Jingyi Deng
Can Deep Research Agents Find and Organize? Evaluating the Synthesis Gap with Expert Taxonomies
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Deep Research Agents are increasingly used for automated survey generation. However, whether they can write surveys like human experts remains unclear. Existing benchmarks focus on fluency or citation accuracy, but none evaluates the core capabilities: retrieving essential papers and organizing them into coherent knowledge structures. We introduce TaxoBench, a diagnostic benchmark derived from 72 highly-cited computer science surveys. We manually extract expert-authored taxonomy trees containing 3,815 precisely categorized citations as ground truth. Our benchmark supports two evaluation modes: Deep Research mode tests end-to-end retrieval and organization given only a topic, while Bottom-Up mode isolates structuring capability by providing the exact papers human experts used. We evaluate 7 leading Deep Research agents and 12 frontier LLMs. Results reveal a dual bottleneck: the best agent recalls only 20.9% of expert-selected papers, and even with perfect input, the best model achieves only 0.31 ARI in organization. Current deep research agents remain far from expert-level survey writing. Our benchmark is publicly available at https://github.com/KongLongGeFDU/TaxoBench.
OpenNovelty: An LLM-powered Agentic System for Verifiable Scholarly Novelty Assessment
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Evaluating novelty is critical yet challenging in peer review, as reviewers must assess submissions against a vast, rapidly evolving literature. This report presents OpenNovelty, an LLM-powered agentic system for transparent, evidence-based novelty analysis. The system operates through four phases: (1) extracting the core task and contribution claims to generate retrieval queries; (2) retrieving relevant prior work based on extracted queries via semantic search engine; (3) constructing a hierarchical taxonomy of core-task-related work and performing contribution-level full-text comparisons against each contribution; and (4) synthesizing all analyses into a structured novelty report with explicit citations and evidence snippets. Unlike naive LLM-based approaches, \textsc{OpenNovelty} grounds all assessments in retrieved real papers, ensuring verifiable judgments. We deploy our system on 500+ ICLR 2026 submissions with all reports publicly available on our website, and preliminary analysis suggests it can identify relevant prior work, including closely related papers that authors may overlook. OpenNovelty aims to empower the research community with a scalable tool that promotes fair, consistent, and evidence-backed peer review.
Multi-modal Deepfake Detection and Localization with FPN-Transformer
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models has enabled the creation of highly realistic deepfake content, posing significant threats to digital trust across audio-visual domains. While unimodal detection methods have shown progress in identifying synthetic media, their inability to leverage cross-modal correlations and precisely localize forged segments limits their practicality against sophisticated, fine-grained manipulations. To address this, we introduce a multi-modal deepfake detection and localization framework based on a Feature Pyramid-Transformer (FPN-Transformer), addressing critical gaps in cross-modal generalization and temporal boundary regression. The proposed approach utilizes pre-trained self-supervised models (WavLM for audio, CLIP for video) to extract hierarchical temporal features. A multi-scale feature pyramid is constructed through R-TLM blocks with localized attention mechanisms, enabling joint analysis of cross-context temporal dependencies. The dual-branch prediction head simultaneously predicts forgery probabilities and refines temporal offsets of manipulated segments, achieving frame-level localization precision. We evaluate our approach on the test set of the IJCAI'25 DDL-AV benchmark, showing a good performance with a final score of 0.7535 for cross-modal deepfake detection and localization in challenging environments. Experimental results confirm the effectiveness of our approach and provide a novel way for generalized deepfake detection. Our code is available at https://github.com/Zig-HS/MM-DDL
LLMEval-3: A Large-Scale Longitudinal Study on Robust and Fair Evaluation of Large Language Models
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Existing evaluation of Large Language Models (LLMs) on static benchmarks is vulnerable to data contamination and leaderboard overfitting, critical issues that obscure true model capabilities. To address this, we introduce LLMEval-3, a framework for dynamic evaluation of LLMs. LLMEval-3 is built on a proprietary bank of 220k graduate-level questions, from which it dynamically samples unseen test sets for each evaluation run. Its automated pipeline ensures integrity via contamination-resistant data curation, a novel anti-cheating architecture, and a calibrated LLM-as-a-judge process achieving 90% agreement with human experts, complemented by a relative ranking system for fair comparison. An 20-month longitudinal study of nearly 50 leading models reveals a performance ceiling on knowledge memorization and exposes data contamination vulnerabilities undetectable by static benchmarks. The framework demonstrates exceptional robustness in ranking stability and consistency, providing strong empirical validation for the dynamic evaluation paradigm. LLMEval-3 offers a robust and credible methodology for assessing the true capabilities of LLMs beyond leaderboard scores, promoting the development of more trustworthy evaluation standards.
A Survey of Defenses against AI-generated Visual Media: Detection, Disruption, and Authentication
Jul 15, 2024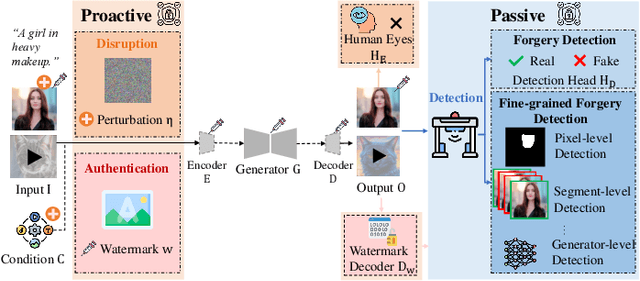
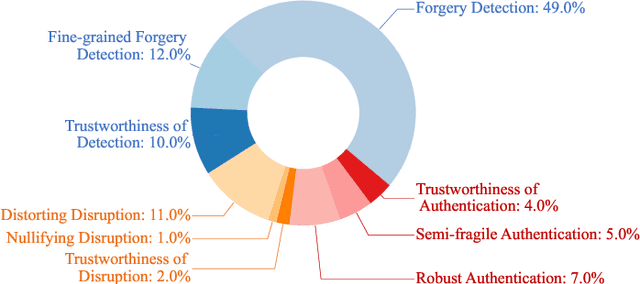
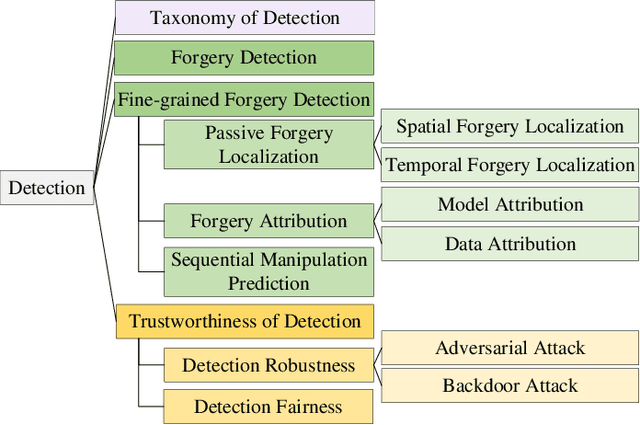
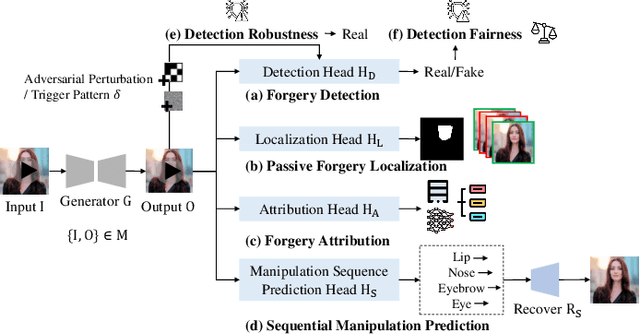
Abstract:Deep generative models have demonstrated impressive performance in various computer vision applications, including image synthesis, video generation, and medical analysis. Despite their significant advancements, these models may be used for malicious purposes, such as misinformation, deception, and copyright violation. In this paper, we provide a systematic and timely review of research efforts on defenses against AI-generated visual media, covering detection, disruption, and authentication. We review existing methods and summarize the mainstream defense-related tasks within a unified passive and proactive framework. Moreover, we survey the derivative tasks concerning the trustworthiness of defenses, such as their robustness and fairness. For each task, we formulate its general pipeline and propose a taxonomy based on methodological strategies that are uniformly applicable to the primary subtasks. Additionally, we summarize the commonly used evaluation datasets, criteria, and metrics. Finally, by analyzing the reviewed studies, we provide insights into current research challenges and suggest possible directions for future research.
From GPT-4 to Gemini and Beyond: Assessing the Landscape of MLLMs on Generalizability, Trustworthiness and Causality through Four Modalities
Jan 29, 2024
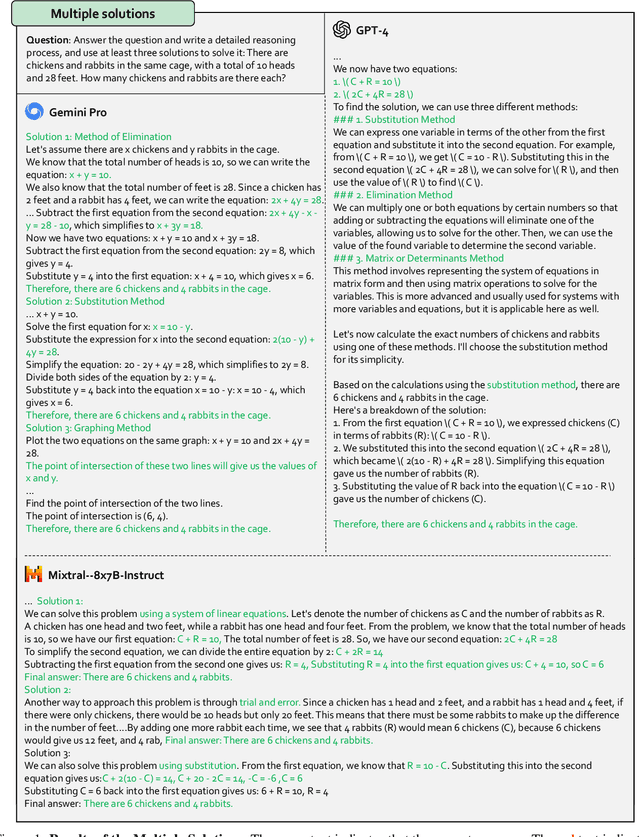
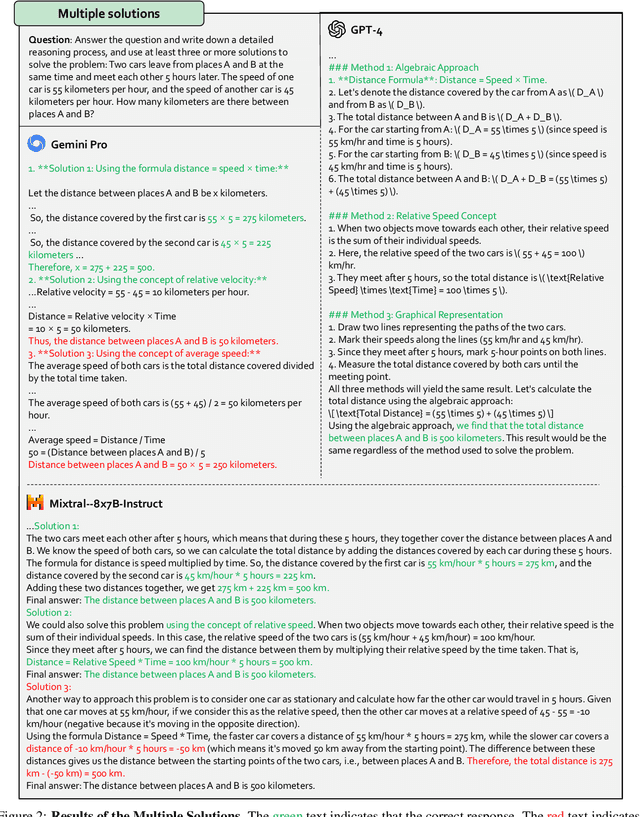

Abstract:Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have shown impressive abilities in generating reasonable responses with respect to multi-modal contents. However, there is still a wide gap between the performance of recent MLLM-based applications and the expectation of the broad public, even though the most powerful OpenAI's GPT-4 and Google's Gemini have been deployed. This paper strives to enhance understanding of the gap through the lens of a qualitative study on the generalizability, trustworthiness, and causal reasoning capabilities of recent proprietary and open-source MLLMs across four modalities: ie, text, code, image, and video, ultimately aiming to improve the transparency of MLLMs. We believe these properties are several representative factors that define the reliability of MLLMs, in supporting various downstream applications. To be specific, we evaluate the closed-source GPT-4 and Gemini and 6 open-source LLMs and MLLMs. Overall we evaluate 230 manually designed cases, where the qualitative results are then summarized into 12 scores (ie, 4 modalities times 3 properties). In total, we uncover 14 empirical findings that are useful to understand the capabilities and limitations of both proprietary and open-source MLLMs, towards more reliable downstream multi-modal applications.
Towards Benchmarking and Evaluating Deepfake Detection
Mar 04, 2022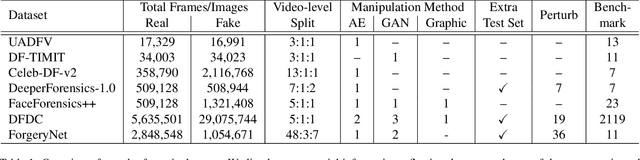
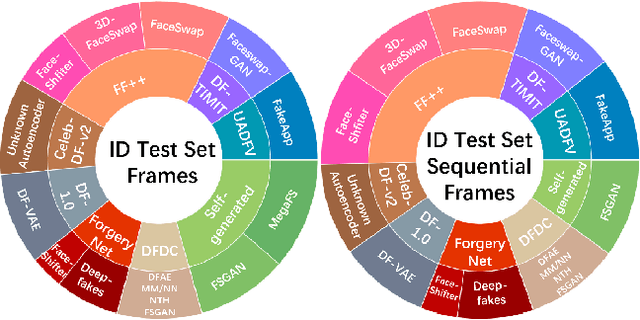

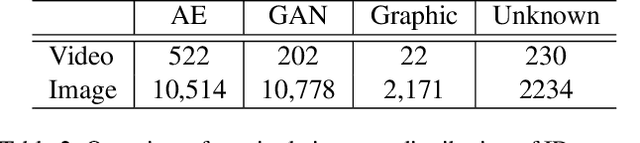
Abstract:Deepfake detection automatically recognizes the manipulated medias through the analysis of the difference between manipulated and non-altered videos. It is natural to ask which are the top performers among the existing deepfake detection approaches to identify promising research directions and provide practical guidance. Unfortunately, it's difficult to conduct a sound benchmarking comparison of existing detection approaches using the results in the literature because evaluation conditions are inconsistent across studies. Our objective is to establish a comprehensive and consistent benchmark, to develop a repeatable evaluation procedure, and to measure the performance of a range of detection approaches so that the results can be compared soundly. A challenging dataset consisting of the manipulated samples generated by more than 13 different methods has been collected, and 11 popular detection approaches (9 algorithms) from the existing literature have been implemented and evaluated with 6 fair-minded and practical evaluation metrics. Finally, 92 models have been trained and 644 experiments have been performed for the evaluation. The results along with the shared data and evaluation methodology constitute a benchmark for comparing deepfake detection approaches and measuring progress.
OpenHI2 -- Open source histopathological image platform
Jan 15, 2020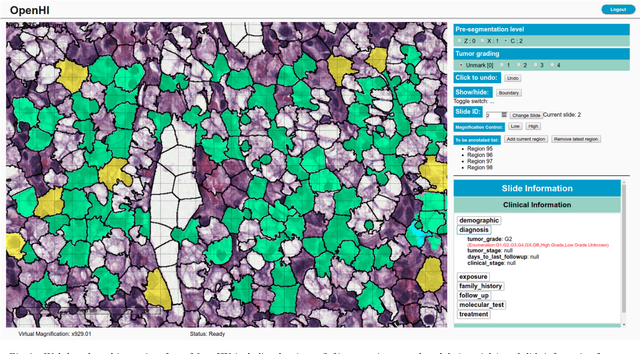
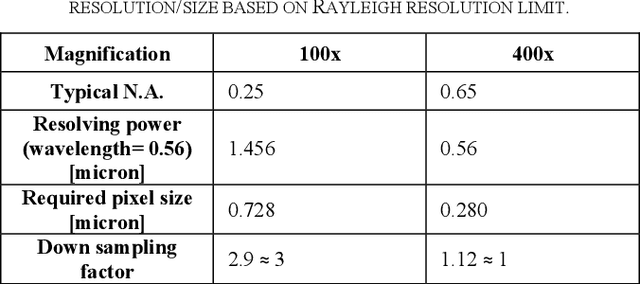
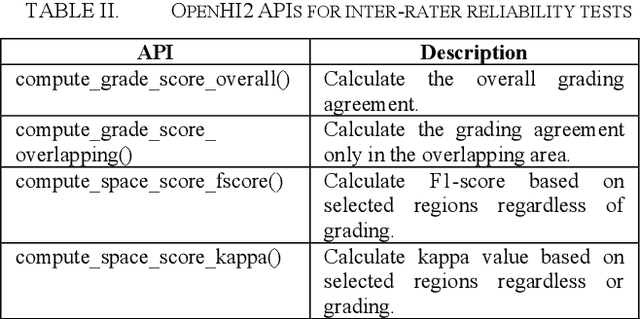
Abstract:Transition from conventional to digital pathology requires a new category of biomedical informatic infrastructure which could facilitate delicate pathological routine. Pathological diagnoses are sensitive to many external factors and is known to be subjective. Only systems that can meet strict requirements in pathology would be able to run along pathological routines and eventually digitized the study area, and the developed platform should comply with existing pathological routines and international standards. Currently, there are a number of available software tools which can perform histopathological tasks including virtual slide viewing, annotating, and basic image analysis, however, none of them can serve as a digital platform for pathology. Here we describe OpenHI2, an enhanced version Open Histopathological Image platform which is capable of supporting all basic pathological tasks and file formats; ready to be deployed in medical institutions on a standard server environment or cloud computing infrastructure. In this paper, we also describe the development decisions for the platform and propose solutions to overcome technical challenges so that OpenHI2 could be used as a platform for histopathological images. Further addition can be made to the platform since each component is modularized and fully documented. OpenHI2 is free, open-source, and available at https://gitlab.com/BioAI/OpenHI.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge