Leonardo Ayala
Computer Assisted Medical Interventions, Medical Faculty, Heidelberg University, Heidelberg, Germany
CARL: Camera-Agnostic Representation Learning for Spectral Image Analysis
Apr 27, 2025Abstract:Spectral imaging offers promising applications across diverse domains, including medicine and urban scene understanding, and is already established as a critical modality in remote sensing. However, variability in channel dimensionality and captured wavelengths among spectral cameras impede the development of AI-driven methodologies, leading to camera-specific models with limited generalizability and inadequate cross-camera applicability. To address this bottleneck, we introduce $\textbf{CARL}$, a model for $\textbf{C}$amera-$\textbf{A}$gnostic $\textbf{R}$epresentation $\textbf{L}$earning across RGB, multispectral, and hyperspectral imaging modalities. To enable the conversion of a spectral image with any channel dimensionality to a camera-agnostic embedding, we introduce wavelength positional encoding and a self-attention-cross-attention mechanism to compress spectral information into learned query representations. Spectral-spatial pre-training is achieved with a novel spectral self-supervised JEPA-inspired strategy tailored to CARL. Large-scale experiments across the domains of medical imaging, autonomous driving, and satellite imaging demonstrate our model's unique robustness to spectral heterogeneity, outperforming on datasets with simulated and real-world cross-camera spectral variations. The scalability and versatility of the proposed approach position our model as a backbone for future spectral foundation models.
Deep intra-operative illumination calibration of hyperspectral cameras
Sep 11, 2024



Abstract:Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) is emerging as a promising novel imaging modality with various potential surgical applications. Currently available cameras, however, suffer from poor integration into the clinical workflow because they require the lights to be switched off, or the camera to be manually recalibrated as soon as lighting conditions change. Given this critical bottleneck, the contribution of this paper is threefold: (1) We demonstrate that dynamically changing lighting conditions in the operating room dramatically affect the performance of HSI applications, namely physiological parameter estimation, and surgical scene segmentation. (2) We propose a novel learning-based approach to automatically recalibrating hyperspectral images during surgery and show that it is sufficiently accurate to replace the tedious process of white reference-based recalibration. (3) Based on a total of 742 HSI cubes from a phantom, porcine models, and rats we show that our recalibration method not only outperforms previously proposed methods, but also generalizes across species, lighting conditions, and image processing tasks. Due to its simple workflow integration as well as high accuracy, speed, and generalization capabilities, our method could evolve as a central component in clinical surgical HSI.
Unsupervised Domain Transfer with Conditional Invertible Neural Networks
Mar 17, 2023Abstract:Synthetic medical image generation has evolved as a key technique for neural network training and validation. A core challenge, however, remains in the domain gap between simulations and real data. While deep learning-based domain transfer using Cycle Generative Adversarial Networks and similar architectures has led to substantial progress in the field, there are use cases in which state-of-the-art approaches still fail to generate training images that produce convincing results on relevant downstream tasks. Here, we address this issue with a domain transfer approach based on conditional invertible neural networks (cINNs). As a particular advantage, our method inherently guarantees cycle consistency through its invertible architecture, and network training can efficiently be conducted with maximum likelihood training. To showcase our method's generic applicability, we apply it to two spectral imaging modalities at different scales, namely hyperspectral imaging (pixel-level) and photoacoustic tomography (image-level). According to comprehensive experiments, our method enables the generation of realistic spectral data and outperforms the state of the art on two downstream classification tasks (binary and multi-class). cINN-based domain transfer could thus evolve as an important method for realistic synthetic data generation in the field of spectral imaging and beyond.
Robust deep learning-based semantic organ segmentation in hyperspectral images
Nov 09, 2021Abstract:Semantic image segmentation is an important prerequisite for context-awareness and autonomous robotics in surgery. The state of the art has focused on conventional RGB video data acquired during minimally invasive surgery, but full-scene semantic segmentation based on spectral imaging data and obtained during open surgery has received almost no attention to date. To address this gap in the literature, we are investigating the following research questions based on hyperspectral imaging (HSI) data of pigs acquired in an open surgery setting: (1) What is an adequate representation of HSI data for neural network-based fully automated organ segmentation, especially with respect to the spatial granularity of the data (pixels vs. superpixels vs. patches vs. full images)? (2) Is there a benefit of using HSI data compared to other modalities, namely RGB data and processed HSI data (e.g. tissue parameters like oxygenation), when performing semantic organ segmentation? According to a comprehensive validation study based on 506 HSI images from 20 pigs, annotated with a total of 19 classes, deep learning-based segmentation performance increases - consistently across modalities - with the spatial context of the input data. Unprocessed HSI data offers an advantage over RGB data or processed data from the camera provider, with the advantage increasing with decreasing size of the input to the neural network. Maximum performance (HSI applied to whole images) yielded a mean dice similarity coefficient (DSC) of 0.89 (standard deviation (SD) 0.04), which is in the range of the inter-rater variability (DSC of 0.89 (SD 0.07)). We conclude that HSI could become a powerful image modality for fully-automatic surgical scene understanding with many advantages over traditional imaging, including the ability to recover additional functional tissue information.
Machine learning-based analysis of hyperspectral images for automated sepsis diagnosis
Jun 15, 2021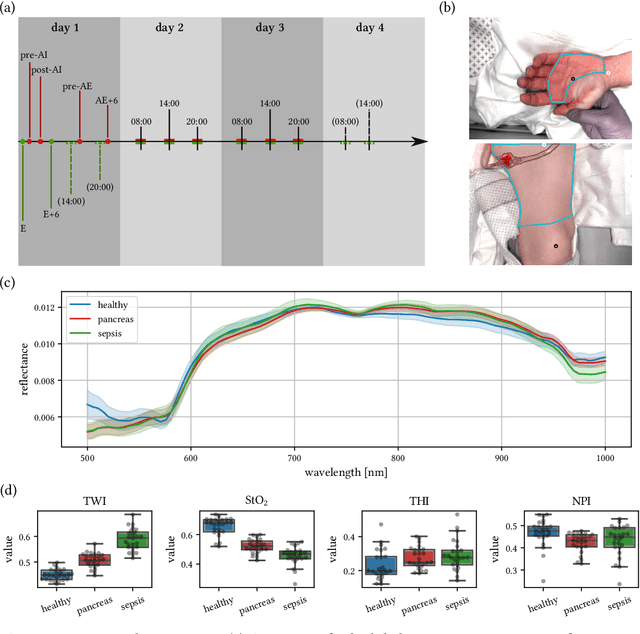
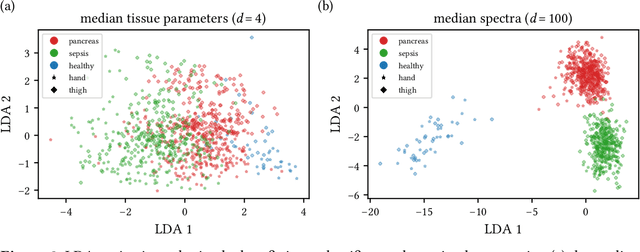
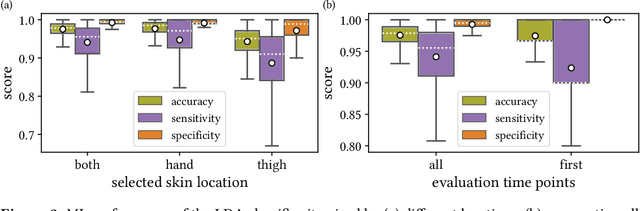
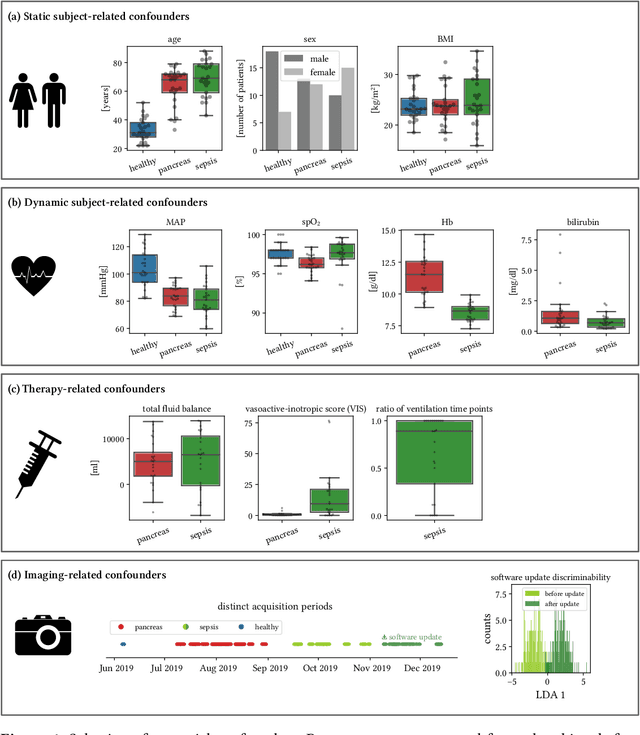
Abstract:Sepsis is a leading cause of mortality and critical illness worldwide. While robust biomarkers for early diagnosis are still missing, recent work indicates that hyperspectral imaging (HSI) has the potential to overcome this bottleneck by monitoring microcirculatory alterations. Automated machine learning-based diagnosis of sepsis based on HSI data, however, has not been explored to date. Given this gap in the literature, we leveraged an existing data set to (1) investigate whether HSI-based automated diagnosis of sepsis is possible and (2) put forth a list of possible confounders relevant for HSI-based tissue classification. While we were able to classify sepsis with an accuracy of over $98\,\%$ using the existing data, our research also revealed several subject-, therapy- and imaging-related confounders that may lead to an overestimation of algorithm performance when not balanced across the patient groups. We conclude that further prospective studies, carefully designed with respect to these confounders, are necessary to confirm the preliminary results obtained in this study.
Video-rate multispectral imaging in laparoscopic surgery: First-in-human application
May 28, 2021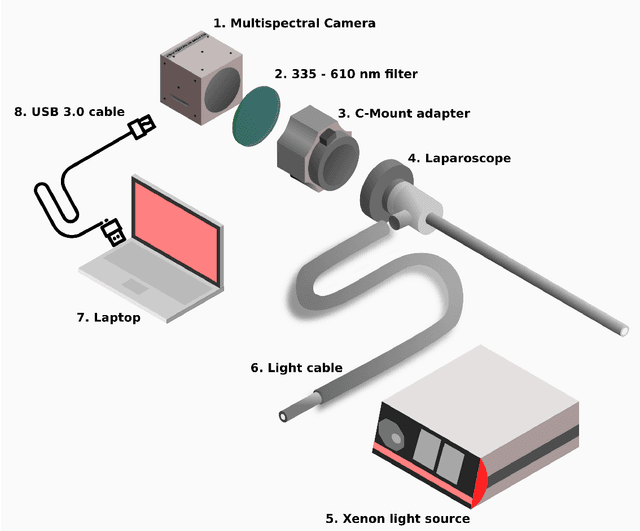
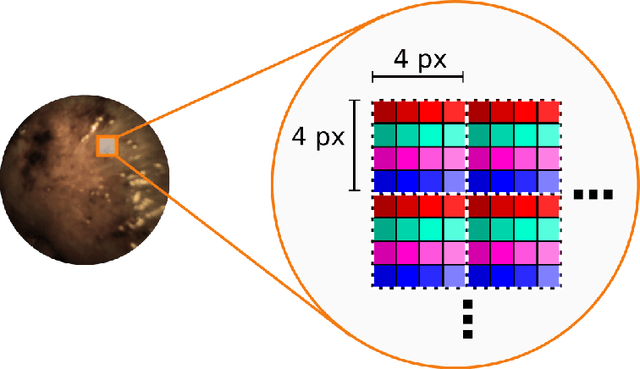
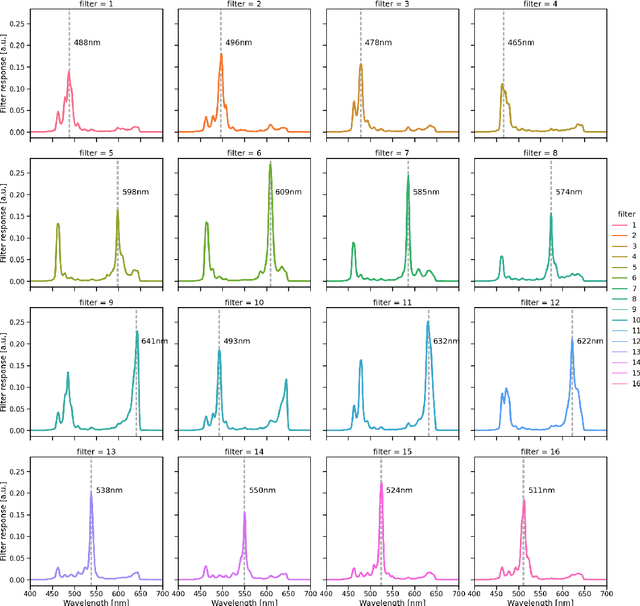
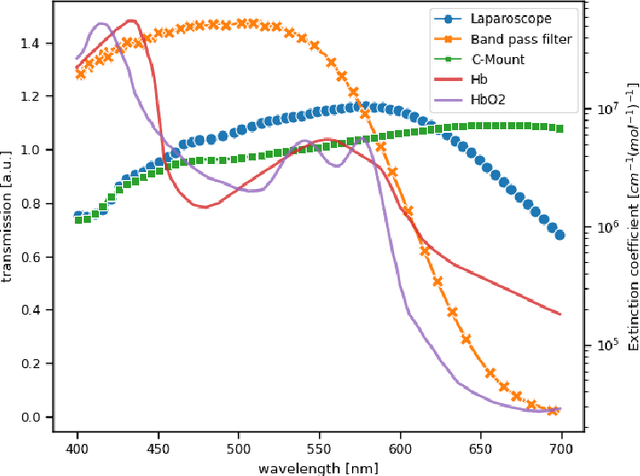
Abstract:Multispectral and hyperspectral imaging (MSI/HSI) can provide clinically relevant information on morphological and functional tissue properties. Application in the operating room (OR), however, has so far been limited by complex hardware setups and slow acquisition times. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel imaging system for video-rate spectral imaging in the clinical workflow. The system integrates a small snapshot multispectral camera with a standard laparoscope and a clinically commonly used light source, enabling the recording of multispectral images with a spectral dimension of 16 at a frame rate of 25 Hz. An ongoing in patient study shows that multispectral recordings from this system can help detect perfusion changes in partial nephrectomy surgery, thus opening the doors to a wide range of clinical applications.
Out of distribution detection for intra-operative functional imaging
Nov 05, 2019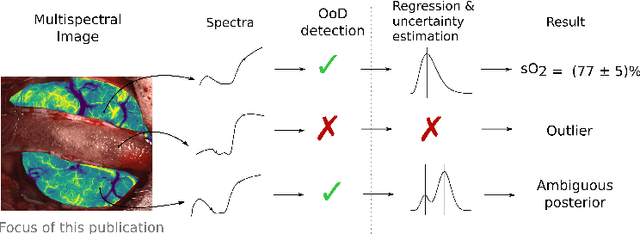
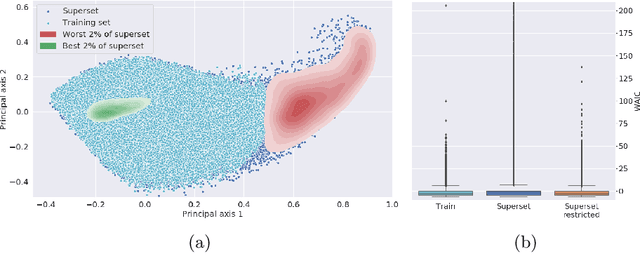
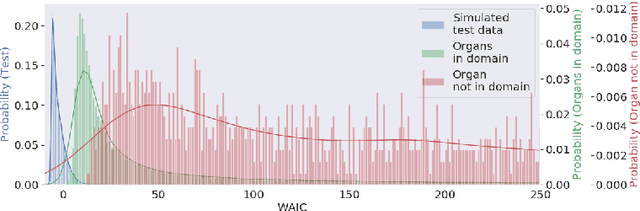
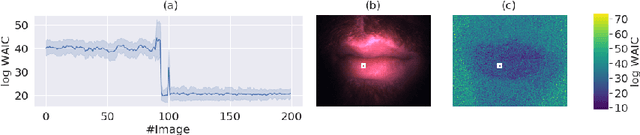
Abstract:Multispectral optical imaging is becoming a key tool in the operating room. Recent research has shown that machine learning algorithms can be used to convert pixel-wise reflectance measurements to tissue parameters, such as oxygenation. However, the accuracy of these algorithms can only be guaranteed if the spectra acquired during surgery match the ones seen during training. It is therefore of great interest to detect so-called out of distribution (OoD) spectra to prevent the algorithm from presenting spurious results. In this paper we present an information theory based approach to OoD detection based on the widely applicable information criterion (WAIC). Our work builds upon recent methodology related to invertible neural networks (INN). Specifically, we make use of an ensemble of INNs as we need their tractable Jacobians in order to compute the WAIC. Comprehensive experiments with in silico, and in vivo multispectral imaging data indicate that our approach is well-suited for OoD detection. Our method could thus be an important step towards reliable functional imaging in the operating room.
* The final authenticated version is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32689-0_8
Uncertainty-aware performance assessment of optical imaging modalities with invertible neural networks
Mar 08, 2019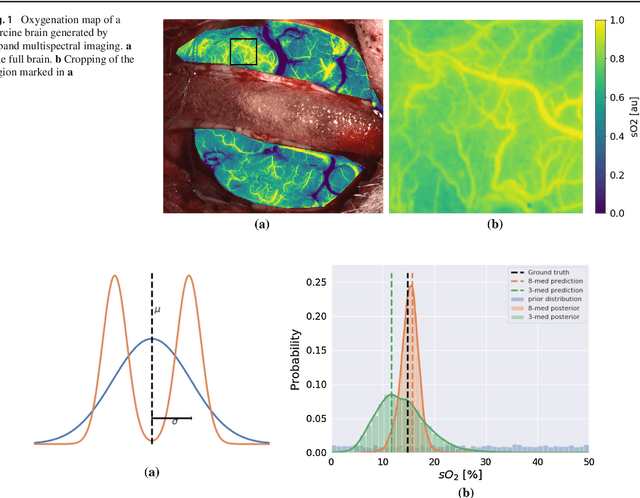
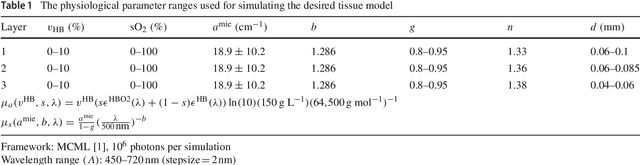

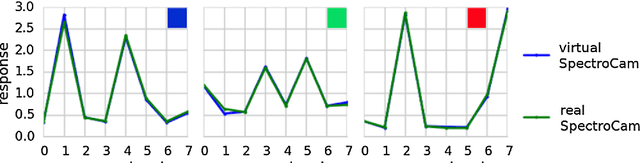
Abstract:Purpose: Optical imaging is evolving as a key technique for advanced sensing in the operating room. Recent research has shown that machine learning algorithms can be used to address the inverse problem of converting pixel-wise multispectral reflectance measurements to underlying tissue parameters, such as oxygenation. Assessment of the specific hardware used in conjunction with such algorithms, however, has not properly addressed the possibility that the problem may be ill-posed. Methods: We present a novel approach to the assessment of optical imaging modalities, which is sensitive to the different types of uncertainties that may occur when inferring tissue parameters. Based on the concept of invertible neural networks, our framework goes beyond point estimates and maps each multispectral measurement to a full posterior probability distribution which is capable of representing ambiguity in the solution via multiple modes. Performance metrics for a hardware setup can then be computed from the characteristics of the posteriors. Results: Application of the assessment framework to the specific use case of camera selection for physiological parameter estimation yields the following insights: (1) Estimation of tissue oxygenation from multispectral images is a well-posed problem, while (2) blood volume fraction may not be recovered without ambiguity. (3) In general, ambiguity may be reduced by increasing the number of spectral bands in the camera. Conclusion: Our method could help to optimize optical camera design in an application-specific manner.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge