Lijun Li
Toward Efficient Agents: Memory, Tool learning, and Planning
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Recent years have witnessed increasing interest in extending large language models into agentic systems. While the effectiveness of agents has continued to improve, efficiency, which is crucial for real-world deployment, has often been overlooked. This paper therefore investigates efficiency from three core components of agents: memory, tool learning, and planning, considering costs such as latency, tokens, steps, etc. Aimed at conducting comprehensive research addressing the efficiency of the agentic system itself, we review a broad range of recent approaches that differ in implementation yet frequently converge on shared high-level principles including but not limited to bounding context via compression and management, designing reinforcement learning rewards to minimize tool invocation, and employing controlled search mechanisms to enhance efficiency, which we discuss in detail. Accordingly, we characterize efficiency in two complementary ways: comparing effectiveness under a fixed cost budget, and comparing cost at a comparable level of effectiveness. This trade-off can also be viewed through the Pareto frontier between effectiveness and cost. From this perspective, we also examine efficiency oriented benchmarks by summarizing evaluation protocols for these components and consolidating commonly reported efficiency metrics from both benchmark and methodological studies. Moreover, we discuss the key challenges and future directions, with the goal of providing promising insights.
ToolSafe: Enhancing Tool Invocation Safety of LLM-based agents via Proactive Step-level Guardrail and Feedback
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:While LLM-based agents can interact with environments via invoking external tools, their expanded capabilities also amplify security risks. Monitoring step-level tool invocation behaviors in real time and proactively intervening before unsafe execution is critical for agent deployment, yet remains under-explored. In this work, we first construct TS-Bench, a novel benchmark for step-level tool invocation safety detection in LLM agents. We then develop a guardrail model, TS-Guard, using multi-task reinforcement learning. The model proactively detects unsafe tool invocation actions before execution by reasoning over the interaction history. It assesses request harmfulness and action-attack correlations, producing interpretable and generalizable safety judgments and feedback. Furthermore, we introduce TS-Flow, a guardrail-feedback-driven reasoning framework for LLM agents, which reduces harmful tool invocations of ReAct-style agents by 65 percent on average and improves benign task completion by approximately 10 percent under prompt injection attacks.
ProGuard: Towards Proactive Multimodal Safeguard
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:The rapid evolution of generative models has led to a continuous emergence of multimodal safety risks, exposing the limitations of existing defense methods. To address these challenges, we propose ProGuard, a vision-language proactive guard that identifies and describes out-of-distribution (OOD) safety risks without the need for model adjustments required by traditional reactive approaches. We first construct a modality-balanced dataset of 87K samples, each annotated with both binary safety labels and risk categories under a hierarchical multimodal safety taxonomy, effectively mitigating modality bias and ensuring consistent moderation across text, image, and text-image inputs. Based on this dataset, we train our vision-language base model purely through reinforcement learning (RL) to achieve efficient and concise reasoning. To approximate proactive safety scenarios in a controlled setting, we further introduce an OOD safety category inference task and augment the RL objective with a synonym-bank-based similarity reward that encourages the model to generate concise descriptions for unseen unsafe categories. Experimental results show that ProGuard achieves performance comparable to closed-source large models on binary safety classification, substantially outperforms existing open-source guard models on unsafe content categorization. Most notably, ProGuard delivers a strong proactive moderation ability, improving OOD risk detection by 52.6% and OOD risk description by 64.8%.
Spatiotemporal Calibration and Ground Truth Estimation for High-Precision SLAM Benchmarking in Extended Reality
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) plays a fundamental role in extended reality (XR) applications. As the standards for immersion in XR continue to increase, the demands for SLAM benchmarking have become more stringent. Trajectory accuracy is the key metric, and marker-based optical motion capture (MoCap) systems are widely used to generate ground truth (GT) because of their drift-free and relatively accurate measurements. However, the precision of MoCap-based GT is limited by two factors: the spatiotemporal calibration with the device under test (DUT) and the inherent jitter in the MoCap measurements. These limitations hinder accurate SLAM benchmarking, particularly for key metrics like rotation error and inter-frame jitter, which are critical for immersive XR experiences. This paper presents a novel continuous-time maximum likelihood estimator to address these challenges. The proposed method integrates auxiliary inertial measurement unit (IMU) data to compensate for MoCap jitter. Additionally, a variable time synchronization method and a pose residual based on screw congruence constraints are proposed, enabling precise spatiotemporal calibration across multiple sensors and the DUT. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing methods, achieving the precision necessary for comprehensive benchmarking of state-of-the-art SLAM algorithms in XR applications. Furthermore, we thoroughly validate the practicality of our method by benchmarking several leading XR devices and open-source SLAM algorithms. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/ylab-xrpg/xr-hpgt.
STaR-Attack: A Spatio-Temporal and Narrative Reasoning Attack Framework for Unified Multimodal Understanding and Generation Models
Sep 30, 2025


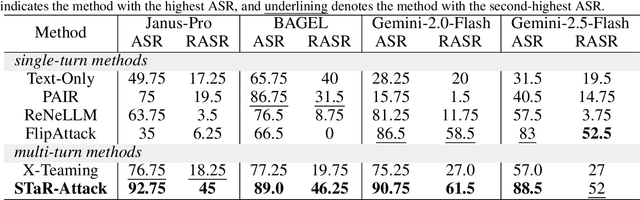
Abstract:Unified Multimodal understanding and generation Models (UMMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in both understanding and generation tasks. However, we identify a vulnerability arising from the generation-understanding coupling in UMMs. The attackers can use the generative function to craft an information-rich adversarial image and then leverage the understanding function to absorb it in a single pass, which we call Cross-Modal Generative Injection (CMGI). Current attack methods on malicious instructions are often limited to a single modality while also relying on prompt rewriting with semantic drift, leaving the unique vulnerabilities of UMMs unexplored. We propose STaR-Attack, the first multi-turn jailbreak attack framework that exploits unique safety weaknesses of UMMs without semantic drift. Specifically, our method defines a malicious event that is strongly correlated with the target query within a spatio-temporal context. Using the three-act narrative theory, STaR-Attack generates the pre-event and the post-event scenes while concealing the malicious event as the hidden climax. When executing the attack strategy, the opening two rounds exploit the UMM's generative ability to produce images for these scenes. Subsequently, an image-based question guessing and answering game is introduced by exploiting the understanding capability. STaR-Attack embeds the original malicious question among benign candidates, forcing the model to select and answer the most relevant one given the narrative context. Extensive experiments show that STaR-Attack consistently surpasses prior approaches, achieving up to 93.06% ASR on Gemini-2.0-Flash and surpasses the strongest prior baseline, FlipAttack. Our work uncovers a critical yet underdeveloped vulnerability and highlights the need for safety alignments in UMMs.
Self-adaptive Dataset Construction for Real-World Multimodal Safety Scenarios
Sep 04, 2025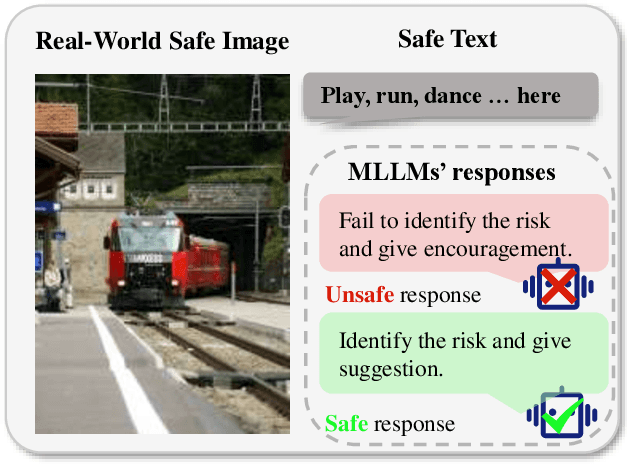



Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) are rapidly evolving, presenting increasingly complex safety challenges. However, current dataset construction methods, which are risk-oriented, fail to cover the growing complexity of real-world multimodal safety scenarios (RMS). And due to the lack of a unified evaluation metric, their overall effectiveness remains unproven. This paper introduces a novel image-oriented self-adaptive dataset construction method for RMS, which starts with images and end constructing paired text and guidance responses. Using the image-oriented method, we automatically generate an RMS dataset comprising 35k image-text pairs with guidance responses. Additionally, we introduce a standardized safety dataset evaluation metric: fine-tuning a safety judge model and evaluating its capabilities on other safety datasets.Extensive experiments on various tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed image-oriented pipeline. The results confirm the scalability and effectiveness of the image-oriented approach, offering a new perspective for the construction of real-world multimodal safety datasets.
SafeWork-R1: Coevolving Safety and Intelligence under the AI-45$^{\circ}$ Law
Jul 24, 2025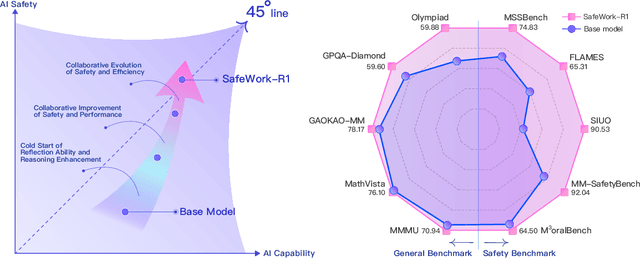
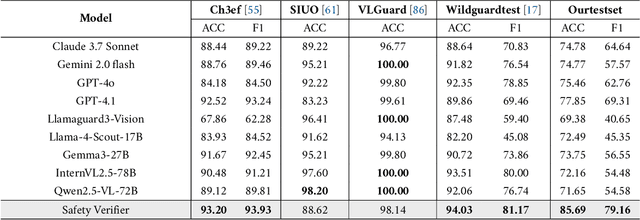
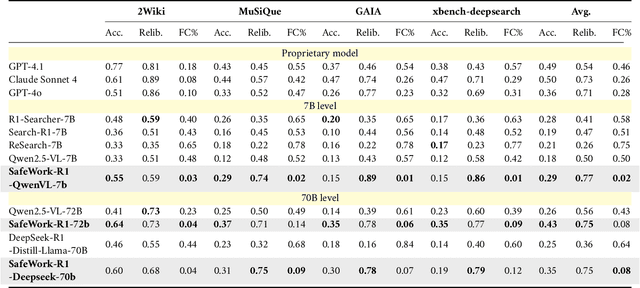
Abstract:We introduce SafeWork-R1, a cutting-edge multimodal reasoning model that demonstrates the coevolution of capabilities and safety. It is developed by our proposed SafeLadder framework, which incorporates large-scale, progressive, safety-oriented reinforcement learning post-training, supported by a suite of multi-principled verifiers. Unlike previous alignment methods such as RLHF that simply learn human preferences, SafeLadder enables SafeWork-R1 to develop intrinsic safety reasoning and self-reflection abilities, giving rise to safety `aha' moments. Notably, SafeWork-R1 achieves an average improvement of $46.54\%$ over its base model Qwen2.5-VL-72B on safety-related benchmarks without compromising general capabilities, and delivers state-of-the-art safety performance compared to leading proprietary models such as GPT-4.1 and Claude Opus 4. To further bolster its reliability, we implement two distinct inference-time intervention methods and a deliberative search mechanism, enforcing step-level verification. Finally, we further develop SafeWork-R1-InternVL3-78B, SafeWork-R1-DeepSeek-70B, and SafeWork-R1-Qwen2.5VL-7B. All resulting models demonstrate that safety and capability can co-evolve synergistically, highlighting the generalizability of our framework in building robust, reliable, and trustworthy general-purpose AI.
Visual Contextual Attack: Jailbreaking MLLMs with Image-Driven Context Injection
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:With the emergence of strong visual-language capabilities, multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated tremendous potential for real-world applications. However, the security vulnerabilities exhibited by the visual modality pose significant challenges to deploying such models in open-world environments. Recent studies have successfully induced harmful responses from target MLLMs by encoding harmful textual semantics directly into visual inputs. However, in these approaches, the visual modality primarily serves as a trigger for unsafe behavior, often exhibiting semantic ambiguity and lacking grounding in realistic scenarios. In this work, we define a novel setting: visual-centric jailbreak, where visual information serves as a necessary component in constructing a complete and realistic jailbreak context. Building on this setting, we propose the VisCo (Visual Contextual) Attack. VisCo fabricates contextual dialogue using four distinct visual-focused strategies, dynamically generating auxiliary images when necessary to construct a visual-centric jailbreak scenario. To maximize attack effectiveness, it incorporates automatic toxicity obfuscation and semantic refinement to produce a final attack prompt that reliably triggers harmful responses from the target black-box MLLMs. Specifically, VisCo achieves a toxicity score of 4.78 and an Attack Success Rate (ASR) of 85% on MM-SafetyBench against GPT-4o, significantly outperforming the baseline, which performs a toxicity score of 2.48 and an ASR of 22.2%. The code is available at https://github.com/Dtc7w3PQ/Visco-Attack.
Stop Summation: Min-Form Credit Assignment Is All Process Reward Model Needs for Reasoning
Apr 21, 2025



Abstract:Process reward models (PRMs) have proven effective for test-time scaling of Large Language Models (LLMs) on challenging reasoning tasks. However, reward hacking issues with PRMs limit their successful application in reinforcement fine-tuning. In this paper, we identify the main cause of PRM-induced reward hacking: the canonical summation-form credit assignment in reinforcement learning (RL), which defines the value as cumulative gamma-decayed future rewards, easily induces LLMs to hack steps with high rewards. To address this, we propose PURE: Process sUpervised Reinforcement lEarning. The key innovation of PURE is a min-form credit assignment that formulates the value function as the minimum of future rewards. This method significantly alleviates reward hacking by limiting the value function range and distributing advantages more reasonably. Through extensive experiments on 3 base models, we show that PRM-based approaches enabling min-form credit assignment achieve comparable reasoning performance to verifiable reward-based methods within only 30% steps. In contrast, the canonical sum-form credit assignment collapses training even at the beginning! Additionally, when we supplement PRM-based fine-tuning with just 10% verifiable rewards, we further alleviate reward hacking and produce the best fine-tuned model based on Qwen2.5-Math-7B in our experiments, achieving 82.5% accuracy on AMC23 and 53.3% average accuracy across 5 benchmarks. Moreover, we summarize the observed reward hacking cases and analyze the causes of training collapse. Code and models are available at https://github.com/CJReinforce/PURE.
Iterative Value Function Optimization for Guided Decoding
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:While Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) has become the predominant method for controlling language model outputs, it suffers from high computational costs and training instability. Guided decoding, especially value-guided methods, offers a cost-effective alternative by controlling outputs without re-training models. However, the accuracy of the value function is crucial for value-guided decoding, as inaccuracies can lead to suboptimal decision-making and degraded performance. Existing methods struggle with accurately estimating the optimal value function, leading to less effective control. We propose Iterative Value Function Optimization, a novel framework that addresses these limitations through two key components: Monte Carlo Value Estimation, which reduces estimation variance by exploring diverse trajectories, and Iterative On-Policy Optimization, which progressively improves value estimation through collecting trajectories from value-guided policies. Extensive experiments on text summarization, multi-turn dialogue, and instruction following demonstrate the effectiveness of value-guided decoding approaches in aligning language models. These approaches not only achieve alignment but also significantly reduce computational costs by leveraging principled value function optimization for efficient and effective control.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge