Cailey I. Kerley
Joint analysis of structural connectivity and cortical surface features: correlates with mild traumatic brain injury
Dec 15, 2020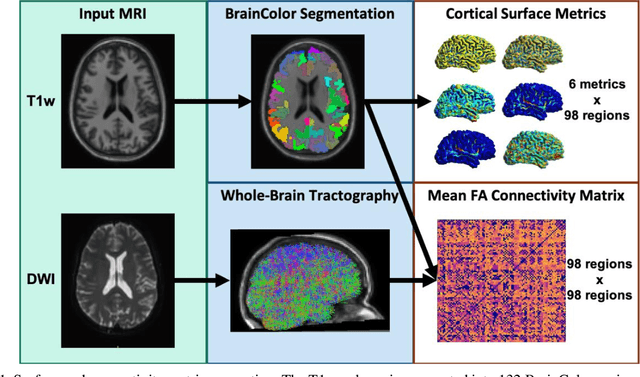
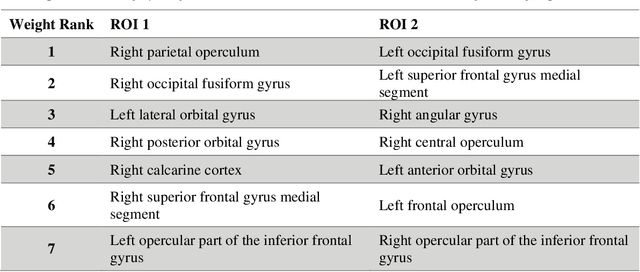
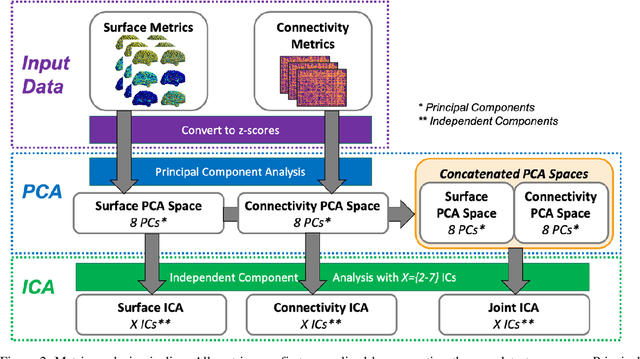
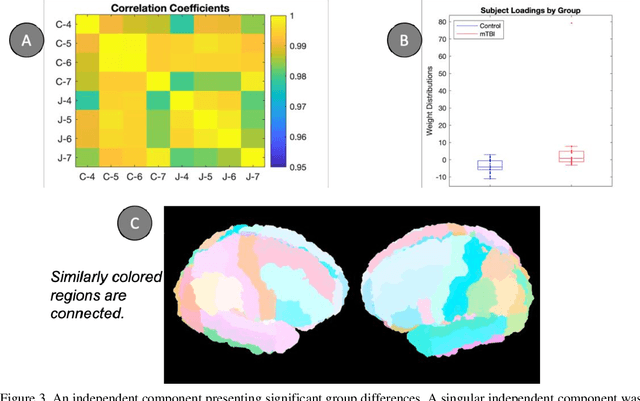
Abstract:Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) is a complex syndrome that affects up to 600 per 100,000 individuals, with a particular concentration among military personnel. About half of all mTBI patients experience a diverse array of chronic symptoms which persist long after the acute injury. Hence, there is an urgent need for better understanding of the white matter and gray matter pathologies associated with mTBI to map which specific brain systems are impacted and identify courses of intervention. Previous works have linked mTBI to disruptions in white matter pathways and cortical surface abnormalities. Herein, we examine these hypothesized links in an exploratory study of joint structural connectivity and cortical surface changes associated with mTBI and its chronic symptoms. Briefly, we consider a cohort of 12 mTBI and 26 control subjects. A set of 588 cortical surface metrics and 4,753 structural connectivity metrics were extracted from cortical surface regions and diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging in each subject. Principal component analysis (PCA) was used to reduce the dimensionality of each metric set. We then applied independent component analysis (ICA) both to each PCA space individually and together in a joint ICA approach. We identified a stable independent component across the connectivity-only and joint ICAs which presented significant group differences in subject loadings (p<0.05, corrected). Additionally, we found that two mTBI symptoms, slowed thinking and forgetfulness, were significantly correlated (p<0.05, corrected) with mTBI subject loadings in a surface-only ICA. These surface-only loadings captured an increase in bilateral cortical thickness.
MRI correlates of chronic symptoms in mild traumatic brain injury
Dec 06, 2019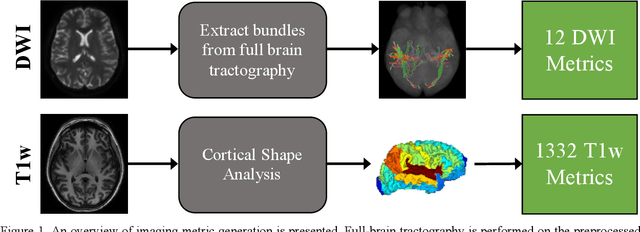
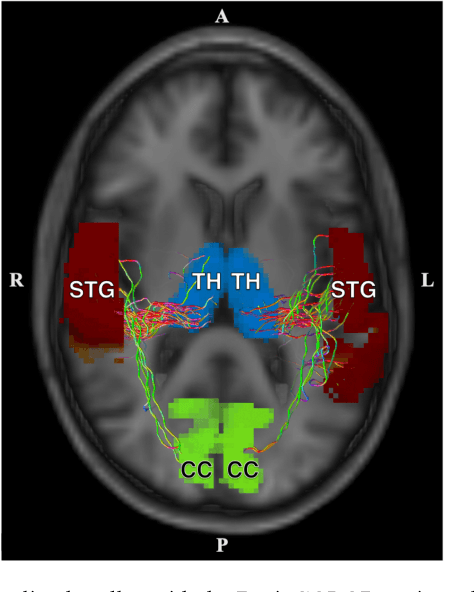
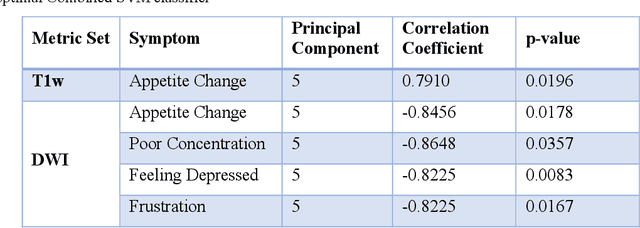
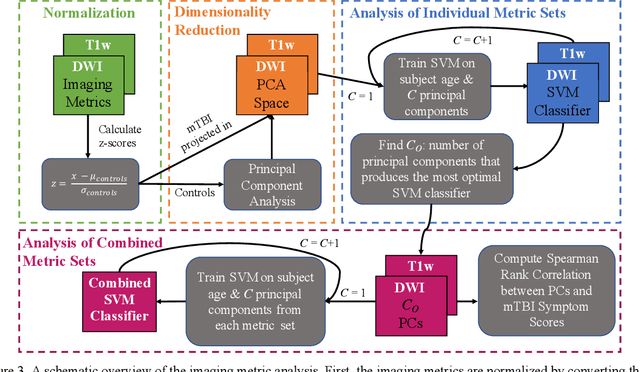
Abstract:Veterans with mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) have reported auditory and visual dysfunction that persists beyond the acute incident. The etiology behind these symptoms is difficult to characterize with current clinical imaging. These functional deficits may be caused by shear injury or micro-bleeds, which can be detected with special imaging modalities. We explore these hypotheses in a pilot study of multi-parametric MRI. We extract over 1,000 imaging and clinical metrics and project them to a low-dimensional space, where we can discriminate between healthy controls and patients with mTBI. We also show correlations between the metric representations and patient symptoms.
Extracting 2D weak labels from volume labels using multiple instance learning in CT hemorrhage detection
Nov 13, 2019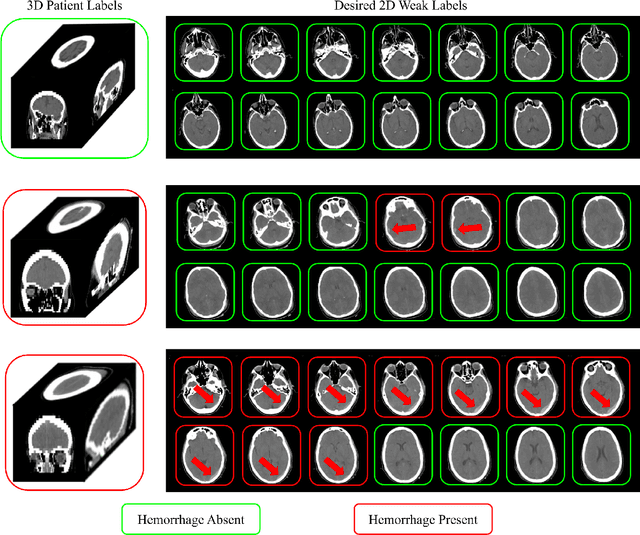
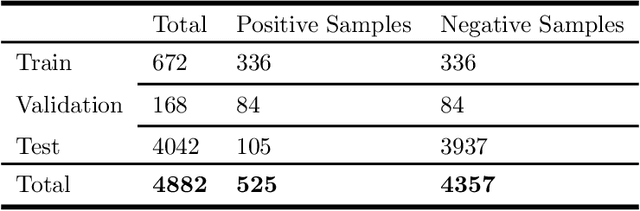
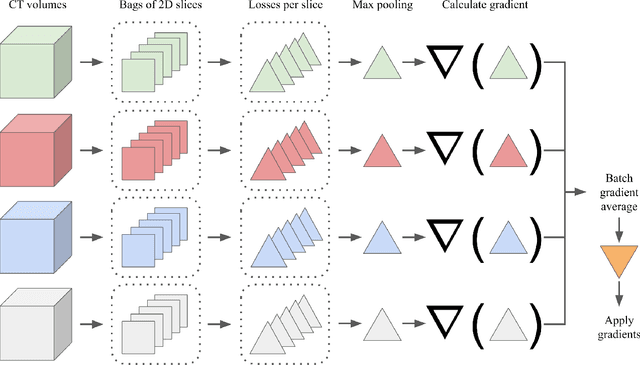
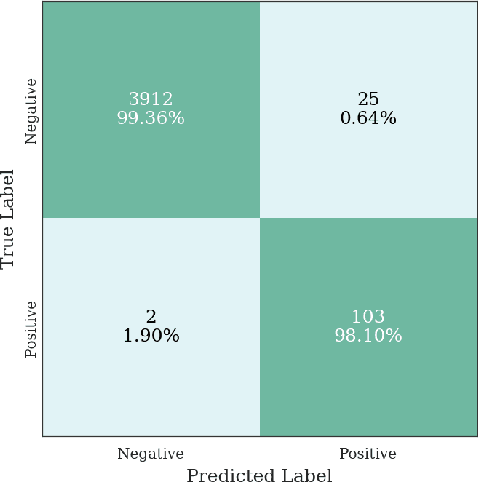
Abstract:Multiple instance learning (MIL) is a supervised learning methodology that aims to allow models to learn instance class labels from bag class labels, where a bag is defined to contain multiple instances. MIL is gaining traction for learning from weak labels but has not been widely applied to 3D medical imaging. MIL is well-suited to clinical CT acquisitions since (1) the highly anisotropic voxels hinder application of traditional 3D networks and (2) patch-based networks have limited ability to learn whole volume labels. In this work, we apply MIL with a deep convolutional neural network to identify whether clinical CT head image volumes possess one or more large hemorrhages (> 20cm$^3$), resulting in a learned 2D model without the need for 2D slice annotations. Individual image volumes are considered separate bags, and the slices in each volume are instances. Such a framework sets the stage for incorporating information obtained in clinical reports to help train a 2D segmentation approach. Within this context, we evaluate the data requirements to enable generalization of MIL by varying the amount of training data. Our results show that a training size of at least 400 patient image volumes was needed to achieve accurate per-slice hemorrhage detection. Over a five-fold cross-validation, the leading model, which made use of the maximum number of training volumes, had an average true positive rate of 98.10%, an average true negative rate of 99.36%, and an average precision of 0.9698. The models have been made available along with source code to enabled continued exploration and adaption of MIL in CT neuroimaging.
Montage based 3D Medical Image Retrieval from Traumatic Brain Injury Cohort using Deep Convolutional Neural Network
Dec 10, 2018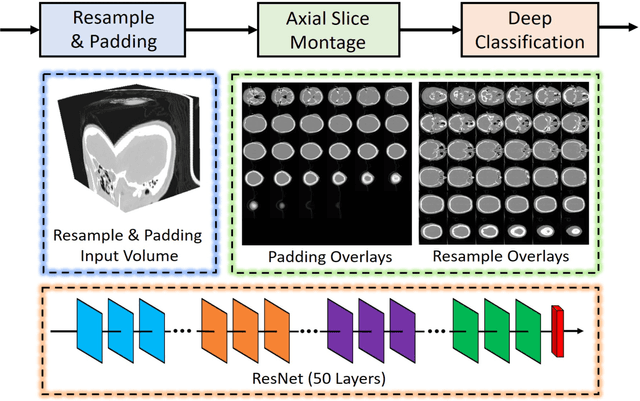
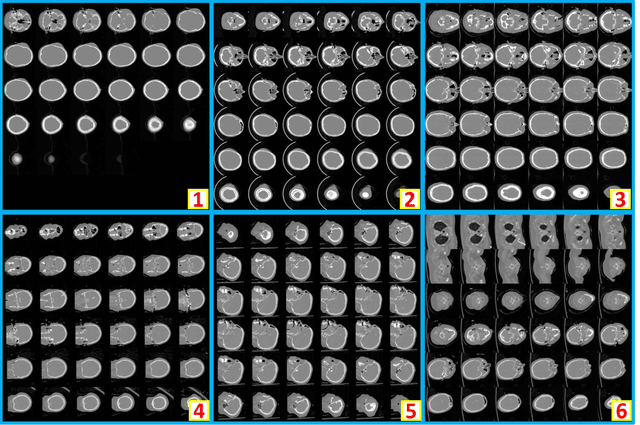
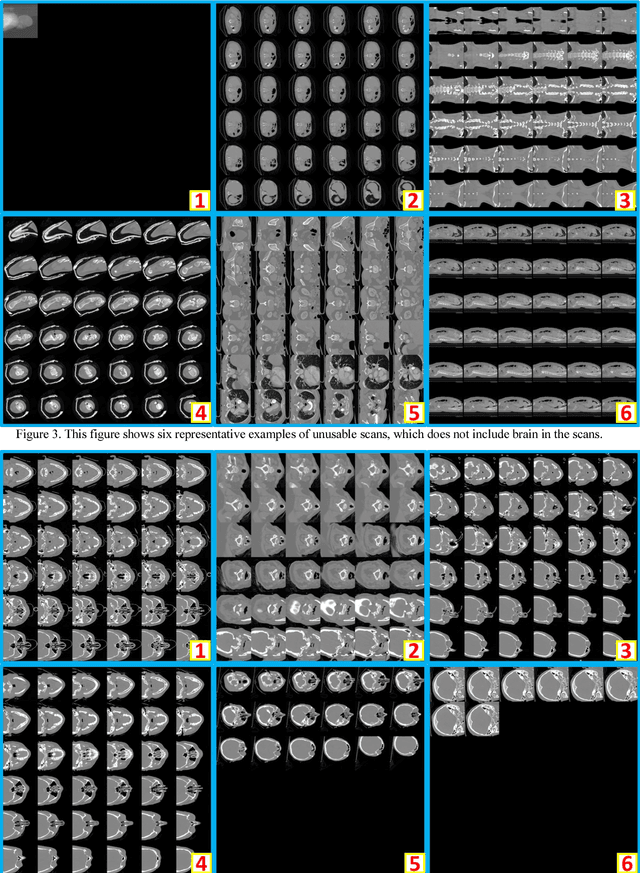
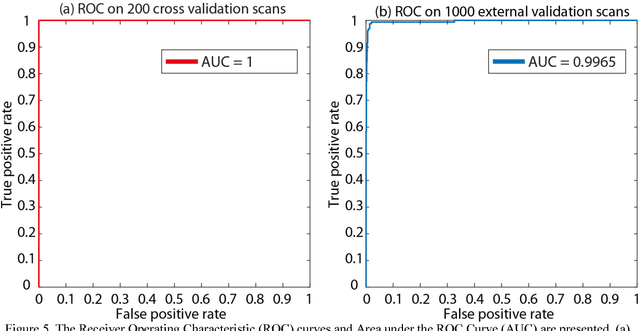
Abstract:Brain imaging analysis on clinically acquired computed tomography (CT) is essential for the diagnosis, risk prediction of progression, and treatment of the structural phenotypes of traumatic brain injury (TBI). However, in real clinical imaging scenarios, entire body CT images (e.g., neck, abdomen, chest, pelvis) are typically captured along with whole brain CT scans. For instance, in a typical sample of clinical TBI imaging cohort, only ~15% of CT scans actually contain whole brain CT images suitable for volumetric brain analyses; the remaining are partial brain or non-brain images. Therefore, a manual image retrieval process is typically required to isolate the whole brain CT scans from the entire cohort. However, the manual image retrieval is time and resource consuming and even more difficult for the larger cohorts. To alleviate the manual efforts, in this paper we propose an automated 3D medical image retrieval pipeline, called deep montage-based image retrieval (dMIR), which performs classification on 2D montage images via a deep convolutional neural network. The novelty of the proposed method for image processing is to characterize the medical image retrieval task based on the montage images. In a cohort of 2000 clinically acquired TBI scans, 794 scans were used as training data, 206 scans were used as validation data, and the remaining 1000 scans were used as testing data. The proposed achieved accuracy=1.0, recall=1.0, precision=1.0, f1=1.0 for validation data, while achieved accuracy=0.988, recall=0.962, precision=0.962, f1=0.962 for testing data. Thus, the proposed dMIR is able to perform accurate CT whole brain image retrieval from large-scale clinical cohorts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge