J. Jeffery Carr
Fully Automatic Liver Attenuation Estimation Combing CNN Segmentation and Morphological Operations
Jun 29, 2019



Abstract:Manually tracing regions of interest (ROIs) within the liver is the de facto standard method for measuring liver attenuation on computed tomography (CT) in diagnosing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). However, manual tracing is resource intensive. To address these limitations and to expand the availability of a quantitative CT measure of hepatic steatosis, we propose the automatic liver attenuation ROI-based measurement (ALARM) method for automated liver attenuation estimation. The ALARM method consists of two major stages: (1) deep convolutional neural network (DCNN)-based liver segmentation and (2) automated ROI extraction. First, liver segmentation was achieved using our previously developed SS-Net. Then, a single central ROI (center-ROI) and three circles ROI (periphery-ROI) were computed based on liver segmentation and morphological operations. The ALARM method is available as an open source Docker container (https://github.com/MASILab/ALARM).246 subjects with 738 abdomen CT scans from the African American-Diabetes Heart Study (AA-DHS) were used for external validation (testing), independent from the training and validation cohort (100 clinically acquired CT abdominal scans).
Coronary Calcium Detection using 3D Attention Identical Dual Deep Network Based on Weakly Supervised Learning
Nov 10, 2018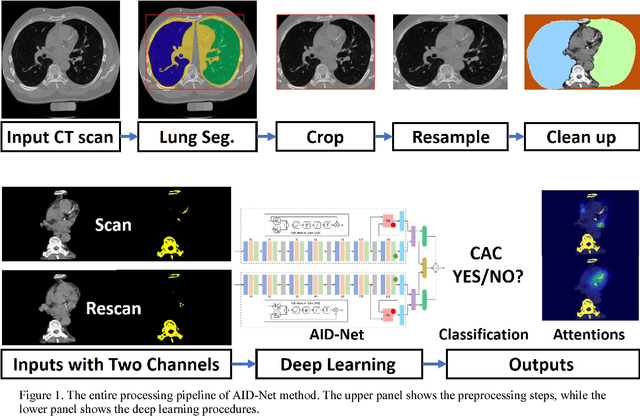
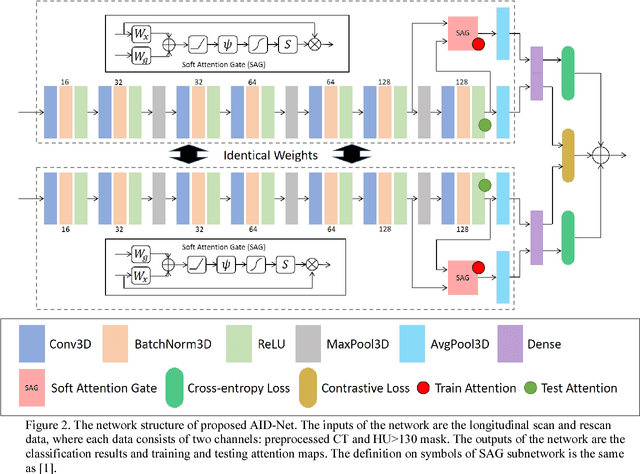

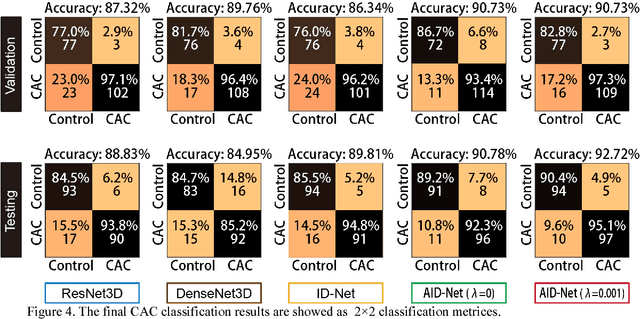
Abstract:Coronary artery calcium (CAC) is biomarker of advanced subclinical coronary artery disease and predicts myocardial infarction and death prior to age 60 years. The slice-wise manual delineation has been regarded as the gold standard of coronary calcium detection. However, manual efforts are time and resource consuming and even impracticable to be applied on large-scale cohorts. In this paper, we propose the attention identical dual network (AID-Net) to perform CAC detection using scan-rescan longitudinal non-contrast CT scans with weakly supervised attention by only using per scan level labels. To leverage the performance, 3D attention mechanisms were integrated into the AID-Net to provide complementary information for classification tasks. Moreover, the 3D Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad-CAM) was also proposed at the testing stage to interpret the behaviors of the deep neural network. 5075 non-contrast chest CT scans were used as training, validation and testing datasets. Baseline performance was assessed on the same cohort. From the results, the proposed AID-Net achieved the superior performance on classification accuracy (0.9272) and AUC (0.9627).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge