Dzung L. Pham
MSRepaint: Multiple Sclerosis Repaint with Conditional Denoising Diffusion Implicit Model for Bidirectional Lesion Filling and Synthesis
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:In multiple sclerosis, lesions interfere with automated magnetic resonance imaging analyses such as brain parcellation and deformable registration, while lesion segmentation models are hindered by the limited availability of annotated training data. To address both issues, we propose MSRepaint, a unified diffusion-based generative model for bidirectional lesion filling and synthesis that restores anatomical continuity for downstream analyses and augments segmentation through realistic data generation. MSRepaint conditions on spatial lesion masks for voxel-level control, incorporates contrast dropout to handle missing inputs, integrates a repainting mechanism to preserve surrounding anatomy during lesion filling and synthesis, and employs a multi-view DDIM inversion and fusion pipeline for 3D consistency with fast inference. Extensive evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of MSRepaint across multiple tasks. For lesion filling, we evaluate both the accuracy within the filled regions and the impact on downstream tasks including brain parcellation and deformable registration. MSRepaint outperforms the traditional lesion filling methods FSL and NiftySeg, and achieves accuracy on par with FastSurfer-LIT, a recent diffusion model-based inpainting method, while offering over 20 times faster inference. For lesion synthesis, state-of-the-art MS lesion segmentation models trained on MSRepaint-synthesized data outperform those trained on CarveMix-synthesized data or real ISBI challenge training data across multiple benchmarks, including the MICCAI 2016 and UMCL datasets. Additionally, we demonstrate that MSRepaint's unified bidirectional filling and synthesis capability, with full spatial control over lesion appearance, enables high-fidelity simulation of lesion evolution in longitudinal MS progression.
UNISELF: A Unified Network with Instance Normalization and Self-Ensembled Lesion Fusion for Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation
Aug 06, 2025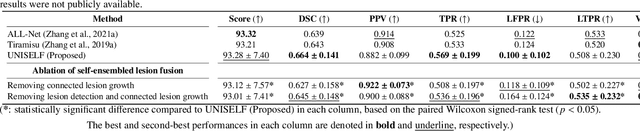
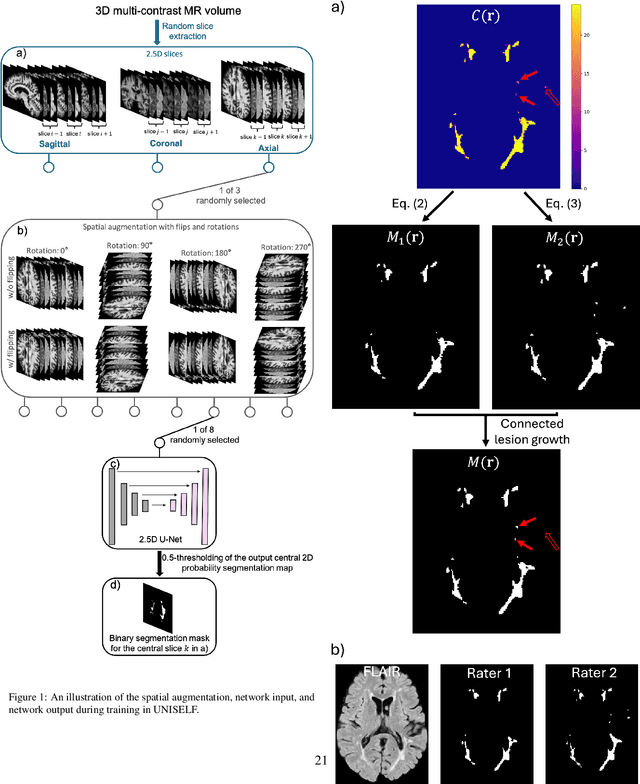
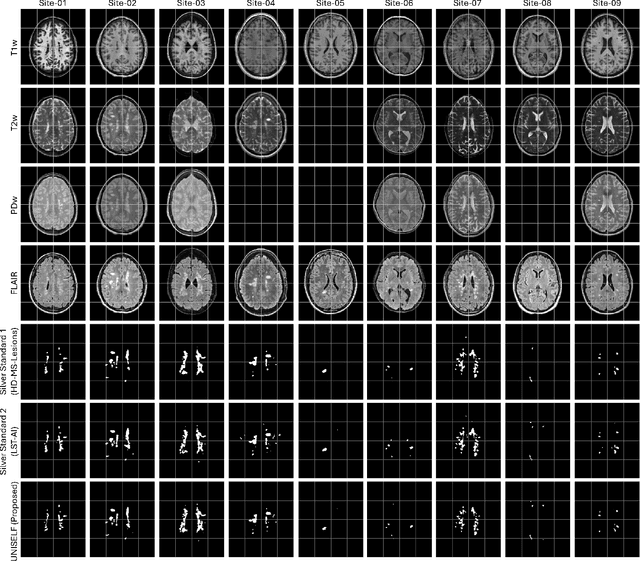

Abstract:Automated segmentation of multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions using multicontrast magnetic resonance (MR) images improves efficiency and reproducibility compared to manual delineation, with deep learning (DL) methods achieving state-of-the-art performance. However, these DL-based methods have yet to simultaneously optimize in-domain accuracy and out-of-domain generalization when trained on a single source with limited data, or their performance has been unsatisfactory. To fill this gap, we propose a method called UNISELF, which achieves high accuracy within a single training domain while demonstrating strong generalizability across multiple out-of-domain test datasets. UNISELF employs a novel test-time self-ensembled lesion fusion to improve segmentation accuracy, and leverages test-time instance normalization (TTIN) of latent features to address domain shifts and missing input contrasts. Trained on the ISBI 2015 longitudinal MS segmentation challenge training dataset, UNISELF ranks among the best-performing methods on the challenge test dataset. Additionally, UNISELF outperforms all benchmark methods trained on the same ISBI training data across diverse out-of-domain test datasets with domain shifts and missing contrasts, including the public MICCAI 2016 and UMCL datasets, as well as a private multisite dataset. These test datasets exhibit domain shifts and/or missing contrasts caused by variations in acquisition protocols, scanner types, and imaging artifacts arising from imperfect acquisition. Our code is available at https://github.com/uponacceptance.
Brightness-Invariant Tracking Estimation in Tagged MRI
May 23, 2025Abstract:Magnetic resonance (MR) tagging is an imaging technique for noninvasively tracking tissue motion in vivo by creating a visible pattern of magnetization saturation (tags) that deforms with the tissue. Due to longitudinal relaxation and progression to steady-state, the tags and tissue brightnesses change over time, which makes tracking with optical flow methods error-prone. Although Fourier methods can alleviate these problems, they are also sensitive to brightness changes as well as spectral spreading due to motion. To address these problems, we introduce the brightness-invariant tracking estimation (BRITE) technique for tagged MRI. BRITE disentangles the anatomy from the tag pattern in the observed tagged image sequence and simultaneously estimates the Lagrangian motion. The inherent ill-posedness of this problem is addressed by leveraging the expressive power of denoising diffusion probabilistic models to represent the probabilistic distribution of the underlying anatomy and the flexibility of physics-informed neural networks to estimate biologically-plausible motion. A set of tagged MR images of a gel phantom was acquired with various tag periods and imaging flip angles to demonstrate the impact of brightness variations and to validate our method. The results show that BRITE achieves more accurate motion and strain estimates as compared to other state of the art methods, while also being resistant to tag fading.
ECLARE: Efficient cross-planar learning for anisotropic resolution enhancement
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:In clinical imaging, magnetic resonance (MR) image volumes are often acquired as stacks of 2D slices, permitting decreased scan times, improved signal-to-noise ratio, and image contrasts unique to 2D MR pulse sequences. While this is sufficient for clinical evaluation, automated algorithms designed for 3D analysis perform sub-optimally on 2D-acquired scans, especially those with thick slices and gaps between slices. Super-resolution (SR) methods aim to address this problem, but previous methods do not address all of the following: slice profile shape estimation, slice gap, domain shift, and non-integer / arbitrary upsampling factors. In this paper, we propose ECLARE (Efficient Cross-planar Learning for Anisotropic Resolution Enhancement), a self-SR method that addresses each of these factors. ECLARE estimates the slice profile from the 2D-acquired multi-slice MR volume, trains a network to learn the mapping from low-resolution to high-resolution in-plane patches from the same volume, and performs SR with anti-aliasing. We compared ECLARE to cubic B-spline interpolation, SMORE, and other contemporary SR methods. We used realistic and representative simulations so that quantitative performance against a ground truth could be computed, and ECLARE outperformed all other methods in both signal recovery and downstream tasks. On real data for which there is no ground truth, ECLARE demonstrated qualitative superiority over other methods as well. Importantly, as ECLARE does not use external training data it cannot suffer from domain shift between training and testing. Our code is open-source and available at https://www.github.com/sremedios/eclare.
Is Registering Raw Tagged-MR Enough for Strain Estimation in the Era of Deep Learning?
Jan 31, 2024Abstract:Magnetic Resonance Imaging with tagging (tMRI) has long been utilized for quantifying tissue motion and strain during deformation. However, a phenomenon known as tag fading, a gradual decrease in tag visibility over time, often complicates post-processing. The first contribution of this study is to model tag fading by considering the interplay between $T_1$ relaxation and the repeated application of radio frequency (RF) pulses during serial imaging sequences. This is a factor that has been overlooked in prior research on tMRI post-processing. Further, we have observed an emerging trend of utilizing raw tagged MRI within a deep learning-based (DL) registration framework for motion estimation. In this work, we evaluate and analyze the impact of commonly used image similarity objectives in training DL registrations on raw tMRI. This is then compared with the Harmonic Phase-based approach, a traditional approach which is claimed to be robust to tag fading. Our findings, derived from both simulated images and an actual phantom scan, reveal the limitations of various similarity losses in raw tMRI and emphasize caution in registration tasks where image intensity changes over time.
Towards an accurate and generalizable multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation model using self-ensembled lesion fusion
Dec 03, 2023



Abstract:Automatic multiple sclerosis (MS) lesion segmentation using multi-contrast magnetic resonance (MR) images provides improved efficiency and reproducibility compared to manual delineation. Current state-of-the-art automatic MS lesion segmentation methods utilize modified U-Net-like architectures. However, in the literature, dedicated architecture modifications were always required to maximize their performance. In addition, the best-performing methods have not proven to be generalizable to diverse test datasets with contrast variations and image artifacts. In this work, we developed an accurate and generalizable MS lesion segmentation model using the well-known U-Net architecture without further modification. A novel test-time self-ensembled lesion fusion strategy is proposed that not only achieved the best performance using the ISBI 2015 MS segmentation challenge data but also demonstrated robustness across various self-ensemble parameter choices. Moreover, equipped with instance normalization rather than batch normalization widely used in literature, the model trained on the ISBI challenge data generalized well on clinical test datasets from different scanners.
Harmonization-enriched domain adaptation with light fine-tuning for multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation
Oct 31, 2023Abstract:Deep learning algorithms utilizing magnetic resonance (MR) images have demonstrated cutting-edge proficiency in autonomously segmenting multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions. Despite their achievements, these algorithms may struggle to extend their performance across various sites or scanners, leading to domain generalization errors. While few-shot or one-shot domain adaptation emerges as a potential solution to mitigate generalization errors, its efficacy might be hindered by the scarcity of labeled data in the target domain. This paper seeks to tackle this challenge by integrating one-shot adaptation data with harmonized training data that incorporates labels. Our approach involves synthesizing new training data with a contrast akin to that of the test domain, a process we refer to as "contrast harmonization" in MRI. Our experiments illustrate that the amalgamation of one-shot adaptation data with harmonized training data surpasses the performance of utilizing either data source in isolation. Notably, domain adaptation using exclusively harmonized training data achieved comparable or even superior performance compared to one-shot adaptation. Moreover, all adaptations required only minimal fine-tuning, ranging from 2 to 5 epochs for convergence.
Deep filter bank regression for super-resolution of anisotropic MR brain images
Sep 06, 2022



Abstract:In 2D multi-slice magnetic resonance (MR) acquisition, the through-plane signals are typically of lower resolution than the in-plane signals. While contemporary super-resolution (SR) methods aim to recover the underlying high-resolution volume, the estimated high-frequency information is implicit via end-to-end data-driven training rather than being explicitly stated and sought. To address this, we reframe the SR problem statement in terms of perfect reconstruction filter banks, enabling us to identify and directly estimate the missing information. In this work, we propose a two-stage approach to approximate the completion of a perfect reconstruction filter bank corresponding to the anisotropic acquisition of a particular scan. In stage 1, we estimate the missing filters using gradient descent and in stage 2, we use deep networks to learn the mapping from coarse coefficients to detail coefficients. In addition, the proposed formulation does not rely on external training data, circumventing the need for domain shift correction. Under our approach, SR performance is improved particularly in "slice gap" scenarios, likely due to the constrained solution space imposed by the framework.
Contrast Adaptive Tissue Classification by Alternating Segmentation and Synthesis
Mar 04, 2021



Abstract:Deep learning approaches to the segmentation of magnetic resonance images have shown significant promise in automating the quantitative analysis of brain images. However, a continuing challenge has been its sensitivity to the variability of acquisition protocols. Attempting to segment images that have different contrast properties from those within the training data generally leads to significantly reduced performance. Furthermore, heterogeneous data sets cannot be easily evaluated because the quantitative variation due to acquisition differences often dwarfs the variation due to the biological differences that one seeks to measure. In this work, we describe an approach using alternating segmentation and synthesis steps that adapts the contrast properties of the training data to the input image. This allows input images that do not resemble the training data to be more consistently segmented. A notable advantage of this approach is that only a single example of the acquisition protocol is required to adapt to its contrast properties. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approaching using brain images from a set of human subjects scanned with two different T1-weighted volumetric protocols.
Extracting 2D weak labels from volume labels using multiple instance learning in CT hemorrhage detection
Nov 13, 2019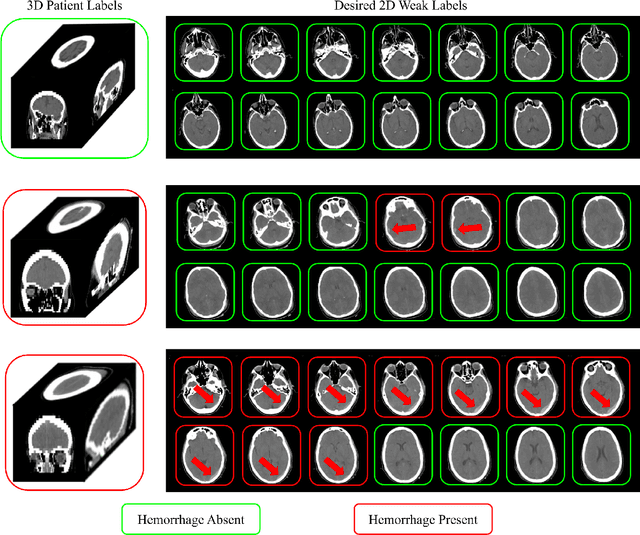
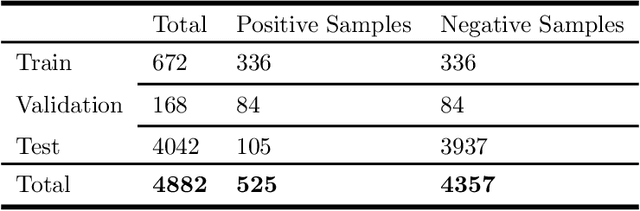
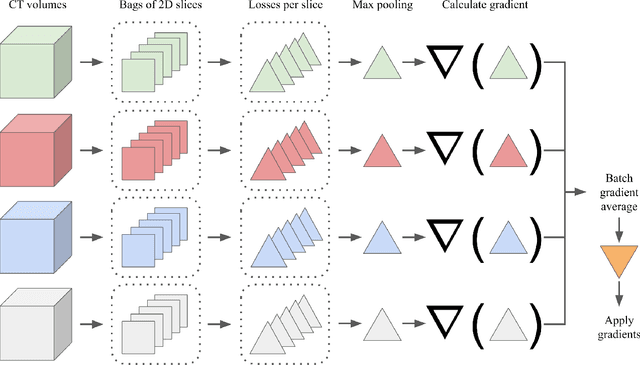
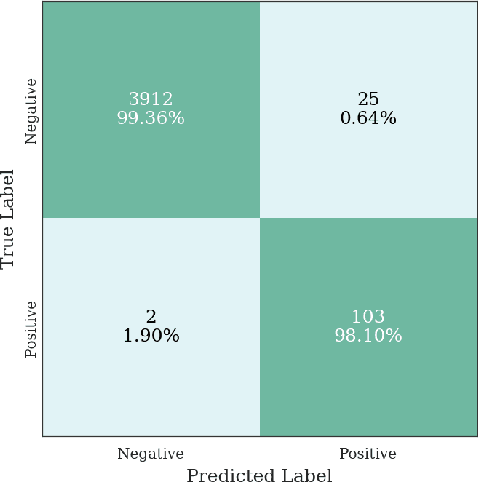
Abstract:Multiple instance learning (MIL) is a supervised learning methodology that aims to allow models to learn instance class labels from bag class labels, where a bag is defined to contain multiple instances. MIL is gaining traction for learning from weak labels but has not been widely applied to 3D medical imaging. MIL is well-suited to clinical CT acquisitions since (1) the highly anisotropic voxels hinder application of traditional 3D networks and (2) patch-based networks have limited ability to learn whole volume labels. In this work, we apply MIL with a deep convolutional neural network to identify whether clinical CT head image volumes possess one or more large hemorrhages (> 20cm$^3$), resulting in a learned 2D model without the need for 2D slice annotations. Individual image volumes are considered separate bags, and the slices in each volume are instances. Such a framework sets the stage for incorporating information obtained in clinical reports to help train a 2D segmentation approach. Within this context, we evaluate the data requirements to enable generalization of MIL by varying the amount of training data. Our results show that a training size of at least 400 patient image volumes was needed to achieve accurate per-slice hemorrhage detection. Over a five-fold cross-validation, the leading model, which made use of the maximum number of training volumes, had an average true positive rate of 98.10%, an average true negative rate of 99.36%, and an average precision of 0.9698. The models have been made available along with source code to enabled continued exploration and adaption of MIL in CT neuroimaging.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge