Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Allen Newton
MRI correlates of chronic symptoms in mild traumatic brain injury
Dec 06, 2019Authors:Cailey I. Kerley, Kurt G. Schilling, Justin Blaber, Beth Miller, Allen Newton, Adam W. Anderson, Bennett A. Landman, Tonia S. Rex
Figures and Tables: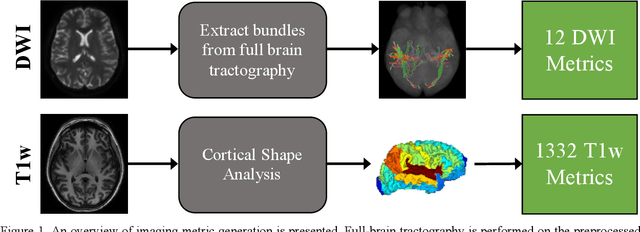
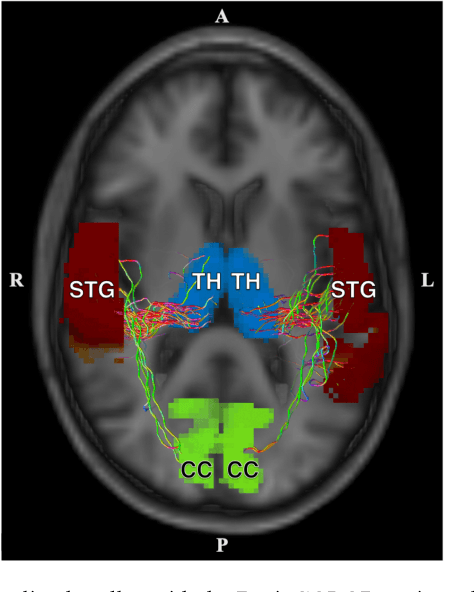
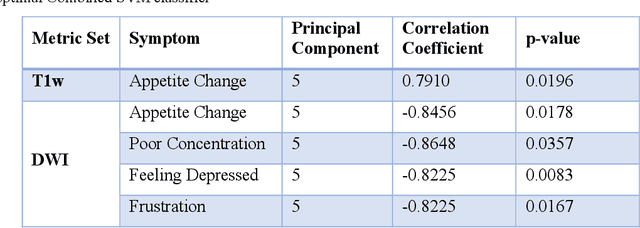
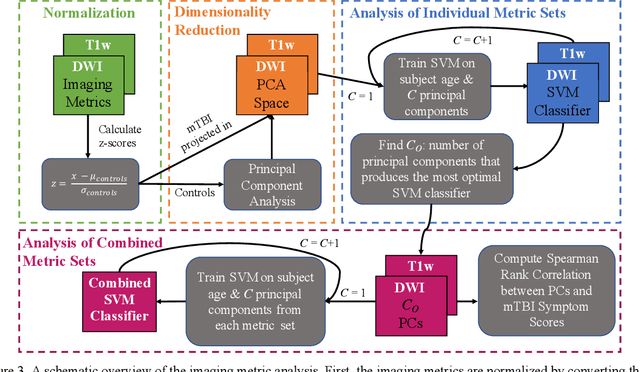




Abstract:Veterans with mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) have reported auditory and visual dysfunction that persists beyond the acute incident. The etiology behind these symptoms is difficult to characterize with current clinical imaging. These functional deficits may be caused by shear injury or micro-bleeds, which can be detected with special imaging modalities. We explore these hypotheses in a pilot study of multi-parametric MRI. We extract over 1,000 imaging and clinical metrics and project them to a low-dimensional space, where we can discriminate between healthy controls and patients with mTBI. We also show correlations between the metric representations and patient symptoms.
* SPIE Medical Imaging 2020
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge