Ntu RGB D 2D
Papers and Code
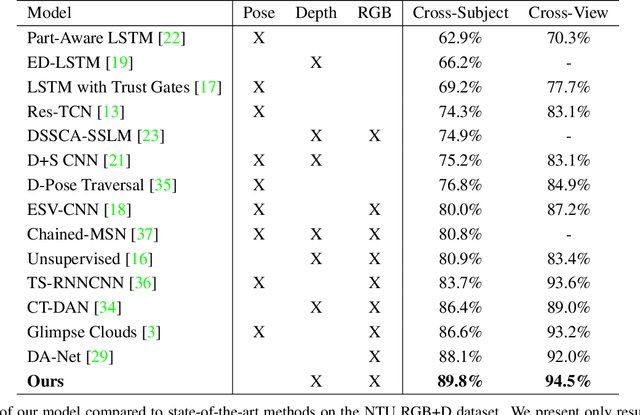
Action Recognition with Domain Invariant Features of Skeleton Image
Nov 19, 2021



Due to the fast processing-speed and robustness it can achieve, skeleton-based action recognition has recently received the attention of the computer vision community. The recent Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-based methods have shown commendable performance in learning spatio-temporal representations for skeleton sequence, which use skeleton image as input to a CNN. Since the CNN-based methods mainly encoding the temporal and skeleton joints simply as rows and columns, respectively, the latent correlation related to all joints may be lost caused by the 2D convolution. To solve this problem, we propose a novel CNN-based method with adversarial training for action recognition. We introduce a two-level domain adversarial learning to align the features of skeleton images from different view angles or subjects, respectively, thus further improve the generalization. We evaluated our proposed method on NTU RGB+D. It achieves competitive results compared with state-of-the-art methods and 2.4$\%$, 1.9$\%$ accuracy gain than the baseline for cross-subject and cross-view.
Video Based Fall Detection Using Human Poses
Jul 29, 2021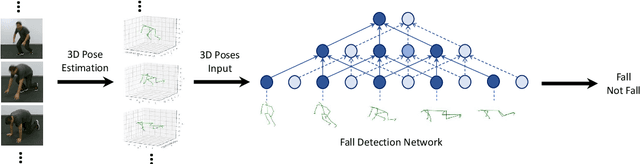
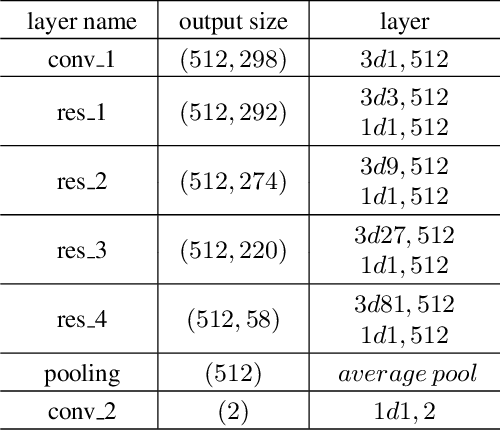

Video based fall detection accuracy has been largely improved due to the recent progress on deep convolutional neural networks. However, there still exists some challenges, such as lighting variation, complex background, which degrade the accuracy and generalization ability of these approaches. Meanwhile, large computation cost limits the application of existing fall detection approaches. To alleviate these problems, a video based fall detection approach using human poses is proposed in this paper. First, a lightweight pose estimator extracts 2D poses from video sequences and then 2D poses are lifted to 3D poses. Second, we introduce a robust fall detection network to recognize fall events using estimated 3D poses, which increases respective filed and maintains low computation cost by dilated convolutions. The experimental results show that the proposed fall detection approach achieves a high accuracy of 99.83% on large benchmark action recognition dataset NTU RGB+D and real-time performance of 18 FPS on a non-GPU platform and 63 FPS on a GPU platform.
Unsupervised View-Invariant Human Posture Representation
Sep 17, 2021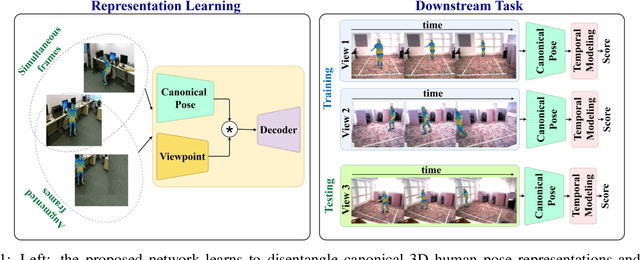

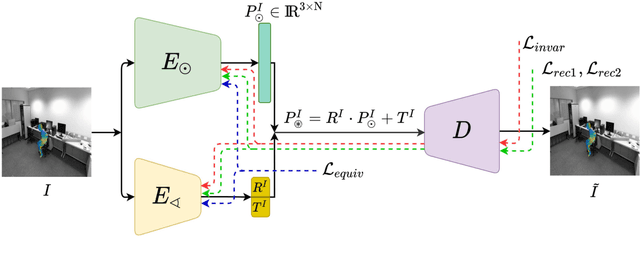
Most recent view-invariant action recognition and performance assessment approaches rely on a large amount of annotated 3D skeleton data to extract view-invariant features. However, acquiring 3D skeleton data can be cumbersome, if not impractical, in in-the-wild scenarios. To overcome this problem, we present a novel unsupervised approach that learns to extract view-invariant 3D human pose representation from a 2D image without using 3D joint data. Our model is trained by exploiting the intrinsic view-invariant properties of human pose between simultaneous frames from different viewpoints and their equivariant properties between augmented frames from the same viewpoint. We evaluate the learned view-invariant pose representations for two downstream tasks. We perform comparative experiments that show improvements on the state-of-the-art unsupervised cross-view action classification accuracy on NTU RGB+D by a significant margin, on both RGB and depth images. We also show the efficiency of transferring the learned representations from NTU RGB+D to obtain the first ever unsupervised cross-view and cross-subject rank correlation results on the multi-view human movement quality dataset, QMAR, and marginally improve on the-state-of-the-art supervised results for this dataset. We also carry out ablation studies to examine the contributions of the different components of our proposed network.
SAR-NAS: Skeleton-based Action Recognition via Neural Architecture Searching
Oct 29, 2020



This paper presents a study of automatic design of neural network architectures for skeleton-based action recognition. Specifically, we encode a skeleton-based action instance into a tensor and carefully define a set of operations to build two types of network cells: normal cells and reduction cells. The recently developed DARTS (Differentiable Architecture Search) is adopted to search for an effective network architecture that is built upon the two types of cells. All operations are 2D based in order to reduce the overall computation and search space. Experiments on the challenging NTU RGB+D and Kinectics datasets have verified that most of the networks developed to date for skeleton-based action recognition are likely not compact and efficient. The proposed method provides an approach to search for such a compact network that is able to achieve comparative or even better performance than the state-of-the-art methods.
Selective Spatio-Temporal Aggregation Based Pose Refinement System: Towards Understanding Human Activities in Real-World Videos
Nov 10, 2020



Taking advantage of human pose data for understanding human activities has attracted much attention these days. However, state-of-the-art pose estimators struggle in obtaining high-quality 2D or 3D pose data due to occlusion, truncation and low-resolution in real-world un-annotated videos. Hence, in this work, we propose 1) a Selective Spatio-Temporal Aggregation mechanism, named SST-A, that refines and smooths the keypoint locations extracted by multiple expert pose estimators, 2) an effective weakly-supervised self-training framework which leverages the aggregated poses as pseudo ground-truth instead of handcrafted annotations for real-world pose estimation. Extensive experiments are conducted for evaluating not only the upstream pose refinement but also the downstream action recognition performance on four datasets, Toyota Smarthome, NTU-RGB+D, Charades, and Kinetics-50. We demonstrate that the skeleton data refined by our Pose-Refinement system (SSTA-PRS) is effective at boosting various existing action recognition models, which achieves competitive or state-of-the-art performance.
Novel-View Human Action Synthesis
Jul 06, 2020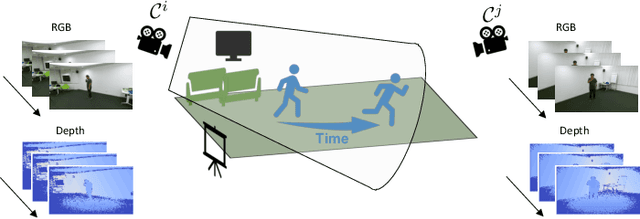

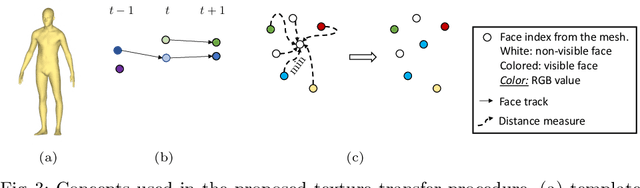
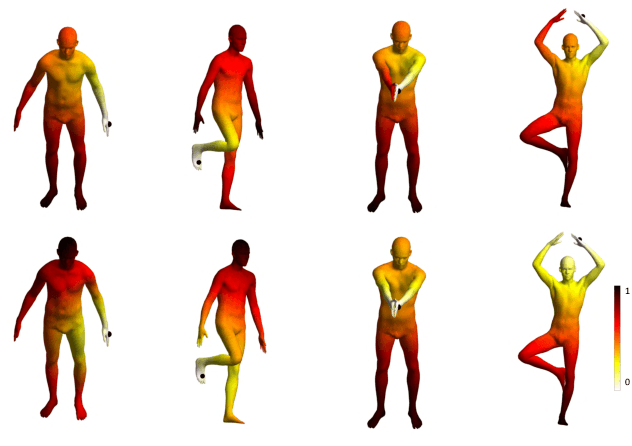
Novel-View Human Action Synthesis aims to synthesize the appearance of a dynamic scene from a virtual viewpoint, given a video from a real viewpoint. Our approach uses a novel 3D reasoning to synthesize the target viewpoint. We first estimate the 3D mesh of the target object, a human actor, and transfer the rough textures from the 2D images to the mesh. This transfer may generate sparse textures on the mesh due to frame resolution or occlusions. To solve this problem, we produce a semi-dense textured mesh by propagating the transferred textures both locally, within local geodesic neighborhoods, and globally, across symmetric semantic parts. Next, we introduce a context-based generator to learn how to correct and complete the residual appearance information. This allows the network to independently focus of learning the foreground and background synthesis tasks. We validate the proposed solution on the public NTU RGB+D dataset. The code and resources are available at \url{https://mlakhal.github.io/novel-view_action_synthesis/}.
Infrared and 3D skeleton feature fusion for RGB-D action recognition
Feb 28, 2020



A challenge of skeleton-based action recognition is the difficulty to classify actions with similar motions and object-related actions. Visual clues from other streams help in that regard. RGB data are sensible to illumination conditions, thus unusable in the dark. To alleviate this issue and still benefit from a visual stream, we propose a modular network (FUSION) combining skeleton and infrared data. A 2D convolutional neural network (CNN) is used as a pose module to extract features from skeleton data. A 3D CNN is used as an infrared module to extract visual cues from videos. Both feature vectors are then concatenated and exploited conjointly using a multilayer perceptron (MLP). Skeleton data also condition the infrared videos, providing a crop around the performing subjects and thus virtually focusing the attention of the infrared module. Ablation studies show that using pre-trained networks on other large scale datasets as our modules and data augmentation yield considerable improvements on the action classification accuracy. The strong contribution of our cropping strategy is also demonstrated. We evaluate our method on the NTU RGB+D dataset, the largest dataset for human action recognition from depth cameras, and report state-of-the-art performances.
Action Recognition Using Volumetric Motion Representations
Nov 19, 2019

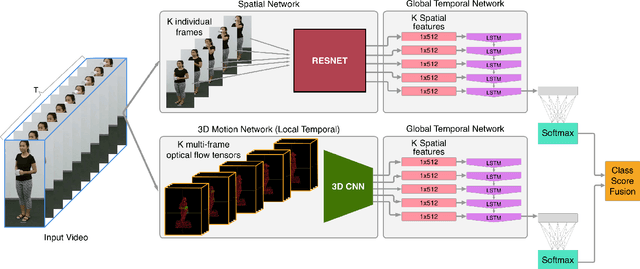
Traditional action recognition models are constructed around the paradigm of 2D perspective imagery. Though sophisticated time-series models have pushed the field forward, much of the information is still not exploited by confining the domain to 2D. In this work, we introduce a novel representation of motion as a voxelized 3D vector field and demonstrate how it can be used to improve performance of action recognition networks. This volumetric representation is a natural fit for 3D CNNs, and allows out-of-plane data augmentation techniques during training of these networks. Both the construction of this representation from RGB-D video and inference can be run in real time. We demonstrate superior results using this representation with our network design on the open-source NTU RGB+D dataset where it outperforms state-of-the-art on both of the defined evaluation metrics. Furthermore, we experimentally show how the out-of-plane augmentation techniques create viewpoint invariance and allow the model trained using this representation to generalize to unseen camera angles. Code is available here: https://github.com/mpeven/ntu_rgb.
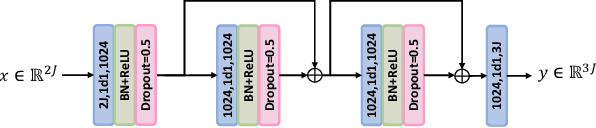
Multi-task Deep Learning for Real-Time 3D Human Pose Estimation and Action Recognition
Dec 15, 2019



Human pose estimation and action recognition are related tasks since both problems are strongly dependent on the human body representation and analysis. Nonetheless, most recent methods in the literature handle the two problems separately. In this work, we propose a multi-task framework for jointly estimating 2D or 3D human poses from monocular color images and classifying human actions from video sequences. We show that a single architecture can be used to solve both problems in an efficient way and still achieves state-of-the-art or comparable results at each task while running at more than 100 frames per second. The proposed method benefits from high parameters sharing between the two tasks by unifying still images and video clips processing in a single pipeline, allowing the model to be trained with data from different categories simultaneously and in a seamlessly way. Additionally, we provide important insights for end-to-end training the proposed multi-task model by decoupling key prediction parts, which consistently leads to better accuracy on both tasks. The reported results on four datasets (MPII, Human3.6M, Penn Action and NTU RGB+D) demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on the targeted tasks. Our source code and trained weights are publicly available at https://github.com/dluvizon/deephar.
Skeleton Image Representation for 3D Action Recognition based on Tree Structure and Reference Joints
Sep 11, 2019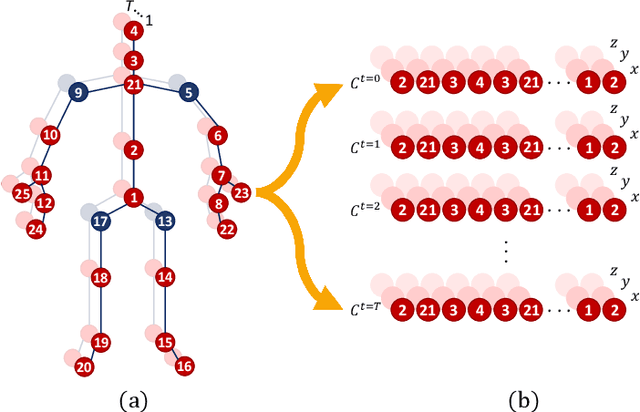
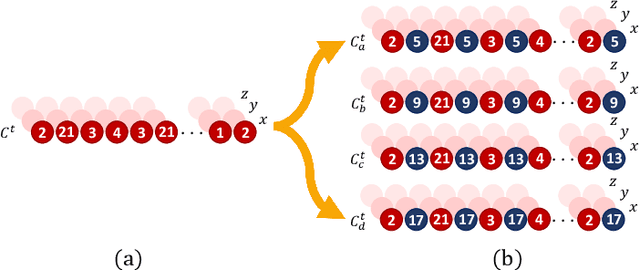
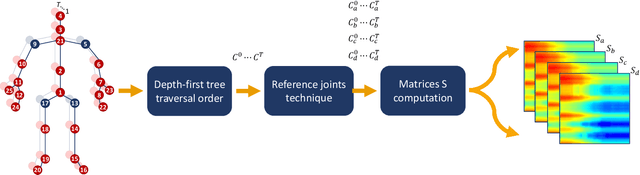
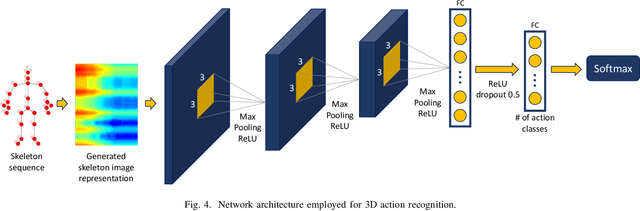
In the last years, the computer vision research community has studied on how to model temporal dynamics in videos to employ 3D human action recognition. To that end, two main baseline approaches have been researched: (i) Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) with Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM); and (ii) skeleton image representations used as input to a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). Although RNN approaches present excellent results, such methods lack the ability to efficiently learn the spatial relations between the skeleton joints. On the other hand, the representations used to feed CNN approaches present the advantage of having the natural ability of learning structural information from 2D arrays (i.e., they learn spatial relations from the skeleton joints). To further improve such representations, we introduce the Tree Structure Reference Joints Image (TSRJI), a novel skeleton image representation to be used as input to CNNs. The proposed representation has the advantage of combining the use of reference joints and a tree structure skeleton. While the former incorporates different spatial relationships between the joints, the latter preserves important spatial relations by traversing a skeleton tree with a depth-first order algorithm. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed representation for 3D action recognition on two datasets achieving state-of-the-art results on the recent NTU RGB+D~120 dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge