Yixin Ye
Real-Time Reasoning Agents in Evolving Environments
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Agents in the real world must make not only logical but also timely judgments. This requires continuous awareness of the dynamic environment: hazards emerge, opportunities arise, and other agents act, while the agent's reasoning is still unfolding. Despite advances in language model reasoning, existing approaches fail to account for this dynamic nature. We introduce real-time reasoning as a new problem formulation for agents in evolving environments and build Real-Time Reasoning Gym to demonstrate it. We study two paradigms for deploying language models in agents: (1) reactive agents, which employ language models with bounded reasoning computation for rapid responses, and (2) planning agents, which allow extended reasoning computation for complex problems. Our experiments show that even state-of-the-art models struggle with making logical and timely judgments in either paradigm. To address this limitation, we propose AgileThinker, which simultaneously engages both reasoning paradigms. AgileThinker consistently outperforms agents engaging only one reasoning paradigm as the task difficulty and time pressure rise, effectively balancing reasoning depth and response latency. Our work establishes real-time reasoning as a critical testbed for developing practical agents and provides a foundation for research in temporally constrained AI systems, highlighting a path toward real-time capable agents.
Generative AI Act II: Test Time Scaling Drives Cognition Engineering
Apr 21, 2025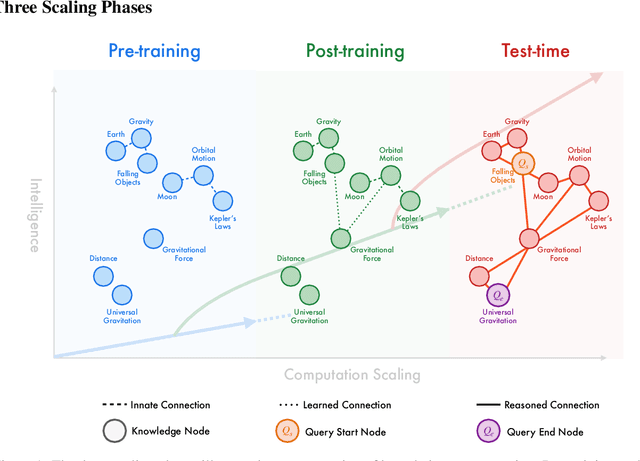
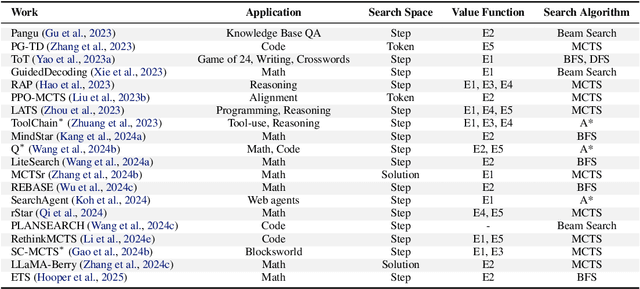
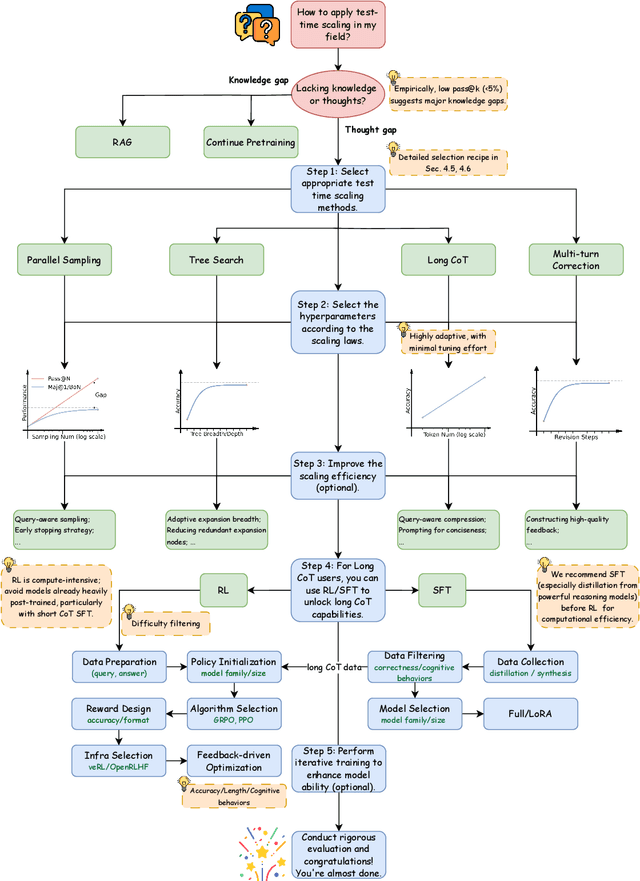
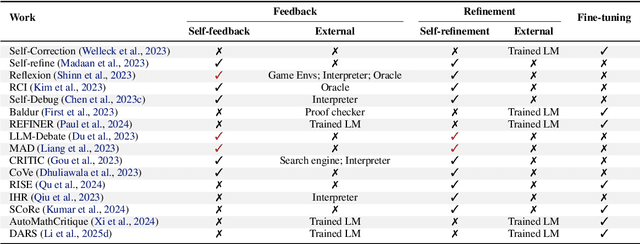
Abstract:The first generation of Large Language Models - what might be called "Act I" of generative AI (2020-2023) - achieved remarkable success through massive parameter and data scaling, yet exhibited fundamental limitations such as knowledge latency, shallow reasoning, and constrained cognitive processes. During this era, prompt engineering emerged as our primary interface with AI, enabling dialogue-level communication through natural language. We now witness the emergence of "Act II" (2024-present), where models are transitioning from knowledge-retrieval systems (in latent space) to thought-construction engines through test-time scaling techniques. This new paradigm establishes a mind-level connection with AI through language-based thoughts. In this paper, we clarify the conceptual foundations of cognition engineering and explain why this moment is critical for its development. We systematically break down these advanced approaches through comprehensive tutorials and optimized implementations, democratizing access to cognition engineering and enabling every practitioner to participate in AI's second act. We provide a regularly updated collection of papers on test-time scaling in the GitHub Repository: https://github.com/GAIR-NLP/cognition-engineering
LIMO: Less is More for Reasoning
Feb 05, 2025Abstract:We present a fundamental discovery that challenges our understanding of how complex reasoning emerges in large language models. While conventional wisdom suggests that sophisticated reasoning tasks demand extensive training data (>100,000 examples), we demonstrate that complex mathematical reasoning abilities can be effectively elicited with surprisingly few examples. Through comprehensive experiments, our proposed model LIMO demonstrates unprecedented performance in mathematical reasoning. With merely 817 curated training samples, LIMO achieves 57.1% accuracy on AIME and 94.8% on MATH, improving from previous SFT-based models' 6.5% and 59.2% respectively, while only using 1% of the training data required by previous approaches. LIMO demonstrates exceptional out-of-distribution generalization, achieving 40.5% absolute improvement across 10 diverse benchmarks, outperforming models trained on 100x more data, challenging the notion that SFT leads to memorization rather than generalization. Based on these results, we propose the Less-Is-More Reasoning Hypothesis (LIMO Hypothesis): In foundation models where domain knowledge has been comprehensively encoded during pre-training, sophisticated reasoning capabilities can emerge through minimal but precisely orchestrated demonstrations of cognitive processes. This hypothesis posits that the elicitation threshold for complex reasoning is determined by two key factors: (1) the completeness of the model's encoded knowledge foundation during pre-training, and (2) the effectiveness of post-training examples as "cognitive templates" that show the model how to utilize its knowledge base to solve complex reasoning tasks. To facilitate reproducibility and future research in data-efficient reasoning, we release LIMO as a comprehensive open-source suite at https://github.com/GAIR-NLP/LIMO.
Lost in Translation: Latent Concept Misalignment in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Aug 05, 2024Abstract:Advancements in text-to-image diffusion models have broadened extensive downstream practical applications, but such models often encounter misalignment issues between text and image. Taking the generation of a combination of two disentangled concepts as an example, say given the prompt "a tea cup of iced coke", existing models usually generate a glass cup of iced coke because the iced coke usually co-occurs with the glass cup instead of the tea one during model training. The root of such misalignment is attributed to the confusion in the latent semantic space of text-to-image diffusion models, and hence we refer to the "a tea cup of iced coke" phenomenon as Latent Concept Misalignment (LC-Mis). We leverage large language models (LLMs) to thoroughly investigate the scope of LC-Mis, and develop an automated pipeline for aligning the latent semantics of diffusion models to text prompts. Empirical assessments confirm the effectiveness of our approach, substantially reducing LC-Mis errors and enhancing the robustness and versatility of text-to-image diffusion models. The code and dataset are here: https://github.com/RossoneriZhao/iced_coke.
Dissecting Dissonance: Benchmarking Large Multimodal Models Against Self-Contradictory Instructions
Aug 05, 2024

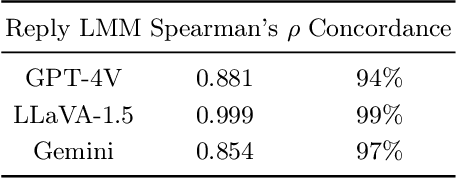

Abstract:Large multimodal models (LMMs) excel in adhering to human instructions. However, self-contradictory instructions may arise due to the increasing trend of multimodal interaction and context length, which is challenging for language beginners and vulnerable populations. We introduce the Self-Contradictory Instructions benchmark to evaluate the capability of LMMs in recognizing conflicting commands. It comprises 20,000 conflicts, evenly distributed between language and vision paradigms. It is constructed by a novel automatic dataset creation framework, which expedites the process and enables us to encompass a wide range of instruction forms. Our comprehensive evaluation reveals current LMMs consistently struggle to identify multimodal instruction discordance due to a lack of self-awareness. Hence, we propose the Cognitive Awakening Prompting to inject cognition from external, largely enhancing dissonance detection. The dataset and code are here: https://selfcontradiction.github.io/.
OlympicArena: Benchmarking Multi-discipline Cognitive Reasoning for Superintelligent AI
Jun 18, 2024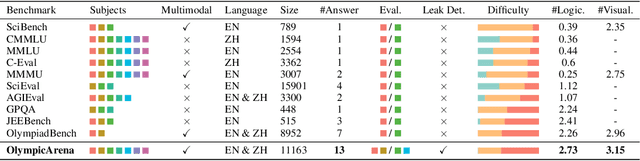
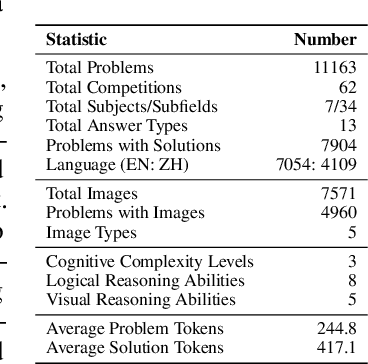
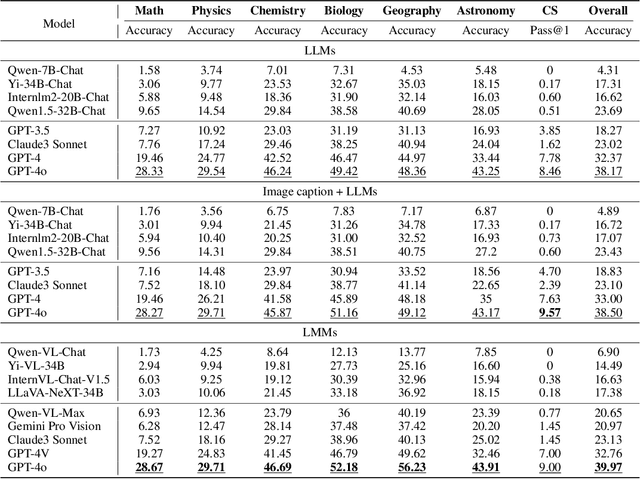
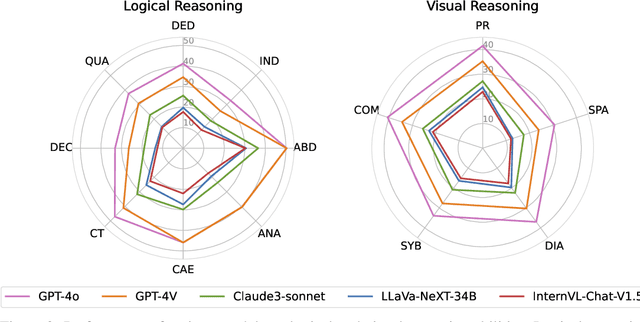
Abstract:The evolution of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been significantly accelerated by advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) and Large Multimodal Models (LMMs), gradually showcasing potential cognitive reasoning abilities in problem-solving and scientific discovery (i.e., AI4Science) once exclusive to human intellect. To comprehensively evaluate current models' performance in cognitive reasoning abilities, we introduce OlympicArena, which includes 11,163 bilingual problems across both text-only and interleaved text-image modalities. These challenges encompass a wide range of disciplines spanning seven fields and 62 international Olympic competitions, rigorously examined for data leakage. We argue that the challenges in Olympic competition problems are ideal for evaluating AI's cognitive reasoning due to their complexity and interdisciplinary nature, which are essential for tackling complex scientific challenges and facilitating discoveries. Beyond evaluating performance across various disciplines using answer-only criteria, we conduct detailed experiments and analyses from multiple perspectives. We delve into the models' cognitive reasoning abilities, their performance across different modalities, and their outcomes in process-level evaluations, which are vital for tasks requiring complex reasoning with lengthy solutions. Our extensive evaluations reveal that even advanced models like GPT-4o only achieve a 39.97% overall accuracy, illustrating current AI limitations in complex reasoning and multimodal integration. Through the OlympicArena, we aim to advance AI towards superintelligence, equipping it to address more complex challenges in science and beyond. We also provide a comprehensive set of resources to support AI research, including a benchmark dataset, an open-source annotation platform, a detailed evaluation tool, and a leaderboard with automatic submission features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge