Xiaomeng Zhu
ProAct: A Benchmark and Multimodal Framework for Structure-Aware Proactive Response
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:While passive agents merely follow instructions, proactive agents align with higher-level objectives, such as assistance and safety by continuously monitoring the environment to determine when and how to act. However, developing proactive agents is hindered by the lack of specialized resources. To address this, we introduce ProAct-75, a benchmark designed to train and evaluate proactive agents across diverse domains, including assistance, maintenance, and safety monitoring. Spanning 75 tasks, our dataset features 91,581 step-level annotations enriched with explicit task graphs. These graphs encode step dependencies and parallel execution possibilities, providing the structural grounding necessary for complex decision-making. Building on this benchmark, we propose ProAct-Helper, a reference baseline powered by a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) that grounds decision-making in state detection, and leveraging task graphs to enable entropy-driven heuristic search for action selection, allowing agents to execute parallel threads independently rather than mirroring the human's next step. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ProAct-Helper outperforms strong closed-source models, improving trigger detection mF1 by 6.21%, saving 0.25 more steps in online one-step decision, and increasing the rate of parallel actions by 15.58%.
DeltaFlow: An Efficient Multi-frame Scene Flow Estimation Method
Aug 23, 2025



Abstract:Previous dominant methods for scene flow estimation focus mainly on input from two consecutive frames, neglecting valuable information in the temporal domain. While recent trends shift towards multi-frame reasoning, they suffer from rapidly escalating computational costs as the number of frames grows. To leverage temporal information more efficiently, we propose DeltaFlow ($\Delta$Flow), a lightweight 3D framework that captures motion cues via a $\Delta$ scheme, extracting temporal features with minimal computational cost, regardless of the number of frames. Additionally, scene flow estimation faces challenges such as imbalanced object class distributions and motion inconsistency. To tackle these issues, we introduce a Category-Balanced Loss to enhance learning across underrepresented classes and an Instance Consistency Loss to enforce coherent object motion, improving flow accuracy. Extensive evaluations on the Argoverse 2 and Waymo datasets show that $\Delta$Flow achieves state-of-the-art performance with up to 22% lower error and $2\times$ faster inference compared to the next-best multi-frame supervised method, while also demonstrating a strong cross-domain generalization ability. The code is open-sourced at https://github.com/Kin-Zhang/DeltaFlow along with trained model weights.
The Structural Sources of Verb Meaning Revisited: Large Language Models Display Syntactic Bootstrapping
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:Syntactic bootstrapping (Gleitman, 1990) is the hypothesis that children use the syntactic environments in which a verb occurs to learn its meaning. In this paper, we examine whether large language models exhibit a similar behavior. We do this by training RoBERTa and GPT-2 on perturbed datasets where syntactic information is ablated. Our results show that models' verb representation degrades more when syntactic cues are removed than when co-occurrence information is removed. Furthermore, the representation of mental verbs, for which syntactic bootstrapping has been shown to be particularly crucial in human verb learning, is more negatively impacted in such training regimes than physical verbs. In contrast, models' representation of nouns is affected more when co-occurrences are distorted than when syntax is distorted. In addition to reinforcing the important role of syntactic bootstrapping in verb learning, our results demonstrated the viability of testing developmental hypotheses on a larger scale through manipulating the learning environments of large language models.
Domain Randomization for Object Detection in Manufacturing Applications using Synthetic Data: A Comprehensive Study
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses key aspects of domain randomization in generating synthetic data for manufacturing object detection applications. To this end, we present a comprehensive data generation pipeline that reflects different factors: object characteristics, background, illumination, camera settings, and post-processing. We also introduce the Synthetic Industrial Parts Object Detection dataset (SIP15-OD) consisting of 15 objects from three industrial use cases under varying environments as a test bed for the study, while also employing an industrial dataset publicly available for robotic applications. In our experiments, we present more abundant results and insights into the feasibility as well as challenges of sim-to-real object detection. In particular, we identified material properties, rendering methods, post-processing, and distractors as important factors. Our method, leveraging these, achieves top performance on the public dataset with Yolov8 models trained exclusively on synthetic data; mAP@50 scores of 96.4% for the robotics dataset, and 94.1%, 99.5%, and 95.3% across three of the SIP15-OD use cases, respectively. The results showcase the effectiveness of the proposed domain randomization, potentially covering the distribution close to real data for the applications.
Afford-X: Generalizable and Slim Affordance Reasoning for Task-oriented Manipulation
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Object affordance reasoning, the ability to infer object functionalities based on physical properties, is fundamental for task-oriented planning and activities in both humans and Artificial Intelligence (AI). This capability, required for planning and executing daily activities in a task-oriented manner, relies on commonsense knowledge of object physics and functionalities, extending beyond simple object recognition. Current computational models for affordance reasoning from perception lack generalizability, limiting their applicability in novel scenarios. Meanwhile, comprehensive Large Language Models (LLMs) with emerging reasoning capabilities are challenging to deploy on local devices for task-oriented manipulations. Here, we introduce LVIS-Aff, a large-scale dataset comprising 1,496 tasks and 119k images, designed to enhance the generalizability of affordance reasoning from perception. Utilizing this dataset, we develop Afford-X, an end-to-end trainable affordance reasoning model that incorporates Verb Attention and Bi-Fusion modules to improve multi-modal understanding. This model achieves up to a 12.1% performance improvement over the best-reported results from non-LLM methods, while also demonstrating a 1.2% enhancement compared to our previous conference paper. Additionally, it maintains a compact 187M parameter size and infers nearly 50 times faster than the GPT-4V API. Our work demonstrates the potential for efficient, generalizable affordance reasoning models that can be deployed on local devices for task-oriented manipulations. We showcase Afford-X's effectiveness in enabling task-oriented manipulations for robots across various tasks and environments, underscoring its efficiency and broad implications for advancing robotics and AI systems in real-world applications.
Meaning Beyond Truth Conditions: Evaluating Discourse Level Understanding via Anaphora Accessibility
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:We present a hierarchy of natural language understanding abilities and argue for the importance of moving beyond assessments of understanding at the lexical and sentence levels to the discourse level. We propose the task of anaphora accessibility as a diagnostic for assessing discourse understanding, and to this end, present an evaluation dataset inspired by theoretical research in dynamic semantics. We evaluate human and LLM performance on our dataset and find that LLMs and humans align on some tasks and diverge on others. Such divergence can be explained by LLMs' reliance on specific lexical items during language comprehension, in contrast to human sensitivity to structural abstractions.
ImpScore: A Learnable Metric For Quantifying The Implicitness Level of Language
Nov 07, 2024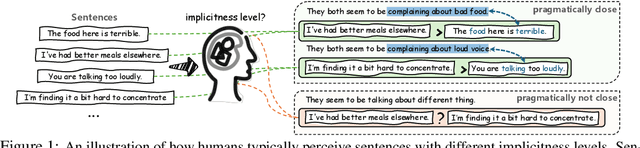
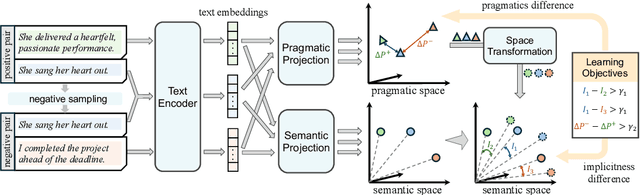

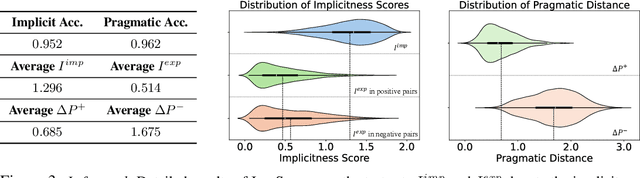
Abstract:Handling implicit language is essential for natural language processing systems to achieve precise text understanding and facilitate natural interactions with users. Despite its importance, the absence of a robust metric for accurately measuring the implicitness of language significantly constrains the depth of analysis possible in evaluating models' comprehension capabilities. This paper addresses this gap by developing a scalar metric that quantifies the implicitness level of language without relying on external references. Drawing on principles from traditional linguistics, we define ''implicitness'' as the divergence between semantic meaning and pragmatic interpretation. To operationalize this definition, we introduce ImpScore, a novel, reference-free metric formulated through an interpretable regression model. This model is trained using pairwise contrastive learning on a specially curated dataset comprising $112,580$ (implicit sentence, explicit sentence) pairs. We validate ImpScore through a user study that compares its assessments with human evaluations on out-of-distribution data, demonstrating its accuracy and strong correlation with human judgments. Additionally, we apply ImpScore to hate speech detection datasets, illustrating its utility and highlighting significant limitations in current large language models' ability to understand highly implicit content. The metric model and its training data are available at https://github.com/audreycs/ImpScore.
Aeroengine performance prediction using a physical-embedded data-driven method
Jun 29, 2024Abstract:Accurate and efficient prediction of aeroengine performance is of paramount importance for engine design, maintenance, and optimization endeavours. However, existing methodologies often struggle to strike an optimal balance among predictive accuracy, computational efficiency, modelling complexity, and data dependency. To address these challenges, we propose a strategy that synergistically combines domain knowledge from both the aeroengine and neural network realms to enable real-time prediction of engine performance parameters. Leveraging aeroengine domain knowledge, we judiciously design the network structure and regulate the internal information flow. Concurrently, drawing upon neural network domain expertise, we devise four distinct feature fusion methods and introduce an innovative loss function formulation. To rigorously evaluate the effectiveness and robustness of our proposed strategy, we conduct comprehensive validation across two distinct datasets. The empirical results demonstrate :(1) the evident advantages of our tailored loss function; (2) our model's ability to maintain equal or superior performance with a reduced parameter count; (3) our model's reduced data dependency compared to generalized neural network architectures; (4)Our model is more interpretable than traditional black box machine learning methods.
Towards Sim-to-Real Industrial Parts Classification with Synthetic Dataset
Apr 12, 2024



Abstract:This paper is about effectively utilizing synthetic data for training deep neural networks for industrial parts classification, in particular, by taking into account the domain gap against real-world images. To this end, we introduce a synthetic dataset that may serve as a preliminary testbed for the Sim-to-Real challenge; it contains 17 objects of six industrial use cases, including isolated and assembled parts. A few subsets of objects exhibit large similarities in shape and albedo for reflecting challenging cases of industrial parts. All the sample images come with and without random backgrounds and post-processing for evaluating the importance of domain randomization. We call it Synthetic Industrial Parts dataset (SIP-17). We study the usefulness of SIP-17 through benchmarking the performance of five state-of-the-art deep network models, supervised and self-supervised, trained only on the synthetic data while testing them on real data. By analyzing the results, we deduce some insights on the feasibility and challenges of using synthetic data for industrial parts classification and for further developing larger-scale synthetic datasets. Our dataset and code are publicly available.
* Published in 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW)
LIEDER: Linguistically-Informed Evaluation for Discourse Entity Recognition
Mar 10, 2024



Abstract:Discourse Entity (DE) recognition is the task of identifying novel and known entities introduced within a text. While previous work has found that large language models have basic, if imperfect, DE recognition abilities (Schuster and Linzen, 2022), it remains largely unassessed which of the fundamental semantic properties that govern the introduction and subsequent reference to DEs they have knowledge of. We propose the Linguistically-Informed Evaluation for Discourse Entity Recognition (LIEDER) dataset that allows for a detailed examination of language models' knowledge of four crucial semantic properties: existence, uniqueness, plurality, and novelty. We find evidence that state-of-the-art large language models exhibit sensitivity to all of these properties except novelty, which demonstrates that they have yet to reach human-level language understanding abilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge