Evangelia Christodoulou
German Cancer Research Center, National Center for Tumor Diseases, AI Health Innovation Cluster, Germany
Performance uncertainty in medical image analysis: a large-scale investigation of confidence intervals
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Performance uncertainty quantification is essential for reliable validation and eventual clinical translation of medical imaging artificial intelligence (AI). Confidence intervals (CIs) play a central role in this process by indicating how precise a reported performance estimate is. Yet, due to the limited amount of work examining CI behavior in medical imaging, the community remains largely unaware of how many diverse CI methods exist and how they behave in specific settings. The purpose of this study is to close this gap. To this end, we conducted a large-scale empirical analysis across a total of 24 segmentation and classification tasks, using 19 trained models per task group, a broad spectrum of commonly used performance metrics, multiple aggregation strategies, and several widely adopted CI methods. Reliability (coverage) and precision (width) of each CI method were estimated across all settings to characterize their dependence on study characteristics. Our analysis revealed five principal findings: 1) the sample size required for reliable CIs varies from a few dozens to several thousands of cases depending on study parameters; 2) CI behavior is strongly affected by the choice of performance metric; 3) aggregation strategy substantially influences the reliability of CIs, e.g. they require more observations for macro than for micro; 4) the machine learning problem (segmentation versus classification) modulates these effects; 5) different CI methods are not equally reliable and precise depending on the use case. These results form key components for the development of future guidelines on reporting performance uncertainty in medical imaging AI.
Medical Imaging AI Competitions Lack Fairness
Dec 19, 2025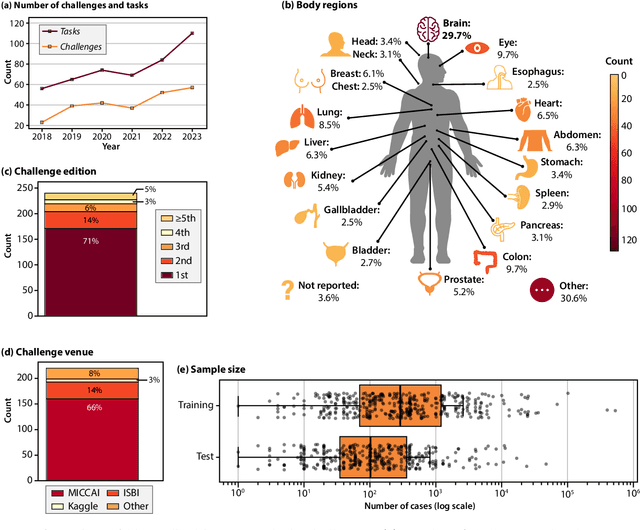
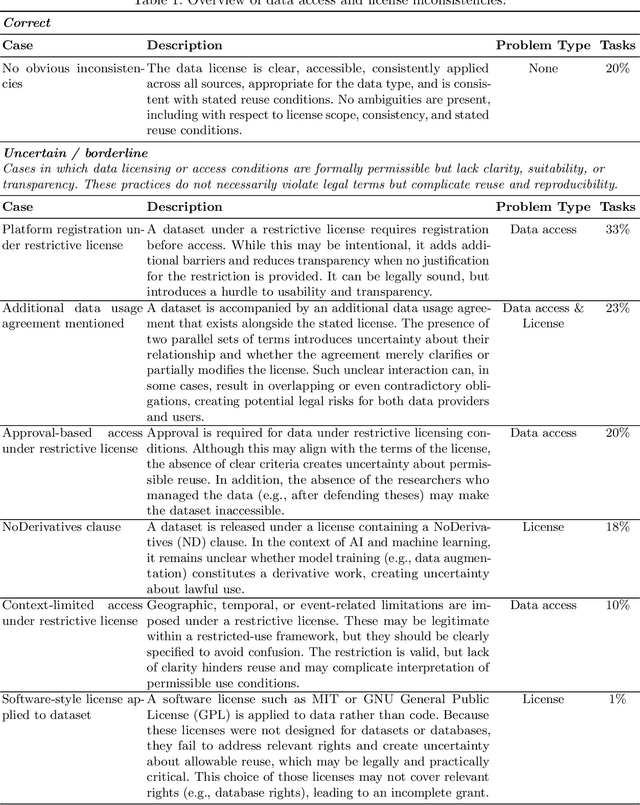
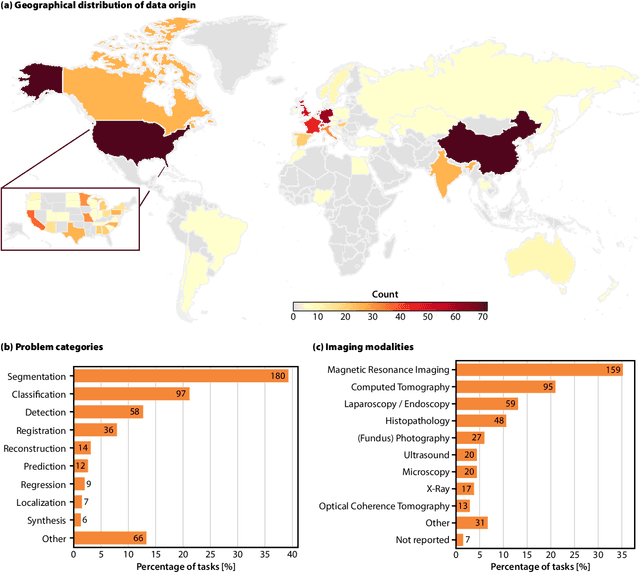
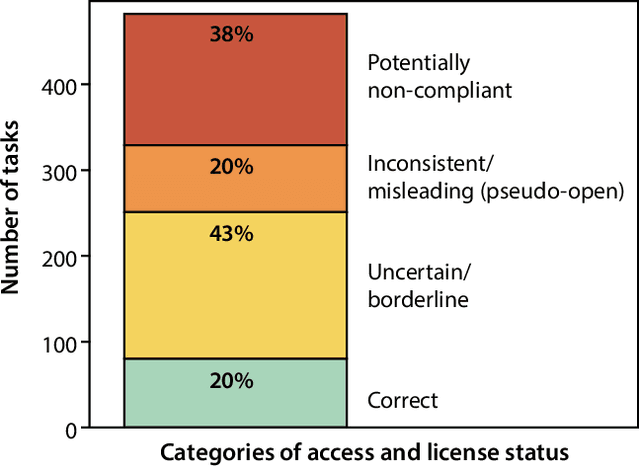
Abstract:Benchmarking competitions are central to the development of artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging, defining performance standards and shaping methodological progress. However, it remains unclear whether these benchmarks provide data that are sufficiently representative, accessible, and reusable to support clinically meaningful AI. In this work, we assess fairness along two complementary dimensions: (1) whether challenge datasets are representative of real-world clinical diversity, and (2) whether they are accessible and legally reusable in line with the FAIR principles. To address this question, we conducted a large-scale systematic study of 241 biomedical image analysis challenges comprising 458 tasks across 19 imaging modalities. Our findings show substantial biases in dataset composition, including geographic location, modality-, and problem type-related biases, indicating that current benchmarks do not adequately reflect real-world clinical diversity. Despite their widespread influence, challenge datasets were frequently constrained by restrictive or ambiguous access conditions, inconsistent or non-compliant licensing practices, and incomplete documentation, limiting reproducibility and long-term reuse. Together, these shortcomings expose foundational fairness limitations in our benchmarking ecosystem and highlight a disconnect between leaderboard success and clinical relevance.
Challenging Vision-Language Models with Surgical Data: A New Dataset and Broad Benchmarking Study
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:While traditional computer vision models have historically struggled to generalize to endoscopic domains, the emergence of foundation models has shown promising cross-domain performance. In this work, we present the first large-scale study assessing the capabilities of Vision Language Models (VLMs) for endoscopic tasks with a specific focus on laparoscopic surgery. Using a diverse set of state-of-the-art models, multiple surgical datasets, and extensive human reference annotations, we address three key research questions: (1) Can current VLMs solve basic perception tasks on surgical images? (2) Can they handle advanced frame-based endoscopic scene understanding tasks? and (3) How do specialized medical VLMs compare to generalist models in this context? Our results reveal that VLMs can effectively perform basic surgical perception tasks, such as object counting and localization, with performance levels comparable to general domain tasks. However, their performance deteriorates significantly when the tasks require medical knowledge. Notably, we find that specialized medical VLMs currently underperform compared to generalist models across both basic and advanced surgical tasks, suggesting that they are not yet optimized for the complexity of surgical environments. These findings highlight the need for further advancements to enable VLMs to handle the unique challenges posed by surgery. Overall, our work provides important insights for the development of next-generation endoscopic AI systems and identifies key areas for improvement in medical visual language models.
False Promises in Medical Imaging AI? Assessing Validity of Outperformance Claims
May 07, 2025Abstract:Performance comparisons are fundamental in medical imaging Artificial Intelligence (AI) research, often driving claims of superiority based on relative improvements in common performance metrics. However, such claims frequently rely solely on empirical mean performance. In this paper, we investigate whether newly proposed methods genuinely outperform the state of the art by analyzing a representative cohort of medical imaging papers. We quantify the probability of false claims based on a Bayesian approach that leverages reported results alongside empirically estimated model congruence to estimate whether the relative ranking of methods is likely to have occurred by chance. According to our results, the majority (>80%) of papers claims outperformance when introducing a new method. Our analysis further revealed a high probability (>5%) of false outperformance claims in 86% of classification papers and 53% of segmentation papers. These findings highlight a critical flaw in current benchmarking practices: claims of outperformance in medical imaging AI are frequently unsubstantiated, posing a risk of misdirecting future research efforts.
Confidence intervals uncovered: Are we ready for real-world medical imaging AI?
Sep 27, 2024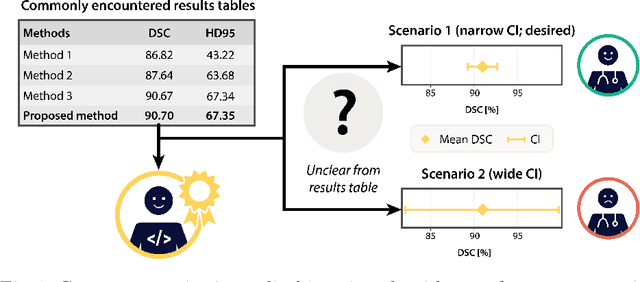
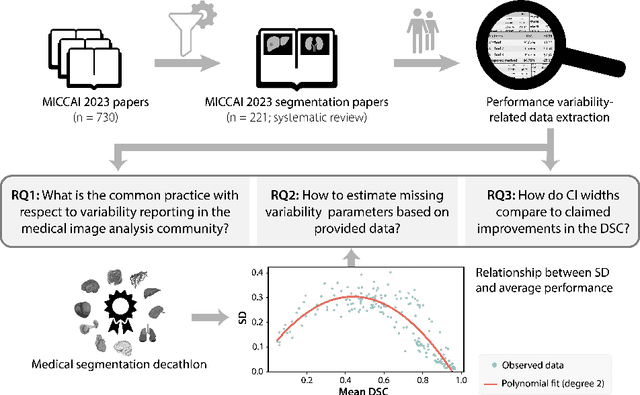
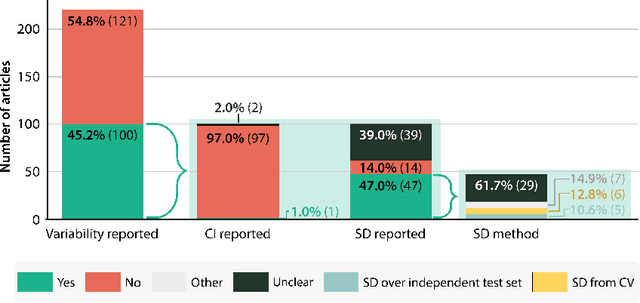

Abstract:Medical imaging is spearheading the AI transformation of healthcare. Performance reporting is key to determine which methods should be translated into clinical practice. Frequently, broad conclusions are simply derived from mean performance values. In this paper, we argue that this common practice is often a misleading simplification as it ignores performance variability. Our contribution is threefold. (1) Analyzing all MICCAI segmentation papers (n = 221) published in 2023, we first observe that more than 50% of papers do not assess performance variability at all. Moreover, only one (0.5%) paper reported confidence intervals (CIs) for model performance. (2) To address the reporting bottleneck, we show that the unreported standard deviation (SD) in segmentation papers can be approximated by a second-order polynomial function of the mean Dice similarity coefficient (DSC). Based on external validation data from 56 previous MICCAI challenges, we demonstrate that this approximation can accurately reconstruct the CI of a method using information provided in publications. (3) Finally, we reconstructed 95% CIs around the mean DSC of MICCAI 2023 segmentation papers. The median CI width was 0.03 which is three times larger than the median performance gap between the first and second ranked method. For more than 60% of papers, the mean performance of the second-ranked method was within the CI of the first-ranked method. We conclude that current publications typically do not provide sufficient evidence to support which models could potentially be translated into clinical practice.
Deployment of Image Analysis Algorithms under Prevalence Shifts
Mar 22, 2023



Abstract:Domain gaps are among the most relevant roadblocks in the clinical translation of machine learning (ML)-based solutions for medical image analysis. While current research focuses on new training paradigms and network architectures, little attention is given to the specific effect of prevalence shifts on an algorithm deployed in practice. Such discrepancies between class frequencies in the data used for a method's development/validation and that in its deployment environment(s) are of great importance, for example in the context of artificial intelligence (AI) democratization, as disease prevalences may vary widely across time and location. Our contribution is twofold. First, we empirically demonstrate the potentially severe consequences of missing prevalence handling by analyzing (i) the extent of miscalibration, (ii) the deviation of the decision threshold from the optimum, and (iii) the ability of validation metrics to reflect neural network performance on the deployment population as a function of the discrepancy between development and deployment prevalence. Second, we propose a workflow for prevalence-aware image classification that uses estimated deployment prevalences to adjust a trained classifier to a new environment, without requiring additional annotated deployment data. Comprehensive experiments based on a diverse set of 30 medical classification tasks showcase the benefit of the proposed workflow in generating better classifier decisions and more reliable performance estimates compared to current practice.
Understanding metric-related pitfalls in image analysis validation
Feb 09, 2023Abstract:Validation metrics are key for the reliable tracking of scientific progress and for bridging the current chasm between artificial intelligence (AI) research and its translation into practice. However, increasing evidence shows that particularly in image analysis, metrics are often chosen inadequately in relation to the underlying research problem. This could be attributed to a lack of accessibility of metric-related knowledge: While taking into account the individual strengths, weaknesses, and limitations of validation metrics is a critical prerequisite to making educated choices, the relevant knowledge is currently scattered and poorly accessible to individual researchers. Based on a multi-stage Delphi process conducted by a multidisciplinary expert consortium as well as extensive community feedback, the present work provides the first reliable and comprehensive common point of access to information on pitfalls related to validation metrics in image analysis. Focusing on biomedical image analysis but with the potential of transfer to other fields, the addressed pitfalls generalize across application domains and are categorized according to a newly created, domain-agnostic taxonomy. To facilitate comprehension, illustrations and specific examples accompany each pitfall. As a structured body of information accessible to researchers of all levels of expertise, this work enhances global comprehension of a key topic in image analysis validation.
Sources of performance variability in deep learning-based polyp detection
Nov 17, 2022Abstract:Validation metrics are a key prerequisite for the reliable tracking of scientific progress and for deciding on the potential clinical translation of methods. While recent initiatives aim to develop comprehensive theoretical frameworks for understanding metric-related pitfalls in image analysis problems, there is a lack of experimental evidence on the concrete effects of common and rare pitfalls on specific applications. We address this gap in the literature in the context of colon cancer screening. Our contribution is twofold. Firstly, we present the winning solution of the Endoscopy computer vision challenge (EndoCV) on colon cancer detection, conducted in conjunction with the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2022. Secondly, we demonstrate the sensitivity of commonly used metrics to a range of hyperparameters as well as the consequences of poor metric choices. Based on comprehensive validation studies performed with patient data from six clinical centers, we found all commonly applied object detection metrics to be subject to high inter-center variability. Furthermore, our results clearly demonstrate that the adaptation of standard hyperparameters used in the computer vision community does not generally lead to the clinically most plausible results. Finally, we present localization criteria that correspond well to clinical relevance. Our work could be a first step towards reconsidering common validation strategies in automatic colon cancer screening applications.
Metrics reloaded: Pitfalls and recommendations for image analysis validation
Jun 03, 2022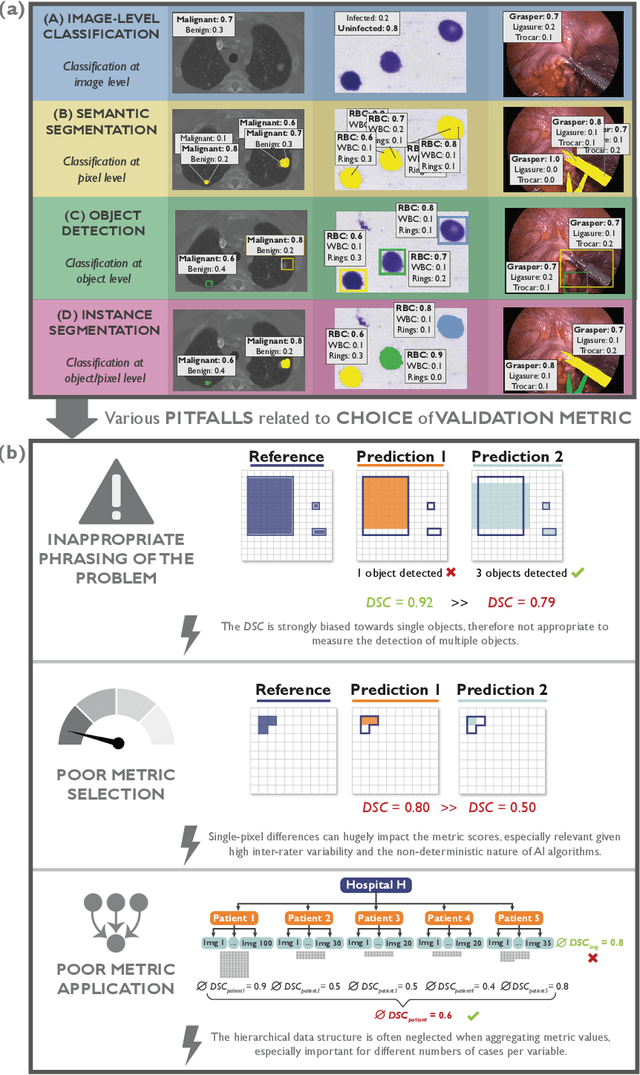
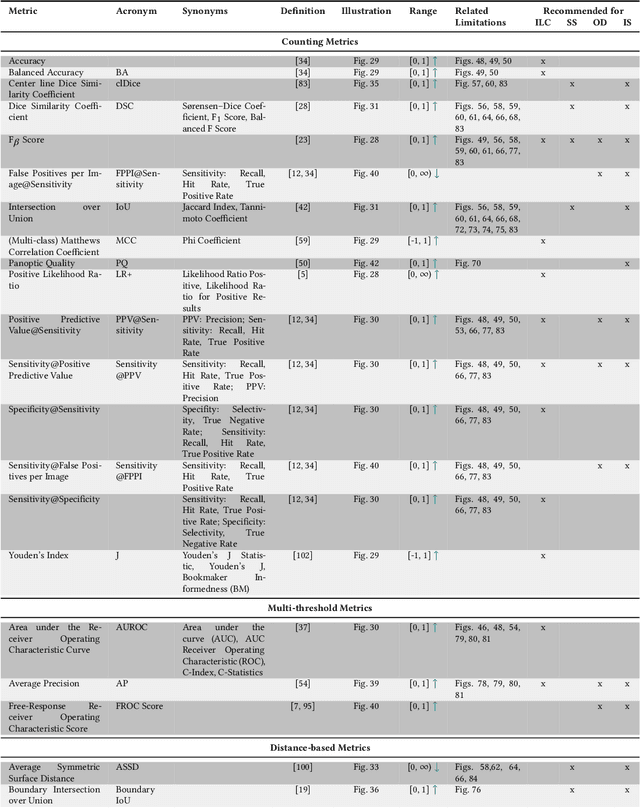
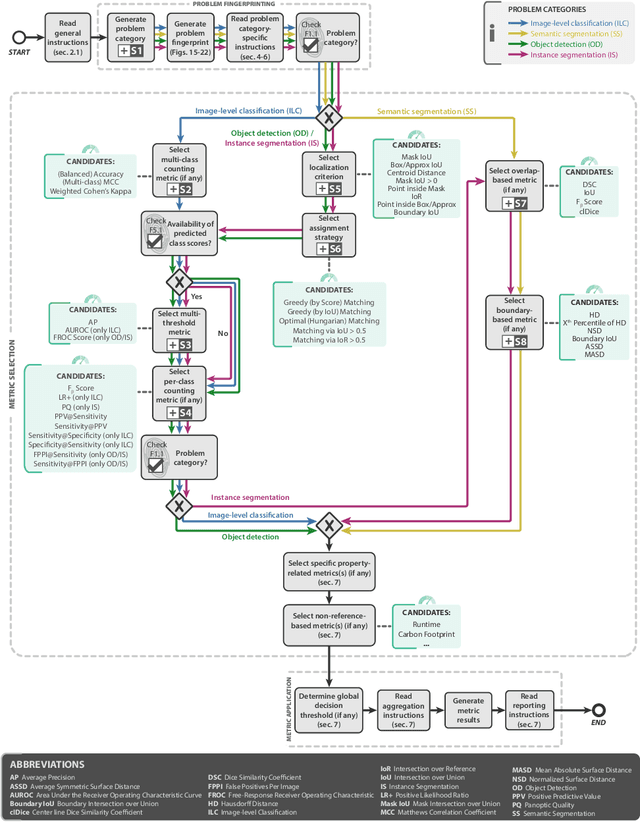
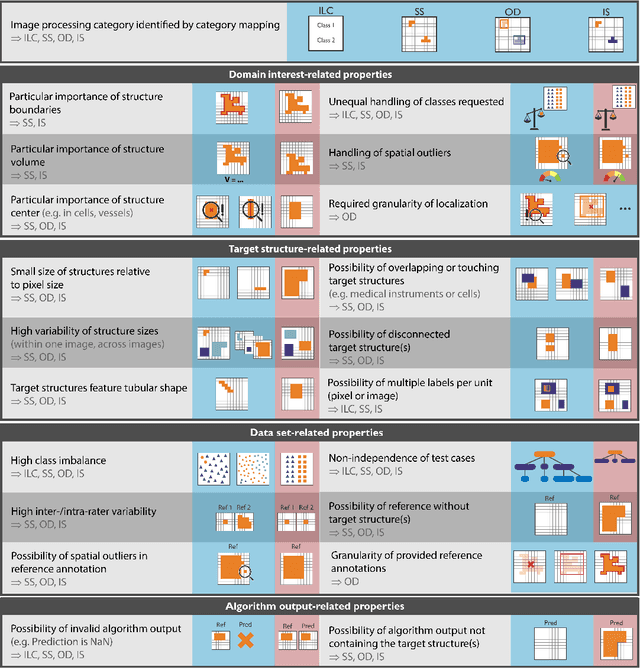
Abstract:The field of automatic biomedical image analysis crucially depends on robust and meaningful performance metrics for algorithm validation. Current metric usage, however, is often ill-informed and does not reflect the underlying domain interest. Here, we present a comprehensive framework that guides researchers towards choosing performance metrics in a problem-aware manner. Specifically, we focus on biomedical image analysis problems that can be interpreted as a classification task at image, object or pixel level. The framework first compiles domain interest-, target structure-, data set- and algorithm output-related properties of a given problem into a problem fingerprint, while also mapping it to the appropriate problem category, namely image-level classification, semantic segmentation, instance segmentation, or object detection. It then guides users through the process of selecting and applying a set of appropriate validation metrics while making them aware of potential pitfalls related to individual choices. In this paper, we describe the current status of the Metrics Reloaded recommendation framework, with the goal of obtaining constructive feedback from the image analysis community. The current version has been developed within an international consortium of more than 60 image analysis experts and will be made openly available as a user-friendly toolkit after community-driven optimization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge