Tattoo tomography: Freehand 3D photoacoustic image reconstruction with an optical pattern
Paper and Code
Nov 11, 2020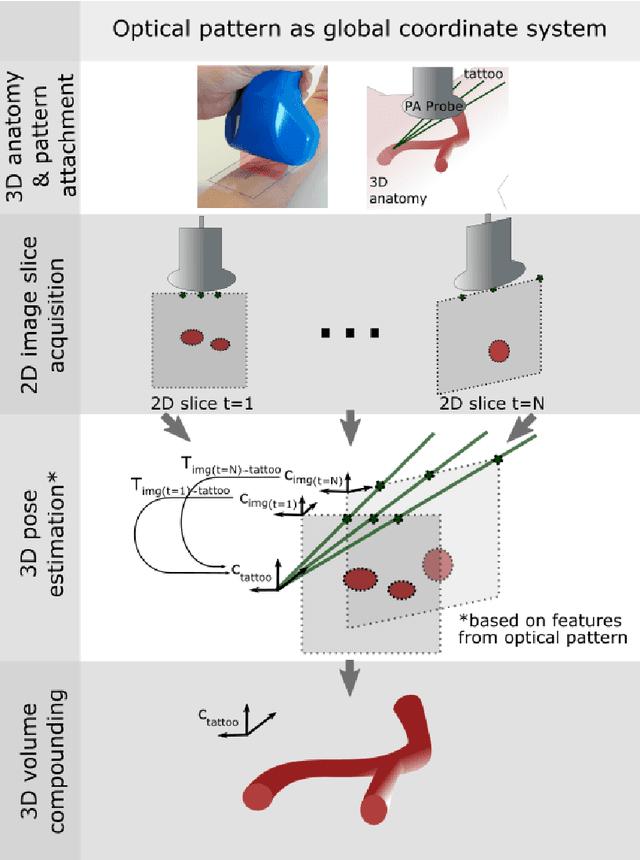
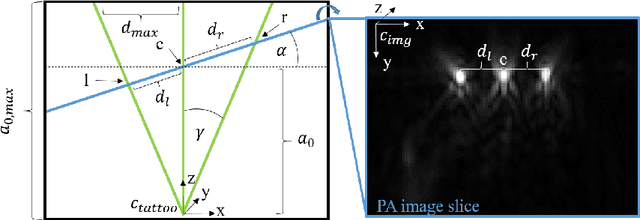
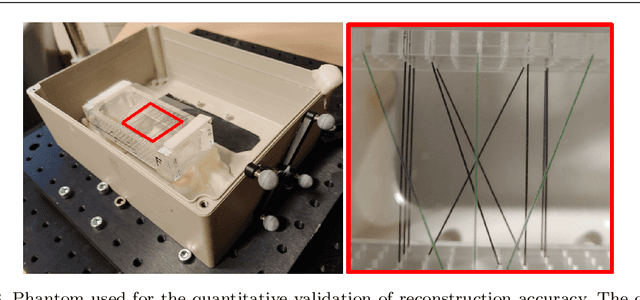
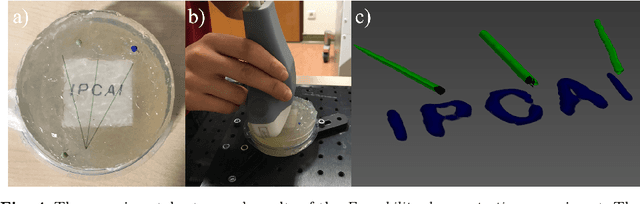
Purpose: Photoacoustic tomography (PAT) is a novel imaging technique that can spatially resolve both morphological and functional tissue properties, such as the vessel topology and tissue oxygenation. While this capacity makes PAT a promising modality for the diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of various diseases, a current drawback is the limited field-of-view (FoV) provided by the conventionally applied 2D probes. Methods: In this paper, we present a novel approach to 3D reconstruction of PAT data (Tattoo tomography) that does not require an external tracking system and can smoothly be integrated into clinical workflows. It is based on an optical pattern placed on the region of interest prior to image acquisition. This pattern is designed in a way that a tomographic image of it enables the recovery of the probe pose relative to the coordinate system of the pattern. This allows the transformation of a sequence of acquired PA images into one common global coordinate system and thus the consistent 3D reconstruction of PAT imaging data. Results: An initial feasibility study conducted with experimental phantom data and in vivo forearm data indicates that the Tattoo approach is well-suited for 3D reconstruction of PAT data with high accuracy and precision. Conclusion: In contrast to previous approaches to 3D ultrasound (US) or PAT reconstruction, the Tattoo approach neither requires complex external hardware nor training data acquired for a specific application. It could thus become a valuable tool for clinical freehand PAT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge