings. Notably, our approach achieves these results without any auxiliary techniques, suggesting that properly designed neural architectures can capture the inherent properties of time series, potentially transforming time series modeling in scientific and industrial applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge