Yizheng Wang
Physics-informed Machine Learning for Static Friction Modeling in Robotic Manipulators Based on Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Friction modeling plays a crucial role in achieving high-precision motion control in robotic operating systems. Traditional static friction models (such as the Stribeck model) are widely used due to their simple forms; however, they typically require predefined functional assumptions, which poses significant challenges when dealing with unknown functional structures. To address this issue, this paper proposes a physics-inspired machine learning approach based on the Kolmogorov Arnold Network (KAN) for static friction modeling of robotic joints. The method integrates spline activation functions with a symbolic regression mechanism, enabling model simplification and physical expression extraction through pruning and attribute scoring, while maintaining both high prediction accuracy and interpretability. We first validate the method's capability to accurately identify key parameters under known functional models, and further demonstrate its robustness and generalization ability under conditions with unknown functional structures and noisy data. Experiments conducted on both synthetic data and real friction data collected from a six-degree-of-freedom industrial manipulator show that the proposed method achieves a coefficient of determination greater than 0.95 across various tasks and successfully extracts concise and physically meaningful friction expressions. This study provides a new perspective for interpretable and data-driven robotic friction modeling with promising engineering applicability.
Transfer Learning in Physics-Informed Neural Networks: Full Fine-Tuning, Lightweight Fine-Tuning, and Low-Rank Adaptation
Feb 02, 2025Abstract:AI for PDEs has garnered significant attention, particularly Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs). However, PINNs are typically limited to solving specific problems, and any changes in problem conditions necessitate retraining. Therefore, we explore the generalization capability of transfer learning in the strong and energy form of PINNs across different boundary conditions, materials, and geometries. The transfer learning methods we employ include full finetuning, lightweight finetuning, and Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA). The results demonstrate that full finetuning and LoRA can significantly improve convergence speed while providing a slight enhancement in accuracy.
Energy-based physics-informed neural network for frictionless contact problems under large deformation
Nov 06, 2024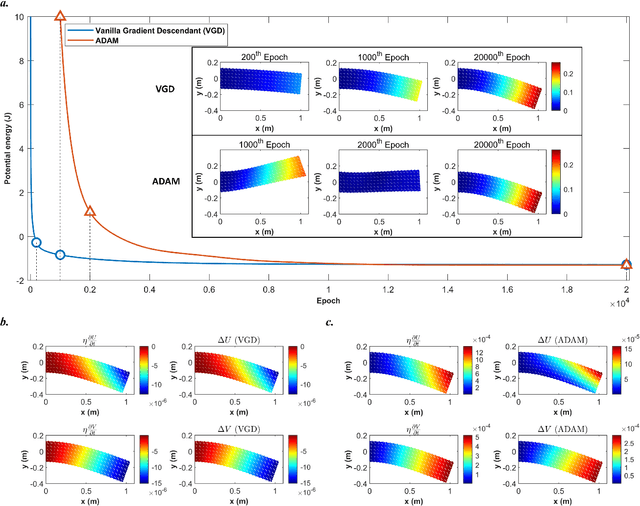
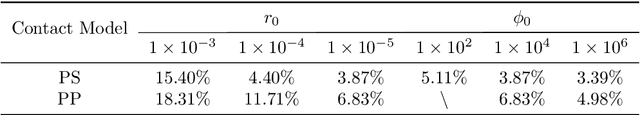
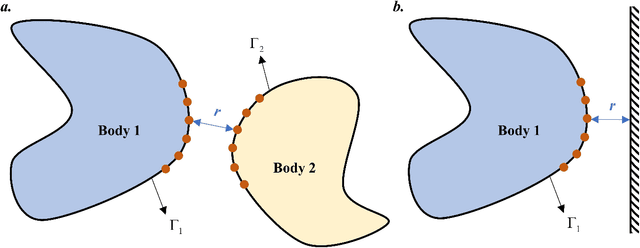
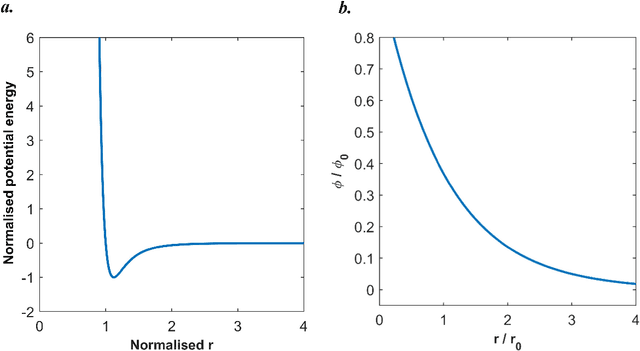
Abstract:Numerical methods for contact mechanics are of great importance in engineering applications, enabling the prediction and analysis of complex surface interactions under various conditions. In this work, we propose an energy-based physics-informed neural network (PINNs) framework for solving frictionless contact problems under large deformation. Inspired by microscopic Lennard-Jones potential, a surface contact energy is used to describe the contact phenomena. To ensure the robustness of the proposed PINN framework, relaxation, gradual loading and output scaling techniques are introduced. In the numerical examples, the well-known Hertz contact benchmark problem is conducted, demonstrating the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed PINNs framework. Moreover, challenging contact problems with the consideration of geometrical and material nonlinearities are tested. It has been shown that the proposed PINNs framework provides a reliable and powerful tool for nonlinear contact mechanics. More importantly, the proposed PINNs framework exhibits competitive computational efficiency to the commercial FEM software when dealing with those complex contact problems. The codes used in this manuscript are available at https://github.com/JinshuaiBai/energy_PINN_Contact.(The code will be available after acceptance)
DeepNetBeam: A Framework for the Analysis of Functionally Graded Porous Beams
Aug 04, 2024
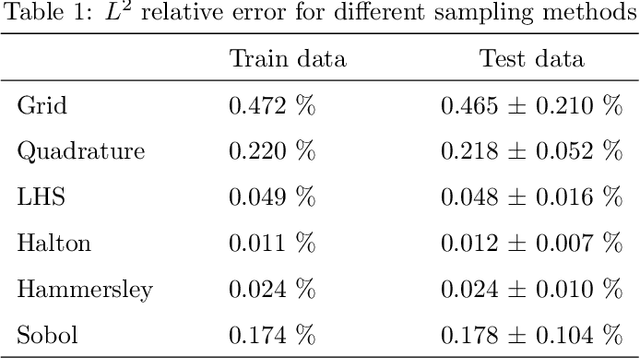
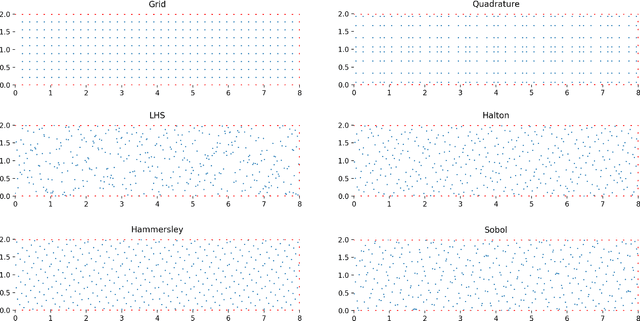
Abstract:This study investigates different Scientific Machine Learning (SciML) approaches for the analysis of functionally graded (FG) porous beams and compares them under a new framework. The beam material properties are assumed to vary as an arbitrary continuous function. The methods consider the output of a neural network/operator as an approximation to the displacement fields and derive the equations governing beam behavior based on the continuum formulation. The methods are implemented in the framework and formulated by three approaches: (a) the vector approach leads to a Physics-Informed Neural Network (PINN), (b) the energy approach brings about the Deep Energy Method (DEM), and (c) the data-driven approach, which results in a class of Neural Operator methods. Finally, a neural operator has been trained to predict the response of the porous beam with functionally graded material under any porosity distribution pattern and any arbitrary traction condition. The results are validated with analytical and numerical reference solutions. The data and code accompanying this manuscript will be publicly available at https://github.com/eshaghi-ms/DeepNetBeam.
Kolmogorov Arnold Informed neural network: A physics-informed deep learning framework for solving PDEs based on Kolmogorov Arnold Networks
Jun 16, 2024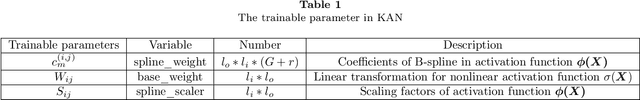
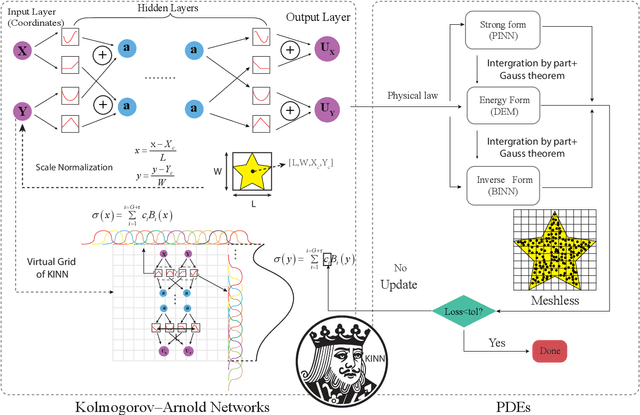
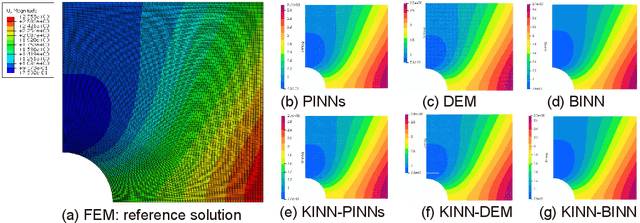
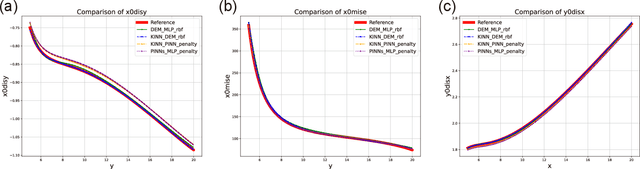
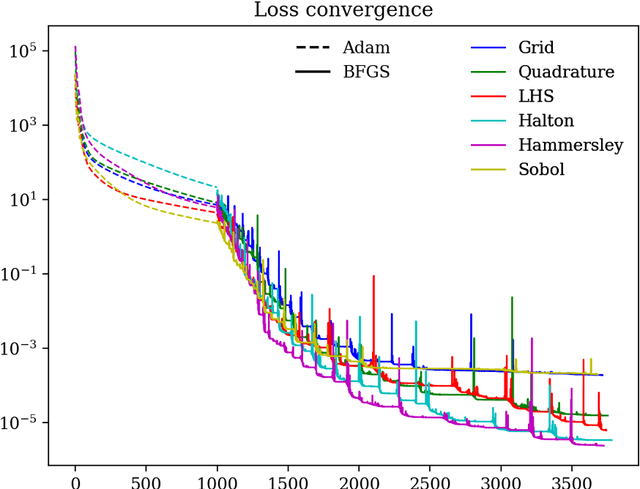
Abstract:AI for partial differential equations (PDEs) has garnered significant attention, particularly with the emergence of Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs). The recent advent of Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN) indicates that there is potential to revisit and enhance the previously MLP-based PINNs. Compared to MLPs, KANs offer interpretability and require fewer parameters. PDEs can be described in various forms, such as strong form, energy form, and inverse form. While mathematically equivalent, these forms are not computationally equivalent, making the exploration of different PDE formulations significant in computational physics. Thus, we propose different PDE forms based on KAN instead of MLP, termed Kolmogorov-Arnold-Informed Neural Network (KINN). We systematically compare MLP and KAN in various numerical examples of PDEs, including multi-scale, singularity, stress concentration, nonlinear hyperelasticity, heterogeneous, and complex geometry problems. Our results demonstrate that KINN significantly outperforms MLP in terms of accuracy and convergence speed for numerous PDEs in computational solid mechanics, except for the complex geometry problem. This highlights KINN's potential for more efficient and accurate PDE solutions in AI for PDEs.
Observation, Analysis, and Solution: Exploring Strong Lightweight Vision Transformers via Masked Image Modeling Pre-Training
Apr 18, 2024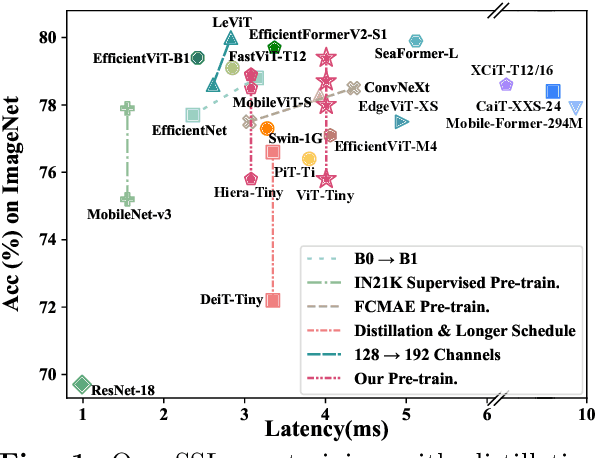
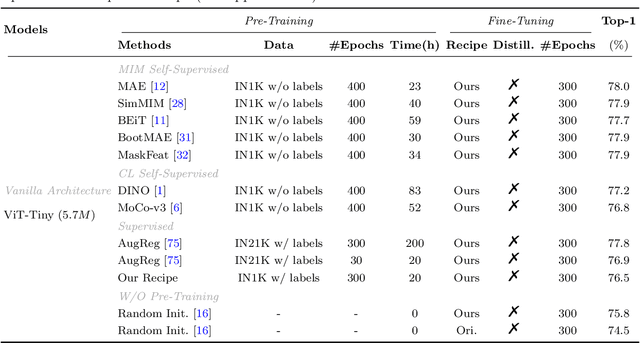

Abstract:Masked image modeling (MIM) pre-training for large-scale vision transformers (ViTs) in computer vision has enabled promising downstream performance on top of the learned self-supervised ViT features. In this paper, we question if the extremely simple ViTs' fine-tuning performance with a small-scale architecture can also benefit from this pre-training paradigm, which is considerably less studied yet in contrast to the well-established lightweight architecture design methodology with sophisticated components introduced. By carefully adapting various typical MIM pre-training methods to this lightweight regime and comparing them with the contrastive learning (CL) pre-training on various downstream image classification and dense prediction tasks, we systematically observe different behaviors between MIM and CL with respect to the downstream fine-tuning data scales. Furthermore, we analyze the frozen features under linear probing evaluation and also the layer representation similarities and attention maps across the obtained models, which clearly show the inferior learning of MIM pre-training on higher layers, leading to unsatisfactory fine-tuning performance on data-insufficient downstream tasks. This finding is naturally a guide to choosing appropriate distillation strategies during pre-training to solve the above deterioration problem. Extensive experiments on various vision tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of our observation-analysis-solution flow. In particular, our pre-training with distillation on pure lightweight ViTs with vanilla/hierarchical design (5.7M/6.5M) can achieve 79.4%/78.9% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1K. It also enables SOTA performance on the ADE20K semantic segmentation task (42.8% mIoU) and LaSOT visual tracking task (66.1% AUC) in the lightweight regime. The latter even surpasses all the current SOTA lightweight CPU-realtime trackers.
ZoomTrack: Target-aware Non-uniform Resizing for Efficient Visual Tracking
Oct 16, 2023



Abstract:Recently, the transformer has enabled the speed-oriented trackers to approach state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance with high-speed thanks to the smaller input size or the lighter feature extraction backbone, though they still substantially lag behind their corresponding performance-oriented versions. In this paper, we demonstrate that it is possible to narrow or even close this gap while achieving high tracking speed based on the smaller input size. To this end, we non-uniformly resize the cropped image to have a smaller input size while the resolution of the area where the target is more likely to appear is higher and vice versa. This enables us to solve the dilemma of attending to a larger visual field while retaining more raw information for the target despite a smaller input size. Our formulation for the non-uniform resizing can be efficiently solved through quadratic programming (QP) and naturally integrated into most of the crop-based local trackers. Comprehensive experiments on five challenging datasets based on two kinds of transformer trackers, \ie, OSTrack and TransT, demonstrate consistent improvements over them. In particular, applying our method to the speed-oriented version of OSTrack even outperforms its performance-oriented counterpart by 0.6% AUC on TNL2K, while running 50% faster and saving over 55% MACs. Codes and models are available at https://github.com/Kou-99/ZoomTrack.
SBSM-Pro: Support Bio-sequence Machine for Proteins
Aug 20, 2023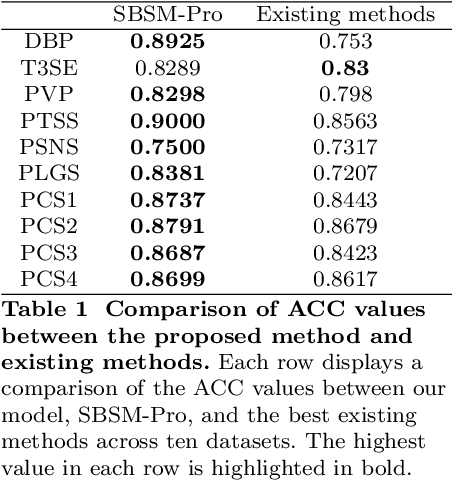



Abstract:Proteins play a pivotal role in biological systems. The use of machine learning algorithms for protein classification can assist and even guide biological experiments, offering crucial insights for biotechnological applications. We propose a support bio-sequence machine for proteins, a model specifically designed for biological sequence classification. This model starts with raw sequences and groups amino acids based on their physicochemical properties. It incorporates sequence alignment to measure the similarities between proteins and uses a novel MKL approach to integrate various types of information, utilizing support vector machines for classification prediction. The results indicate that our model demonstrates commendable performance across 10 datasets in terms of the identification of protein function and posttranslational modification. This research not only showcases state-of-the-art work in protein classification but also paves the way for new directions in this domain, representing a beneficial endeavour in the development of platforms tailored for biological sequence classification. SBSM-Pro is available for access at http://lab.malab.cn/soft/SBSM-Pro/.
Optimizing Carbon Storage Operations for Long-Term Safety
Apr 19, 2023Abstract:To combat global warming and mitigate the risks associated with climate change, carbon capture and storage (CCS) has emerged as a crucial technology. However, safely sequestering CO2 in geological formations for long-term storage presents several challenges. In this study, we address these issues by modeling the decision-making process for carbon storage operations as a partially observable Markov decision process (POMDP). We solve the POMDP using belief state planning to optimize injector and monitoring well locations, with the goal of maximizing stored CO2 while maintaining safety. Empirical results in simulation demonstrate that our approach is effective in ensuring safe long-term carbon storage operations. We showcase the flexibility of our approach by introducing three different monitoring strategies and examining their impact on decision quality. Additionally, we introduce a neural network surrogate model for the POMDP decision-making process to handle the complex dynamics of the multi-phase flow. We also investigate the effects of different fidelity levels of the surrogate model on decision qualities.
DCM: Deep complementary energy method based on the principle of minimum complementary energy
Feb 13, 2023Abstract:The principle of minimum potential and complementary energy are the most important variational principles in solid mechanics. The deep energy method (DEM), which has received much attention, is based on the principle of minimum potential energy, but it lacks the important form of minimum complementary energy. To fill the gap, we propose a deep complementary energy method (DCM) based on the principle of minimum complementary energy. The output function of DCM is the stress function that naturally satisfies the equilibrium equation. We extend the proposed DCM algorithm to DCM-Plus (DCM-P), adding the terms that naturally satisfy the biharmonic equation in the Airy stress function. We combine operator learning with physical equations and propose a deep complementary energy operator method (DCM-O), including branch net, trunk net, basis net, and particular net. DCM-O first combines existing high-fidelity numerical results to train DCM-O through data. Then the complementary energy is used to train the branch net and trunk net in DCM-O. To analyze DCM performance, we present the numerical result of the most common stress functions, the Prandtl and Airy stress function. The proposed method DCM is used to model the representative mechanical problems with different types of boundary conditions. We compare DCM with the existing PINNs and DEM algorithms. The result shows the advantage of the proposed DCM is suitable for dealing with problems of dominated displacement boundary conditions, which is proved by mathematical derivations, as well as with numerical experiments. DCM-P and DCM-O can improve the accuracy and efficiency of DCM. DCM is an essential supplementary energy form to the deep energy method. Operator learning based on the energy method can balance data and physical equations well, giving computational mechanics broad research prospects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge