Yulun Wu
P1-VL: Bridging Visual Perception and Scientific Reasoning in Physics Olympiads
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:The transition from symbolic manipulation to science-grade reasoning represents a pivotal frontier for Large Language Models (LLMs), with physics serving as the critical test anchor for binding abstract logic to physical reality. Physics demands that a model maintain physical consistency with the laws governing the universe, a task that fundamentally requires multimodal perception to ground abstract logic in reality. At the Olympiad level, diagrams are often constitutive rather than illustrative, containing essential constraints, such as boundary conditions and spatial symmetries, that are absent from the text. To bridge this visual-logical gap, we introduce P1-VL, a family of open-source vision-language models engineered for advanced scientific reasoning. Our method harmonizes Curriculum Reinforcement Learning, which employs progressive difficulty expansion to stabilize post-training, with Agentic Augmentation, enabling iterative self-verification at inference. Evaluated on HiPhO, a rigorous benchmark of 13 exams from 2024-2025, our flagship P1-VL-235B-A22B becomes the first open-source Vision-Language Model (VLM) to secure 12 gold medals and achieves the state-of-the-art performance in the open-source models. Our agent-augmented system achieves the No.2 overall rank globally, trailing only Gemini-3-Pro. Beyond physics, P1-VL demonstrates remarkable scientific reasoning capacity and generalizability, establishing significant leads over base models in STEM benchmarks. By open-sourcing P1-VL, we provide a foundational step toward general-purpose physical intelligence to better align visual perceptions with abstract physical laws for machine scientific discovery.
FreeOrbit4D: Training-Free Arbitrary Camera Redirection for Monocular Videos via Geometry-Complete 4D Reconstruction
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Camera redirection aims to replay a dynamic scene from a single monocular video under a user-specified camera trajectory. However, large-angle redirection is inherently ill-posed: a monocular video captures only a narrow spatio-temporal view of a dynamic 3D scene, providing highly partial observations of the underlying 4D world. The key challenge is therefore to recover a complete and coherent representation from this limited input, with consistent geometry and motion. While recent diffusion-based methods achieve impressive results, they often break down under large-angle viewpoint changes far from the original trajectory, where missing visual grounding leads to severe geometric ambiguity and temporal inconsistency. To address this, we present FreeOrbit4D, an effective training-free framework that tackles this geometric ambiguity by recovering a geometry-complete 4D proxy as structural grounding for video generation. We obtain this proxy by decoupling foreground and background reconstructions: we unproject the monocular video into a static background and geometry-incomplete foreground point clouds in a unified global space, then leverage an object-centric multi-view diffusion model to synthesize multi-view images and reconstruct geometry-complete foreground point clouds in canonical object space. By aligning the canonical foreground point cloud to the global scene space via dense pixel-synchronized 3D--3D correspondences and projecting the geometry-complete 4D proxy onto target camera viewpoints, we provide geometric scaffolds that guide a conditional video diffusion model. Extensive experiments show that FreeOrbit4D produces more faithful redirected videos under challenging large-angle trajectories, and our geometry-complete 4D proxy further opens a potential avenue for practical applications such as edit propagation and 4D data generation. Project page and code will be released soon.
AVMeme Exam: A Multimodal Multilingual Multicultural Benchmark for LLMs' Contextual and Cultural Knowledge and Thinking
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Internet audio-visual clips convey meaning through time-varying sound and motion, which extend beyond what text alone can represent. To examine whether AI models can understand such signals in human cultural contexts, we introduce AVMeme Exam, a human-curated benchmark of over one thousand iconic Internet sounds and videos spanning speech, songs, music, and sound effects. Each meme is paired with a unique Q&A assessing levels of understanding from surface content to context and emotion to usage and world knowledge, along with metadata such as original year, transcript, summary, and sensitivity. We systematically evaluate state-of-the-art multimodal large language models (MLLMs) alongside human participants using this benchmark. Our results reveal a consistent limitation: current models perform poorly on textless music and sound effects, and struggle to think in context and in culture compared to surface content. These findings highlight a key gap in human-aligned multimodal intelligence and call for models that can perceive contextually and culturally beyond the surface of what they hear and see. Project page: avmemeexam.github.io/public
PersonaLedger: Generating Realistic Financial Transactions with Persona Conditioned LLMs and Rule Grounded Feedback
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Strict privacy regulations limit access to real transaction data, slowing open research in financial AI. Synthetic data can bridge this gap, but existing generators do not jointly achieve behavioral diversity and logical groundedness. Rule-driven simulators rely on hand-crafted workflows and shallow stochasticity, which miss the richness of human behavior. Learning-based generators such as GANs capture correlations yet often violate hard financial constraints and still require training on private data. We introduce PersonaLedger, a generation engine that uses a large language model conditioned on rich user personas to produce diverse transaction streams, coupled with an expert configurable programmatic engine that maintains correctness. The LLM and engine interact in a closed loop: after each event, the engine updates the user state, enforces financial rules, and returns a context aware "nextprompt" that guides the LLM toward feasible next actions. With this engine, we create a public dataset of 30 million transactions from 23,000 users and a benchmark suite with two tasks, illiquidity classification and identity theft segmentation. PersonaLedger offers a realistic, privacy preserving resource that supports rigorous evaluation of forecasting and anomaly detection models. PersonaLedger offers the community a rich, realistic, and privacy preserving resource -- complete with code, rules, and generation logs -- to accelerate innovation in financial AI and enable rigorous, reproducible evaluation.
Evaluating Parameter Efficient Methods for RLVR
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:We systematically evaluate Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods under the paradigm of Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR). RLVR incentivizes language models to enhance their reasoning capabilities through verifiable feedback; however, while methods like LoRA are commonly used, the optimal PEFT architecture for RLVR remains unidentified. In this work, we conduct the first comprehensive evaluation of over 12 PEFT methodologies across the DeepSeek-R1-Distill families on mathematical reasoning benchmarks. Our empirical results challenge the default adoption of standard LoRA with three main findings. First, we demonstrate that structural variants, such as DoRA, AdaLoRA, and MiSS, consistently outperform LoRA. Second, we uncover a spectral collapse phenomenon in SVD-informed initialization strategies (\textit{e.g.,} PiSSA, MiLoRA), attributing their failure to a fundamental misalignment between principal-component updates and RL optimization. Furthermore, our ablations reveal that extreme parameter reduction (\textit{e.g.,} VeRA, Rank-1) severely bottlenecks reasoning capacity. We further conduct ablation studies and scaling experiments to validate our findings. This work provides a definitive guide for advocating for more exploration for parameter-efficient RL methods.
P1: Mastering Physics Olympiads with Reinforcement Learning
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Recent progress in large language models (LLMs) has moved the frontier from puzzle-solving to science-grade reasoning-the kind needed to tackle problems whose answers must stand against nature, not merely fit a rubric. Physics is the sharpest test of this shift, which binds symbols to reality in a fundamental way, serving as the cornerstone of most modern technologies. In this work, we manage to advance physics research by developing large language models with exceptional physics reasoning capabilities, especially excel at solving Olympiad-level physics problems. We introduce P1, a family of open-source physics reasoning models trained entirely through reinforcement learning (RL). Among them, P1-235B-A22B is the first open-source model with Gold-medal performance at the latest International Physics Olympiad (IPhO 2025), and wins 12 gold medals out of 13 international/regional physics competitions in 2024/2025. P1-30B-A3B also surpasses almost all other open-source models on IPhO 2025, getting a silver medal. Further equipped with an agentic framework PhysicsMinions, P1-235B-A22B+PhysicsMinions achieves overall No.1 on IPhO 2025, and obtains the highest average score over the 13 physics competitions. Besides physics, P1 models also present great performance on other reasoning tasks like math and coding, showing the great generalibility of P1 series.
HiPhO: How Far Are (M)LLMs from Humans in the Latest High School Physics Olympiad Benchmark?
Sep 10, 2025

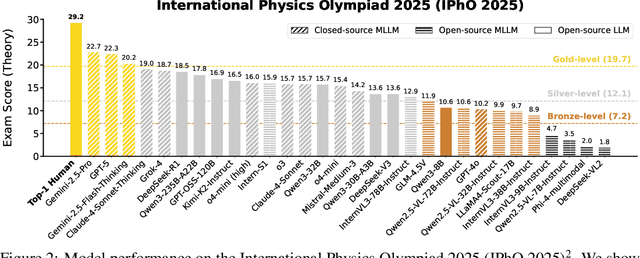

Abstract:Recently, the physical capabilities of (M)LLMs have garnered increasing attention. However, existing benchmarks for physics suffer from two major gaps: they neither provide systematic and up-to-date coverage of real-world physics competitions such as physics Olympiads, nor enable direct performance comparison with humans. To bridge these gaps, we present HiPhO, the first benchmark dedicated to high school physics Olympiads with human-aligned evaluation. Specifically, HiPhO highlights three key innovations. (1) Comprehensive Data: It compiles 13 latest Olympiad exams from 2024-2025, spanning both international and regional competitions, and covering mixed modalities that encompass problems spanning text-only to diagram-based. (2) Professional Evaluation: We adopt official marking schemes to perform fine-grained grading at both the answer and step level, fully aligned with human examiners to ensure high-quality and domain-specific evaluation. (3) Comparison with Human Contestants: We assign gold, silver, and bronze medals to models based on official medal thresholds, thereby enabling direct comparison between (M)LLMs and human contestants. Our large-scale evaluation of 30 state-of-the-art (M)LLMs shows that: across 13 exams, open-source MLLMs mostly remain at or below the bronze level; open-source LLMs show promising progress with occasional golds; closed-source reasoning MLLMs can achieve 6 to 12 gold medals; and most models still have a significant gap from full marks. These results highlight a substantial performance gap between open-source models and top students, the strong physical reasoning capabilities of closed-source reasoning models, and the fact that there is still significant room for improvement. HiPhO, as a rigorous, human-aligned, and Olympiad-focused benchmark for advancing multimodal physical reasoning, is open-source and available at https://github.com/SciYu/HiPhO.
Advancing Multimodal Reasoning: From Optimized Cold Start to Staged Reinforcement Learning
Jun 04, 2025



Abstract:Inspired by the remarkable reasoning capabilities of Deepseek-R1 in complex textual tasks, many works attempt to incentivize similar capabilities in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by directly applying reinforcement learning (RL). However, they still struggle to activate complex reasoning. In this paper, rather than examining multimodal RL in isolation, we delve into current training pipelines and identify three crucial phenomena: 1) Effective cold start initialization is critical for enhancing MLLM reasoning. Intriguingly, we find that initializing with carefully selected text data alone can lead to performance surpassing many recent multimodal reasoning models, even before multimodal RL. 2) Standard GRPO applied to multimodal RL suffers from gradient stagnation, which degrades training stability and performance. 3) Subsequent text-only RL training, following the multimodal RL phase, further enhances multimodal reasoning. This staged training approach effectively balances perceptual grounding and cognitive reasoning development. By incorporating the above insights and addressing multimodal RL issues, we introduce ReVisual-R1, achieving a new state-of-the-art among open-source 7B MLLMs on challenging benchmarks including MathVerse, MathVision, WeMath, LogicVista, DynaMath, and challenging AIME2024 and AIME2025.
AuditVotes: A Framework Towards More Deployable Certified Robustness for Graph Neural Networks
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Despite advancements in Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), adaptive attacks continue to challenge their robustness. Certified robustness based on randomized smoothing has emerged as a promising solution, offering provable guarantees that a model's predictions remain stable under adversarial perturbations within a specified range. However, existing methods face a critical trade-off between accuracy and robustness, as achieving stronger robustness requires introducing greater noise into the input graph. This excessive randomization degrades data quality and disrupts prediction consistency, limiting the practical deployment of certifiably robust GNNs in real-world scenarios where both accuracy and robustness are essential. To address this challenge, we propose \textbf{AuditVotes}, the first framework to achieve both high clean accuracy and certifiably robust accuracy for GNNs. It integrates randomized smoothing with two key components, \underline{au}gmentation and con\underline{dit}ional smoothing, aiming to improve data quality and prediction consistency. The augmentation, acting as a pre-processing step, de-noises the randomized graph, significantly improving data quality and clean accuracy. The conditional smoothing, serving as a post-processing step, employs a filtering function to selectively count votes, thereby filtering low-quality predictions and improving voting consistency. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that AuditVotes significantly enhances clean accuracy, certified robustness, and empirical robustness while maintaining high computational efficiency. Notably, compared to baseline randomized smoothing, AuditVotes improves clean accuracy by $437.1\%$ and certified accuracy by $409.3\%$ when the attacker can arbitrarily insert $20$ edges on the Cora-ML datasets, representing a substantial step toward deploying certifiably robust GNNs in real-world applications.
Streaming Piano Transcription Based on Consistent Onset and Offset Decoding with Sustain Pedal Detection
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:This paper describes a streaming audio-to-MIDI piano transcription approach that aims to sequentially translate a music signal into a sequence of note onset and offset events. The sequence-to-sequence nature of this task may call for the computationally-intensive transformer model for better performance, which has recently been used for offline transcription benchmarks and could be extended for streaming transcription with causal attention mechanisms. We assume that the performance limitation of this naive approach lies in the decoder. Although time-frequency features useful for onset detection are considerably different from those for offset detection, the single decoder is trained to output a mixed sequence of onset and offset events without guarantee of the correspondence between the onset and offset events of the same note. To overcome this limitation, we propose a streaming encoder-decoder model that uses a convolutional encoder aggregating local acoustic features, followed by an autoregressive Transformer decoder detecting a variable number of onset events and another decoder detecting the offset events for the active pitches with validation of the sustain pedal at each time frame. Experiments using the MAESTRO dataset showed that the proposed streaming method performed comparably with or even better than the state-of-the-art offline methods while significantly reducing the computational cost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge