Hongjie Li
UniAct: Unified Motion Generation and Action Streaming for Humanoid Robots
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:A long-standing objective in humanoid robotics is the realization of versatile agents capable of following diverse multimodal instructions with human-level flexibility. Despite advances in humanoid control, bridging high-level multimodal perception with whole-body execution remains a significant bottleneck. Existing methods often struggle to translate heterogeneous instructions -- such as language, music, and trajectories -- into stable, real-time actions. Here we show that UniAct, a two-stage framework integrating a fine-tuned MLLM with a causal streaming pipeline, enables humanoid robots to execute multimodal instructions with sub-500 ms latency. By unifying inputs through a shared discrete codebook via FSQ, UniAct ensures cross-modal alignment while constraining motions to a physically grounded manifold. This approach yields a 19% improvement in the success rate of zero-shot tracking of imperfect reference motions. We validate UniAct on UniMoCap, our 20-hour humanoid motion benchmark, demonstrating robust generalization across diverse real-world scenarios. Our results mark a critical step toward responsive, general-purpose humanoid assistants capable of seamless interaction through unified perception and control.
LoG3D: Ultra-High-Resolution 3D Shape Modeling via Local-to-Global Partitioning
Nov 18, 2025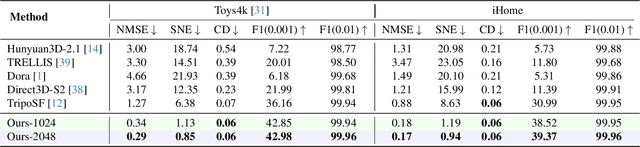
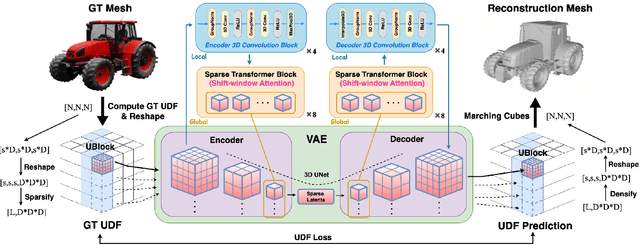
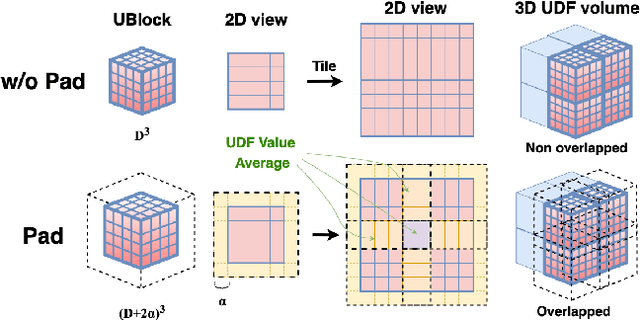
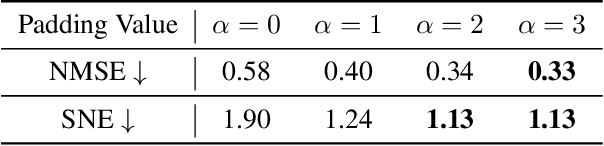
Abstract:Generating high-fidelity 3D contents remains a fundamental challenge due to the complexity of representing arbitrary topologies-such as open surfaces and intricate internal structures-while preserving geometric details. Prevailing methods based on signed distance fields (SDFs) are hampered by costly watertight preprocessing and struggle with non-manifold geometries, while point-cloud representations often suffer from sampling artifacts and surface discontinuities. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel 3D variational autoencoder (VAE) framework built upon unsigned distance fields (UDFs)-a more robust and computationally efficient representation that naturally handles complex and incomplete shapes. Our core innovation is a local-to-global (LoG) architecture that processes the UDF by partitioning it into uniform subvolumes, termed UBlocks. This architecture couples 3D convolutions for capturing local detail with sparse transformers for enforcing global coherence. A Pad-Average strategy further ensures smooth transitions at subvolume boundaries during reconstruction. This modular design enables seamless scaling to ultra-high resolutions up to $2048^3$-a regime previously unattainable for 3D VAEs. Experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in both reconstruction accuracy and generative quality, yielding superior surface smoothness and geometric flexibility.
Dynamic Motion Blending for Versatile Motion Editing
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Text-guided motion editing enables high-level semantic control and iterative modifications beyond traditional keyframe animation. Existing methods rely on limited pre-collected training triplets, which severely hinders their versatility in diverse editing scenarios. We introduce MotionCutMix, an online data augmentation technique that dynamically generates training triplets by blending body part motions based on input text. While MotionCutMix effectively expands the training distribution, the compositional nature introduces increased randomness and potential body part incoordination. To model such a rich distribution, we present MotionReFit, an auto-regressive diffusion model with a motion coordinator. The auto-regressive architecture facilitates learning by decomposing long sequences, while the motion coordinator mitigates the artifacts of motion composition. Our method handles both spatial and temporal motion edits directly from high-level human instructions, without relying on additional specifications or Large Language Models. Through extensive experiments, we show that MotionReFit achieves state-of-the-art performance in text-guided motion editing.
ZeroHSI: Zero-Shot 4D Human-Scene Interaction by Video Generation
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Human-scene interaction (HSI) generation is crucial for applications in embodied AI, virtual reality, and robotics. While existing methods can synthesize realistic human motions in 3D scenes and generate plausible human-object interactions, they heavily rely on datasets containing paired 3D scene and motion capture data, which are expensive and time-consuming to collect across diverse environments and interactions. We present ZeroHSI, a novel approach that enables zero-shot 4D human-scene interaction synthesis by integrating video generation and neural human rendering. Our key insight is to leverage the rich motion priors learned by state-of-the-art video generation models, which have been trained on vast amounts of natural human movements and interactions, and use differentiable rendering to reconstruct human-scene interactions. ZeroHSI can synthesize realistic human motions in both static scenes and environments with dynamic objects, without requiring any ground-truth motion data. We evaluate ZeroHSI on a curated dataset of different types of various indoor and outdoor scenes with different interaction prompts, demonstrating its ability to generate diverse and contextually appropriate human-scene interactions.
GeoTexDensifier: Geometry-Texture-Aware Densification for High-Quality Photorealistic 3D Gaussian Splatting
Dec 22, 2024



Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently attracted wide attentions in various areas such as 3D navigation, Virtual Reality (VR) and 3D simulation, due to its photorealistic and efficient rendering performance. High-quality reconstrution of 3DGS relies on sufficient splats and a reasonable distribution of these splats to fit real geometric surface and texture details, which turns out to be a challenging problem. We present GeoTexDensifier, a novel geometry-texture-aware densification strategy to reconstruct high-quality Gaussian splats which better comply with the geometric structure and texture richness of the scene. Specifically, our GeoTexDensifier framework carries out an auxiliary texture-aware densification method to produce a denser distribution of splats in fully textured areas, while keeping sparsity in low-texture regions to maintain the quality of Gaussian point cloud. Meanwhile, a geometry-aware splitting strategy takes depth and normal priors to guide the splitting sampling and filter out the noisy splats whose initial positions are far from the actual geometric surfaces they aim to fit, under a Validation of Depth Ratio Change checking. With the help of relative monocular depth prior, such geometry-aware validation can effectively reduce the influence of scattered Gaussians to the final rendering quality, especially in regions with weak textures or without sufficient training views. The texture-aware densification and geometry-aware splitting strategies are fully combined to obtain a set of high-quality Gaussian splats. We experiment our GeoTexDensifier framework on various datasets and compare our Novel View Synthesis results to other state-of-the-art 3DGS approaches, with detailed quantitative and qualitative evaluations to demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in producing more photorealistic 3DGS models.
Autonomous Character-Scene Interaction Synthesis from Text Instruction
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:Synthesizing human motions in 3D environments, particularly those with complex activities such as locomotion, hand-reaching, and human-object interaction, presents substantial demands for user-defined waypoints and stage transitions. These requirements pose challenges for current models, leading to a notable gap in automating the animation of characters from simple human inputs. This paper addresses this challenge by introducing a comprehensive framework for synthesizing multi-stage scene-aware interaction motions directly from a single text instruction and goal location. Our approach employs an auto-regressive diffusion model to synthesize the next motion segment, along with an autonomous scheduler predicting the transition for each action stage. To ensure that the synthesized motions are seamlessly integrated within the environment, we propose a scene representation that considers the local perception both at the start and the goal location. We further enhance the coherence of the generated motion by integrating frame embeddings with language input. Additionally, to support model training, we present a comprehensive motion-captured dataset comprising 16 hours of motion sequences in 120 indoor scenes covering 40 types of motions, each annotated with precise language descriptions. Experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of our method in generating high-quality, multi-stage motions closely aligned with environmental and textual conditions.
Scaling Up Dynamic Human-Scene Interaction Modeling
Mar 13, 2024Abstract:Confronting the challenges of data scarcity and advanced motion synthesis in human-scene interaction modeling, we introduce the TRUMANS dataset alongside a novel HSI motion synthesis method. TRUMANS stands as the most comprehensive motion-captured HSI dataset currently available, encompassing over 15 hours of human interactions across 100 indoor scenes. It intricately captures whole-body human motions and part-level object dynamics, focusing on the realism of contact. This dataset is further scaled up by transforming physical environments into exact virtual models and applying extensive augmentations to appearance and motion for both humans and objects while maintaining interaction fidelity. Utilizing TRUMANS, we devise a diffusion-based autoregressive model that efficiently generates HSI sequences of any length, taking into account both scene context and intended actions. In experiments, our approach shows remarkable zero-shot generalizability on a range of 3D scene datasets (e.g., PROX, Replica, ScanNet, ScanNet++), producing motions that closely mimic original motion-captured sequences, as confirmed by quantitative experiments and human studies.
Learning Deformable Hypothesis Sampling for Accurate PatchMatch Multi-View Stereo
Dec 26, 2023Abstract:This paper introduces a learnable Deformable Hypothesis Sampler (DeformSampler) to address the challenging issue of noisy depth estimation for accurate PatchMatch Multi-View Stereo (MVS). We observe that the heuristic depth hypothesis sampling modes employed by PatchMatch MVS solvers are insensitive to (i) the piece-wise smooth distribution of depths across the object surface, and (ii) the implicit multi-modal distribution of depth prediction probabilities along the ray direction on the surface points. Accordingly, we develop DeformSampler to learn distribution-sensitive sample spaces to (i) propagate depths consistent with the scene's geometry across the object surface, and (ii) fit a Laplace Mixture model that approaches the point-wise probabilities distribution of the actual depths along the ray direction. We integrate DeformSampler into a learnable PatchMatch MVS system to enhance depth estimation in challenging areas, such as piece-wise discontinuous surface boundaries and weakly-textured regions. Experimental results on DTU and Tanks \& Temples datasets demonstrate its superior performance and generalization capabilities compared to state-of-the-art competitors. Code is available at https://github.com/Geo-Tell/DS-PMNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge