Rupayan Mallick
GIFT: Gradient-aware Immunization of diffusion models against malicious Fine-Tuning with safe concepts retention
Jul 18, 2025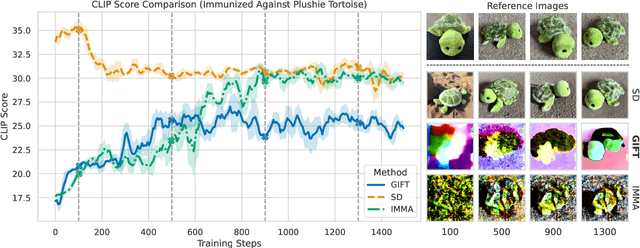
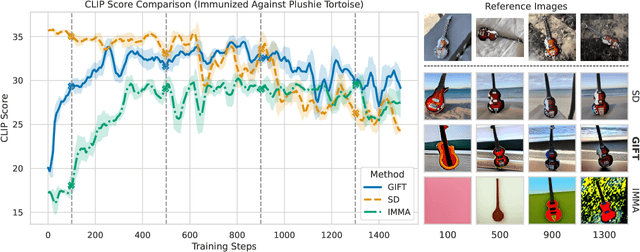
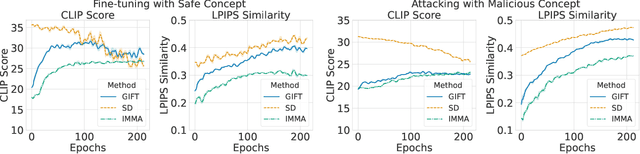
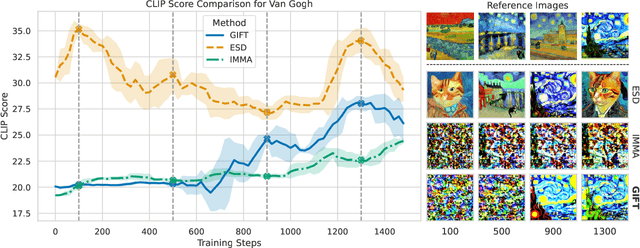
Abstract:We present GIFT: a {G}radient-aware {I}mmunization technique to defend diffusion models against malicious {F}ine-{T}uning while preserving their ability to generate safe content. Existing safety mechanisms like safety checkers are easily bypassed, and concept erasure methods fail under adversarial fine-tuning. GIFT addresses this by framing immunization as a bi-level optimization problem: the upper-level objective degrades the model's ability to represent harmful concepts using representation noising and maximization, while the lower-level objective preserves performance on safe data. GIFT achieves robust resistance to malicious fine-tuning while maintaining safe generative quality. Experimental results show that our method significantly impairs the model's ability to re-learn harmful concepts while maintaining performance on safe content, offering a promising direction for creating inherently safer generative models resistant to adversarial fine-tuning attacks.
ViSTA: Visual Storytelling using Multi-modal Adapters for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models have achieved remarkable success, yet generating coherent image sequences for visual storytelling remains challenging. A key challenge is effectively leveraging all previous text-image pairs, referred to as history text-image pairs, which provide contextual information for maintaining consistency across frames. Existing auto-regressive methods condition on all past image-text pairs but require extensive training, while training-free subject-specific approaches ensure consistency but lack adaptability to narrative prompts. To address these limitations, we propose a multi-modal history adapter for text-to-image diffusion models, \textbf{ViSTA}. It consists of (1) a multi-modal history fusion module to extract relevant history features and (2) a history adapter to condition the generation on the extracted relevant features. We also introduce a salient history selection strategy during inference, where the most salient history text-image pair is selected, improving the quality of the conditioning. Furthermore, we propose to employ a Visual Question Answering-based metric TIFA to assess text-image alignment in visual storytelling, providing a more targeted and interpretable assessment of generated images. Evaluated on the StorySalon and FlintStonesSV dataset, our proposed ViSTA model is not only consistent across different frames, but also well-aligned with the narrative text descriptions.
GenEAva: Generating Cartoon Avatars with Fine-Grained Facial Expressions from Realistic Diffusion-based Faces
Apr 10, 2025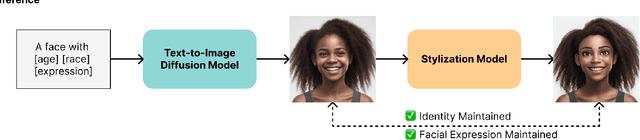
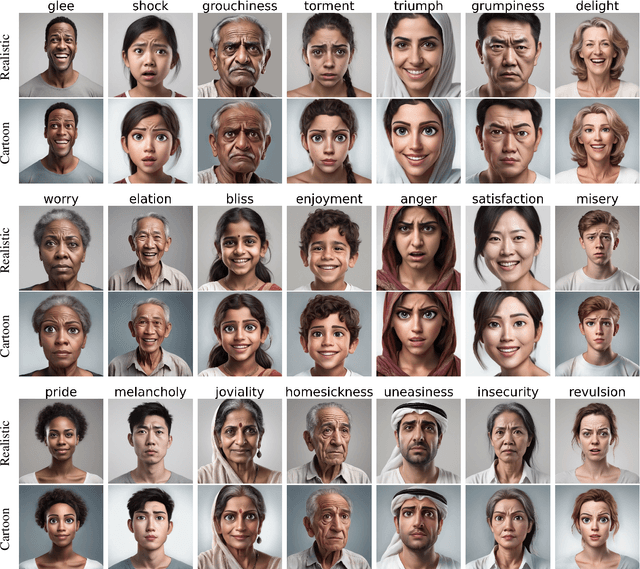

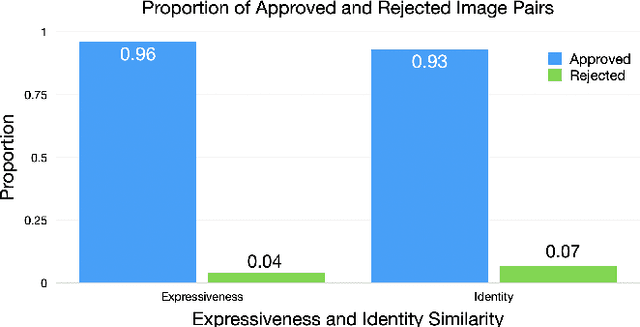
Abstract:Cartoon avatars have been widely used in various applications, including social media, online tutoring, and gaming. However, existing cartoon avatar datasets and generation methods struggle to present highly expressive avatars with fine-grained facial expressions and are often inspired from real-world identities, raising privacy concerns. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework, GenEAva, for generating high-quality cartoon avatars with fine-grained facial expressions. Our approach fine-tunes a state-of-the-art text-to-image diffusion model to synthesize highly detailed and expressive facial expressions. We then incorporate a stylization model that transforms these realistic faces into cartoon avatars while preserving both identity and expression. Leveraging this framework, we introduce the first expressive cartoon avatar dataset, GenEAva 1.0, specifically designed to capture 135 fine-grained facial expressions, featuring 13,230 expressive cartoon avatars with a balanced distribution across genders, racial groups, and age ranges. We demonstrate that our fine-tuned model generates more expressive faces than the state-of-the-art text-to-image diffusion model SDXL. We also verify that the cartoon avatars generated by our framework do not include memorized identities from fine-tuning data. The proposed framework and dataset provide a diverse and expressive benchmark for future research in cartoon avatar generation.
D-Feat Occlusions: Diffusion Features for Robustness to Partial Visual Occlusions in Object Recognition
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Applications of diffusion models for visual tasks have been quite noteworthy. This paper targets making classification models more robust to occlusions for the task of object recognition by proposing a pipeline that utilizes a frozen diffusion model. Diffusion features have demonstrated success in image generation and image completion while understanding image context. Occlusion can be posed as an image completion problem by deeming the pixels of the occluder to be `missing.' We hypothesize that such features can help hallucinate object visual features behind occluding objects, and hence we propose using them to enable models to become more occlusion robust. We design experiments to include input-based augmentations as well as feature-based augmentations. Input-based augmentations involve finetuning on images where the occluder pixels are inpainted, and feature-based augmentations involve augmenting classification features with intermediate diffusion features. We demonstrate that our proposed use of diffusion-based features results in models that are more robust to partial object occlusions for both Transformers and ConvNets on ImageNet with simulated occlusions. We also propose a dataset that encompasses real-world occlusions and demonstrate that our method is more robust to partial object occlusions.
FaithFill: Faithful Inpainting for Object Completion Using a Single Reference Image
Jun 12, 2024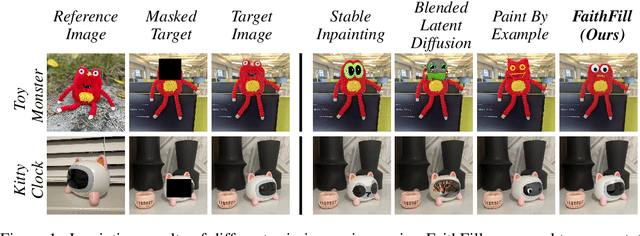
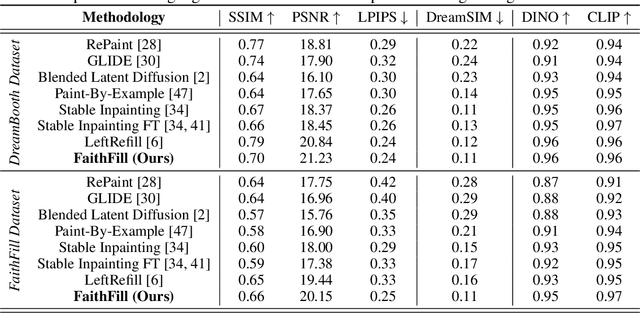
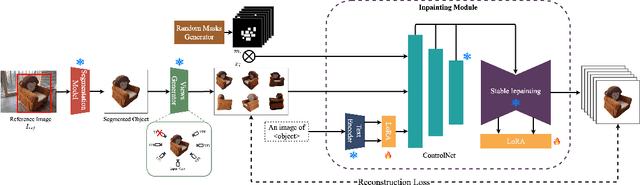
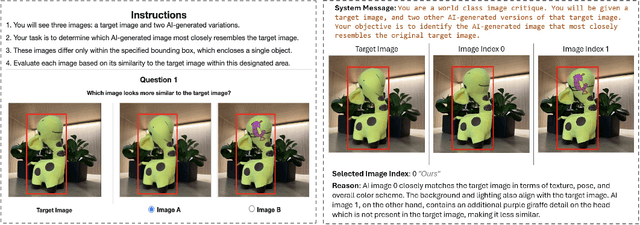
Abstract:We present FaithFill, a diffusion-based inpainting object completion approach for realistic generation of missing object parts. Typically, multiple reference images are needed to achieve such realistic generation, otherwise the generation would not faithfully preserve shape, texture, color, and background. In this work, we propose a pipeline that utilizes only a single input reference image -having varying lighting, background, object pose, and/or viewpoint. The singular reference image is used to generate multiple views of the object to be inpainted. We demonstrate that FaithFill produces faithful generation of the object's missing parts, together with background/scene preservation, from a single reference image. This is demonstrated through standard similarity metrics, human judgement, and GPT evaluation. Our results are presented on the DreamBooth dataset, and a novel proposed dataset.
Lasagna: Layered Score Distillation for Disentangled Object Relighting
Nov 30, 2023



Abstract:Professional artists, photographers, and other visual content creators use object relighting to establish their photo's desired effect. Unfortunately, manual tools that allow relighting have a steep learning curve and are difficult to master. Although generative editing methods now enable some forms of image editing, relighting is still beyond today's capabilities; existing methods struggle to keep other aspects of the image -- colors, shapes, and textures -- consistent after the edit. We propose Lasagna, a method that enables intuitive text-guided relighting control. Lasagna learns a lighting prior by using score distillation sampling to distill the prior of a diffusion model, which has been finetuned on synthetic relighting data. To train Lasagna, we curate a new synthetic dataset ReLiT, which contains 3D object assets re-lit from multiple light source locations. Despite training on synthetic images, quantitative results show that Lasagna relights real-world images while preserving other aspects of the input image, outperforming state-of-the-art text-guided image editing methods. Lasagna enables realistic and controlled results on natural images and digital art pieces and is preferred by humans over other methods in over 91% of cases. Finally, we demonstrate the versatility of our learning objective by extending it to allow colorization, another form of image editing.
Selective Spatio-Temporal Aggregation Based Pose Refinement System: Towards Understanding Human Activities in Real-World Videos
Nov 10, 2020



Abstract:Taking advantage of human pose data for understanding human activities has attracted much attention these days. However, state-of-the-art pose estimators struggle in obtaining high-quality 2D or 3D pose data due to occlusion, truncation and low-resolution in real-world un-annotated videos. Hence, in this work, we propose 1) a Selective Spatio-Temporal Aggregation mechanism, named SST-A, that refines and smooths the keypoint locations extracted by multiple expert pose estimators, 2) an effective weakly-supervised self-training framework which leverages the aggregated poses as pseudo ground-truth instead of handcrafted annotations for real-world pose estimation. Extensive experiments are conducted for evaluating not only the upstream pose refinement but also the downstream action recognition performance on four datasets, Toyota Smarthome, NTU-RGB+D, Charades, and Kinetics-50. We demonstrate that the skeleton data refined by our Pose-Refinement system (SSTA-PRS) is effective at boosting various existing action recognition models, which achieves competitive or state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge