Sophie Loizillon
for The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, APPRIMAGE Study Group
Confidence intervals uncovered: Are we ready for real-world medical imaging AI?
Sep 27, 2024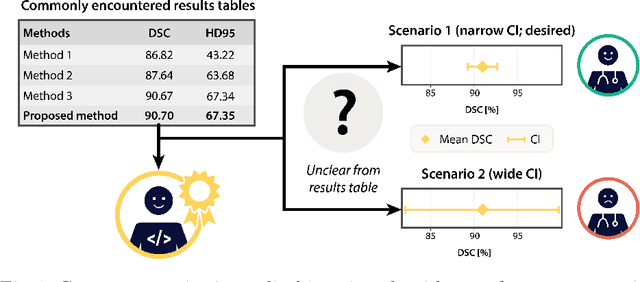
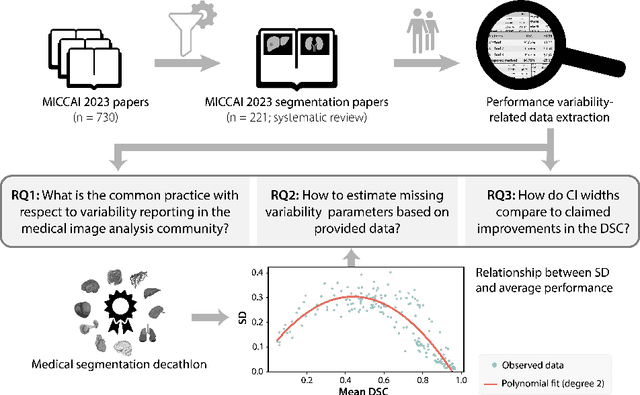
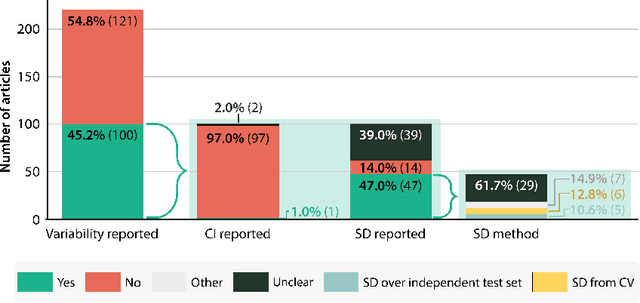

Abstract:Medical imaging is spearheading the AI transformation of healthcare. Performance reporting is key to determine which methods should be translated into clinical practice. Frequently, broad conclusions are simply derived from mean performance values. In this paper, we argue that this common practice is often a misleading simplification as it ignores performance variability. Our contribution is threefold. (1) Analyzing all MICCAI segmentation papers (n = 221) published in 2023, we first observe that more than 50% of papers do not assess performance variability at all. Moreover, only one (0.5%) paper reported confidence intervals (CIs) for model performance. (2) To address the reporting bottleneck, we show that the unreported standard deviation (SD) in segmentation papers can be approximated by a second-order polynomial function of the mean Dice similarity coefficient (DSC). Based on external validation data from 56 previous MICCAI challenges, we demonstrate that this approximation can accurately reconstruct the CI of a method using information provided in publications. (3) Finally, we reconstructed 95% CIs around the mean DSC of MICCAI 2023 segmentation papers. The median CI width was 0.03 which is three times larger than the median performance gap between the first and second ranked method. For more than 60% of papers, the mean performance of the second-ranked method was within the CI of the first-ranked method. We conclude that current publications typically do not provide sufficient evidence to support which models could potentially be translated into clinical practice.
Automated MRI Quality Assessment of Brain T1-weighted MRI in Clinical Data Warehouses: A Transfer Learning Approach Relying on Artefact Simulation
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:The emergence of clinical data warehouses (CDWs), which contain the medical data of millions of patients, has paved the way for vast data sharing for research. The quality of MRIs gathered in CDWs differs greatly from what is observed in research settings and reflects a certain clinical reality. Consequently, a significant proportion of these images turns out to be unusable due to their poor quality. Given the massive volume of MRIs contained in CDWs, the manual rating of image quality is impossible. Thus, it is necessary to develop an automated solution capable of effectively identifying corrupted images in CDWs. This study presents an innovative transfer learning method for automated quality control of 3D gradient echo T1-weighted brain MRIs within a CDW, leveraging artefact simulation. We first intentionally corrupt images from research datasets by inducing poorer contrast, adding noise and introducing motion artefacts. Subsequently, three artefact-specific models are pre-trained using these corrupted images to detect distinct types of artefacts. Finally, the models are generalised to routine clinical data through a transfer learning technique, utilising 3660 manually annotated images. The overall image quality is inferred from the results of the three models, each designed to detect a specific type of artefact. Our method was validated on an independent test set of 385 3D gradient echo T1-weighted MRIs. Our proposed approach achieved excellent results for the detection of bad quality MRIs, with a balanced accuracy of over 87%, surpassing our previous approach by 3.5 percent points. Additionally, we achieved a satisfactory balanced accuracy of 79% for the detection of moderate quality MRIs, outperforming our previous performance by 5 percent points. Our framework provides a valuable tool for exploiting the potential of MRIs in CDWs.
* Accepted for publication at the Journal of Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging (MELBA) https://melba-journal.org/2024:012
Frequency Disentangled Learning for Segmentation of Midbrain Structures from Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping Data
Feb 25, 2023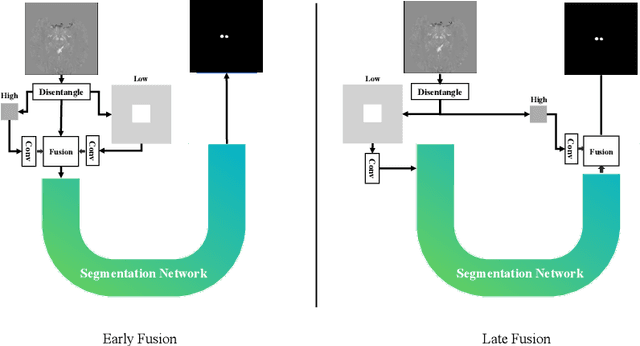

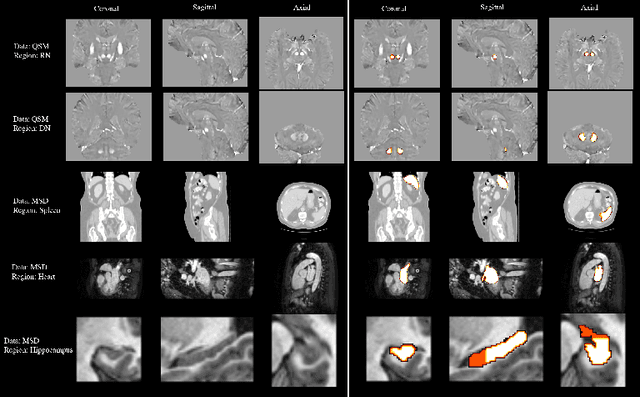
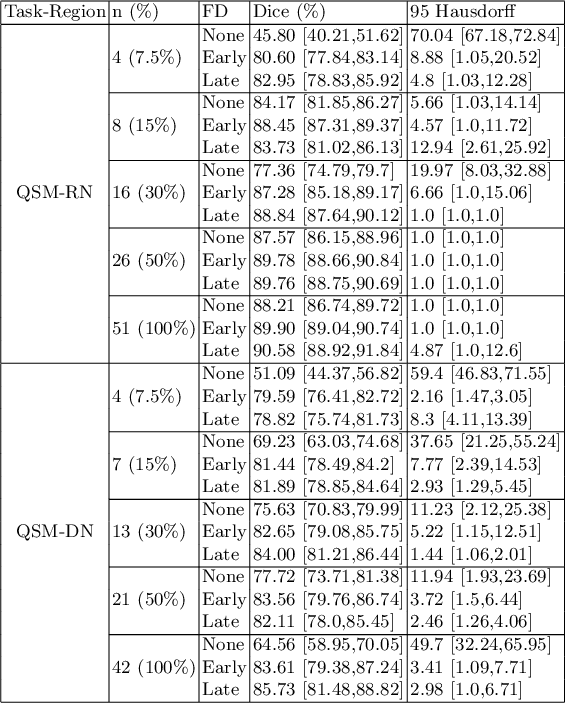
Abstract:One often lacks sufficient annotated samples for training deep segmentation models. This is in particular the case for less common imaging modalities such as Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM). It has been shown that deep models tend to fit the target function from low to high frequencies. One may hypothesize that such property can be leveraged for better training of deep learning models. In this paper, we exploit this property to propose a new training method based on frequency-domain disentanglement. It consists of two main steps: i) disentangling the image into high- and low-frequency parts and feature learning; ii) frequency-domain fusion to complete the task. The approach can be used with any backbone segmentation network. We apply the approach to the segmentation of the red and dentate nuclei from QSM data which is particularly relevant for the study of parkinsonian syndromes. We demonstrate that the proposed method provides considerable performance improvements for these tasks. We further applied it to three public datasets from the Medical Segmentation Decathlon (MSD) challenge. For two MSD tasks, it provided smaller but still substantial improvements (up to 7 points of Dice), especially under small training set situations.
Fourier Disentangled Multimodal Prior Knowledge Fusion for Red Nucleus Segmentation in Brain MRI
Nov 02, 2022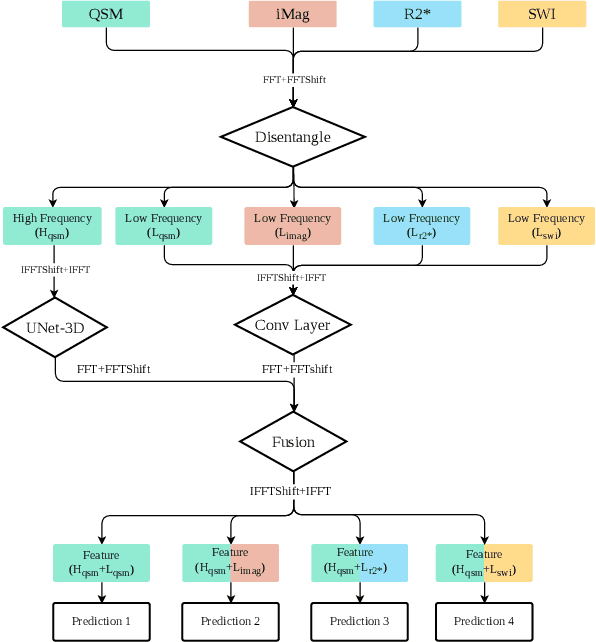
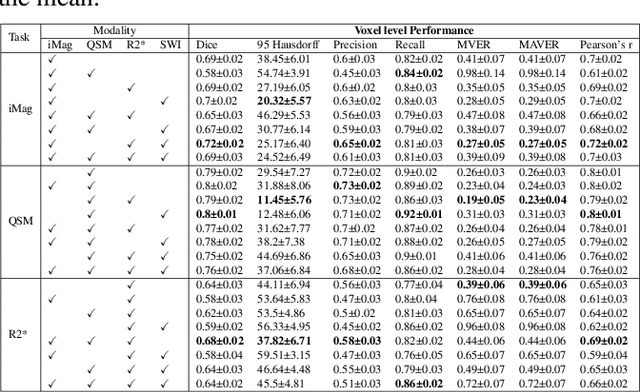
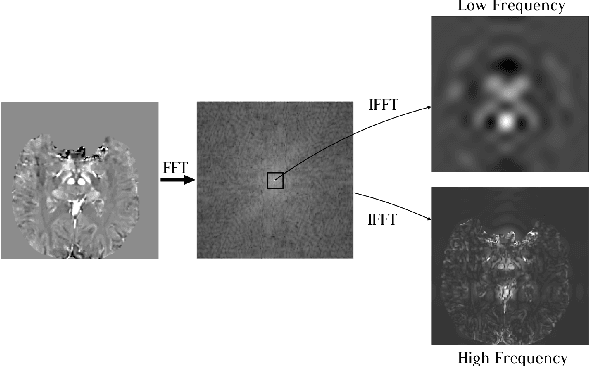
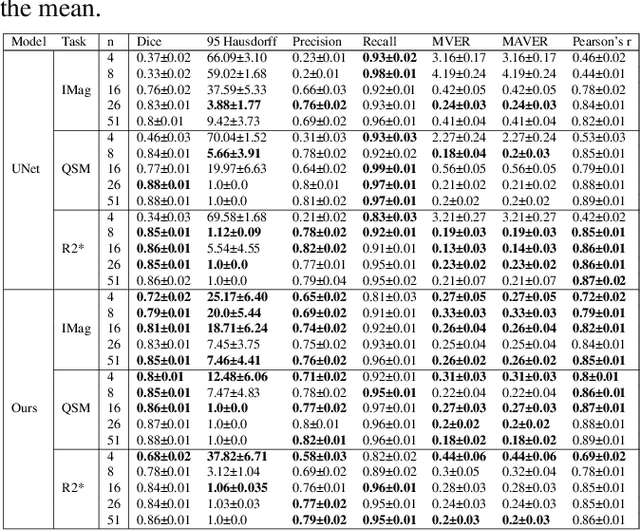
Abstract:Early and accurate diagnosis of parkinsonian syndromes is critical to provide appropriate care to patients and for inclusion in therapeutic trials. The red nucleus is a structure of the midbrain that plays an important role in these disorders. It can be visualized using iron-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sequences. Different iron-sensitive contrasts can be produced with MRI. Combining such multimodal data has the potential to improve segmentation of the red nucleus. Current multimodal segmentation algorithms are computationally consuming, cannot deal with missing modalities and need annotations for all modalities. In this paper, we propose a new model that integrates prior knowledge from different contrasts for red nucleus segmentation. The method consists of three main stages. First, it disentangles the image into high-level information representing the brain structure, and low-frequency information representing the contrast. The high-frequency information is then fed into a network to learn anatomical features, while the list of multimodal low-frequency information is processed by another module. Finally, feature fusion is performed to complete the segmentation task. The proposed method was used with several iron-sensitive contrasts (iMag, QSM, R2*, SWI). Experiments demonstrate that our proposed model substantially outperforms a baseline UNet model when the training set size is very small.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge