Jin Gao
SoLA-Vision: Fine-grained Layer-wise Linear Softmax Hybrid Attention
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Standard softmax self-attention excels in vision tasks but incurs quadratic complexity O(N^2), limiting high-resolution deployment. Linear attention reduces the cost to O(N), yet its compressed state representations can impair modeling capacity and accuracy. We present an analytical study that contrasts linear and softmax attention for visual representation learning from a layer-stacking perspective. We further conduct systematic experiments on layer-wise hybridization patterns of linear and softmax attention. Our results show that, compared with rigid intra-block hybrid designs, fine-grained layer-wise hybridization can match or surpass performance while requiring fewer softmax layers. Building on these findings, we propose SoLA-Vision (Softmax-Linear Attention Vision), a flexible layer-wise hybrid attention backbone that enables fine-grained control over how linear and softmax attention are integrated. By strategically inserting a small number of global softmax layers, SoLA-Vision achieves a strong trade-off between accuracy and computational cost. On ImageNet-1K, SoLA-Vision outperforms purely linear and other hybrid attention models. On dense prediction tasks, it consistently surpasses strong baselines by a considerable margin. Code will be released.
Integrating Diverse Assignment Strategies into DETRs
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Label assignment is a critical component in object detectors, particularly within DETR-style frameworks where the one-to-one matching strategy, despite its end-to-end elegance, suffers from slow convergence due to sparse supervision. While recent works have explored one-to-many assignments to enrich supervisory signals, they often introduce complex, architecture-specific modifications and typically focus on a single auxiliary strategy, lacking a unified and scalable design. In this paper, we first systematically investigate the effects of ``one-to-many'' supervision and reveal a surprising insight that performance gains are driven not by the sheer quantity of supervision, but by the diversity of the assignment strategies employed. This finding suggests that a more elegant, parameter-efficient approach is attainable. Building on this insight, we propose LoRA-DETR, a flexible and lightweight framework that seamlessly integrates diverse assignment strategies into any DETR-style detector. Our method augments the primary network with multiple Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) branches during training, each instantiating a different one-to-many assignment rule. These branches act as auxiliary modules that inject rich, varied supervisory gradients into the main model and are discarded during inference, thus incurring no additional computational cost. This design promotes robust joint optimization while maintaining the architectural simplicity of the original detector. Extensive experiments on different baselines validate the effectiveness of our approach. Our work presents a new paradigm for enhancing detectors, demonstrating that diverse ``one-to-many'' supervision can be integrated to achieve state-of-the-art results without compromising model elegance.
From Idea to Co-Creation: A Planner-Actor-Critic Framework for Agent Augmented 3D Modeling
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We present a framework that extends the Actor-Critic architecture to creative 3D modeling through multi-agent self-reflection and human-in-the-loop supervision. While existing approaches rely on single-prompt agents that directly execute modeling commands via tools like Blender MCP, our approach introduces a Planner-Actor-Critic architecture. In this design, the Planner coordinates modeling steps, the Actor executes them, and the Critic provides iterative feedback, while human users act as supervisors and advisors throughout the process. Through systematic comparison between single-prompt modeling and our reflective multi-agent approach, we demonstrate improvements in geometric accuracy, aesthetic quality, and task completion rates across diverse 3D modeling scenarios. Our evaluation reveals that critic-guided reflection, combined with human supervisory input, reduces modeling errors and increases complexity and quality of the result compared to direct single-prompt execution. This work establishes that structured agent self-reflection, when augmented by human oversight and advisory guidance, produces higher-quality 3D models while maintaining efficient workflow integration through real-time Blender synchronization.
Step-GUI Technical Report
Dec 19, 2025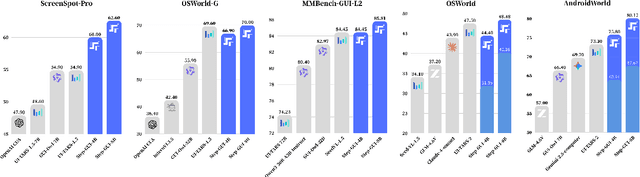
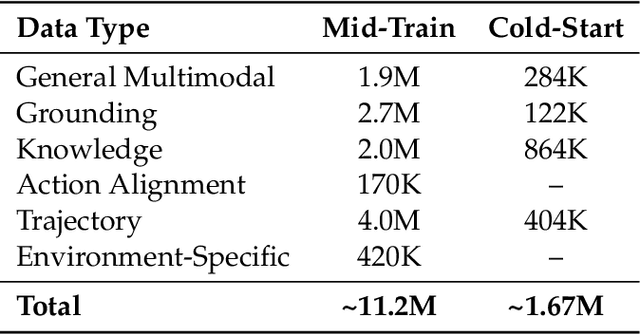
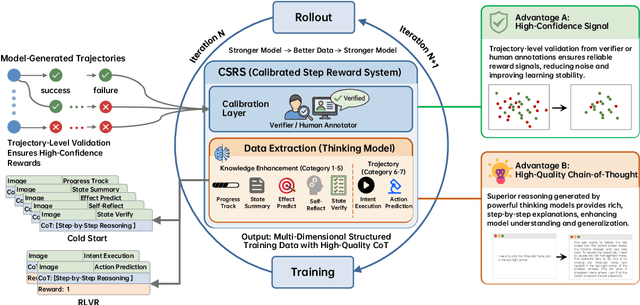

Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal large language models unlock unprecedented opportunities for GUI automation. However, a fundamental challenge remains: how to efficiently acquire high-quality training data while maintaining annotation reliability? We introduce a self-evolving training pipeline powered by the Calibrated Step Reward System, which converts model-generated trajectories into reliable training signals through trajectory-level calibration, achieving >90% annotation accuracy with 10-100x lower cost. Leveraging this pipeline, we introduce Step-GUI, a family of models (4B/8B) that achieves state-of-the-art GUI performance (8B: 80.2% AndroidWorld, 48.5% OSWorld, 62.6% ScreenShot-Pro) while maintaining robust general capabilities. As GUI agent capabilities improve, practical deployment demands standardized interfaces across heterogeneous devices while protecting user privacy. To this end, we propose GUI-MCP, the first Model Context Protocol for GUI automation with hierarchical architecture that combines low-level atomic operations and high-level task delegation to local specialist models, enabling high-privacy execution where sensitive data stays on-device. Finally, to assess whether agents can handle authentic everyday usage, we introduce AndroidDaily, a benchmark grounded in real-world mobile usage patterns with 3146 static actions and 235 end-to-end tasks across high-frequency daily scenarios (8B: static 89.91%, end-to-end 52.50%). Our work advances the development of practical GUI agents and demonstrates strong potential for real-world deployment in everyday digital interactions.
Online Segment Any 3D Thing as Instance Tracking
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Online, real-time, and fine-grained 3D segmentation constitutes a fundamental capability for embodied intelligent agents to perceive and comprehend their operational environments. Recent advancements employ predefined object queries to aggregate semantic information from Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) outputs that are lifted into 3D point clouds, facilitating spatial information propagation through inter-query interactions. Nevertheless, perception is an inherently dynamic process, rendering temporal understanding a critical yet overlooked dimension within these prevailing query-based pipelines. Therefore, to further unlock the temporal environmental perception capabilities of embodied agents, our work reconceptualizes online 3D segmentation as an instance tracking problem (AutoSeg3D). Our core strategy involves utilizing object queries for temporal information propagation, where long-term instance association promotes the coherence of features and object identities, while short-term instance update enriches instant observations. Given that viewpoint variations in embodied robotics often lead to partial object visibility across frames, this mechanism aids the model in developing a holistic object understanding beyond incomplete instantaneous views. Furthermore, we introduce spatial consistency learning to mitigate the fragmentation problem inherent in VFMs, yielding more comprehensive instance information for enhancing the efficacy of both long-term and short-term temporal learning. The temporal information exchange and consistency learning facilitated by these sparse object queries not only enhance spatial comprehension but also circumvent the computational burden associated with dense temporal point cloud interactions. Our method establishes a new state-of-the-art, surpassing ESAM by 2.8 AP on ScanNet200 and delivering consistent gains on ScanNet, SceneNN, and 3RScan datasets.
PFSD: A Multi-Modal Pedestrian-Focus Scene Dataset for Rich Tasks in Semi-Structured Environments
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in autonomous driving perception have revealed exceptional capabilities within structured environments dominated by vehicular traffic. However, current perception models exhibit significant limitations in semi-structured environments, where dynamic pedestrians with more diverse irregular movement and occlusion prevail. We attribute this shortcoming to the scarcity of high-quality datasets in semi-structured scenes, particularly concerning pedestrian perception and prediction. In this work, we present the multi-modal Pedestrian-Focused Scene Dataset(PFSD), rigorously annotated in semi-structured scenes with the format of nuScenes. PFSD provides comprehensive multi-modal data annotations with point cloud segmentation, detection, and object IDs for tracking. It encompasses over 130,000 pedestrian instances captured across various scenarios with varying densities, movement patterns, and occlusions. Furthermore, to demonstrate the importance of addressing the challenges posed by more diverse and complex semi-structured environments, we propose a novel Hybrid Multi-Scale Fusion Network (HMFN). Specifically, to detect pedestrians in densely populated and occluded scenarios, our method effectively captures and fuses multi-scale features using a meticulously designed hybrid framework that integrates sparse and vanilla convolutions. Extensive experiments on PFSD demonstrate that HMFN attains improvement in mean Average Precision (mAP) over existing methods, thereby underscoring its efficacy in addressing the challenges of 3D pedestrian detection in complex semi-structured environments. Coding and benchmark are available.
MedForge: Building Medical Foundation Models Like Open Source Software Development
Feb 22, 2025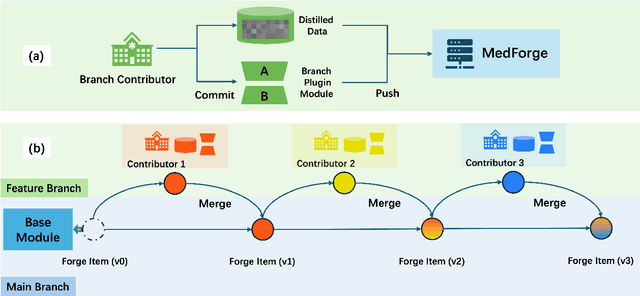
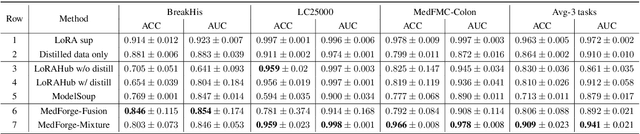
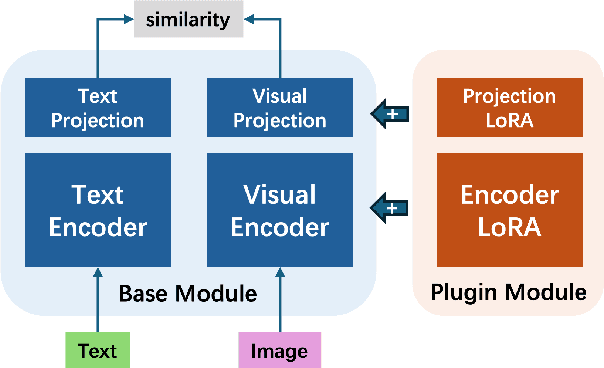
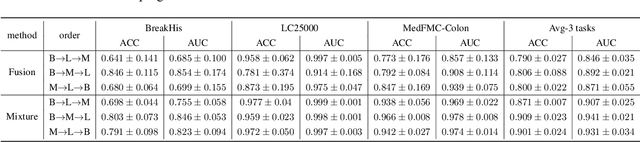
Abstract:Foundational models (FMs) have made significant strides in the healthcare domain. Yet the data silo challenge and privacy concern remain in healthcare systems, hindering safe medical data sharing and collaborative model development among institutions. The collection and curation of scalable clinical datasets increasingly become the bottleneck for training strong FMs. In this study, we propose Medical Foundation Models Merging (MedForge), a cooperative framework enabling a community-driven medical foundation model development, meanwhile preventing the information leakage of raw patient data and mitigating synchronization model development issues across clinical institutions. MedForge offers a bottom-up model construction mechanism by flexibly merging task-specific Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) modules, which can adapt to downstream tasks while retaining original model parameters. Through an asynchronous LoRA module integration scheme, the resulting composite model can progressively enhance its comprehensive performance on various clinical tasks. MedForge shows strong performance on multiple clinical datasets (e.g., breast cancer, lung cancer, and colon cancer) collected from different institutions. Our major findings highlight the value of collaborative foundation models in advancing multi-center clinical collaboration effectively and cohesively. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/TanZheling/MedForge.
HSTrack: Bootstrap End-to-End Multi-Camera 3D Multi-object Tracking with Hybrid Supervision
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:In camera-based 3D multi-object tracking (MOT), the prevailing methods follow the tracking-by-query-propagation paradigm, which employs track queries to manage the lifecycle of identity-consistent tracklets while object queries handle the detection of new-born tracklets. However, this intertwined paradigm leads the inter-temporal tracking task and the single-frame detection task utilize the same model parameters, complicating training optimization. Drawing inspiration from studies on the roles of attention components in transformer-based decoders, we identify that the dispersing effect of self-attention necessitates object queries to match with new-born tracklets. This matching strategy diverges from the detection pre-training phase, where object queries align with all ground-truth targets, resulting in insufficient supervision signals. To address these issues, we present HSTrack, a novel plug-and-play method designed to co-facilitate multi-task learning for detection and tracking. HSTrack constructs a parallel weight-share decoder devoid of self-attention layers, circumventing competition between different types of queries. Considering the characteristics of cross-attention layer and distinct query types, our parallel decoder adopt one-to-one and one-to-many label assignment strategies for track queries and object queries, respectively. Leveraging the shared architecture, HSTrack further improve trackers for spatio-temporal modeling and quality candidates generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HSTrack consistently delivers improvements when integrated with various query-based 3D MOT trackers. For example, HSTrack improves the state-of-the-art PF-Track method by $+2.3\%$ AMOTA and $+1.7\%$ mAP on the nuScenes dataset.
VQ-Map: Bird's-Eye-View Map Layout Estimation in Tokenized Discrete Space via Vector Quantization
Nov 03, 2024



Abstract:Bird's-eye-view (BEV) map layout estimation requires an accurate and full understanding of the semantics for the environmental elements around the ego car to make the results coherent and realistic. Due to the challenges posed by occlusion, unfavourable imaging conditions and low resolution, \emph{generating} the BEV semantic maps corresponding to corrupted or invalid areas in the perspective view (PV) is appealing very recently. \emph{The question is how to align the PV features with the generative models to facilitate the map estimation}. In this paper, we propose to utilize a generative model similar to the Vector Quantized-Variational AutoEncoder (VQ-VAE) to acquire prior knowledge for the high-level BEV semantics in the tokenized discrete space. Thanks to the obtained BEV tokens accompanied with a codebook embedding encapsulating the semantics for different BEV elements in the groundtruth maps, we are able to directly align the sparse backbone image features with the obtained BEV tokens from the discrete representation learning based on a specialized token decoder module, and finally generate high-quality BEV maps with the BEV codebook embedding serving as a bridge between PV and BEV. We evaluate the BEV map layout estimation performance of our model, termed VQ-Map, on both the nuScenes and Argoverse benchmarks, achieving 62.2/47.6 mean IoU for surround-view/monocular evaluation on nuScenes, as well as 73.4 IoU for monocular evaluation on Argoverse, which all set a new record for this map layout estimation task. The code and models are available on \url{https://github.com/Z1zyw/VQ-Map}.
Dissecting Dissonance: Benchmarking Large Multimodal Models Against Self-Contradictory Instructions
Aug 05, 2024

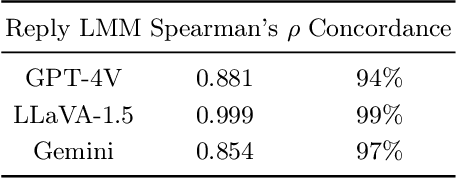

Abstract:Large multimodal models (LMMs) excel in adhering to human instructions. However, self-contradictory instructions may arise due to the increasing trend of multimodal interaction and context length, which is challenging for language beginners and vulnerable populations. We introduce the Self-Contradictory Instructions benchmark to evaluate the capability of LMMs in recognizing conflicting commands. It comprises 20,000 conflicts, evenly distributed between language and vision paradigms. It is constructed by a novel automatic dataset creation framework, which expedites the process and enables us to encompass a wide range of instruction forms. Our comprehensive evaluation reveals current LMMs consistently struggle to identify multimodal instruction discordance due to a lack of self-awareness. Hence, we propose the Cognitive Awakening Prompting to inject cognition from external, largely enhancing dissonance detection. The dataset and code are here: https://selfcontradiction.github.io/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge