Jan-Hinrich Nölke
Application-driven Validation of Posteriors in Inverse Problems
Sep 18, 2023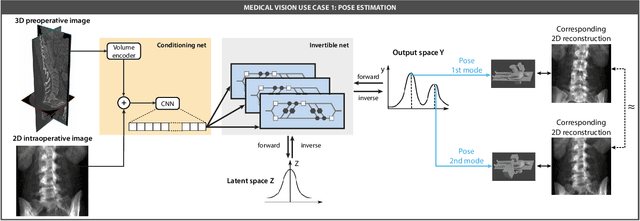
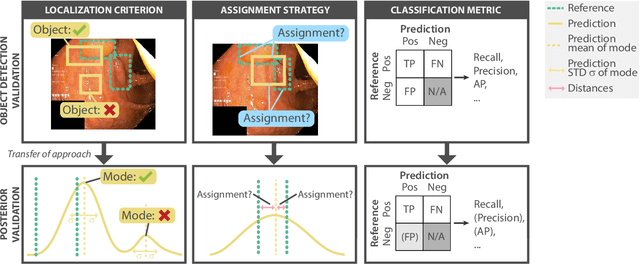
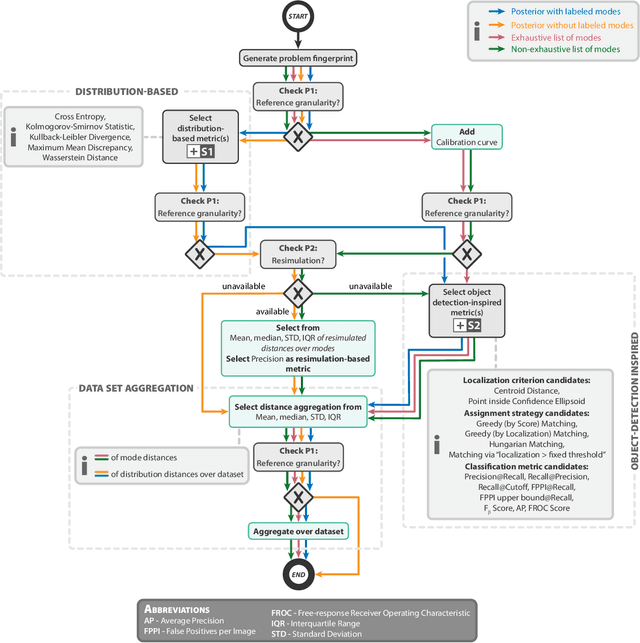
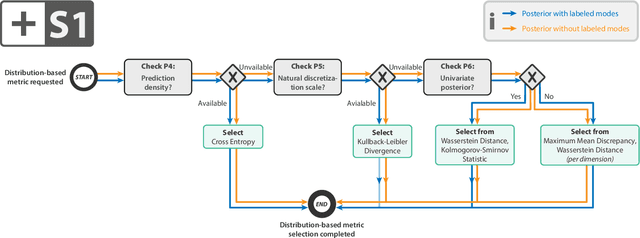
Abstract:Current deep learning-based solutions for image analysis tasks are commonly incapable of handling problems to which multiple different plausible solutions exist. In response, posterior-based methods such as conditional Diffusion Models and Invertible Neural Networks have emerged; however, their translation is hampered by a lack of research on adequate validation. In other words, the way progress is measured often does not reflect the needs of the driving practical application. Closing this gap in the literature, we present the first systematic framework for the application-driven validation of posterior-based methods in inverse problems. As a methodological novelty, it adopts key principles from the field of object detection validation, which has a long history of addressing the question of how to locate and match multiple object instances in an image. Treating modes as instances enables us to perform mode-centric validation, using well-interpretable metrics from the application perspective. We demonstrate the value of our framework through instantiations for a synthetic toy example and two medical vision use cases: pose estimation in surgery and imaging-based quantification of functional tissue parameters for diagnostics. Our framework offers key advantages over common approaches to posterior validation in all three examples and could thus revolutionize performance assessment in inverse problems.
Unsupervised Domain Transfer with Conditional Invertible Neural Networks
Mar 17, 2023Abstract:Synthetic medical image generation has evolved as a key technique for neural network training and validation. A core challenge, however, remains in the domain gap between simulations and real data. While deep learning-based domain transfer using Cycle Generative Adversarial Networks and similar architectures has led to substantial progress in the field, there are use cases in which state-of-the-art approaches still fail to generate training images that produce convincing results on relevant downstream tasks. Here, we address this issue with a domain transfer approach based on conditional invertible neural networks (cINNs). As a particular advantage, our method inherently guarantees cycle consistency through its invertible architecture, and network training can efficiently be conducted with maximum likelihood training. To showcase our method's generic applicability, we apply it to two spectral imaging modalities at different scales, namely hyperspectral imaging (pixel-level) and photoacoustic tomography (image-level). According to comprehensive experiments, our method enables the generation of realistic spectral data and outperforms the state of the art on two downstream classification tasks (binary and multi-class). cINN-based domain transfer could thus evolve as an important method for realistic synthetic data generation in the field of spectral imaging and beyond.
CholecTriplet2022: Show me a tool and tell me the triplet -- an endoscopic vision challenge for surgical action triplet detection
Feb 13, 2023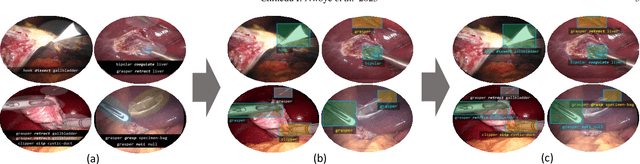
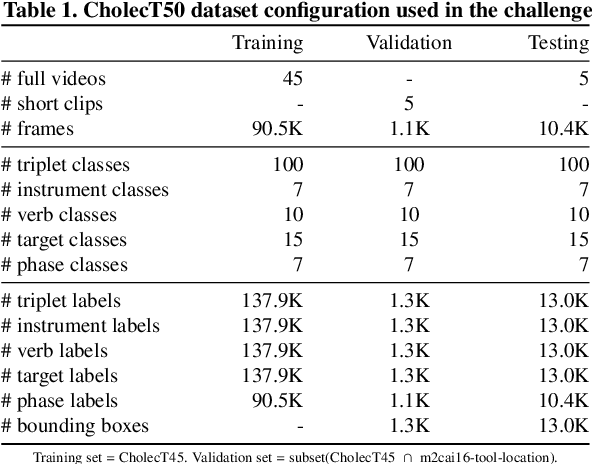
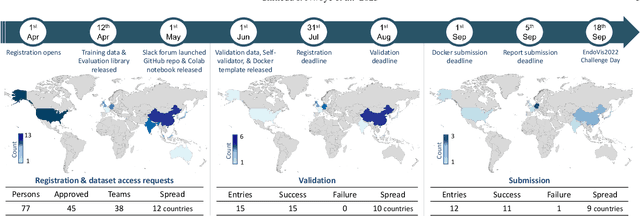
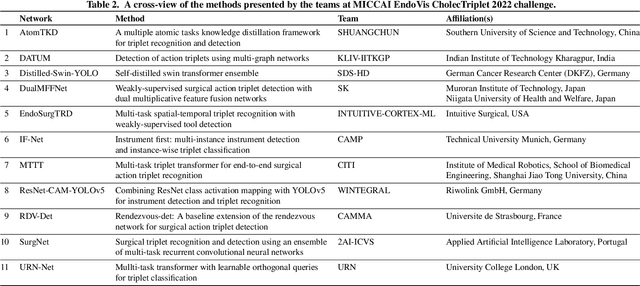
Abstract:Formalizing surgical activities as triplets of the used instruments, actions performed, and target anatomies is becoming a gold standard approach for surgical activity modeling. The benefit is that this formalization helps to obtain a more detailed understanding of tool-tissue interaction which can be used to develop better Artificial Intelligence assistance for image-guided surgery. Earlier efforts and the CholecTriplet challenge introduced in 2021 have put together techniques aimed at recognizing these triplets from surgical footage. Estimating also the spatial locations of the triplets would offer a more precise intraoperative context-aware decision support for computer-assisted intervention. This paper presents the CholecTriplet2022 challenge, which extends surgical action triplet modeling from recognition to detection. It includes weakly-supervised bounding box localization of every visible surgical instrument (or tool), as the key actors, and the modeling of each tool-activity in the form of <instrument, verb, target> triplet. The paper describes a baseline method and 10 new deep learning algorithms presented at the challenge to solve the task. It also provides thorough methodological comparisons of the methods, an in-depth analysis of the obtained results, their significance, and useful insights for future research directions and applications in surgery.
Tattoo tomography: Freehand 3D photoacoustic image reconstruction with an optical pattern
Nov 11, 2020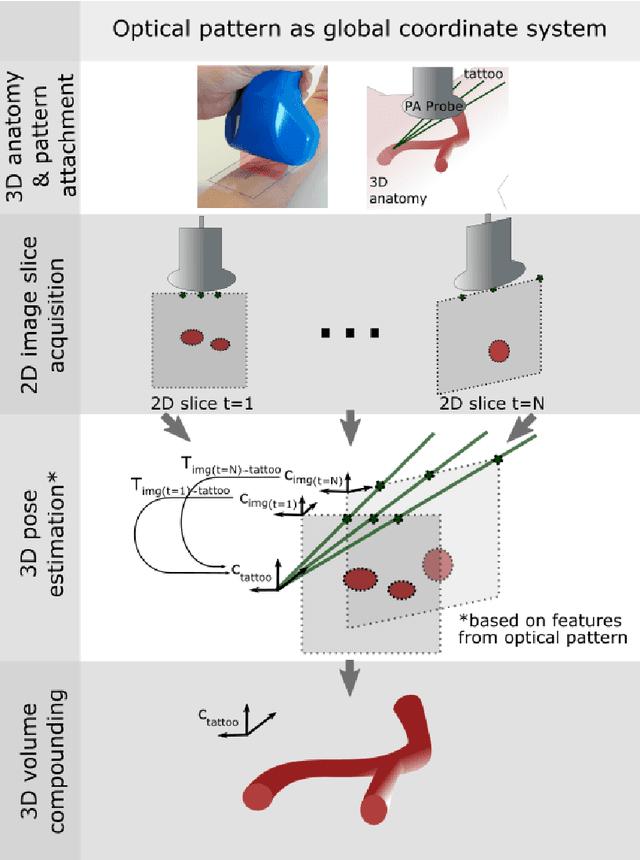
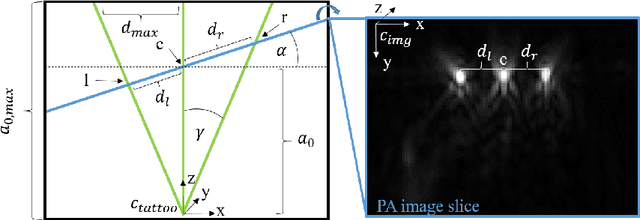
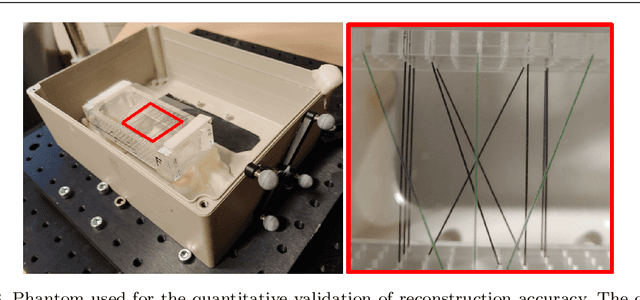
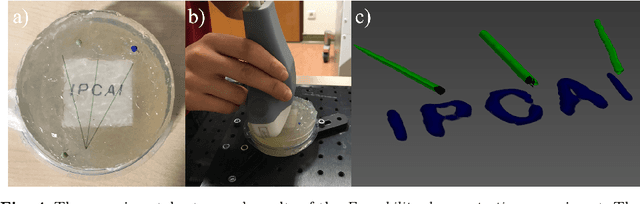
Abstract:Purpose: Photoacoustic tomography (PAT) is a novel imaging technique that can spatially resolve both morphological and functional tissue properties, such as the vessel topology and tissue oxygenation. While this capacity makes PAT a promising modality for the diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of various diseases, a current drawback is the limited field-of-view (FoV) provided by the conventionally applied 2D probes. Methods: In this paper, we present a novel approach to 3D reconstruction of PAT data (Tattoo tomography) that does not require an external tracking system and can smoothly be integrated into clinical workflows. It is based on an optical pattern placed on the region of interest prior to image acquisition. This pattern is designed in a way that a tomographic image of it enables the recovery of the probe pose relative to the coordinate system of the pattern. This allows the transformation of a sequence of acquired PA images into one common global coordinate system and thus the consistent 3D reconstruction of PAT imaging data. Results: An initial feasibility study conducted with experimental phantom data and in vivo forearm data indicates that the Tattoo approach is well-suited for 3D reconstruction of PAT data with high accuracy and precision. Conclusion: In contrast to previous approaches to 3D ultrasound (US) or PAT reconstruction, the Tattoo approach neither requires complex external hardware nor training data acquired for a specific application. It could thus become a valuable tool for clinical freehand PAT.
Invertible Neural Networks for Uncertainty Quantification in Photoacoustic Imaging
Nov 10, 2020



Abstract:Multispectral photoacoustic imaging (PAI) is an emerging imaging modality which enables the recovery of functional tissue parameters such as blood oxygenation. However, the underlying inverse problems are potentially ill-posed, meaning that radically different tissue properties may - in theory - yield comparable measurements. In this work, we present a new approach for handling this specific type of uncertainty by leveraging the concept of conditional invertible neural networks (cINNs). Specifically, we propose going beyond commonly used point estimates for tissue oxygenation and converting single-pixel initial pressure spectra to the full posterior probability density. This way, the inherent ambiguity of a problem can be encoded with multiple modes in the output. Based on the presented architecture, we demonstrate two use cases which leverage this information to not only detect and quantify but also to compensate for uncertainties: (1) photoacoustic device design and (2) optimization of photoacoustic image acquisition. Our in silico studies demonstrate the potential of the proposed methodology to become an important building block for uncertainty-aware reconstruction of physiological parameters with PAI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge