Scott Hauck
Building Machine Learning Challenges for Anomaly Detection in Science
Mar 03, 2025



Abstract:Scientific discoveries are often made by finding a pattern or object that was not predicted by the known rules of science. Oftentimes, these anomalous events or objects that do not conform to the norms are an indication that the rules of science governing the data are incomplete, and something new needs to be present to explain these unexpected outliers. The challenge of finding anomalies can be confounding since it requires codifying a complete knowledge of the known scientific behaviors and then projecting these known behaviors on the data to look for deviations. When utilizing machine learning, this presents a particular challenge since we require that the model not only understands scientific data perfectly but also recognizes when the data is inconsistent and out of the scope of its trained behavior. In this paper, we present three datasets aimed at developing machine learning-based anomaly detection for disparate scientific domains covering astrophysics, genomics, and polar science. We present the different datasets along with a scheme to make machine learning challenges around the three datasets findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable (FAIR). Furthermore, we present an approach that generalizes to future machine learning challenges, enabling the possibility of large, more compute-intensive challenges that can ultimately lead to scientific discovery.
Low Latency Transformer Inference on FPGAs for Physics Applications with hls4ml
Sep 08, 2024



Abstract:This study presents an efficient implementation of transformer architectures in Field-Programmable Gate Arrays(FPGAs) using hls4ml. We demonstrate the strategy for implementing the multi-head attention, softmax, and normalization layer and evaluate three distinct models. Their deployment on VU13P FPGA chip achieved latency less than 2us, demonstrating the potential for real-time applications. HLS4ML compatibility with any TensorFlow-built transformer model further enhances the scalability and applicability of this work. Index Terms: FPGAs, machine learning, transformers, high energy physics, LIGO
FPGA Deployment of LFADS for Real-time Neuroscience Experiments
Feb 02, 2024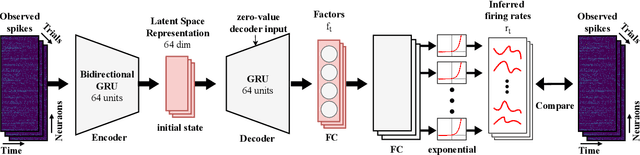

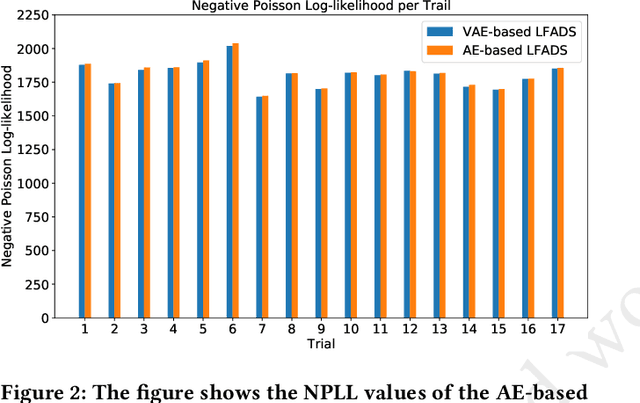
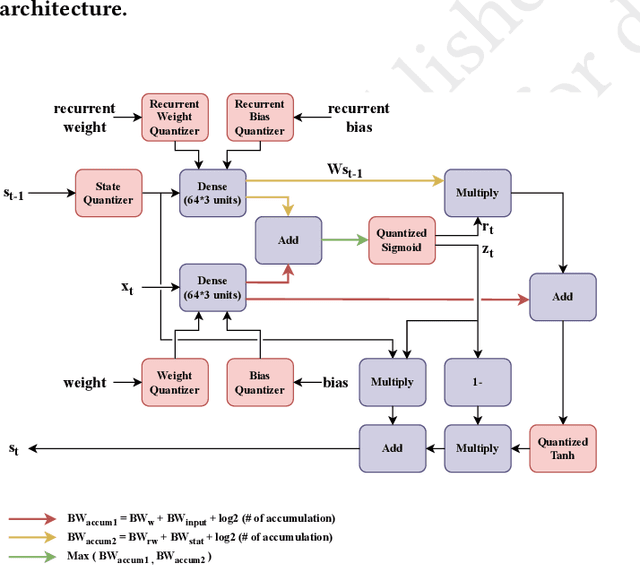
Abstract:Large-scale recordings of neural activity are providing new opportunities to study neural population dynamics. A powerful method for analyzing such high-dimensional measurements is to deploy an algorithm to learn the low-dimensional latent dynamics. LFADS (Latent Factor Analysis via Dynamical Systems) is a deep learning method for inferring latent dynamics from high-dimensional neural spiking data recorded simultaneously in single trials. This method has shown a remarkable performance in modeling complex brain signals with an average inference latency in milliseconds. As our capacity of simultaneously recording many neurons is increasing exponentially, it is becoming crucial to build capacity for deploying low-latency inference of the computing algorithms. To improve the real-time processing ability of LFADS, we introduce an efficient implementation of the LFADS models onto Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGA). Our implementation shows an inference latency of 41.97 $\mu$s for processing the data in a single trial on a Xilinx U55C.
* 6 pages, 8 figures
Ultra Fast Transformers on FPGAs for Particle Physics Experiments
Feb 01, 2024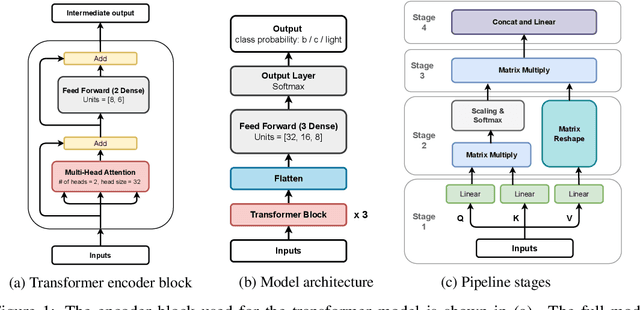
Abstract:This work introduces a highly efficient implementation of the transformer architecture on a Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) by using the \texttt{hls4ml} tool. Given the demonstrated effectiveness of transformer models in addressing a wide range of problems, their application in experimental triggers within particle physics becomes a subject of significant interest. In this work, we have implemented critical components of a transformer model, such as multi-head attention and softmax layers. To evaluate the effectiveness of our implementation, we have focused on a particle physics jet flavor tagging problem, employing a public dataset. We recorded latency under 2 $\mu$s on the Xilinx UltraScale+ FPGA, which is compatible with hardware trigger requirements at the CERN Large Hadron Collider experiments.
* 6 pages, 2 figures
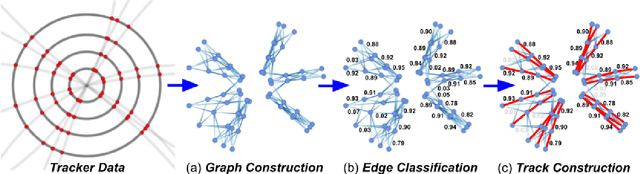
Low Latency Edge Classification GNN for Particle Trajectory Tracking on FPGAs
Jun 27, 2023Abstract:In-time particle trajectory reconstruction in the Large Hadron Collider is challenging due to the high collision rate and numerous particle hits. Using GNN (Graph Neural Network) on FPGA has enabled superior accuracy with flexible trajectory classification. However, existing GNN architectures have inefficient resource usage and insufficient parallelism for edge classification. This paper introduces a resource-efficient GNN architecture on FPGAs for low latency particle tracking. The modular architecture facilitates design scalability to support large graphs. Leveraging the geometric properties of hit detectors further reduces graph complexity and resource usage. Our results on Xilinx UltraScale+ VU9P demonstrate 1625x and 1574x performance improvement over CPU and GPU respectively.
Ultra-low latency recurrent neural network inference on FPGAs for physics applications with hls4ml
Jul 01, 2022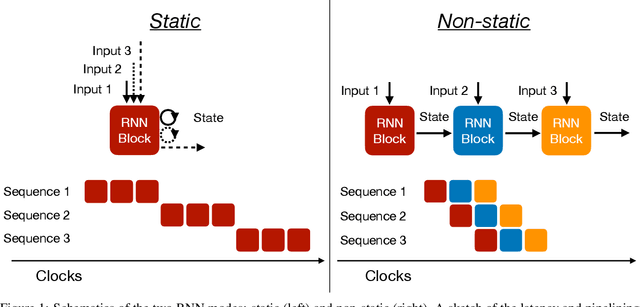
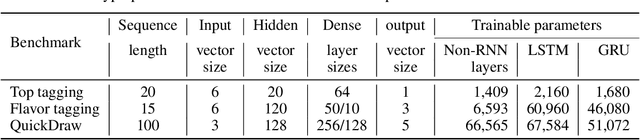
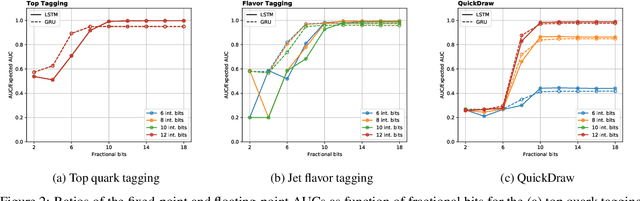

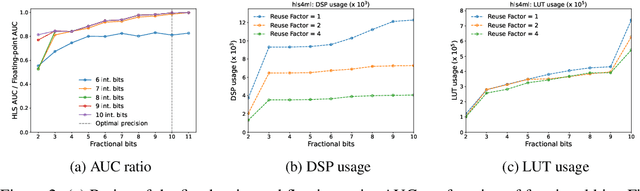
Abstract:Recurrent neural networks have been shown to be effective architectures for many tasks in high energy physics, and thus have been widely adopted. Their use in low-latency environments has, however, been limited as a result of the difficulties of implementing recurrent architectures on field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). In this paper we present an implementation of two types of recurrent neural network layers -- long short-term memory and gated recurrent unit -- within the hls4ml framework. We demonstrate that our implementation is capable of producing effective designs for both small and large models, and can be customized to meet specific design requirements for inference latencies and FPGA resources. We show the performance and synthesized designs for multiple neural networks, many of which are trained specifically for jet identification tasks at the CERN Large Hadron Collider.
Open-source FPGA-ML codesign for the MLPerf Tiny Benchmark
Jun 23, 2022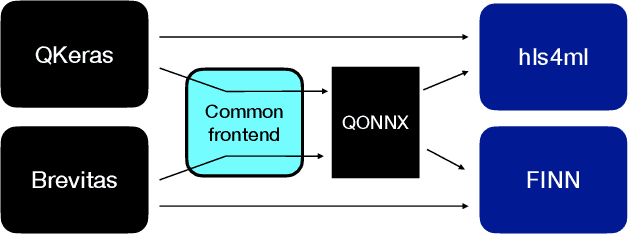
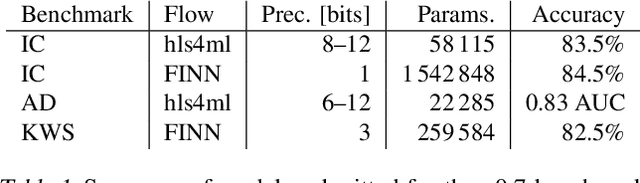
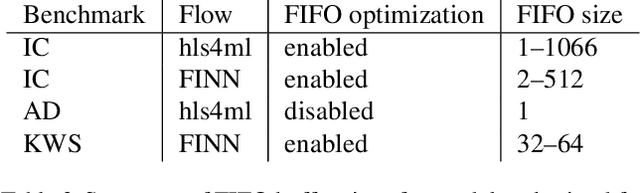
Abstract:We present our development experience and recent results for the MLPerf Tiny Inference Benchmark on field-programmable gate array (FPGA) platforms. We use the open-source hls4ml and FINN workflows, which aim to democratize AI-hardware codesign of optimized neural networks on FPGAs. We present the design and implementation process for the keyword spotting, anomaly detection, and image classification benchmark tasks. The resulting hardware implementations are quantized, configurable, spatial dataflow architectures tailored for speed and efficiency and introduce new generic optimizations and common workflows developed as a part of this work. The full workflow is presented from quantization-aware training to FPGA implementation. The solutions are deployed on system-on-chip (Pynq-Z2) and pure FPGA (Arty A7-100T) platforms. The resulting submissions achieve latencies as low as 20 $\mu$s and energy consumption as low as 30 $\mu$J per inference. We demonstrate how emerging ML benchmarks on heterogeneous hardware platforms can catalyze collaboration and the development of new techniques and more accessible tools.
QONNX: Representing Arbitrary-Precision Quantized Neural Networks
Jun 17, 2022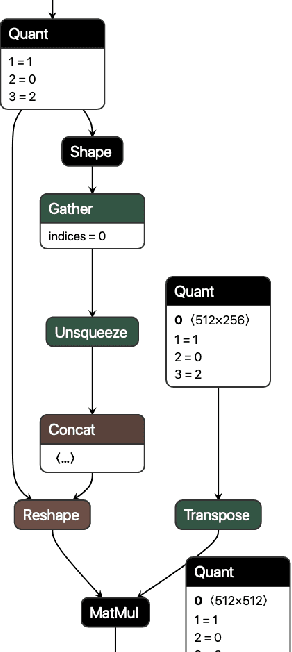
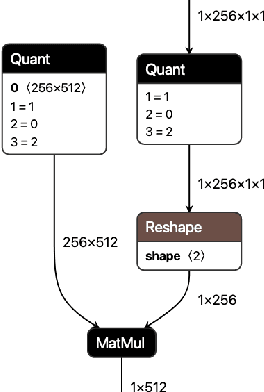
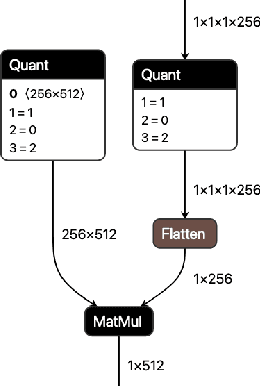
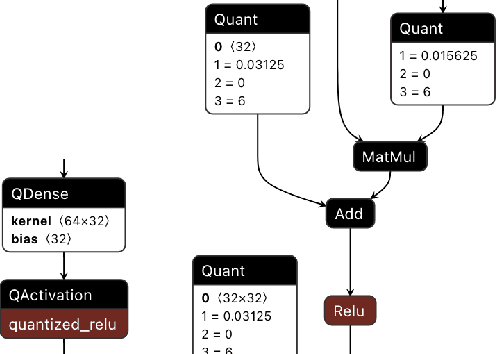
Abstract:We present extensions to the Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX) intermediate representation format to represent arbitrary-precision quantized neural networks. We first introduce support for low precision quantization in existing ONNX-based quantization formats by leveraging integer clipping, resulting in two new backward-compatible variants: the quantized operator format with clipping and quantize-clip-dequantize (QCDQ) format. We then introduce a novel higher-level ONNX format called quantized ONNX (QONNX) that introduces three new operators -- Quant, BipolarQuant, and Trunc -- in order to represent uniform quantization. By keeping the QONNX IR high-level and flexible, we enable targeting a wider variety of platforms. We also present utilities for working with QONNX, as well as examples of its usage in the FINN and hls4ml toolchains. Finally, we introduce the QONNX model zoo to share low-precision quantized neural networks.
Physics Community Needs, Tools, and Resources for Machine Learning
Mar 30, 2022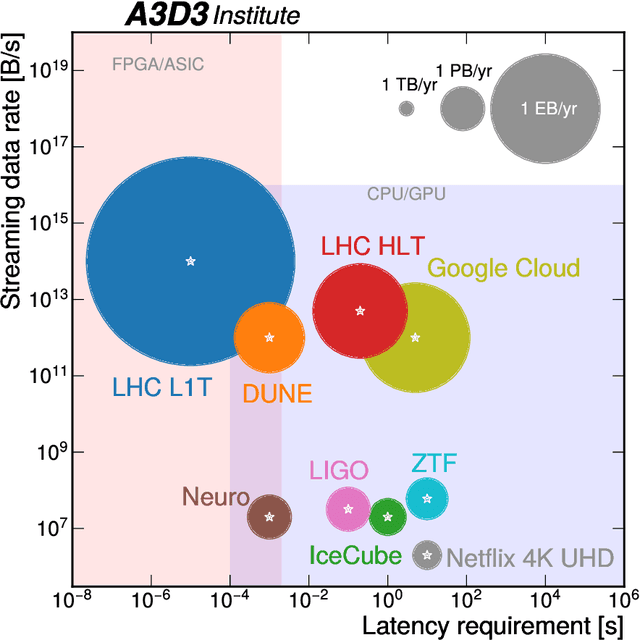
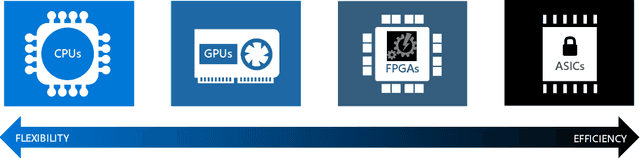
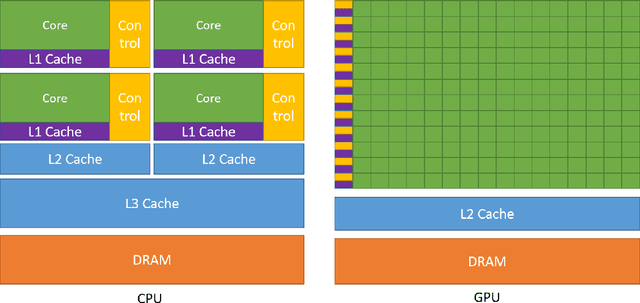
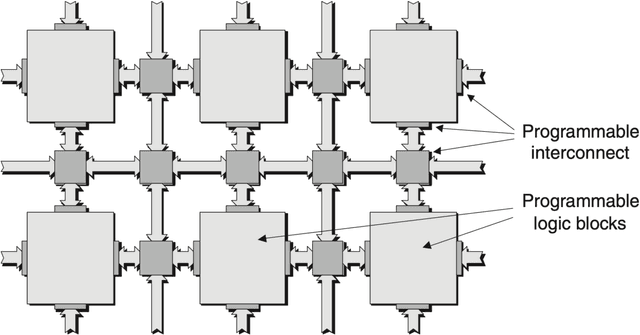
Abstract:Machine learning (ML) is becoming an increasingly important component of cutting-edge physics research, but its computational requirements present significant challenges. In this white paper, we discuss the needs of the physics community regarding ML across latency and throughput regimes, the tools and resources that offer the possibility of addressing these needs, and how these can be best utilized and accessed in the coming years.
Applications and Techniques for Fast Machine Learning in Science
Oct 25, 2021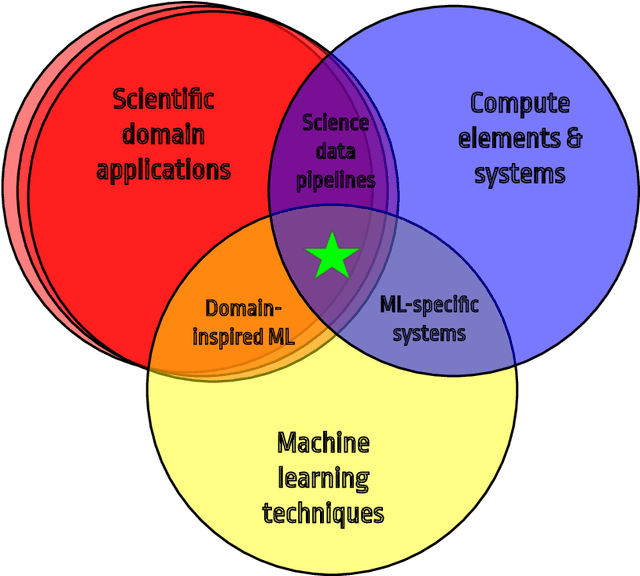
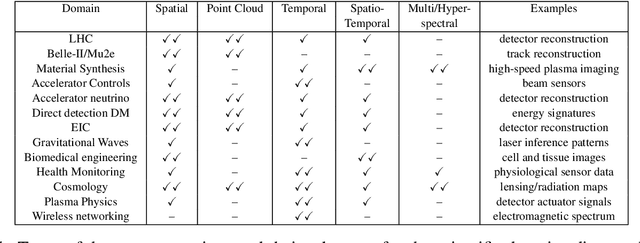
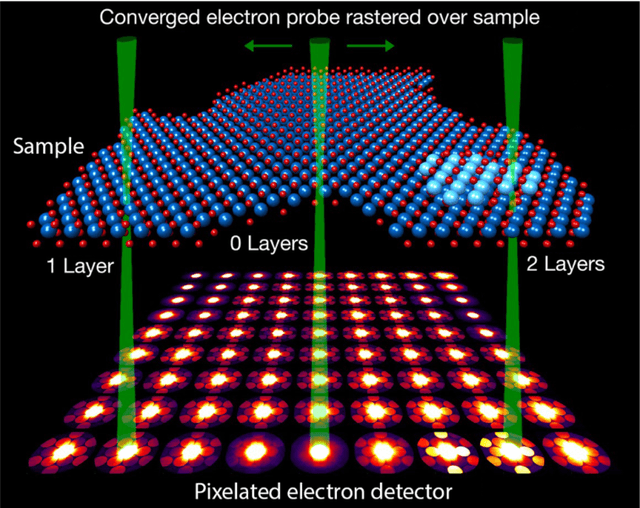
Abstract:In this community review report, we discuss applications and techniques for fast machine learning (ML) in science -- the concept of integrating power ML methods into the real-time experimental data processing loop to accelerate scientific discovery. The material for the report builds on two workshops held by the Fast ML for Science community and covers three main areas: applications for fast ML across a number of scientific domains; techniques for training and implementing performant and resource-efficient ML algorithms; and computing architectures, platforms, and technologies for deploying these algorithms. We also present overlapping challenges across the multiple scientific domains where common solutions can be found. This community report is intended to give plenty of examples and inspiration for scientific discovery through integrated and accelerated ML solutions. This is followed by a high-level overview and organization of technical advances, including an abundance of pointers to source material, which can enable these breakthroughs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge