Cheng Ling
End-to-End Learnable Item Tokenization for Generative Recommendation
Sep 09, 2024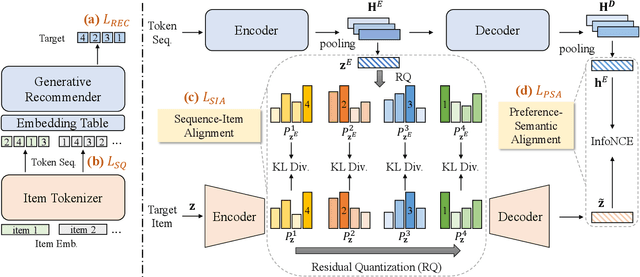
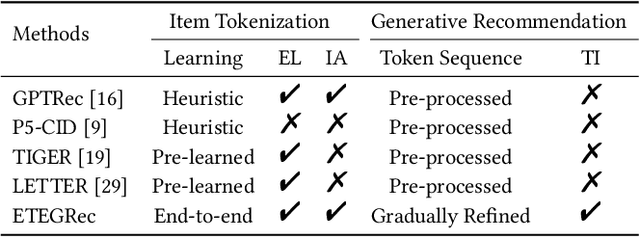
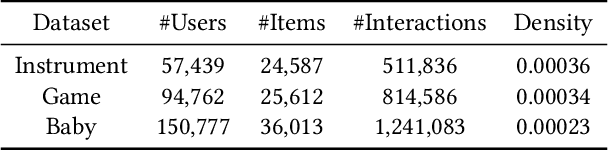
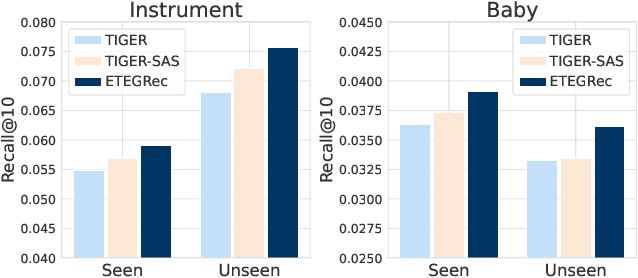
Abstract:Recently, generative recommendation has emerged as a promising new paradigm that directly generates item identifiers for recommendation. However, a key challenge lies in how to effectively construct item identifiers that are suitable for recommender systems. Existing methods typically decouple item tokenization from subsequent generative recommendation training, likely resulting in suboptimal performance. To address this limitation, we propose ETEGRec, a novel End-To-End Generative Recommender by seamlessly integrating item tokenization and generative recommendation. Our framework is developed based on the dual encoder-decoder architecture, which consists of an item tokenizer and a generative recommender. In order to achieve mutual enhancement between the two components, we propose a recommendation-oriented alignment approach by devising two specific optimization objectives: sequence-item alignment and preference-semantic alignment. These two alignment objectives can effectively couple the learning of item tokenizer and generative recommender, thereby fostering the mutual enhancement between the two components. Finally, we further devise an alternating optimization method, to facilitate stable and effective end-to-end learning of the entire framework. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed framework compared to a series of traditional sequential recommendation models and generative recommendation baselines.
Modeling User Fatigue for Sequential Recommendation
May 22, 2024



Abstract:Recommender systems filter out information that meets user interests. However, users may be tired of the recommendations that are too similar to the content they have been exposed to in a short historical period, which is the so-called user fatigue. Despite the significance for a better user experience, user fatigue is seldom explored by existing recommenders. In fact, there are three main challenges to be addressed for modeling user fatigue, including what features support it, how it influences user interests, and how its explicit signals are obtained. In this paper, we propose to model user Fatigue in interest learning for sequential Recommendations (FRec). To address the first challenge, based on a multi-interest framework, we connect the target item with historical items and construct an interest-aware similarity matrix as features to support fatigue modeling. Regarding the second challenge, built upon feature cross, we propose a fatigue-enhanced multi-interest fusion to capture long-term interest. In addition, we develop a fatigue-gated recurrent unit for short-term interest learning, with temporal fatigue representations as important inputs for constructing update and reset gates. For the last challenge, we propose a novel sequence augmentation to obtain explicit fatigue signals for contrastive learning. We conduct extensive experiments on real-world datasets, including two public datasets and one large-scale industrial dataset. Experimental results show that FRec can improve AUC and GAUC up to 0.026 and 0.019 compared with state-of-the-art models, respectively. Moreover, large-scale online experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of FRec for fatigue reduction. Our codes are released at https://github.com/tsinghua-fib-lab/SIGIR24-FRec.
A Large Language Model Enhanced Sequential Recommender for Joint Video and Comment Recommendation
Mar 20, 2024
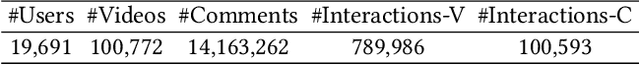

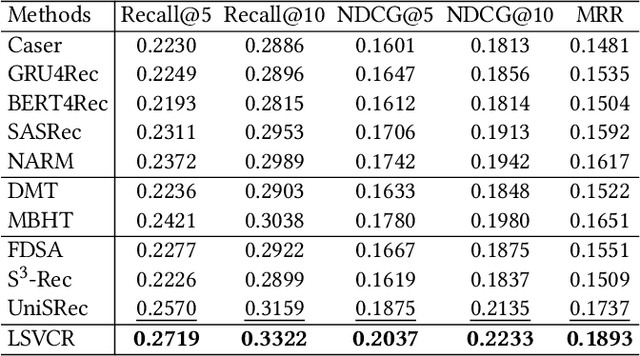
Abstract:In online video platforms, reading or writing comments on interesting videos has become an essential part of the video watching experience. However, existing video recommender systems mainly model users' interaction behaviors with videos, lacking consideration of comments in user behavior modeling. In this paper, we propose a novel recommendation approach called LSVCR by leveraging user interaction histories with both videos and comments, so as to jointly conduct personalized video and comment recommendation. Specifically, our approach consists of two key components, namely sequential recommendation (SR) model and supplemental large language model (LLM) recommender. The SR model serves as the primary recommendation backbone (retained in deployment) of our approach, allowing for efficient user preference modeling. Meanwhile, we leverage the LLM recommender as a supplemental component (discarded in deployment) to better capture underlying user preferences from heterogeneous interaction behaviors. In order to integrate the merits of the SR model and the supplemental LLM recommender, we design a twostage training paradigm. The first stage is personalized preference alignment, which aims to align the preference representations from both components, thereby enhancing the semantics of the SR model. The second stage is recommendation-oriented fine-tuning, in which the alignment-enhanced SR model is fine-tuned according to specific objectives. Extensive experiments in both video and comment recommendation tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of LSVCR. Additionally, online A/B testing on the KuaiShou platform verifies the actual benefits brought by our approach. In particular, we achieve a significant overall gain of 4.13% in comment watch time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge