Kurt G. Schilling
Personalized White Matter Bundle Segmentation for Early Childhood
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:White matter segmentation methods from diffusion magnetic resonance imaging range from streamline clustering-based approaches to bundle mask delineation, but none have proposed a pediatric-specific approach. We hypothesize that a deep learning model with a similar approach to TractSeg will improve similarity between an algorithm-generated mask and an expert-labeled ground truth. Given a cohort of 56 manually labelled white matter bundles, we take inspiration from TractSeg's 2D UNet architecture, and we modify inputs to match bundle definitions as determined by pediatric experts, evaluation to use k fold cross validation, the loss function to masked Dice loss. We evaluate Dice score, volume overlap, and volume overreach of 16 major regions of interest compared to the expert labeled dataset. To test whether our approach offers statistically significant improvements over TractSeg, we compare Dice voxels, volume overlap, and adjacency voxels with a Wilcoxon signed rank test followed by false discovery rate correction. We find statistical significance across all bundles for all metrics with one exception in volume overlap. After we run TractSeg and our model, we combine their output masks into a 60 label atlas to evaluate if TractSeg and our model combined can generate a robust, individualized atlas, and observe smoothed, continuous masks in cases that TractSeg did not produce an anatomically plausible output. With the improvement of white matter pathway segmentation masks, we can further understand neurodevelopment on a population level scale, and we can produce reliable estimates of individualized anatomy in pediatric white matter diseases and disorders.
Fully Differentiable dMRI Streamline Propagation in PyTorch
Nov 17, 2025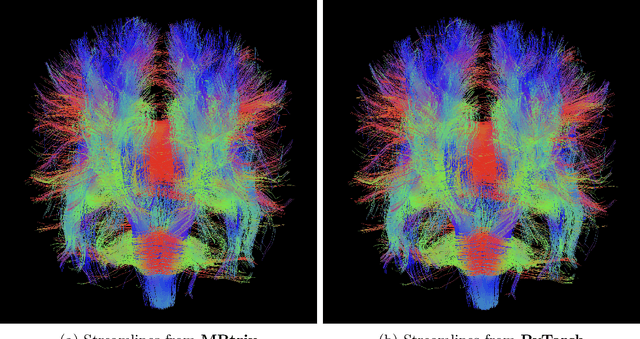
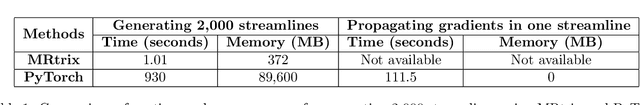
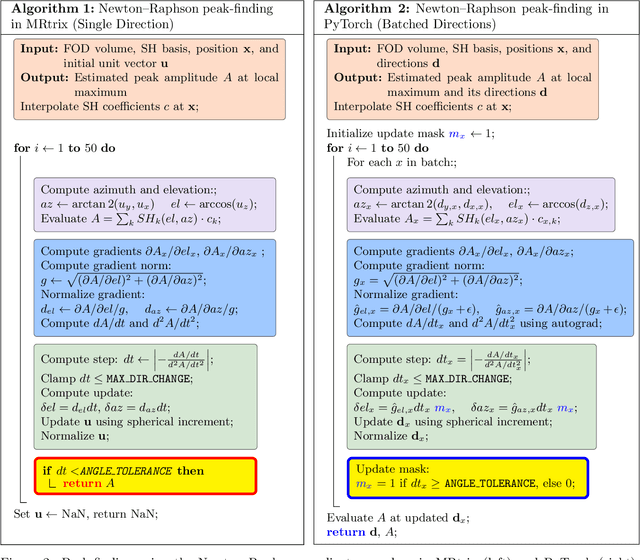
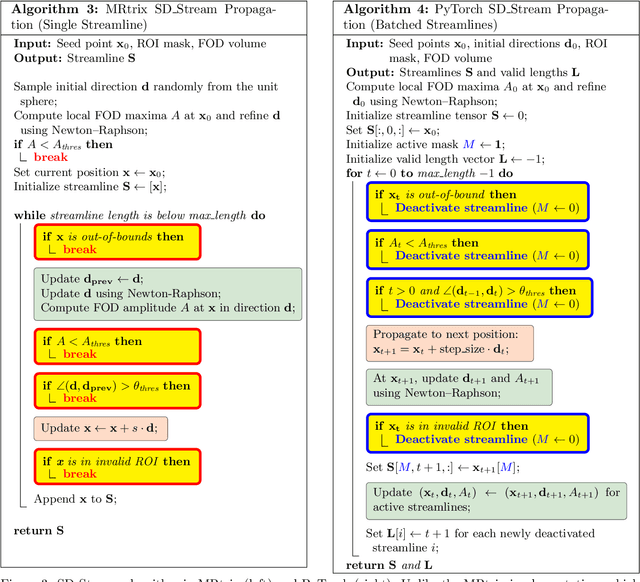
Abstract:Diffusion MRI (dMRI) provides a distinctive means to probe the microstructural architecture of living tissue, facilitating applications such as brain connectivity analysis, modeling across multiple conditions, and the estimation of macrostructural features. Tractography, which emerged in the final years of the 20th century and accelerated in the early 21st century, is a technique for visualizing white matter pathways in the brain using dMRI. Most diffusion tractography methods rely on procedural streamline propagators or global energy minimization methods. Although recent advancements in deep learning have enabled tasks that were previously challenging, existing tractography approaches are often non-differentiable, limiting their integration in end-to-end learning frameworks. While progress has been made in representing streamlines in differentiable frameworks, no existing method offers fully differentiable propagation. In this work, we propose a fully differentiable solution that retains numerical fidelity with a leading streamline algorithm. The key is that our PyTorch-engineered streamline propagator has no components that block gradient flow, making it fully differentiable. We show that our method matches standard propagators while remaining differentiable. By translating streamline propagation into a differentiable PyTorch framework, we enable deeper integration of tractography into deep learning workflows, laying the foundation for a new category of macrostructural reasoning that is not only computationally robust but also scientifically rigorous.
ECLARE: Efficient cross-planar learning for anisotropic resolution enhancement
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:In clinical imaging, magnetic resonance (MR) image volumes are often acquired as stacks of 2D slices, permitting decreased scan times, improved signal-to-noise ratio, and image contrasts unique to 2D MR pulse sequences. While this is sufficient for clinical evaluation, automated algorithms designed for 3D analysis perform sub-optimally on 2D-acquired scans, especially those with thick slices and gaps between slices. Super-resolution (SR) methods aim to address this problem, but previous methods do not address all of the following: slice profile shape estimation, slice gap, domain shift, and non-integer / arbitrary upsampling factors. In this paper, we propose ECLARE (Efficient Cross-planar Learning for Anisotropic Resolution Enhancement), a self-SR method that addresses each of these factors. ECLARE estimates the slice profile from the 2D-acquired multi-slice MR volume, trains a network to learn the mapping from low-resolution to high-resolution in-plane patches from the same volume, and performs SR with anti-aliasing. We compared ECLARE to cubic B-spline interpolation, SMORE, and other contemporary SR methods. We used realistic and representative simulations so that quantitative performance against a ground truth could be computed, and ECLARE outperformed all other methods in both signal recovery and downstream tasks. On real data for which there is no ground truth, ECLARE demonstrated qualitative superiority over other methods as well. Importantly, as ECLARE does not use external training data it cannot suffer from domain shift between training and testing. Our code is open-source and available at https://www.github.com/sremedios/eclare.
Brain age identification from diffusion MRI synergistically predicts neurodegenerative disease
Oct 29, 2024



Abstract:Estimated brain age from magnetic resonance image (MRI) and its deviation from chronological age can provide early insights into potential neurodegenerative diseases, supporting early detection and implementation of prevention strategies. Diffusion MRI (dMRI), a widely used modality for brain age estimation, presents an opportunity to build an earlier biomarker for neurodegenerative disease prediction because it captures subtle microstructural changes that precede more perceptible macrostructural changes. However, the coexistence of macro- and micro-structural information in dMRI raises the question of whether current dMRI-based brain age estimation models are leveraging the intended microstructural information or if they inadvertently rely on the macrostructural information. To develop a microstructure-specific brain age, we propose a method for brain age identification from dMRI that minimizes the model's use of macrostructural information by non-rigidly registering all images to a standard template. Imaging data from 13,398 participants across 12 datasets were used for the training and evaluation. We compare our brain age models, trained with and without macrostructural information minimized, with an architecturally similar T1-weighted (T1w) MRI-based brain age model and two state-of-the-art T1w MRI-based brain age models that primarily use macrostructural information. We observe difference between our dMRI-based brain age and T1w MRI-based brain age across stages of neurodegeneration, with dMRI-based brain age being older than T1w MRI-based brain age in participants transitioning from cognitively normal (CN) to mild cognitive impairment (MCI), but younger in participants already diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Approximately 4 years before MCI diagnosis, dMRI-based brain age yields better performance than T1w MRI-based brain ages in predicting transition from CN to MCI.
Sensitivity of quantitative diffusion MRI tractography and microstructure to anisotropic spatial sampling
Sep 26, 2024Abstract:Purpose: Diffusion weighted MRI (dMRI) and its models of neural structure provide insight into human brain organization and variations in white matter. A recent study by McMaster, et al. showed that complex graph measures of the connectome, the graphical representation of a tractogram, vary with spatial sampling changes, but biases introduced by anisotropic voxels in the process have not been well characterized. This study uses microstructural measures (fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity) and white matter bundle properties (bundle volume, length, and surface area) to further understand the effect of anisotropic voxels on microstructure and tractography. Methods: The statistical significance of the selected measures derived from dMRI data were assessed by comparing three white matter bundles at different spatial resolutions with 44 subjects from the Human Connectome Project Young Adult dataset scan/rescan data using the Wilcoxon Signed Rank test. The original isotropic resolution (1.25 mm isotropic) was explored with six anisotropic resolutions with 0.25 mm incremental steps in the z dimension. Then, all generated resolutions were upsampled to 1.25 mm isotropic and 1 mm isotropic. Results: There were statistically significant differences between at least one microstructural and one bundle measure at every resolution (p less than or equal to 0.05, corrected for multiple comparisons). Cohen's d coefficient evaluated the effect size of anisotropic voxels on microstructure and tractography. Conclusion: Fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity cannot be recovered with basic up sampling from low quality data with gold standard data. However, the bundle measures from tractogram become more repeatable when voxels are resampled to 1 mm isotropic.
Multi-Modality Conditioned Variational U-Net for Field-of-View Extension in Brain Diffusion MRI
Sep 20, 2024
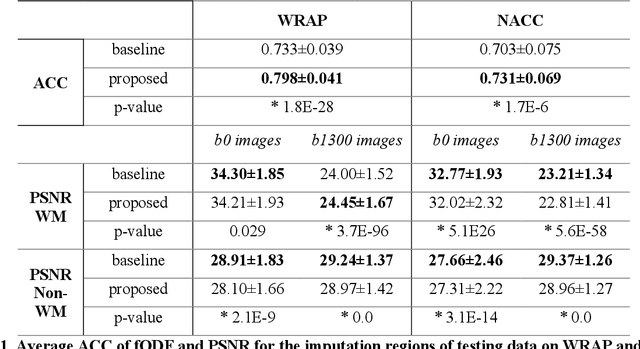

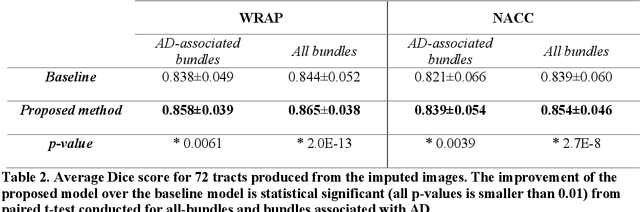
Abstract:An incomplete field-of-view (FOV) in diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (dMRI) can severely hinder the volumetric and bundle analyses of whole-brain white matter connectivity. Although existing works have investigated imputing the missing regions using deep generative models, it remains unclear how to specifically utilize additional information from paired multi-modality data and whether this can enhance the imputation quality and be useful for downstream tractography. To fill this gap, we propose a novel framework for imputing dMRI scans in the incomplete part of the FOV by integrating the learned diffusion features in the acquired part of the FOV to the complete brain anatomical structure. We hypothesize that by this design the proposed framework can enhance the imputation performance of the dMRI scans and therefore be useful for repairing whole-brain tractography in corrupted dMRI scans with incomplete FOV. We tested our framework on two cohorts from different sites with a total of 96 subjects and compared it with a baseline imputation method that treats the information from T1w and dMRI scans equally. The proposed framework achieved significant improvements in imputation performance, as demonstrated by angular correlation coefficient (p < 1E-5), and in downstream tractography accuracy, as demonstrated by Dice score (p < 0.01). Results suggest that the proposed framework improved imputation performance in dMRI scans by specifically utilizing additional information from paired multi-modality data, compared with the baseline method. The imputation achieved by the proposed framework enhances whole brain tractography, and therefore reduces the uncertainty when analyzing bundles associated with neurodegenerative.
Harmonized connectome resampling for variance in voxel sizes
Aug 02, 2024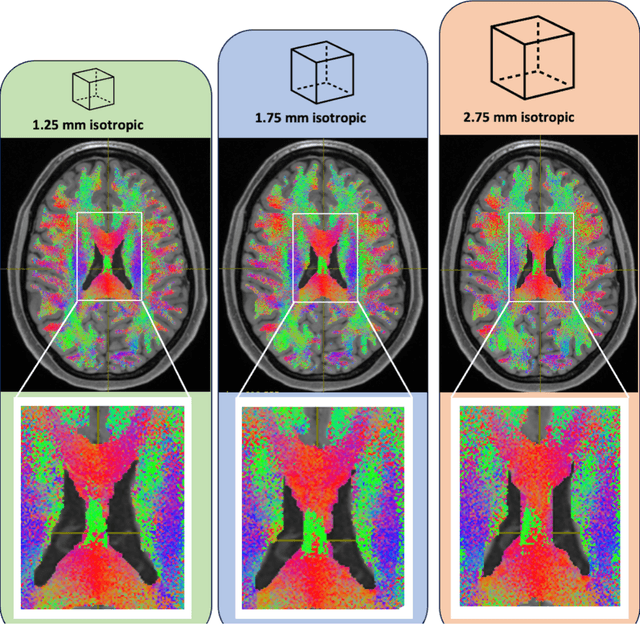
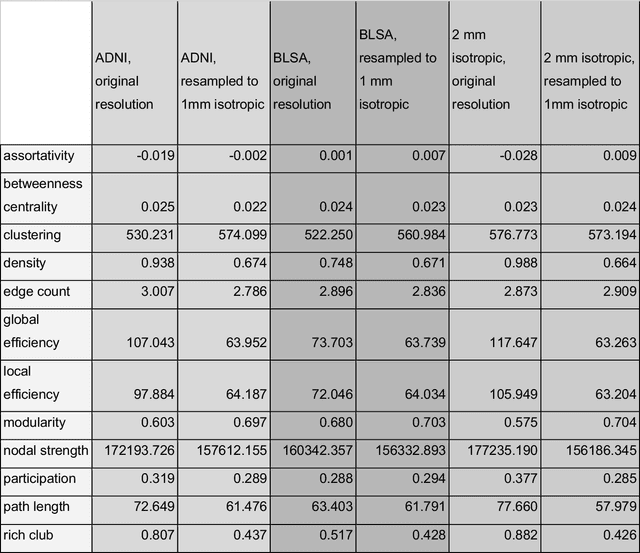
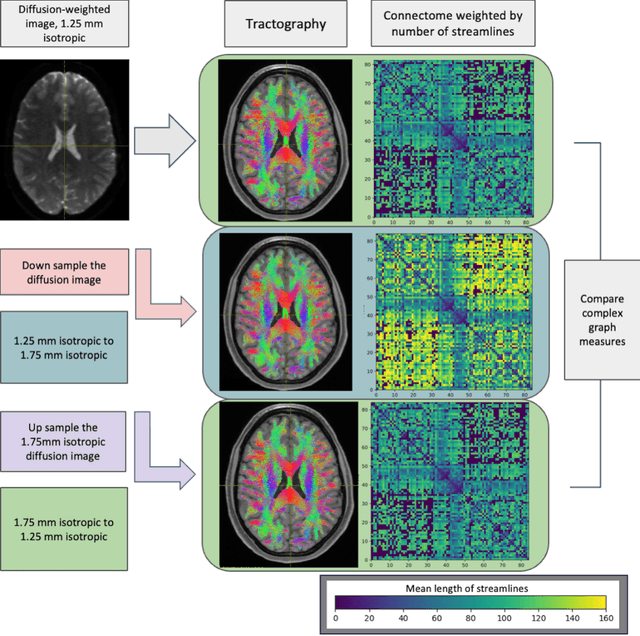
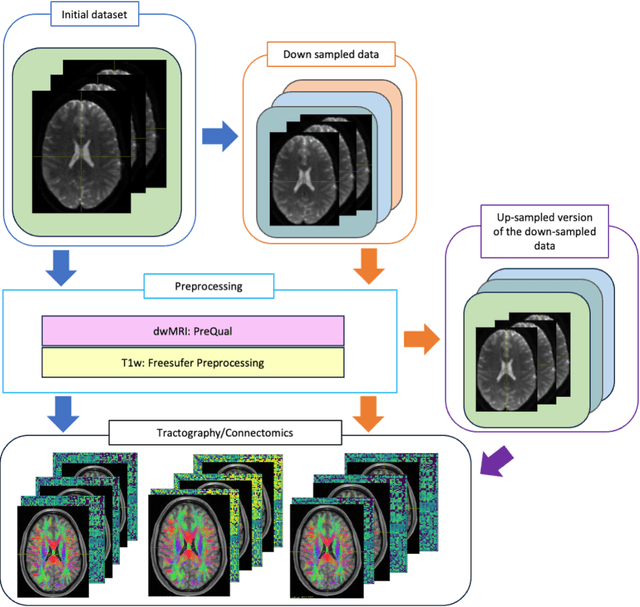
Abstract:To date, there has been no comprehensive study characterizing the effect of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging voxel resolution on the resulting connectome for high resolution subject data. Similarity in results improved with higher resolution, even after initial down-sampling. To ensure robust tractography and connectomes, resample data to 1 mm isotropic resolution.
Tractography with T1-weighted MRI and associated anatomical constraints on clinical quality diffusion MRI
Mar 27, 2024Abstract:Diffusion MRI (dMRI) streamline tractography, the gold standard for in vivo estimation of brain white matter (WM) pathways, has long been considered indicative of macroscopic relationships with WM microstructure. However, recent advances in tractography demonstrated that convolutional recurrent neural networks (CoRNN) trained with a teacher-student framework have the ability to learn and propagate streamlines directly from T1 and anatomical contexts. Training for this network has previously relied on high-resolution dMRI. In this paper, we generalize the training mechanism to traditional clinical resolution data, which allows generalizability across sensitive and susceptible study populations. We train CoRNN on a small subset of the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging (BLSA), which better resembles clinical protocols. Then, we define a metric, termed the epsilon ball seeding method, to compare T1 tractography and traditional diffusion tractography at the streamline level. Under this metric, T1 tractography generated by CoRNN reproduces diffusion tractography with approximately two millimeters of error.
Evaluation of Mean Shift, ComBat, and CycleGAN for Harmonizing Brain Connectivity Matrices Across Sites
Jan 24, 2024



Abstract:Connectivity matrices derived from diffusion MRI (dMRI) provide an interpretable and generalizable way of understanding the human brain connectome. However, dMRI suffers from inter-site and between-scanner variation, which impedes analysis across datasets to improve robustness and reproducibility of results. To evaluate different harmonization approaches on connectivity matrices, we compared graph measures derived from these matrices before and after applying three harmonization techniques: mean shift, ComBat, and CycleGAN. The sample comprises 168 age-matched, sex-matched normal subjects from two studies: the Vanderbilt Memory and Aging Project (VMAP) and the Biomarkers of Cognitive Decline Among Normal Individuals (BIOCARD). First, we plotted the graph measures and used coefficient of variation (CoV) and the Mann-Whitney U test to evaluate different methods' effectiveness in removing site effects on the matrices and the derived graph measures. ComBat effectively eliminated site effects for global efficiency and modularity and outperformed the other two methods. However, all methods exhibited poor performance when harmonizing average betweenness centrality. Second, we tested whether our harmonization methods preserved correlations between age and graph measures. All methods except for CycleGAN in one direction improved correlations between age and global efficiency and between age and modularity from insignificant to significant with p-values less than 0.05.
Predicting Age from White Matter Diffusivity with Residual Learning
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:Imaging findings inconsistent with those expected at specific chronological age ranges may serve as early indicators of neurological disorders and increased mortality risk. Estimation of chronological age, and deviations from expected results, from structural MRI data has become an important task for developing biomarkers that are sensitive to such deviations. Complementary to structural analysis, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) has proven effective in identifying age-related microstructural changes within the brain white matter, thereby presenting itself as a promising additional modality for brain age prediction. Although early studies have sought to harness DTI's advantages for age estimation, there is no evidence that the success of this prediction is owed to the unique microstructural and diffusivity features that DTI provides, rather than the macrostructural features that are also available in DTI data. Therefore, we seek to develop white-matter-specific age estimation to capture deviations from normal white matter aging. Specifically, we deliberately disregard the macrostructural information when predicting age from DTI scalar images, using two distinct methods. The first method relies on extracting only microstructural features from regions of interest. The second applies 3D residual neural networks (ResNets) to learn features directly from the images, which are non-linearly registered and warped to a template to minimize macrostructural variations. When tested on unseen data, the first method yields mean absolute error (MAE) of 6.11 years for cognitively normal participants and MAE of 6.62 years for cognitively impaired participants, while the second method achieves MAE of 4.69 years for cognitively normal participants and MAE of 4.96 years for cognitively impaired participants. We find that the ResNet model captures subtler, non-macrostructural features for brain age prediction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge