Lantao Hu
Towards End-to-End Alignment of User Satisfaction via Questionnaire in Video Recommendation
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Short-video recommender systems typically optimize ranking models using dense user behavioral signals, such as clicks and watch time. However, these signals are only indirect proxies of user satisfaction and often suffer from noise and bias. Recently, explicit satisfaction feedback collected through questionnaires has emerged as a high-quality direct alignment supervision, but is extremely sparse and easily overwhelmed by abundant behavioral data, making it difficult to incorporate into online recommendation models. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework which is towards End-to-End Alignment of user Satisfaction via Questionaire, named EASQ, to enable real-time alignment of ranking models with true user satisfaction. Specifically, we first construct an independent parameter pathway for sparse questionnaire signals by combining a multi-task architecture and a lightweight LoRA module. The multi-task design separates sparse satisfaction supervision from dense behavioral signals, preventing the former from being overwhelmed. The LoRA module pre-inject these preferences in a parameter-isolated manner, ensuring stability in the backbone while optimizing user satisfaction. Furthermore, we employ a DPO-based optimization objective tailored for online learning, which aligns the main model outputs with sparse satisfaction signals in real time. This design enables end-to-end online learning, allowing the model to continuously adapt to new questionnaire feedback while maintaining the stability and effectiveness of the backbone. Extensive offline experiments and large-scale online A/B tests demonstrate that EASQ consistently improves user satisfaction metrics across multiple scenarios. EASQ has been successfully deployed in a production short-video recommendation system, delivering significant and stable business gains.
GoalRank: Group-Relative Optimization for a Large Ranking Model
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Mainstream ranking approaches typically follow a Generator-Evaluator two-stage paradigm, where a generator produces candidate lists and an evaluator selects the best one. Recent work has attempted to enhance performance by expanding the number of candidate lists, for example, through multi-generator settings. However, ranking involves selecting a recommendation list from a combinatorially large space. Simply enlarging the candidate set remains ineffective, and performance gains quickly saturate. At the same time, recent advances in large recommendation models have shown that end-to-end one-stage models can achieve promising performance with the expectation of scaling laws. Motivated by this, we revisit ranking from a generator-only one-stage perspective. We theoretically prove that, for any (finite Multi-)Generator-Evaluator model, there always exists a generator-only model that achieves strictly smaller approximation error to the optimal ranking policy, while also enjoying scaling laws as its size increases. Building on this result, we derive an evidence upper bound of the one-stage optimization objective, from which we find that one can leverage a reward model trained on real user feedback to construct a reference policy in a group-relative manner. This reference policy serves as a practical surrogate of the optimal policy, enabling effective training of a large generator-only ranker. Based on these insights, we propose GoalRank, a generator-only ranking framework. Extensive offline experiments on public benchmarks and large-scale online A/B tests demonstrate that GoalRank consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
OneRec-V2 Technical Report
Aug 28, 2025



Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in generative AI have transformed recommender systems through end-to-end generation. OneRec reformulates recommendation as an autoregressive generation task, achieving high Model FLOPs Utilization. While OneRec-V1 has shown significant empirical success in real-world deployment, two critical challenges hinder its scalability and performance: (1) inefficient computational allocation where 97.66% of resources are consumed by sequence encoding rather than generation, and (2) limitations in reinforcement learning relying solely on reward models. To address these challenges, we propose OneRec-V2, featuring: (1) Lazy Decoder-Only Architecture: Eliminates encoder bottlenecks, reducing total computation by 94% and training resources by 90%, enabling successful scaling to 8B parameters. (2) Preference Alignment with Real-World User Interactions: Incorporates Duration-Aware Reward Shaping and Adaptive Ratio Clipping to better align with user preferences using real-world feedback. Extensive A/B tests on Kuaishou demonstrate OneRec-V2's effectiveness, improving App Stay Time by 0.467%/0.741% while balancing multi-objective recommendations. This work advances generative recommendation scalability and alignment with real-world feedback, representing a step forward in the development of end-to-end recommender systems.
An End-to-End Multi-objective Ensemble Ranking Framework for Video Recommendation
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:We propose a novel End-to-end Multi-objective Ensemble Ranking framework (EMER) for the multi-objective ensemble ranking module, which is the most critical component of the short video recommendation system. EMER enhances personalization by replacing manually-designed heuristic formulas with an end-to-end modeling paradigm. EMER introduces a meticulously designed loss function to address the fundamental challenge of defining effective supervision for ensemble ranking, where no single ground-truth signal can fully capture user satisfaction. Moreover, EMER introduces novel sample organization method and transformer-based network architecture to capture the comparative relationships among candidates, which are critical for effective ranking. Additionally, we have proposed an offline-online consistent evaluation system to enhance the efficiency of offline model optimization, which is an established yet persistent challenge within the multi-objective ranking domain in industry. Abundant empirical tests are conducted on a real industrial dataset, and the results well demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed framework. In addition, our framework has been deployed in the primary scenarios of Kuaishou, a short video recommendation platform with hundreds of millions of daily active users, achieving a 1.39% increase in overall App Stay Time and a 0.196% increase in 7-day user Lifetime(LT7), which are substantial improvements.
OneRec Technical Report
Jun 16, 2025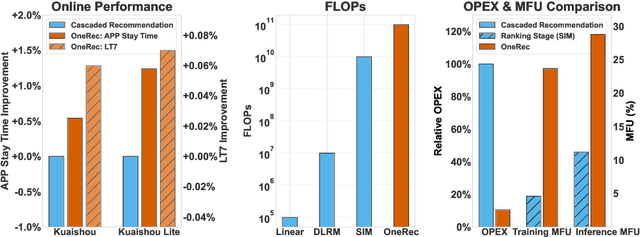

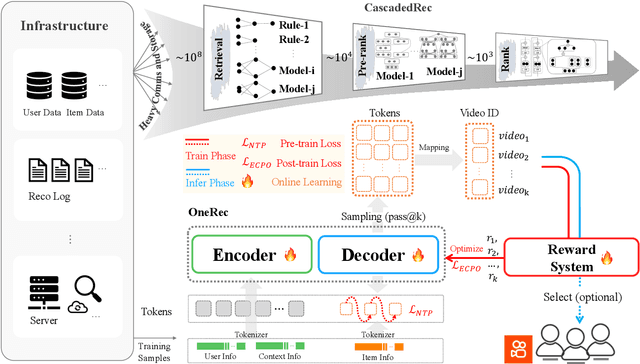

Abstract:Recommender systems have been widely used in various large-scale user-oriented platforms for many years. However, compared to the rapid developments in the AI community, recommendation systems have not achieved a breakthrough in recent years. For instance, they still rely on a multi-stage cascaded architecture rather than an end-to-end approach, leading to computational fragmentation and optimization inconsistencies, and hindering the effective application of key breakthrough technologies from the AI community in recommendation scenarios. To address these issues, we propose OneRec, which reshapes the recommendation system through an end-to-end generative approach and achieves promising results. Firstly, we have enhanced the computational FLOPs of the current recommendation model by 10 $\times$ and have identified the scaling laws for recommendations within certain boundaries. Secondly, reinforcement learning techniques, previously difficult to apply for optimizing recommendations, show significant potential in this framework. Lastly, through infrastructure optimizations, we have achieved 23.7% and 28.8% Model FLOPs Utilization (MFU) on flagship GPUs during training and inference, respectively, aligning closely with the LLM community. This architecture significantly reduces communication and storage overhead, resulting in operating expense that is only 10.6% of traditional recommendation pipelines. Deployed in Kuaishou/Kuaishou Lite APP, it handles 25% of total queries per second, enhancing overall App Stay Time by 0.54% and 1.24%, respectively. Additionally, we have observed significant increases in metrics such as 7-day Lifetime, which is a crucial indicator of recommendation experience. We also provide practical lessons and insights derived from developing, optimizing, and maintaining a production-scale recommendation system with significant real-world impact.
Who You Are Matters: Bridging Topics and Social Roles via LLM-Enhanced Logical Recommendation
May 16, 2025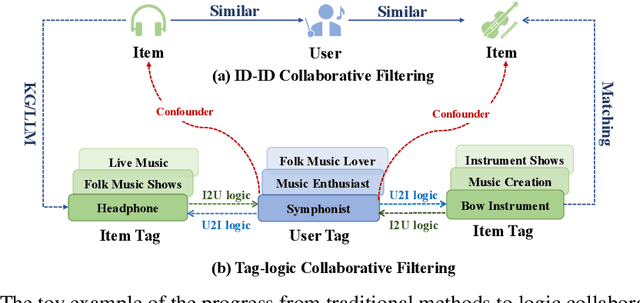
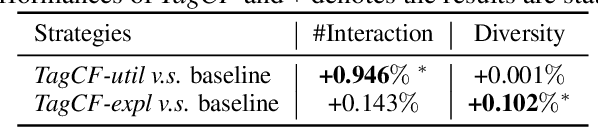
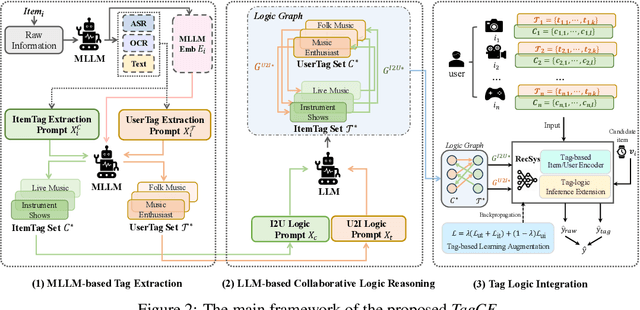
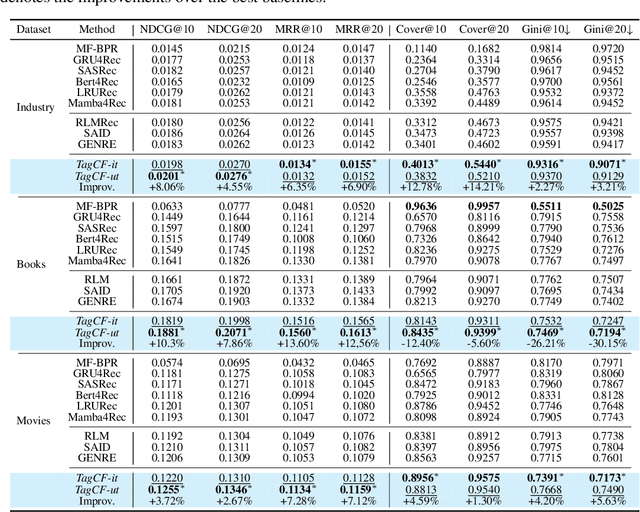
Abstract:Recommender systems filter contents/items valuable to users by inferring preferences from user features and historical behaviors. Mainstream approaches follow the learning-to-rank paradigm, which focus on discovering and modeling item topics (e.g., categories), and capturing user preferences on these topics based on historical interactions. However, this paradigm often neglects the modeling of user characteristics and their social roles, which are logical confounders influencing the correlated interest and user preference transition. To bridge this gap, we introduce the user role identification task and the behavioral logic modeling task that aim to explicitly model user roles and learn the logical relations between item topics and user social roles. We show that it is possible to explicitly solve these tasks through an efficient integration framework of Large Language Model (LLM) and recommendation systems, for which we propose TagCF. On the one hand, the exploitation of the LLM's world knowledge and logic inference ability produces a virtual logic graph that reveals dynamic and expressive knowledge of users, augmenting the recommendation performance. On the other hand, the user role aligns the user behavioral logic with the observed user feedback, refining our understanding of user behaviors. Additionally, we also show that the extracted user-item logic graph is empirically a general knowledge that can benefit a wide range of recommendation tasks, and conduct experiments on industrial and several public datasets as verification.
Comprehensive List Generation for Multi-Generator Reranking
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Reranking models solve the final recommendation lists that best fulfill users' demands. While existing solutions focus on finding parametric models that approximate optimal policies, recent approaches find that it is better to generate multiple lists to compete for a ``pass'' ticket from an evaluator, where the evaluator serves as the supervisor who accurately estimates the performance of the candidate lists. In this work, we show that we can achieve a more efficient and effective list proposal with a multi-generator framework and provide empirical evidence on two public datasets and online A/B tests. More importantly, we verify that the effectiveness of a generator is closely related to how much it complements the views of other generators with sufficiently different rerankings, which derives the metric of list comprehensiveness. With this intuition, we design an automatic complementary generator-finding framework that learns a policy that simultaneously aligns the users' preferences and maximizes the list comprehensiveness metric. The experimental results indicate that the proposed framework can further improve the multi-generator reranking performance.
* 11 pages, 6 figures, 9 tables
Explicit Uncertainty Modeling for Video Watch Time Prediction
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:In video recommendation, a critical component that determines the system's recommendation accuracy is the watch-time prediction module, since how long a user watches a video directly reflects personalized preferences. One of the key challenges of this problem is the user's stochastic watch-time behavior. To improve the prediction accuracy for such an uncertain behavior, existing approaches show that one can either reduce the noise through duration bias modeling or formulate a distribution modeling task to capture the uncertainty. However, the uncontrolled uncertainty is not always equally distributed across users and videos, inducing a balancing paradox between the model accuracy and the ability to capture out-of-distribution samples. In practice, we find that the uncertainty of the watch-time prediction model also provides key information about user behavior, which, in turn, could benefit the prediction task itself. Following this notion, we derive an explicit uncertainty modeling strategy for the prediction model and propose an adversarial optimization framework that can better exploit the user watch-time behavior. This framework has been deployed online on an industrial video sharing platform that serves hundreds of millions of daily active users, which obtains a significant increase in users' video watch time by 0.31% through the online A/B test. Furthermore, extended offline experiments on two public datasets verify the effectiveness of the proposed framework across various watch-time prediction backbones.
Value Function Decomposition in Markov Recommendation Process
Jan 29, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in recommender systems have shown that user-system interaction essentially formulates long-term optimization problems, and online reinforcement learning can be adopted to improve recommendation performance. The general solution framework incorporates a value function that estimates the user's expected cumulative rewards in the future and guides the training of the recommendation policy. To avoid local maxima, the policy may explore potential high-quality actions during inference to increase the chance of finding better future rewards. To accommodate the stepwise recommendation process, one widely adopted approach to learning the value function is learning from the difference between the values of two consecutive states of a user. However, we argue that this paradigm involves an incorrect approximation in the stochastic process. Specifically, between the current state and the next state in each training sample, there exist two separate random factors from the stochastic policy and the uncertain user environment. Original temporal difference (TD) learning under these mixed random factors may result in a suboptimal estimation of the long-term rewards. As a solution, we show that these two factors can be separately approximated by decomposing the original temporal difference loss. The disentangled learning framework can achieve a more accurate estimation with faster learning and improved robustness against action exploration. As empirical verification of our proposed method, we conduct offline experiments with online simulated environments built based on public datasets.
Coarse-to-fine Dynamic Uplift Modeling for Real-time Video Recommendation
Oct 22, 2024Abstract:With the rise of short video platforms, video recommendation technology faces more complex challenges. Currently, there are multiple non-personalized modules in the video recommendation pipeline that urgently need personalized modeling techniques for improvement. Inspired by the success of uplift modeling in online marketing, we attempt to implement uplift modeling in the video recommendation scenario. However, we face two main challenges: 1) Design and utilization of treatments, and 2) Capture of user real-time interest. To address them, we design adjusting the distribution of videos with varying durations as the treatment and propose Coarse-to-fine Dynamic Uplift Modeling (CDUM) for real-time video recommendation. CDUM consists of two modules, CPM and FIC. The former module fully utilizes the offline features of users to model their long-term preferences, while the latter module leverages online real-time contextual features and request-level candidates to model users' real-time interests. These two modules work together to dynamically identify and targeting specific user groups and applying treatments effectively. Further, we conduct comprehensive experiments on the offline public and industrial datasets and online A/B test, demonstrating the superiority and effectiveness of our proposed CDUM. Our proposed CDUM is eventually fully deployed on the Kuaishou platform, serving hundreds of millions of users every day. The source code will be provided after the paper is accepted.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge