Camilo Bermudez
Contrast Phase Classification with a Generative Adversarial Network
Nov 14, 2019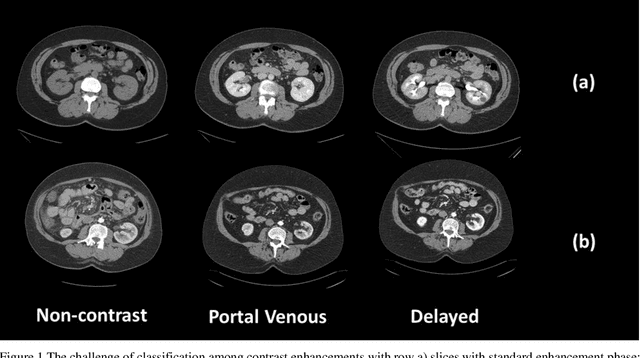
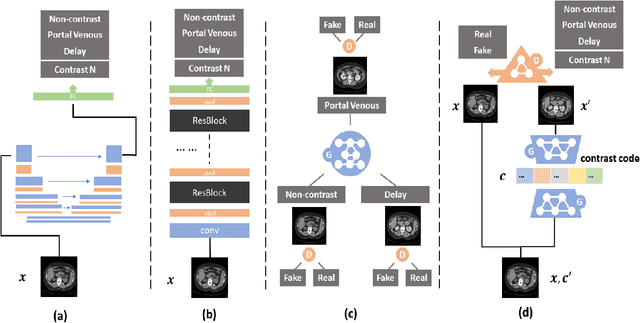
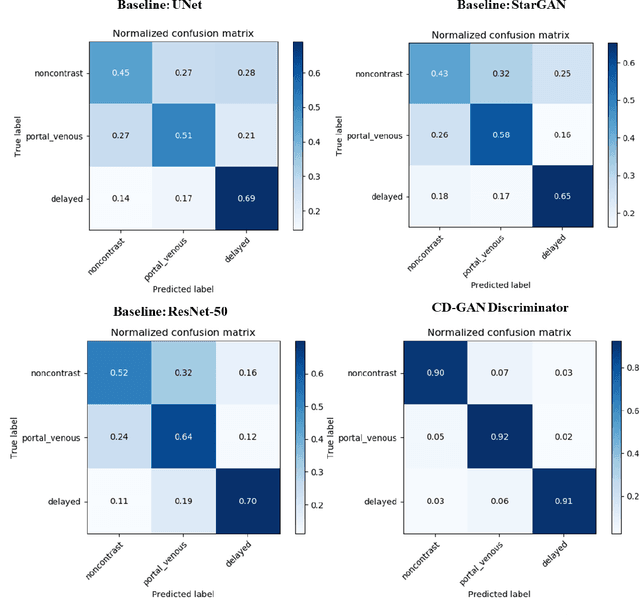
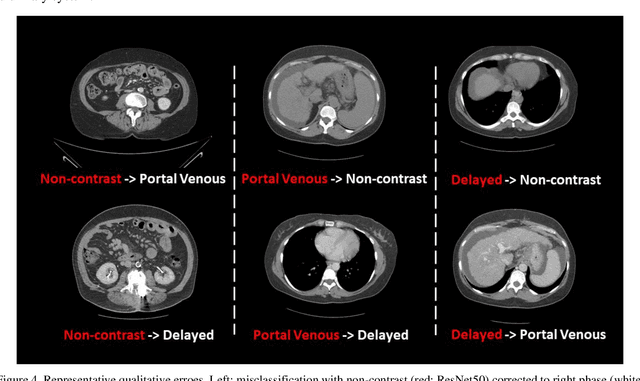
Abstract:Dynamic contrast enhanced computed tomography (CT) is an imaging technique that provides critical information on the relationship of vascular structure and dynamics in the context of underlying anatomy. A key challenge for image processing with contrast enhanced CT is that phase discrepancies are latent in different tissues due to contrast protocols, vascular dynamics, and metabolism variance. Previous studies with deep learning frameworks have been proposed for classifying contrast enhancement with networks inspired by computer vision. Here, we revisit the challenge in the context of whole abdomen contrast enhanced CTs. To capture and compensate for the complex contrast changes, we propose a novel discriminator in the form of a multi-domain disentangled representation learning network. The goal of this network is to learn an intermediate representation that separates contrast enhancement from anatomy and enables classification of images with varying contrast time. Briefly, our unpaired contrast disentangling GAN(CD-GAN) Discriminator follows the ResNet architecture to classify a CT scan from different enhancement phases. To evaluate the approach, we trained the enhancement phase classifier on 21060 slices from two clinical cohorts of 230 subjects. Testing was performed on 9100 slices from 30 independent subjects who had been imaged with CT scans from all contrast phases. Performance was quantified in terms of the multi-class normalized confusion matrix. The proposed network significantly improved correspondence over baseline UNet, ResNet50 and StarGAN performance of accuracy scores 0.54. 0.55, 0.62 and 0.91, respectively. The proposed discriminator from the disentangled network presents a promising technique that may allow deeper modeling of dynamic imaging against patient specific anatomies.
* 8 pages, 4 figures
Extracting 2D weak labels from volume labels using multiple instance learning in CT hemorrhage detection
Nov 13, 2019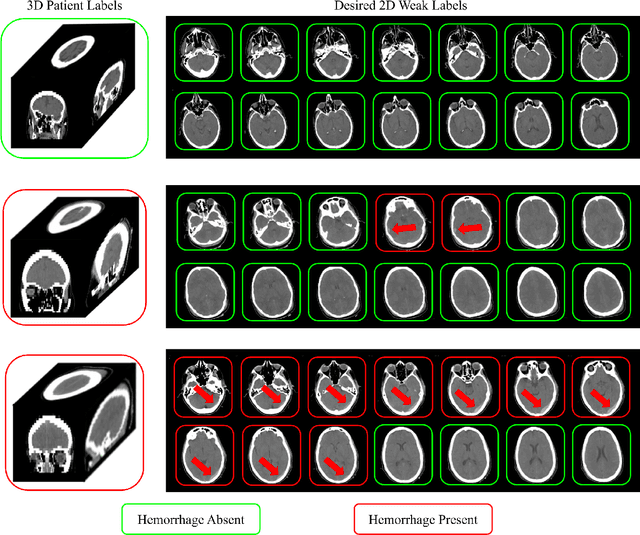
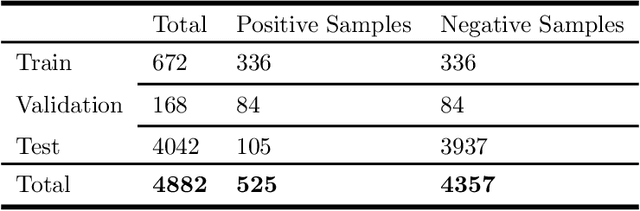
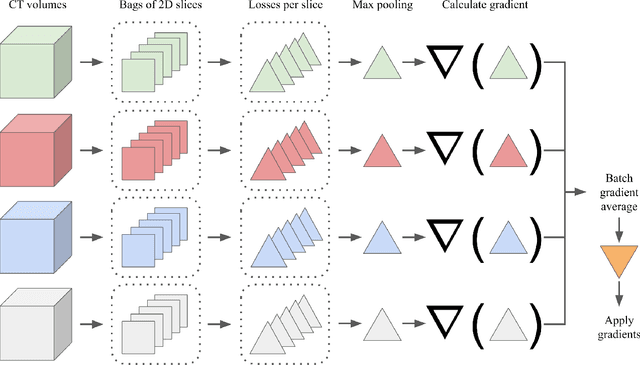
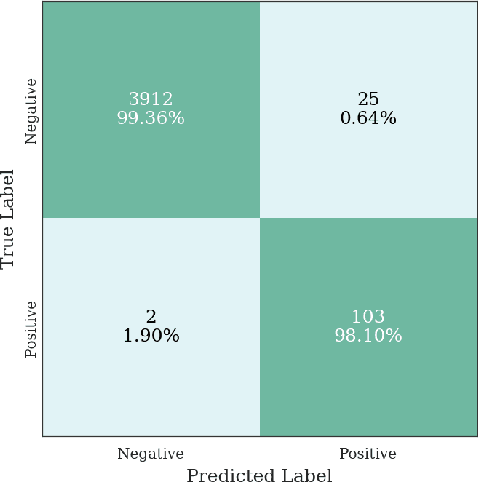
Abstract:Multiple instance learning (MIL) is a supervised learning methodology that aims to allow models to learn instance class labels from bag class labels, where a bag is defined to contain multiple instances. MIL is gaining traction for learning from weak labels but has not been widely applied to 3D medical imaging. MIL is well-suited to clinical CT acquisitions since (1) the highly anisotropic voxels hinder application of traditional 3D networks and (2) patch-based networks have limited ability to learn whole volume labels. In this work, we apply MIL with a deep convolutional neural network to identify whether clinical CT head image volumes possess one or more large hemorrhages (> 20cm$^3$), resulting in a learned 2D model without the need for 2D slice annotations. Individual image volumes are considered separate bags, and the slices in each volume are instances. Such a framework sets the stage for incorporating information obtained in clinical reports to help train a 2D segmentation approach. Within this context, we evaluate the data requirements to enable generalization of MIL by varying the amount of training data. Our results show that a training size of at least 400 patient image volumes was needed to achieve accurate per-slice hemorrhage detection. Over a five-fold cross-validation, the leading model, which made use of the maximum number of training volumes, had an average true positive rate of 98.10%, an average true negative rate of 99.36%, and an average precision of 0.9698. The models have been made available along with source code to enabled continued exploration and adaption of MIL in CT neuroimaging.
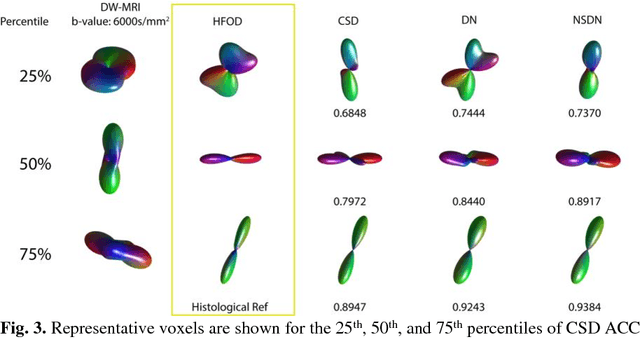
Deep Learning Captures More Accurate Diffusion Fiber Orientations Distributions than Constrained Spherical Deconvolution
Nov 13, 2019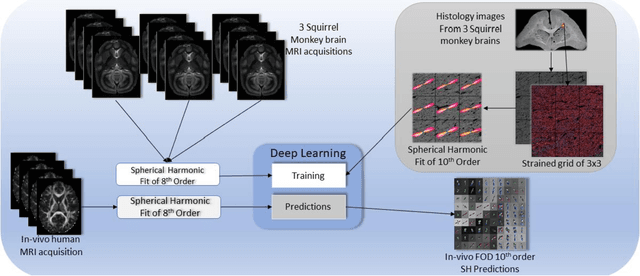
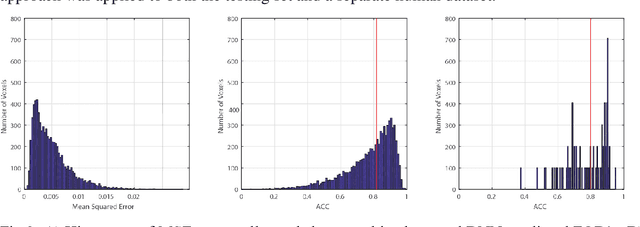
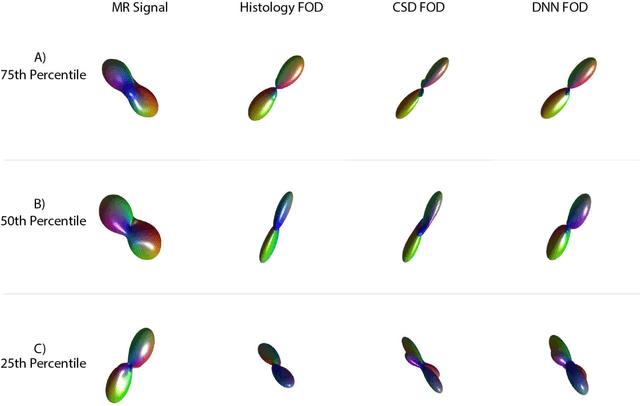
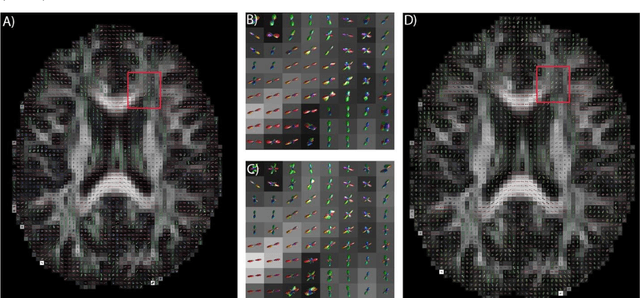
Abstract:Confocal histology provides an opportunity to establish intra-voxel fiber orientation distributions that can be used to quantitatively assess the biological relevance of diffusion weighted MRI models, e.g., constrained spherical deconvolution (CSD). Here, we apply deep learning to investigate the potential of single shell diffusion weighted MRI to explain histologically observed fiber orientation distributions (FOD) and compare the derived deep learning model with a leading CSD approach. This study (1) demonstrates that there exists additional information in the diffusion signal that is not currently exploited by CSD, and (2) provides an illustrative data-driven model that makes use of this information.
Generalizing Deep Whole Brain Segmentation for Pediatric and Post-Contrast MRI with Augmented Transfer Learning
Aug 13, 2019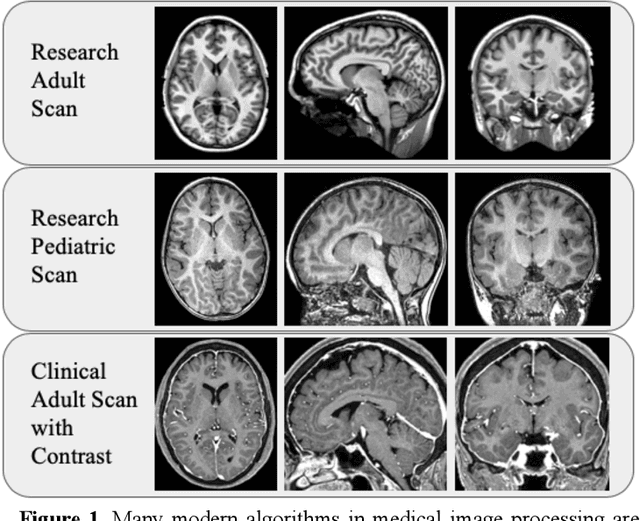
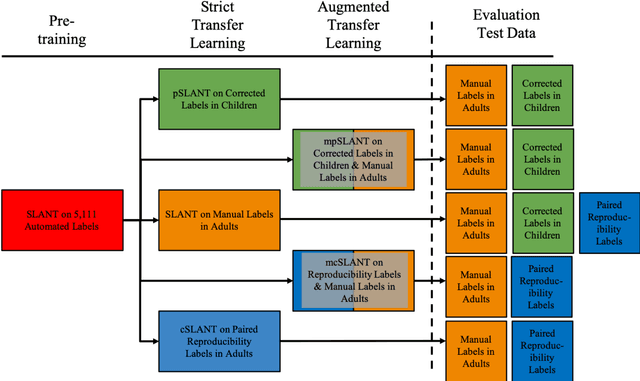

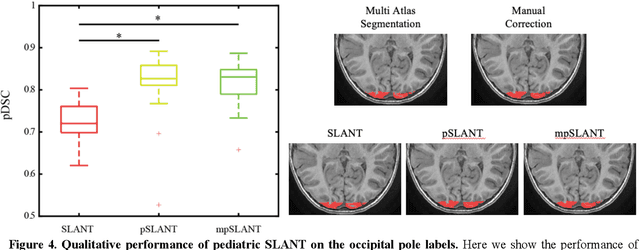
Abstract:Generalizability is an important problem in deep neural networks, especially in the context of the variability of data acquisition in clinical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Recently, the Spatially Localized Atlas Network Tiles (SLANT) approach has been shown to effectively segment whole brain non-contrast T1w MRI with 132 volumetric labels. Enhancing generalizability of SLANT would enable broader application of volumetric assessment in multi-site studies. Transfer learning (TL) is commonly used to update the neural network weights for local factors; yet, it is commonly recognized to risk degradation of performance on the original validation/test cohorts. Here, we explore TL by data augmentation to address these concerns in the context of adapting SLANT to anatomical variation and scanning protocol. We consider two datasets: First, we optimize for age with 30 T1w MRI of young children with manually corrected volumetric labels, and accuracy of automated segmentation defined relative to the manually provided truth. Second, we optimize for acquisition with 36 paired datasets of pre- and post-contrast clinically acquired T1w MRI, and accuracy of the post-contrast segmentations assessed relative to the pre-contrast automated assessment. For both studies, we augment the original TL step of SLANT with either only the new data or with both original and new data. Over baseline SLANT, both approaches yielded significantly improved performance (signed rank tests; pediatric: 0.89 vs. 0.82 DSC, p<0.001; contrast: 0.80 vs 0.76, p<0.001). The performance on the original test set decreased with the new-data only transfer learning approach, so data augmentation was superior to strict transfer learning.
3D Whole Brain Segmentation using Spatially Localized Atlas Network Tiles
Mar 28, 2019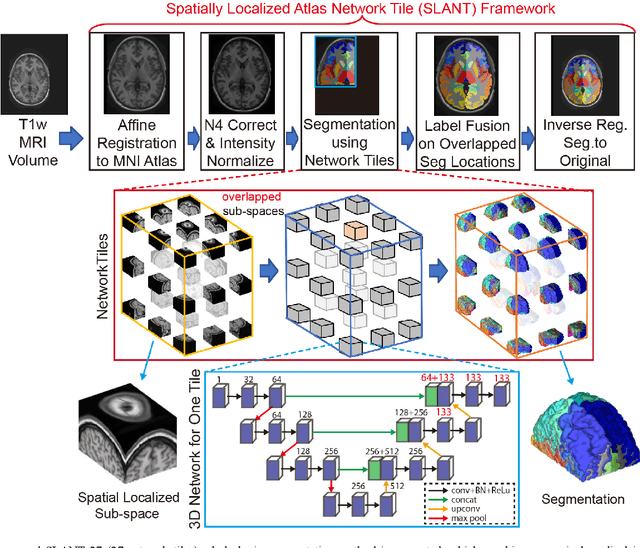
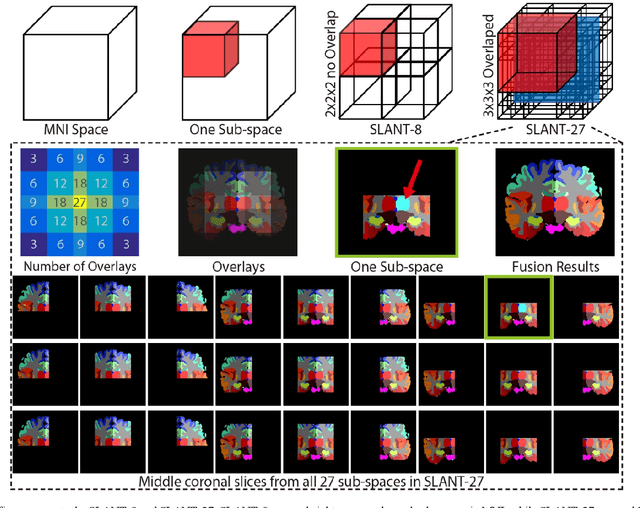
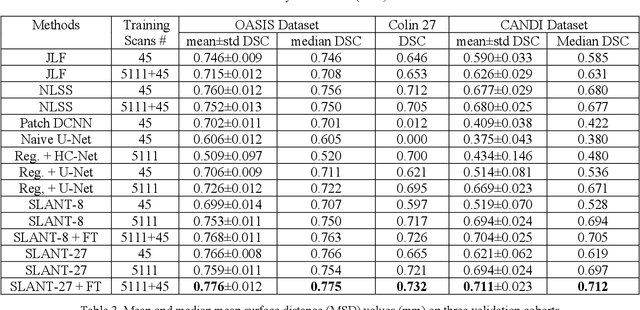
Abstract:Detailed whole brain segmentation is an essential quantitative technique, which provides a non-invasive way of measuring brain regions from a structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Recently, deep convolution neural network (CNN) has been applied to whole brain segmentation. However, restricted by current GPU memory, 2D based methods, downsampling based 3D CNN methods, and patch-based high-resolution 3D CNN methods have been the de facto standard solutions. 3D patch-based high resolution methods typically yield superior performance among CNN approaches on detailed whole brain segmentation (>100 labels), however, whose performance are still commonly inferior compared with multi-atlas segmentation methods (MAS) due to the following challenges: (1) a single network is typically used to learn both spatial and contextual information for the patches, (2) limited manually traced whole brain volumes are available (typically less than 50) for training a network. In this work, we propose the spatially localized atlas network tiles (SLANT) method to distribute multiple independent 3D fully convolutional networks (FCN) for high-resolution whole brain segmentation. To address the first challenge, multiple spatially distributed networks were used in the SLANT method, in which each network learned contextual information for a fixed spatial location. To address the second challenge, auxiliary labels on 5111 initially unlabeled scans were created by multi-atlas segmentation for training. Since the method integrated multiple traditional medical image processing methods with deep learning, we developed a containerized pipeline to deploy the end-to-end solution. From the results, the proposed method achieved superior performance compared with multi-atlas segmentation methods, while reducing the computational time from >30 hours to 15 minutes (https://github.com/MASILab/SLANTbrainSeg).
Distributed deep learning for robust multi-site segmentation of CT imaging after traumatic brain injury
Mar 11, 2019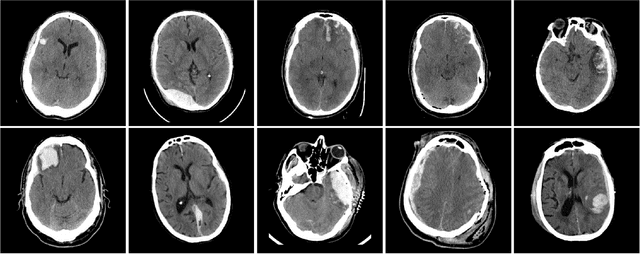

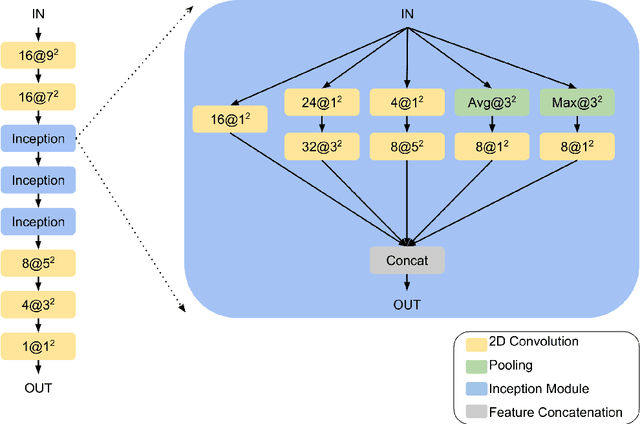
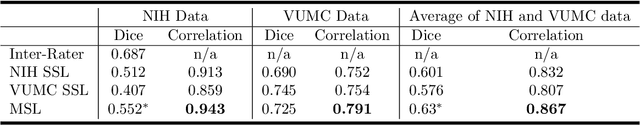
Abstract:Machine learning models are becoming commonplace in the domain of medical imaging, and with these methods comes an ever-increasing need for more data. However, to preserve patient anonymity it is frequently impractical or prohibited to transfer protected health information (PHI) between institutions. Additionally, due to the nature of some studies, there may not be a large public dataset available on which to train models. To address this conundrum, we analyze the efficacy of transferring the model itself in lieu of data between different sites. By doing so we accomplish two goals: 1) the model gains access to training on a larger dataset that it could not normally obtain and 2) the model better generalizes, having trained on data from separate locations. In this paper, we implement multi-site learning with disparate datasets from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) without compromising PHI. Three neural networks are trained to convergence on a computed tomography (CT) brain hematoma segmentation task: one only with NIH data,one only with VUMC data, and one multi-site model alternating between NIH and VUMC data. Resultant lesion masks with the multi-site model attain an average Dice similarity coefficient of 0.64 and the automatically segmented hematoma volumes correlate to those done manually with a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.87,corresponding to an 8% and 5% improvement, respectively, over the single-site model counterparts.
Towards Machine Learning Prediction of Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) Intra-operative Efficacy Maps
Nov 26, 2018
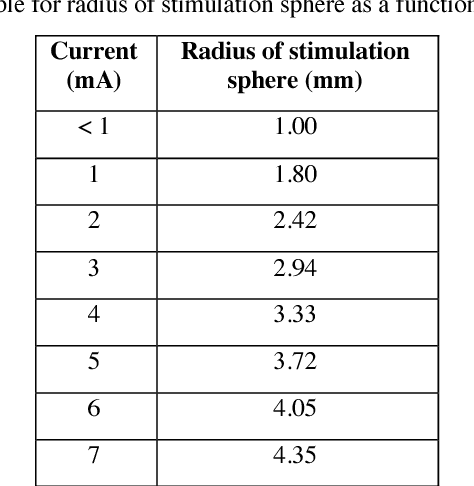


Abstract:Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has the potential to improve the quality of life of people with a variety of neurological diseases. A key challenge in DBS is in the placement of a stimulation electrode in the anatomical location that maximizes efficacy and minimizes side effects. Pre-operative localization of the optimal stimulation zone can reduce surgical times and morbidity. Current methods of producing efficacy probability maps follow an anatomical guidance on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to identify the areas with the highest efficacy in a population. In this work, we propose to revisit this problem as a classification problem, where each voxel in the MRI is a sample informed by the surrounding anatomy. We use a patch-based convolutional neural network to classify a stimulation coordinate as having a positive reduction in symptoms during surgery. We use a cohort of 187 patients with a total of 2,869 stimulation coordinates, upon which 3D patches were extracted and associated with an efficacy score. We compare our results with a registration-based method of surgical planning. We show an improvement in the classification of intraoperative stimulation coordinates as a positive response in reduction of symptoms with AUC of 0.670 compared to a baseline registration-based approach, which achieves an AUC of 0.627 (p < 0.01). Although additional validation is needed, the proposed classification framework and deep learning method appear well-suited for improving pre-surgical planning and personalize treatment strategies.
Coronary Calcium Detection using 3D Attention Identical Dual Deep Network Based on Weakly Supervised Learning
Nov 10, 2018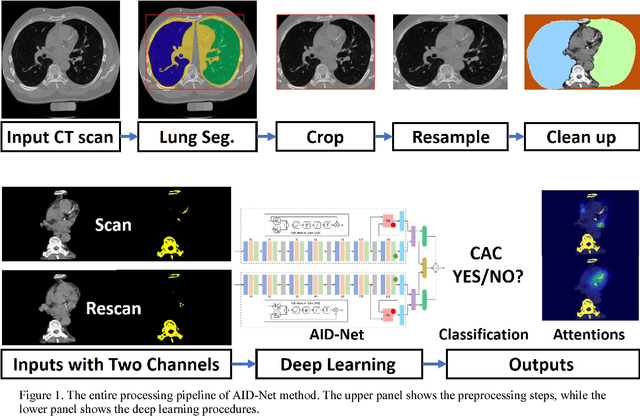
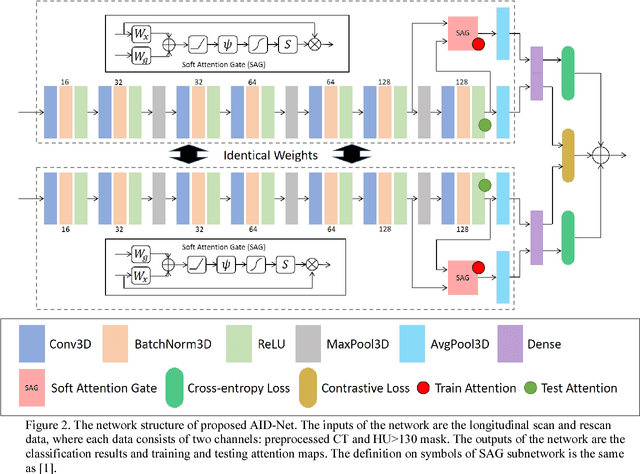

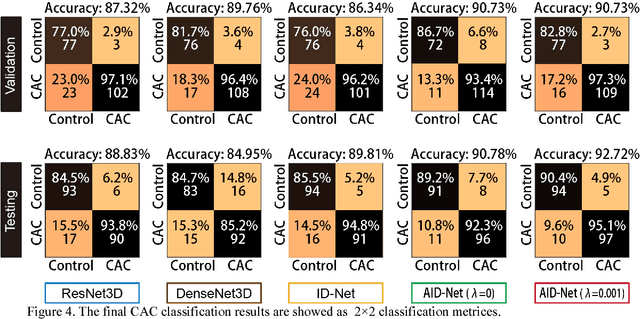
Abstract:Coronary artery calcium (CAC) is biomarker of advanced subclinical coronary artery disease and predicts myocardial infarction and death prior to age 60 years. The slice-wise manual delineation has been regarded as the gold standard of coronary calcium detection. However, manual efforts are time and resource consuming and even impracticable to be applied on large-scale cohorts. In this paper, we propose the attention identical dual network (AID-Net) to perform CAC detection using scan-rescan longitudinal non-contrast CT scans with weakly supervised attention by only using per scan level labels. To leverage the performance, 3D attention mechanisms were integrated into the AID-Net to provide complementary information for classification tasks. Moreover, the 3D Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad-CAM) was also proposed at the testing stage to interpret the behaviors of the deep neural network. 5075 non-contrast chest CT scans were used as training, validation and testing datasets. Baseline performance was assessed on the same cohort. From the results, the proposed AID-Net achieved the superior performance on classification accuracy (0.9272) and AUC (0.9627).
Splenomegaly Segmentation on Multi-modal MRI using Deep Convolutional Networks
Nov 09, 2018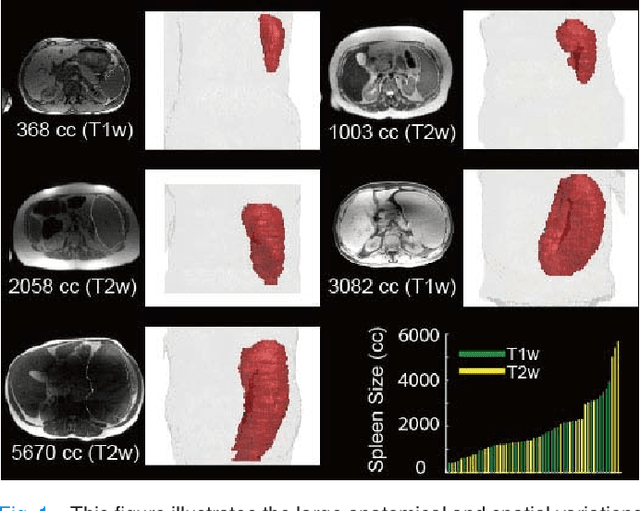
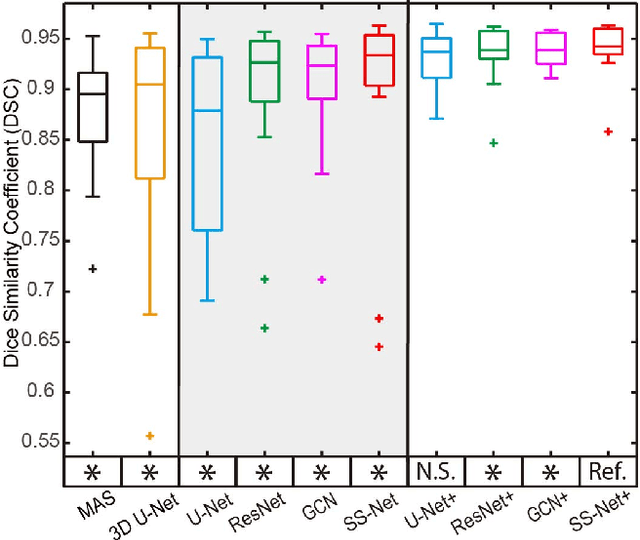
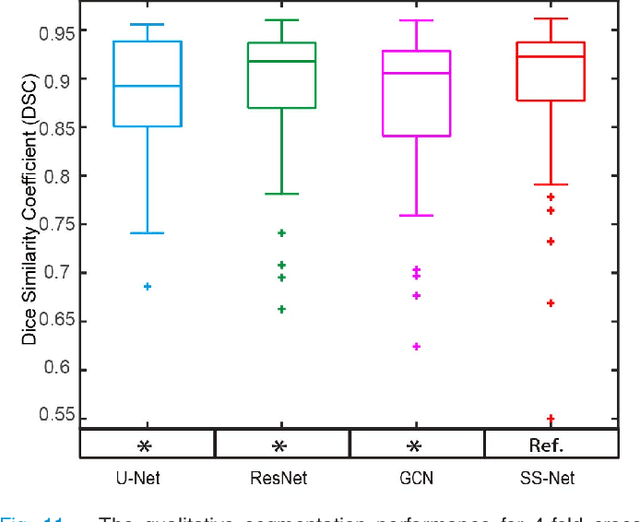
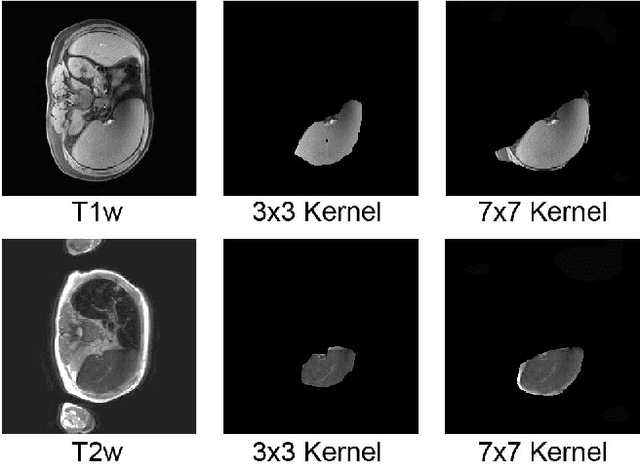
Abstract:The findings of splenomegaly, abnormal enlargement of the spleen, is a non-invasive clinical biomarker for liver and spleen disease. Automated segmentation methods are essential to efficiently quantify splenomegaly from clinically acquired abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. However, the task is challenging due to (1) large anatomical and spatial variations of splenomegaly, (2) large inter- and intra-scan intensity variations on multi-modal MRI, and (3) limited numbers of labeled splenomegaly scans. In this paper, we propose the Splenomegaly Segmentation Network (SS-Net) to introduce the deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) approaches in multi-modal MRI splenomegaly segmentation. Large convolutional kernel layers were used to address the spatial and anatomical variations, while the conditional generative adversarial networks (GAN) were employed to leverage the segmentation performance of SS-Net in an end-to-end manner. A clinically acquired cohort containing both T1-weighted (T1w) and T2-weighted (T2w) MRI splenomegaly scans was used to train and evaluate the performance of multi-atlas segmentation (MAS), 2D DCNN networks, and a 3D DCNN network. From the experimental results, the DCNN methods achieved superior performance to the state-of-the-art MAS method. The proposed SS-Net method achieved the highest median and mean Dice scores among investigated baseline DCNN methods.
Inter-Scanner Harmonization of High Angular Resolution DW-MRI using Null Space Deep Learning
Oct 09, 2018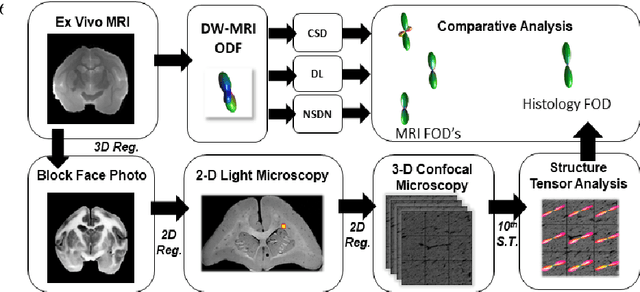
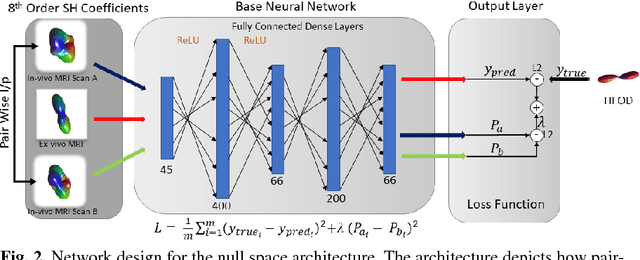
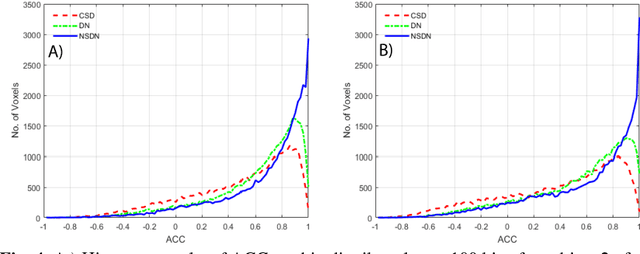
Abstract:Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) allows for non-invasive imaging of the local fiber architecture of the human brain at a millimetric scale. Multiple classical approaches have been proposed to detect both single (e.g., tensors) and multiple (e.g., constrained spherical deconvolution, CSD) fiber population orientations per voxel. However, existing techniques generally exhibit low reproducibility across MRI scanners. Herein, we propose a data-driven tech-nique using a neural network design which exploits two categories of data. First, training data were acquired on three squirrel monkey brains using ex-vivo DW-MRI and histology of the brain. Second, repeated scans of human subjects were acquired on two different scanners to augment the learning of the network pro-posed. To use these data, we propose a new network architecture, the null space deep network (NSDN), to simultaneously learn on traditional observed/truth pairs (e.g., MRI-histology voxels) along with repeated observations without a known truth (e.g., scan-rescan MRI). The NSDN was tested on twenty percent of the histology voxels that were kept completely blind to the network. NSDN significantly improved absolute performance relative to histology by 3.87% over CSD and 1.42% over a recently proposed deep neural network approach. More-over, it improved reproducibility on the paired data by 21.19% over CSD and 10.09% over a recently proposed deep approach. Finally, NSDN improved gen-eralizability of the model to a third in vivo human scanner (which was not used in training) by 16.08% over CSD and 10.41% over a recently proposed deep learn-ing approach. This work suggests that data-driven approaches for local fiber re-construction are more reproducible, informative and precise and offers a novel, practical method for determining these models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge