Felix Nickel
Helmholtz Information and Data Science School for Health, Karlsruhe/Heidelberg, Germany, Department of General, Visceral, and Transplantation Surgery, Heidelberg University Hospital, Heidelberg, Germany, Medical Faculty, Heidelberg University, Heidelberg, Germany
Handling Geometric Domain Shifts in Semantic Segmentation of Surgical RGB and Hyperspectral Images
Aug 27, 2024



Abstract:Robust semantic segmentation of intraoperative image data holds promise for enabling automatic surgical scene understanding and autonomous robotic surgery. While model development and validation are primarily conducted on idealistic scenes, geometric domain shifts, such as occlusions of the situs, are common in real-world open surgeries. To close this gap, we (1) present the first analysis of state-of-the-art (SOA) semantic segmentation models when faced with geometric out-of-distribution (OOD) data, and (2) propose an augmentation technique called "Organ Transplantation", to enhance generalizability. Our comprehensive validation on six different OOD datasets, comprising 600 RGB and hyperspectral imaging (HSI) cubes from 33 pigs, each annotated with 19 classes, reveals a large performance drop in SOA organ segmentation models on geometric OOD data. This performance decline is observed not only in conventional RGB data (with a dice similarity coefficient (DSC) drop of 46 %) but also in HSI data (with a DSC drop of 45 %), despite the richer spectral information content. The performance decline increases with the spatial granularity of the input data. Our augmentation technique improves SOA model performance by up to 67 % for RGB data and 90 % for HSI data, achieving performance at the level of in-distribution performance on real OOD test data. Given the simplicity and effectiveness of our augmentation method, it is a valuable tool for addressing geometric domain shifts in surgical scene segmentation, regardless of the underlying model. Our code and pre-trained models are publicly available at https://github.com/IMSY-DKFZ/htc.
Semantic segmentation of surgical hyperspectral images under geometric domain shifts
Mar 20, 2023



Abstract:Robust semantic segmentation of intraoperative image data could pave the way for automatic surgical scene understanding and autonomous robotic surgery. Geometric domain shifts, however, although common in real-world open surgeries due to variations in surgical procedures or situs occlusions, remain a topic largely unaddressed in the field. To address this gap in the literature, we (1) present the first analysis of state-of-the-art (SOA) semantic segmentation networks in the presence of geometric out-of-distribution (OOD) data, and (2) address generalizability with a dedicated augmentation technique termed "Organ Transplantation" that we adapted from the general computer vision community. According to a comprehensive validation on six different OOD data sets comprising 600 RGB and hyperspectral imaging (HSI) cubes from 33 pigs semantically annotated with 19 classes, we demonstrate a large performance drop of SOA organ segmentation networks applied to geometric OOD data. Surprisingly, this holds true not only for conventional RGB data (drop of Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) by 46 %) but also for HSI data (drop by 45 %), despite the latter's rich information content per pixel. Using our augmentation scheme improves on the SOA DSC by up to 67 % (RGB) and 90 % (HSI) and renders performance on par with in-distribution performance on real OOD test data. The simplicity and effectiveness of our augmentation scheme makes it a valuable network-independent tool for addressing geometric domain shifts in semantic scene segmentation of intraoperative data. Our code and pre-trained models will be made publicly available.
Unsupervised Domain Transfer with Conditional Invertible Neural Networks
Mar 17, 2023Abstract:Synthetic medical image generation has evolved as a key technique for neural network training and validation. A core challenge, however, remains in the domain gap between simulations and real data. While deep learning-based domain transfer using Cycle Generative Adversarial Networks and similar architectures has led to substantial progress in the field, there are use cases in which state-of-the-art approaches still fail to generate training images that produce convincing results on relevant downstream tasks. Here, we address this issue with a domain transfer approach based on conditional invertible neural networks (cINNs). As a particular advantage, our method inherently guarantees cycle consistency through its invertible architecture, and network training can efficiently be conducted with maximum likelihood training. To showcase our method's generic applicability, we apply it to two spectral imaging modalities at different scales, namely hyperspectral imaging (pixel-level) and photoacoustic tomography (image-level). According to comprehensive experiments, our method enables the generation of realistic spectral data and outperforms the state of the art on two downstream classification tasks (binary and multi-class). cINN-based domain transfer could thus evolve as an important method for realistic synthetic data generation in the field of spectral imaging and beyond.
Understanding metric-related pitfalls in image analysis validation
Feb 09, 2023Abstract:Validation metrics are key for the reliable tracking of scientific progress and for bridging the current chasm between artificial intelligence (AI) research and its translation into practice. However, increasing evidence shows that particularly in image analysis, metrics are often chosen inadequately in relation to the underlying research problem. This could be attributed to a lack of accessibility of metric-related knowledge: While taking into account the individual strengths, weaknesses, and limitations of validation metrics is a critical prerequisite to making educated choices, the relevant knowledge is currently scattered and poorly accessible to individual researchers. Based on a multi-stage Delphi process conducted by a multidisciplinary expert consortium as well as extensive community feedback, the present work provides the first reliable and comprehensive common point of access to information on pitfalls related to validation metrics in image analysis. Focusing on biomedical image analysis but with the potential of transfer to other fields, the addressed pitfalls generalize across application domains and are categorized according to a newly created, domain-agnostic taxonomy. To facilitate comprehension, illustrations and specific examples accompany each pitfall. As a structured body of information accessible to researchers of all levels of expertise, this work enhances global comprehension of a key topic in image analysis validation.
Metrics reloaded: Pitfalls and recommendations for image analysis validation
Jun 03, 2022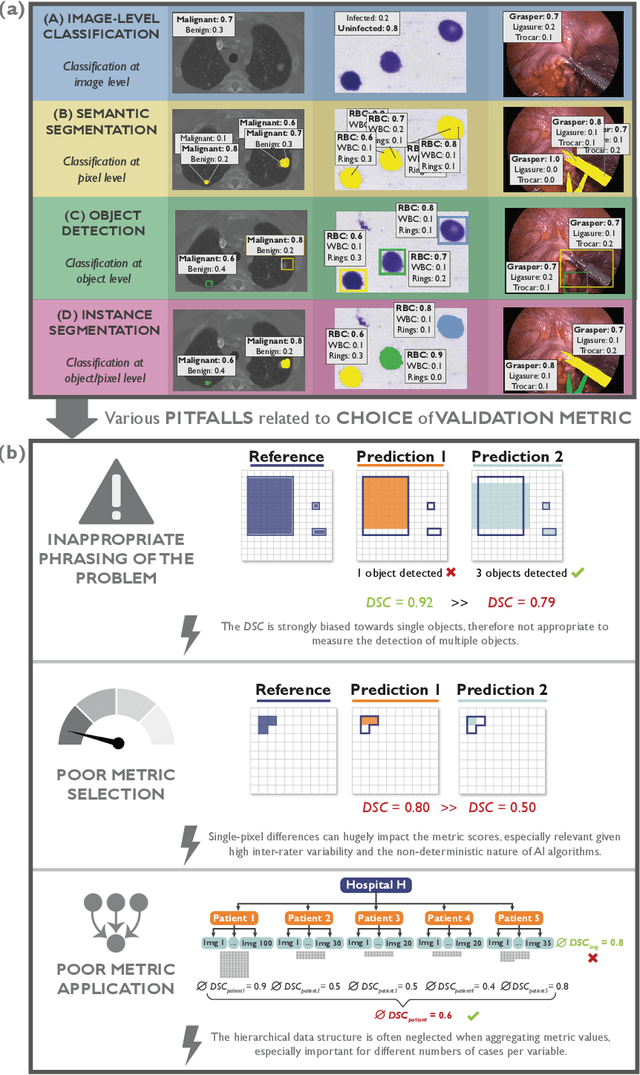
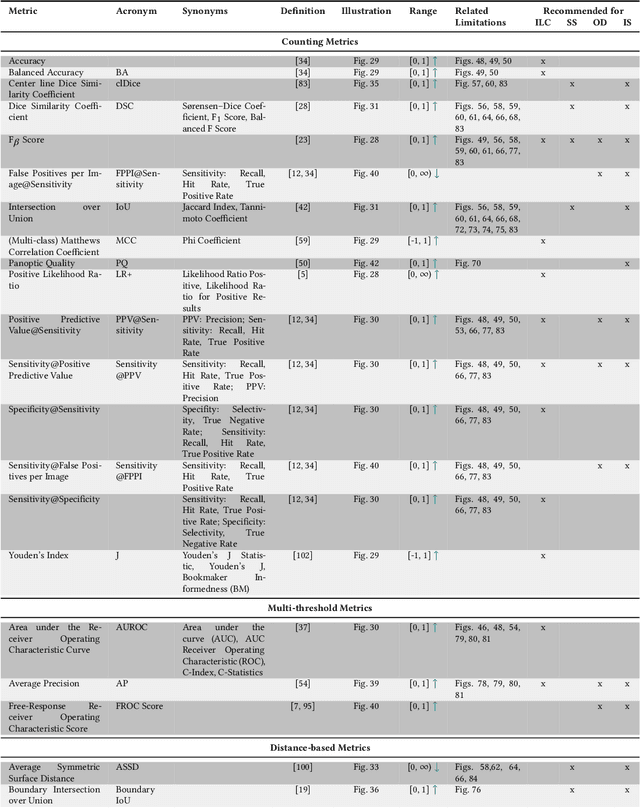
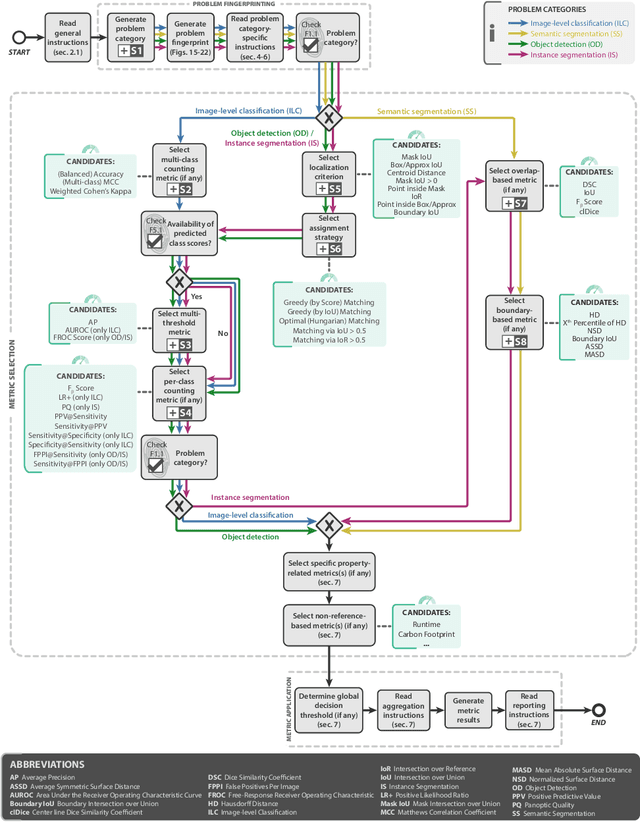
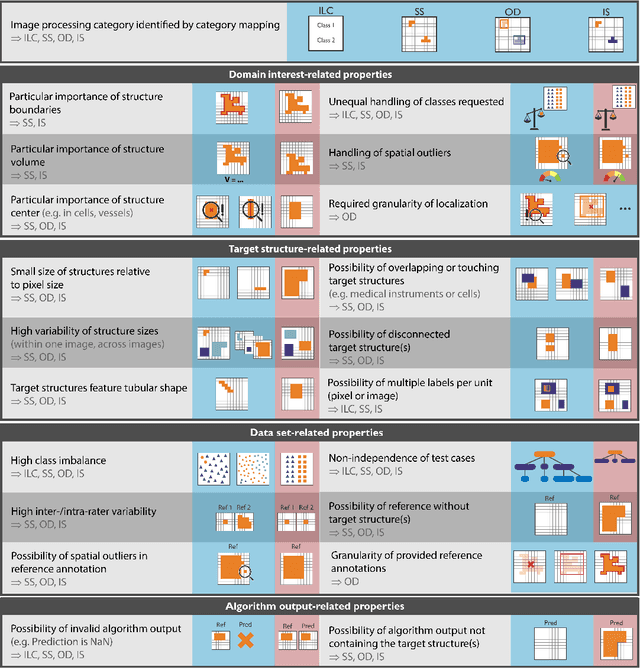
Abstract:The field of automatic biomedical image analysis crucially depends on robust and meaningful performance metrics for algorithm validation. Current metric usage, however, is often ill-informed and does not reflect the underlying domain interest. Here, we present a comprehensive framework that guides researchers towards choosing performance metrics in a problem-aware manner. Specifically, we focus on biomedical image analysis problems that can be interpreted as a classification task at image, object or pixel level. The framework first compiles domain interest-, target structure-, data set- and algorithm output-related properties of a given problem into a problem fingerprint, while also mapping it to the appropriate problem category, namely image-level classification, semantic segmentation, instance segmentation, or object detection. It then guides users through the process of selecting and applying a set of appropriate validation metrics while making them aware of potential pitfalls related to individual choices. In this paper, we describe the current status of the Metrics Reloaded recommendation framework, with the goal of obtaining constructive feedback from the image analysis community. The current version has been developed within an international consortium of more than 60 image analysis experts and will be made openly available as a user-friendly toolkit after community-driven optimization.
Robust deep learning-based semantic organ segmentation in hyperspectral images
Nov 09, 2021Abstract:Semantic image segmentation is an important prerequisite for context-awareness and autonomous robotics in surgery. The state of the art has focused on conventional RGB video data acquired during minimally invasive surgery, but full-scene semantic segmentation based on spectral imaging data and obtained during open surgery has received almost no attention to date. To address this gap in the literature, we are investigating the following research questions based on hyperspectral imaging (HSI) data of pigs acquired in an open surgery setting: (1) What is an adequate representation of HSI data for neural network-based fully automated organ segmentation, especially with respect to the spatial granularity of the data (pixels vs. superpixels vs. patches vs. full images)? (2) Is there a benefit of using HSI data compared to other modalities, namely RGB data and processed HSI data (e.g. tissue parameters like oxygenation), when performing semantic organ segmentation? According to a comprehensive validation study based on 506 HSI images from 20 pigs, annotated with a total of 19 classes, deep learning-based segmentation performance increases - consistently across modalities - with the spatial context of the input data. Unprocessed HSI data offers an advantage over RGB data or processed data from the camera provider, with the advantage increasing with decreasing size of the input to the neural network. Maximum performance (HSI applied to whole images) yielded a mean dice similarity coefficient (DSC) of 0.89 (standard deviation (SD) 0.04), which is in the range of the inter-rater variability (DSC of 0.89 (SD 0.07)). We conclude that HSI could become a powerful image modality for fully-automatic surgical scene understanding with many advantages over traditional imaging, including the ability to recover additional functional tissue information.
Comparative Validation of Machine Learning Algorithms for Surgical Workflow and Skill Analysis with the HeiChole Benchmark
Sep 30, 2021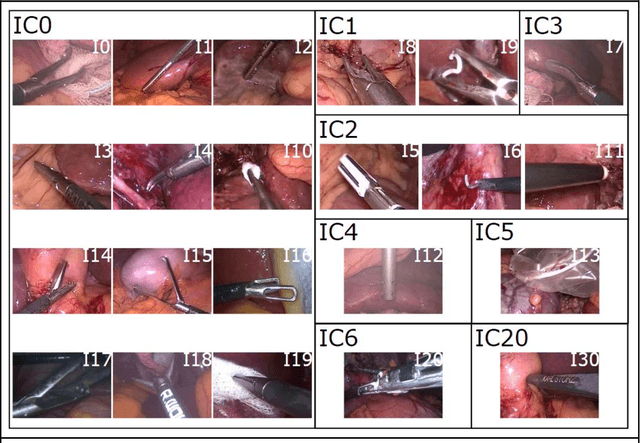
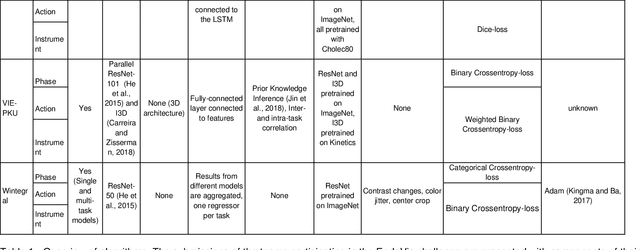
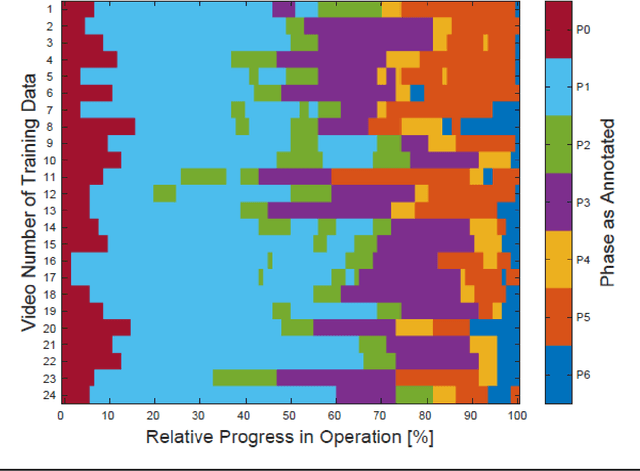
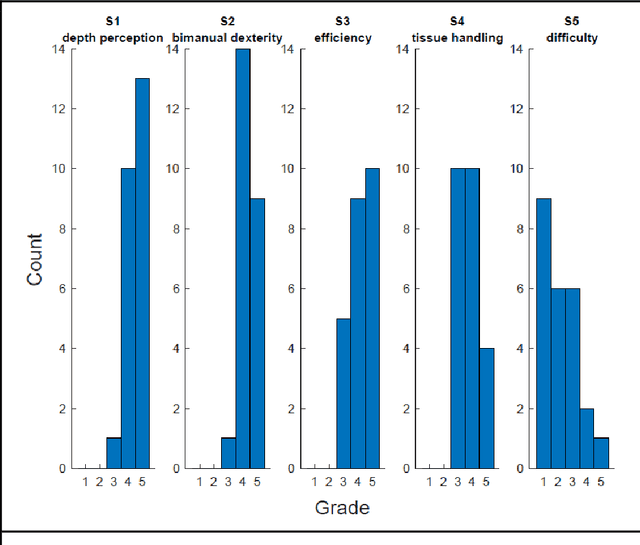
Abstract:PURPOSE: Surgical workflow and skill analysis are key technologies for the next generation of cognitive surgical assistance systems. These systems could increase the safety of the operation through context-sensitive warnings and semi-autonomous robotic assistance or improve training of surgeons via data-driven feedback. In surgical workflow analysis up to 91% average precision has been reported for phase recognition on an open data single-center dataset. In this work we investigated the generalizability of phase recognition algorithms in a multi-center setting including more difficult recognition tasks such as surgical action and surgical skill. METHODS: To achieve this goal, a dataset with 33 laparoscopic cholecystectomy videos from three surgical centers with a total operation time of 22 hours was created. Labels included annotation of seven surgical phases with 250 phase transitions, 5514 occurences of four surgical actions, 6980 occurences of 21 surgical instruments from seven instrument categories and 495 skill classifications in five skill dimensions. The dataset was used in the 2019 Endoscopic Vision challenge, sub-challenge for surgical workflow and skill analysis. Here, 12 teams submitted their machine learning algorithms for recognition of phase, action, instrument and/or skill assessment. RESULTS: F1-scores were achieved for phase recognition between 23.9% and 67.7% (n=9 teams), for instrument presence detection between 38.5% and 63.8% (n=8 teams), but for action recognition only between 21.8% and 23.3% (n=5 teams). The average absolute error for skill assessment was 0.78 (n=1 team). CONCLUSION: Surgical workflow and skill analysis are promising technologies to support the surgical team, but are not solved yet, as shown by our comparison of algorithms. This novel benchmark can be used for comparable evaluation and validation of future work.
Machine learning-based analysis of hyperspectral images for automated sepsis diagnosis
Jun 15, 2021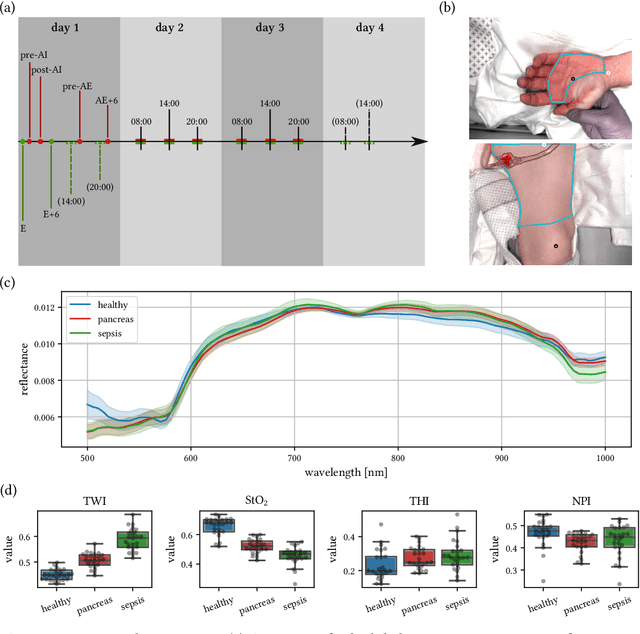
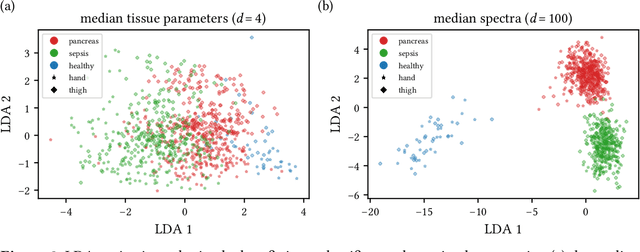
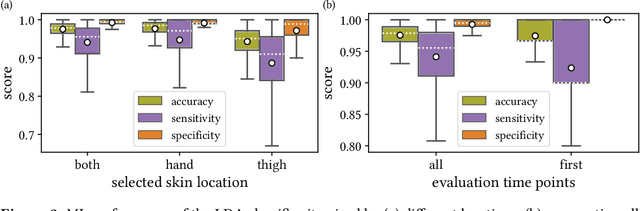
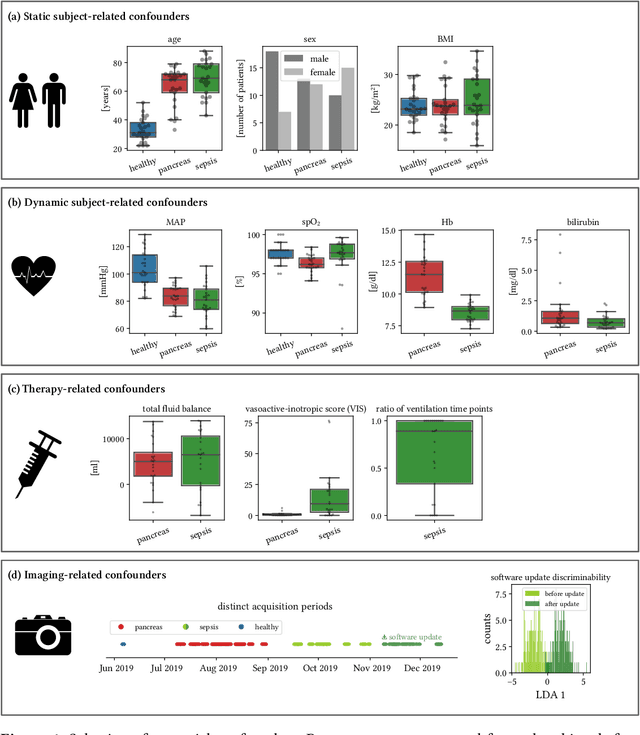
Abstract:Sepsis is a leading cause of mortality and critical illness worldwide. While robust biomarkers for early diagnosis are still missing, recent work indicates that hyperspectral imaging (HSI) has the potential to overcome this bottleneck by monitoring microcirculatory alterations. Automated machine learning-based diagnosis of sepsis based on HSI data, however, has not been explored to date. Given this gap in the literature, we leveraged an existing data set to (1) investigate whether HSI-based automated diagnosis of sepsis is possible and (2) put forth a list of possible confounders relevant for HSI-based tissue classification. While we were able to classify sepsis with an accuracy of over $98\,\%$ using the existing data, our research also revealed several subject-, therapy- and imaging-related confounders that may lead to an overestimation of algorithm performance when not balanced across the patient groups. We conclude that further prospective studies, carefully designed with respect to these confounders, are necessary to confirm the preliminary results obtained in this study.
Towards Augmented Reality-based Suturing in Monocular Laparoscopic Training
Jan 19, 2020



Abstract:Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS) techniques have gained rapid popularity among surgeons since they offer significant clinical benefits including reduced recovery time and diminished post-operative adverse effects. However, conventional endoscopic systems output monocular video which compromises depth perception, spatial orientation and field of view. Suturing is one of the most complex tasks performed under these circumstances. Key components of this tasks are the interplay between needle holder and the surgical needle. Reliable 3D localization of needle and instruments in real time could be used to augment the scene with additional parameters that describe their quantitative geometric relation, e.g. the relation between the estimated needle plane and its rotation center and the instrument. This could contribute towards standardization and training of basic skills and operative techniques, enhance overall surgical performance, and reduce the risk of complications. The paper proposes an Augmented Reality environment with quantitative and qualitative visual representations to enhance laparoscopic training outcomes performed on a silicone pad. This is enabled by a multi-task supervised deep neural network which performs multi-class segmentation and depth map prediction. Scarcity of labels has been conquered by creating a virtual environment which resembles the surgical training scenario to generate dense depth maps and segmentation maps. The proposed convolutional neural network was tested on real surgical training scenarios and showed to be robust to occlusion of the needle. The network achieves a dice score of 0.67 for surgical needle segmentation, 0.81 for needle holder instrument segmentation and a mean absolute error of 6.5 mm for depth estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge