Lena Maier-Hein
German Cancer Research Center, DKFZ Heidelberg, Helmholtz Imaging, Germany, National Center for Tumor Diseases, Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science, Heidelberg University, Germany, Medical Faculty, Heidelberg University, Germany
Performance uncertainty in medical image analysis: a large-scale investigation of confidence intervals
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Performance uncertainty quantification is essential for reliable validation and eventual clinical translation of medical imaging artificial intelligence (AI). Confidence intervals (CIs) play a central role in this process by indicating how precise a reported performance estimate is. Yet, due to the limited amount of work examining CI behavior in medical imaging, the community remains largely unaware of how many diverse CI methods exist and how they behave in specific settings. The purpose of this study is to close this gap. To this end, we conducted a large-scale empirical analysis across a total of 24 segmentation and classification tasks, using 19 trained models per task group, a broad spectrum of commonly used performance metrics, multiple aggregation strategies, and several widely adopted CI methods. Reliability (coverage) and precision (width) of each CI method were estimated across all settings to characterize their dependence on study characteristics. Our analysis revealed five principal findings: 1) the sample size required for reliable CIs varies from a few dozens to several thousands of cases depending on study parameters; 2) CI behavior is strongly affected by the choice of performance metric; 3) aggregation strategy substantially influences the reliability of CIs, e.g. they require more observations for macro than for micro; 4) the machine learning problem (segmentation versus classification) modulates these effects; 5) different CI methods are not equally reliable and precise depending on the use case. These results form key components for the development of future guidelines on reporting performance uncertainty in medical imaging AI.
Medical Imaging AI Competitions Lack Fairness
Dec 19, 2025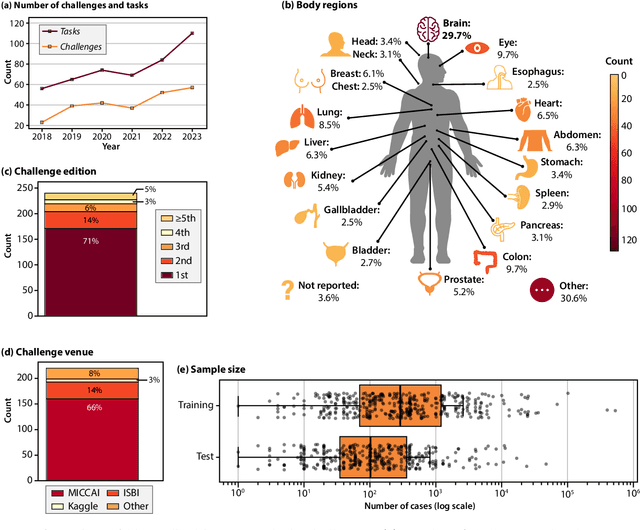
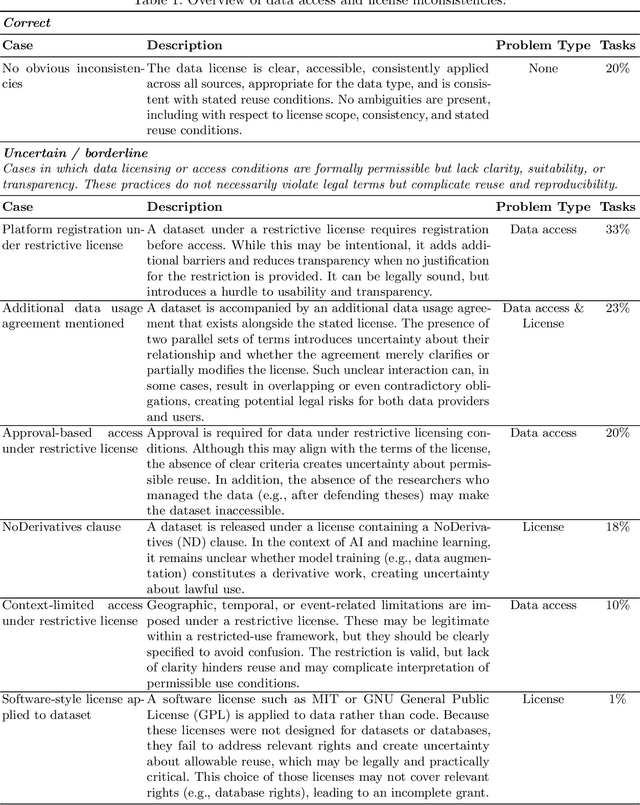
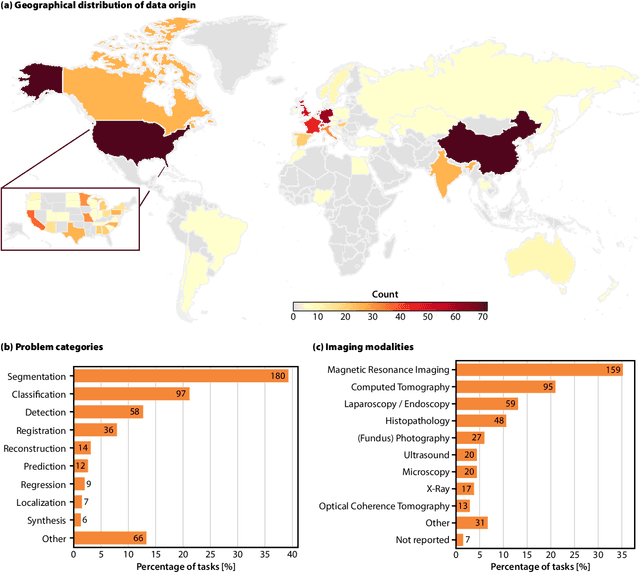
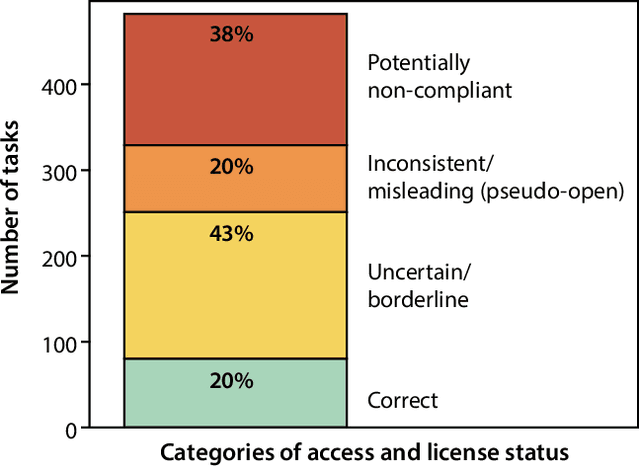
Abstract:Benchmarking competitions are central to the development of artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging, defining performance standards and shaping methodological progress. However, it remains unclear whether these benchmarks provide data that are sufficiently representative, accessible, and reusable to support clinically meaningful AI. In this work, we assess fairness along two complementary dimensions: (1) whether challenge datasets are representative of real-world clinical diversity, and (2) whether they are accessible and legally reusable in line with the FAIR principles. To address this question, we conducted a large-scale systematic study of 241 biomedical image analysis challenges comprising 458 tasks across 19 imaging modalities. Our findings show substantial biases in dataset composition, including geographic location, modality-, and problem type-related biases, indicating that current benchmarks do not adequately reflect real-world clinical diversity. Despite their widespread influence, challenge datasets were frequently constrained by restrictive or ambiguous access conditions, inconsistent or non-compliant licensing practices, and incomplete documentation, limiting reproducibility and long-term reuse. Together, these shortcomings expose foundational fairness limitations in our benchmarking ecosystem and highlight a disconnect between leaderboard success and clinical relevance.
Federated Learning for Surgical Vision in Appendicitis Classification: Results of the FedSurg EndoVis 2024 Challenge
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Purpose: The FedSurg challenge was designed to benchmark the state of the art in federated learning for surgical video classification. Its goal was to assess how well current methods generalize to unseen clinical centers and adapt through local fine-tuning while enabling collaborative model development without sharing patient data. Methods: Participants developed strategies to classify inflammation stages in appendicitis using a preliminary version of the multi-center Appendix300 video dataset. The challenge evaluated two tasks: generalization to an unseen center and center-specific adaptation after fine-tuning. Submitted approaches included foundation models with linear probing, metric learning with triplet loss, and various FL aggregation schemes (FedAvg, FedMedian, FedSAM). Performance was assessed using F1-score and Expected Cost, with ranking robustness evaluated via bootstrapping and statistical testing. Results: In the generalization task, performance across centers was limited. In the adaptation task, all teams improved after fine-tuning, though ranking stability was low. The ViViT-based submission achieved the strongest overall performance. The challenge highlighted limitations in generalization, sensitivity to class imbalance, and difficulties in hyperparameter tuning in decentralized training, while spatiotemporal modeling and context-aware preprocessing emerged as promising strategies. Conclusion: The FedSurg Challenge establishes the first benchmark for evaluating FL strategies in surgical video classification. Findings highlight the trade-off between local personalization and global robustness, and underscore the importance of architecture choice, preprocessing, and loss design. This benchmarking offers a reference point for future development of imbalance-aware, adaptive, and robust FL methods in clinical surgical AI.
Comparative validation of surgical phase recognition, instrument keypoint estimation, and instrument instance segmentation in endoscopy: Results of the PhaKIR 2024 challenge
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:Reliable recognition and localization of surgical instruments in endoscopic video recordings are foundational for a wide range of applications in computer- and robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery (RAMIS), including surgical training, skill assessment, and autonomous assistance. However, robust performance under real-world conditions remains a significant challenge. Incorporating surgical context - such as the current procedural phase - has emerged as a promising strategy to improve robustness and interpretability. To address these challenges, we organized the Surgical Procedure Phase, Keypoint, and Instrument Recognition (PhaKIR) sub-challenge as part of the Endoscopic Vision (EndoVis) challenge at MICCAI 2024. We introduced a novel, multi-center dataset comprising thirteen full-length laparoscopic cholecystectomy videos collected from three distinct medical institutions, with unified annotations for three interrelated tasks: surgical phase recognition, instrument keypoint estimation, and instrument instance segmentation. Unlike existing datasets, ours enables joint investigation of instrument localization and procedural context within the same data while supporting the integration of temporal information across entire procedures. We report results and findings in accordance with the BIAS guidelines for biomedical image analysis challenges. The PhaKIR sub-challenge advances the field by providing a unique benchmark for developing temporally aware, context-driven methods in RAMIS and offers a high-quality resource to support future research in surgical scene understanding.
Challenging Vision-Language Models with Surgical Data: A New Dataset and Broad Benchmarking Study
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:While traditional computer vision models have historically struggled to generalize to endoscopic domains, the emergence of foundation models has shown promising cross-domain performance. In this work, we present the first large-scale study assessing the capabilities of Vision Language Models (VLMs) for endoscopic tasks with a specific focus on laparoscopic surgery. Using a diverse set of state-of-the-art models, multiple surgical datasets, and extensive human reference annotations, we address three key research questions: (1) Can current VLMs solve basic perception tasks on surgical images? (2) Can they handle advanced frame-based endoscopic scene understanding tasks? and (3) How do specialized medical VLMs compare to generalist models in this context? Our results reveal that VLMs can effectively perform basic surgical perception tasks, such as object counting and localization, with performance levels comparable to general domain tasks. However, their performance deteriorates significantly when the tasks require medical knowledge. Notably, we find that specialized medical VLMs currently underperform compared to generalist models across both basic and advanced surgical tasks, suggesting that they are not yet optimized for the complexity of surgical environments. These findings highlight the need for further advancements to enable VLMs to handle the unique challenges posed by surgery. Overall, our work provides important insights for the development of next-generation endoscopic AI systems and identifies key areas for improvement in medical visual language models.
False Promises in Medical Imaging AI? Assessing Validity of Outperformance Claims
May 07, 2025Abstract:Performance comparisons are fundamental in medical imaging Artificial Intelligence (AI) research, often driving claims of superiority based on relative improvements in common performance metrics. However, such claims frequently rely solely on empirical mean performance. In this paper, we investigate whether newly proposed methods genuinely outperform the state of the art by analyzing a representative cohort of medical imaging papers. We quantify the probability of false claims based on a Bayesian approach that leverages reported results alongside empirically estimated model congruence to estimate whether the relative ranking of methods is likely to have occurred by chance. According to our results, the majority (>80%) of papers claims outperformance when introducing a new method. Our analysis further revealed a high probability (>5%) of false outperformance claims in 86% of classification papers and 53% of segmentation papers. These findings highlight a critical flaw in current benchmarking practices: claims of outperformance in medical imaging AI are frequently unsubstantiated, posing a risk of misdirecting future research efforts.
CARL: Camera-Agnostic Representation Learning for Spectral Image Analysis
Apr 27, 2025Abstract:Spectral imaging offers promising applications across diverse domains, including medicine and urban scene understanding, and is already established as a critical modality in remote sensing. However, variability in channel dimensionality and captured wavelengths among spectral cameras impede the development of AI-driven methodologies, leading to camera-specific models with limited generalizability and inadequate cross-camera applicability. To address this bottleneck, we introduce $\textbf{CARL}$, a model for $\textbf{C}$amera-$\textbf{A}$gnostic $\textbf{R}$epresentation $\textbf{L}$earning across RGB, multispectral, and hyperspectral imaging modalities. To enable the conversion of a spectral image with any channel dimensionality to a camera-agnostic embedding, we introduce wavelength positional encoding and a self-attention-cross-attention mechanism to compress spectral information into learned query representations. Spectral-spatial pre-training is achieved with a novel spectral self-supervised JEPA-inspired strategy tailored to CARL. Large-scale experiments across the domains of medical imaging, autonomous driving, and satellite imaging demonstrate our model's unique robustness to spectral heterogeneity, outperforming on datasets with simulated and real-world cross-camera spectral variations. The scalability and versatility of the proposed approach position our model as a backbone for future spectral foundation models.
Bridging vision language model (VLM) evaluation gaps with a framework for scalable and cost-effective benchmark generation
Feb 21, 2025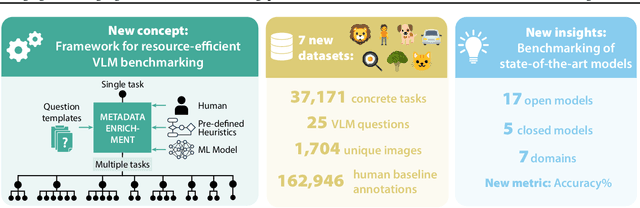
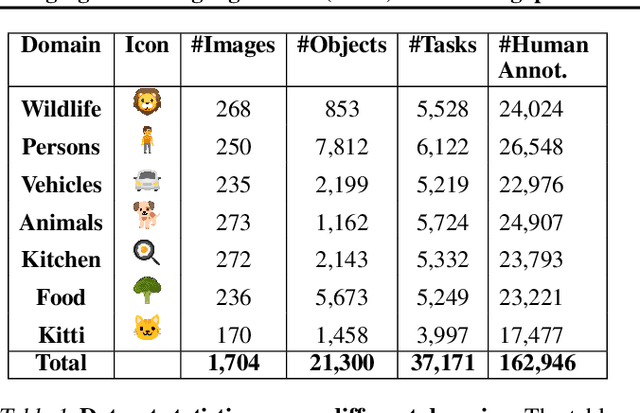
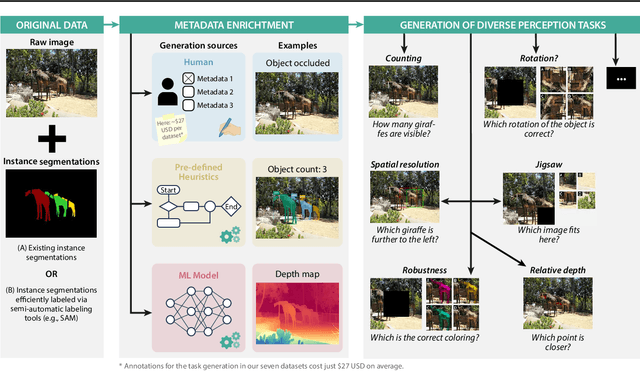
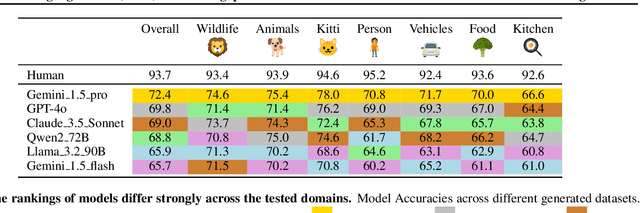
Abstract:Reliable evaluation of AI models is critical for scientific progress and practical application. While existing VLM benchmarks provide general insights into model capabilities, their heterogeneous designs and limited focus on a few imaging domains pose significant challenges for both cross-domain performance comparison and targeted domain-specific evaluation. To address this, we propose three key contributions: (1) a framework for the resource-efficient creation of domain-specific VLM benchmarks enabled by task augmentation for creating multiple diverse tasks from a single existing task, (2) the release of new VLM benchmarks for seven domains, created according to the same homogeneous protocol and including 162,946 thoroughly human-validated answers, and (3) an extensive benchmarking of 22 state-of-the-art VLMs on a total of 37,171 tasks, revealing performance variances across domains and tasks, thereby supporting the need for tailored VLM benchmarks. Adoption of our methodology will pave the way for the resource-efficient domain-specific selection of models and guide future research efforts toward addressing core open questions.
Beyond Knowledge Silos: Task Fingerprinting for Democratization of Medical Imaging AI
Dec 11, 2024Abstract:The field of medical imaging AI is currently undergoing rapid transformations, with methodical research increasingly translated into clinical practice. Despite these successes, research suffers from knowledge silos, hindering collaboration and progress: Existing knowledge is scattered across publications and many details remain unpublished, while privacy regulations restrict data sharing. In the spirit of democratizing of AI, we propose a framework for secure knowledge transfer in the field of medical image analysis. The key to our approach is dataset "fingerprints", structured representations of feature distributions, that enable quantification of task similarity. We tested our approach across 71 distinct tasks and 12 medical imaging modalities by transferring neural architectures, pretraining, augmentation policies, and multi-task learning. According to comprehensive analyses, our method outperforms traditional methods for identifying relevant knowledge and facilitates collaborative model training. Our framework fosters the democratization of AI in medical imaging and could become a valuable tool for promoting faster scientific advancement.
SURE-VQA: Systematic Understanding of Robustness Evaluation in Medical VQA Tasks
Nov 29, 2024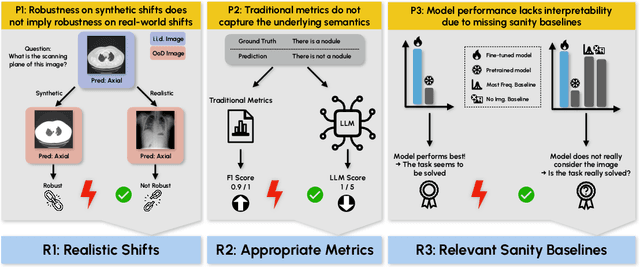
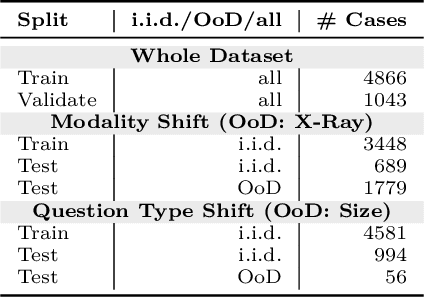
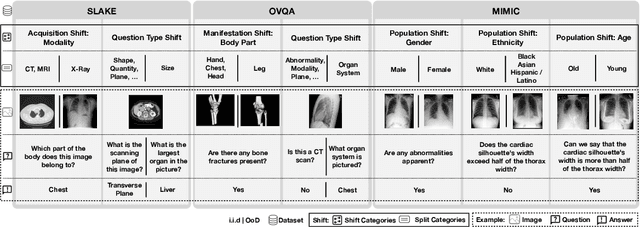
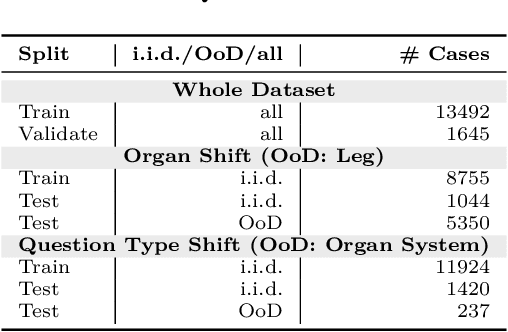
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have great potential in medical tasks, like Visual Question Answering (VQA), where they could act as interactive assistants for both patients and clinicians. Yet their robustness to distribution shifts on unseen data remains a critical concern for safe deployment. Evaluating such robustness requires a controlled experimental setup that allows for systematic insights into the model's behavior. However, we demonstrate that current setups fail to offer sufficiently thorough evaluations, limiting their ability to accurately assess model robustness. To address this gap, our work introduces a novel framework, called SURE-VQA, centered around three key requirements to overcome the current pitfalls and systematically analyze the robustness of VLMs: 1) Since robustness on synthetic shifts does not necessarily translate to real-world shifts, robustness should be measured on real-world shifts that are inherent to the VQA data; 2) Traditional token-matching metrics often fail to capture underlying semantics, necessitating the use of large language models (LLMs) for more accurate semantic evaluation; 3) Model performance often lacks interpretability due to missing sanity baselines, thus meaningful baselines should be reported that allow assessing the multimodal impact on the VLM. To demonstrate the relevance of this framework, we conduct a study on the robustness of various fine-tuning methods across three medical datasets with four different types of distribution shifts. Our study reveals several important findings: 1) Sanity baselines that do not utilize image data can perform surprisingly well; 2) We confirm LoRA as the best-performing PEFT method; 3) No PEFT method consistently outperforms others in terms of robustness to shifts. Code is provided at https://github.com/IML-DKFZ/sure-vqa.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge