Yujun Shi
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Token-Shuffle: Towards High-Resolution Image Generation with Autoregressive Models
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) models, long dominant in language generation, are increasingly applied to image synthesis but are often considered less competitive than Diffusion-based models. A primary limitation is the substantial number of image tokens required for AR models, which constrains both training and inference efficiency, as well as image resolution. To address this, we present Token-Shuffle, a novel yet simple method that reduces the number of image tokens in Transformer. Our key insight is the dimensional redundancy of visual vocabularies in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), where low-dimensional visual codes from visual encoder are directly mapped to high-dimensional language vocabularies. Leveraging this, we consider two key operations: token-shuffle, which merges spatially local tokens along channel dimension to decrease the input token number, and token-unshuffle, which untangles the inferred tokens after Transformer blocks to restore the spatial arrangement for output. Jointly training with textual prompts, our strategy requires no additional pretrained text-encoder and enables MLLMs to support extremely high-resolution image synthesis in a unified next-token prediction way while maintaining efficient training and inference. For the first time, we push the boundary of AR text-to-image generation to a resolution of 2048x2048 with gratifying generation performance. In GenAI-benchmark, our 2.7B model achieves 0.77 overall score on hard prompts, outperforming AR models LlamaGen by 0.18 and diffusion models LDM by 0.15. Exhaustive large-scale human evaluations also demonstrate our prominent image generation ability in terms of text-alignment, visual flaw, and visual appearance. We hope that Token-Shuffle can serve as a foundational design for efficient high-resolution image generation within MLLMs.
Identity-Preserving Text-to-Video Generation by Frequency Decomposition
Nov 26, 2024
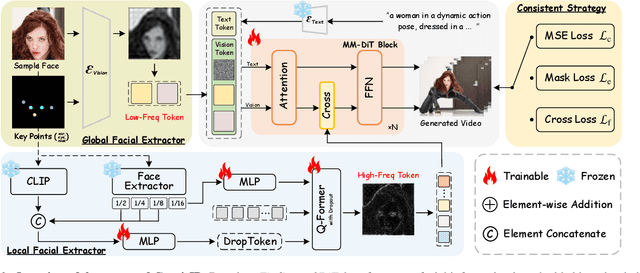
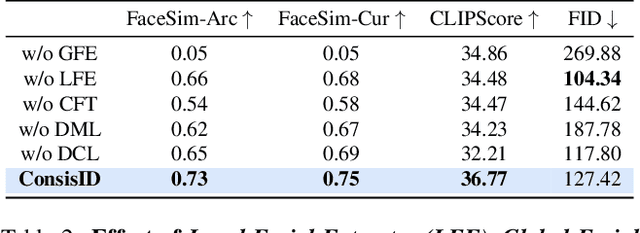
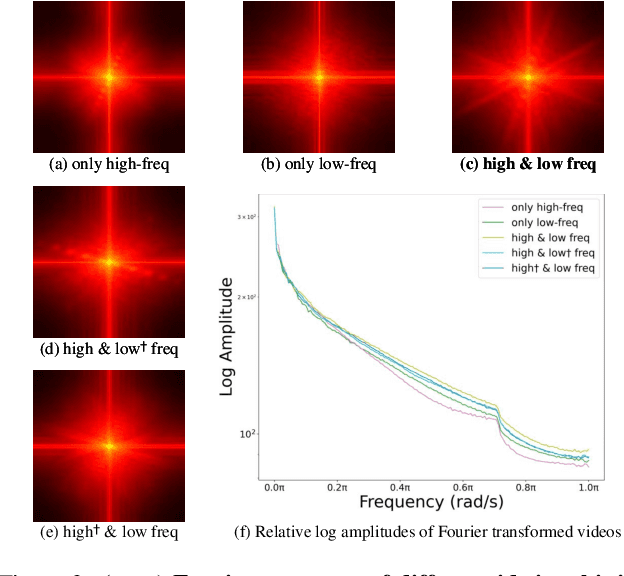
Abstract:Identity-preserving text-to-video (IPT2V) generation aims to create high-fidelity videos with consistent human identity. It is an important task in video generation but remains an open problem for generative models. This paper pushes the technical frontier of IPT2V in two directions that have not been resolved in literature: (1) A tuning-free pipeline without tedious case-by-case finetuning, and (2) A frequency-aware heuristic identity-preserving DiT-based control scheme. We propose ConsisID, a tuning-free DiT-based controllable IPT2V model to keep human identity consistent in the generated video. Inspired by prior findings in frequency analysis of diffusion transformers, it employs identity-control signals in the frequency domain, where facial features can be decomposed into low-frequency global features and high-frequency intrinsic features. First, from a low-frequency perspective, we introduce a global facial extractor, which encodes reference images and facial key points into a latent space, generating features enriched with low-frequency information. These features are then integrated into shallow layers of the network to alleviate training challenges associated with DiT. Second, from a high-frequency perspective, we design a local facial extractor to capture high-frequency details and inject them into transformer blocks, enhancing the model's ability to preserve fine-grained features. We propose a hierarchical training strategy to leverage frequency information for identity preservation, transforming a vanilla pre-trained video generation model into an IPT2V model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our frequency-aware heuristic scheme provides an optimal control solution for DiT-based models. Thanks to this scheme, our ConsisID generates high-quality, identity-preserving videos, making strides towards more effective IPT2V.
ChronoMagic-Bench: A Benchmark for Metamorphic Evaluation of Text-to-Time-lapse Video Generation
Jun 26, 2024



Abstract:We propose a novel text-to-video (T2V) generation benchmark, ChronoMagic-Bench, to evaluate the temporal and metamorphic capabilities of the T2V models (e.g. Sora and Lumiere) in time-lapse video generation. In contrast to existing benchmarks that focus on the visual quality and textual relevance of generated videos, ChronoMagic-Bench focuses on the model's ability to generate time-lapse videos with significant metamorphic amplitude and temporal coherence. The benchmark probes T2V models for their physics, biology, and chemistry capabilities, in a free-form text query. For these purposes, ChronoMagic-Bench introduces 1,649 prompts and real-world videos as references, categorized into four major types of time-lapse videos: biological, human-created, meteorological, and physical phenomena, which are further divided into 75 subcategories. This categorization comprehensively evaluates the model's capacity to handle diverse and complex transformations. To accurately align human preference with the benchmark, we introduce two new automatic metrics, MTScore and CHScore, to evaluate the videos' metamorphic attributes and temporal coherence. MTScore measures the metamorphic amplitude, reflecting the degree of change over time, while CHScore assesses the temporal coherence, ensuring the generated videos maintain logical progression and continuity. Based on the ChronoMagic-Bench, we conduct comprehensive manual evaluations of ten representative T2V models, revealing their strengths and weaknesses across different categories of prompts, and providing a thorough evaluation framework that addresses current gaps in video generation research. Moreover, we create a large-scale ChronoMagic-Pro dataset, containing 460k high-quality pairs of 720p time-lapse videos and detailed captions ensuring high physical pertinence and large metamorphic amplitude.
InstaDrag: Lightning Fast and Accurate Drag-based Image Editing Emerging from Videos
May 22, 2024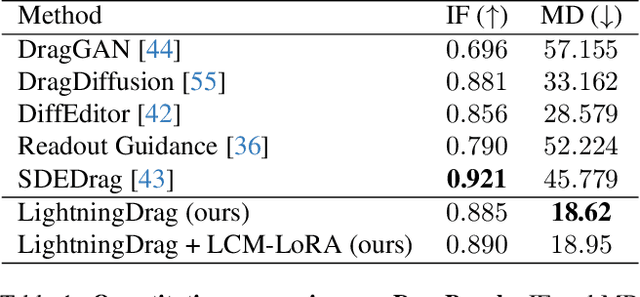


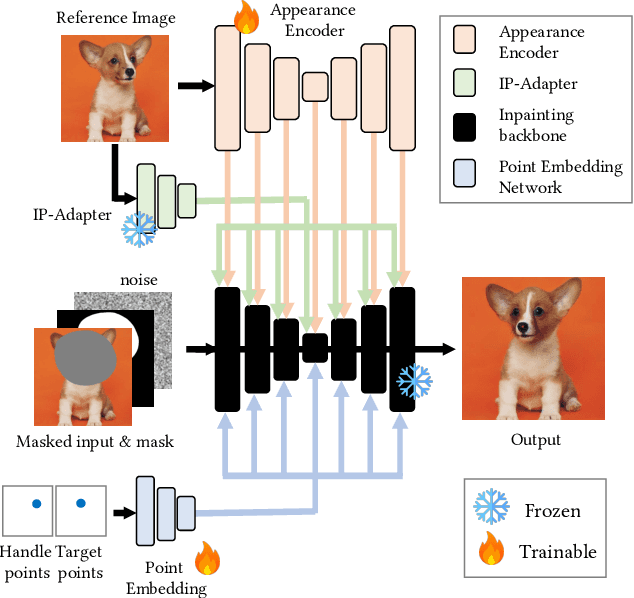
Abstract:Accuracy and speed are critical in image editing tasks. Pan et al. introduced a drag-based image editing framework that achieves pixel-level control using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). A flurry of subsequent studies enhanced this framework's generality by leveraging large-scale diffusion models. However, these methods often suffer from inordinately long processing times (exceeding 1 minute per edit) and low success rates. Addressing these issues head on, we present InstaDrag, a rapid approach enabling high quality drag-based image editing in ~1 second. Unlike most previous methods, we redefine drag-based editing as a conditional generation task, eliminating the need for time-consuming latent optimization or gradient-based guidance during inference. In addition, the design of our pipeline allows us to train our model on large-scale paired video frames, which contain rich motion information such as object translations, changing poses and orientations, zooming in and out, etc. By learning from videos, our approach can significantly outperform previous methods in terms of accuracy and consistency. Despite being trained solely on videos, our model generalizes well to perform local shape deformations not presented in the training data (e.g., lengthening of hair, twisting rainbows, etc.). Extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations on benchmark datasets corroborate the superiority of our approach. The code and model will be released at https://github.com/magic-research/InstaDrag.
MagicTime: Time-lapse Video Generation Models as Metamorphic Simulators
Apr 07, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in Text-to-Video generation (T2V) have achieved remarkable success in synthesizing high-quality general videos from textual descriptions. A largely overlooked problem in T2V is that existing models have not adequately encoded physical knowledge of the real world, thus generated videos tend to have limited motion and poor variations. In this paper, we propose \textbf{MagicTime}, a metamorphic time-lapse video generation model, which learns real-world physics knowledge from time-lapse videos and implements metamorphic generation. First, we design a MagicAdapter scheme to decouple spatial and temporal training, encode more physical knowledge from metamorphic videos, and transform pre-trained T2V models to generate metamorphic videos. Second, we introduce a Dynamic Frames Extraction strategy to adapt to metamorphic time-lapse videos, which have a wider variation range and cover dramatic object metamorphic processes, thus embodying more physical knowledge than general videos. Finally, we introduce a Magic Text-Encoder to improve the understanding of metamorphic video prompts. Furthermore, we create a time-lapse video-text dataset called \textbf{ChronoMagic}, specifically curated to unlock the metamorphic video generation ability. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of MagicTime for generating high-quality and dynamic metamorphic videos, suggesting time-lapse video generation is a promising path toward building metamorphic simulators of the physical world.
Envision3D: One Image to 3D with Anchor Views Interpolation
Mar 13, 2024



Abstract:We present Envision3D, a novel method for efficiently generating high-quality 3D content from a single image. Recent methods that extract 3D content from multi-view images generated by diffusion models show great potential. However, it is still challenging for diffusion models to generate dense multi-view consistent images, which is crucial for the quality of 3D content extraction. To address this issue, we propose a novel cascade diffusion framework, which decomposes the challenging dense views generation task into two tractable stages, namely anchor views generation and anchor views interpolation. In the first stage, we train the image diffusion model to generate global consistent anchor views conditioning on image-normal pairs. Subsequently, leveraging our video diffusion model fine-tuned on consecutive multi-view images, we conduct interpolation on the previous anchor views to generate extra dense views. This framework yields dense, multi-view consistent images, providing comprehensive 3D information. To further enhance the overall generation quality, we introduce a coarse-to-fine sampling strategy for the reconstruction algorithm to robustly extract textured meshes from the generated dense images. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method is capable of generating high-quality 3D content in terms of texture and geometry, surpassing previous image-to-3D baseline methods.
DragDiffusion: Harnessing Diffusion Models for Interactive Point-based Image Editing
Jul 09, 2023



Abstract:Precise and controllable image editing is a challenging task that has attracted significant attention. Recently, DragGAN enables an interactive point-based image editing framework and achieves impressive editing results with pixel-level precision. However, since this method is based on generative adversarial networks (GAN), its generality is upper-bounded by the capacity of the pre-trained GAN models. In this work, we extend such an editing framework to diffusion models and propose DragDiffusion. By leveraging large-scale pretrained diffusion models, we greatly improve the applicability of interactive point-based editing in real world scenarios. While most existing diffusion-based image editing methods work on text embeddings, DragDiffusion optimizes the diffusion latent to achieve precise spatial control. Although diffusion models generate images in an iterative manner, we empirically show that optimizing diffusion latent at one single step suffices to generate coherent results, enabling DragDiffusion to complete high-quality editing efficiently. Extensive experiments across a wide range of challenging cases (e.g., multi-objects, diverse object categories, various styles, etc.) demonstrate the versatility and generality of DragDiffusion. Code: https://github.com/Yujun-Shi/DragDiffusion.
Mix-of-Show: Decentralized Low-Rank Adaptation for Multi-Concept Customization of Diffusion Models
May 29, 2023Abstract:Public large-scale text-to-image diffusion models, such as Stable Diffusion, have gained significant attention from the community. These models can be easily customized for new concepts using low-rank adaptations (LoRAs). However, the utilization of multiple concept LoRAs to jointly support multiple customized concepts presents a challenge. We refer to this scenario as decentralized multi-concept customization, which involves single-client concept tuning and center-node concept fusion. In this paper, we propose a new framework called Mix-of-Show that addresses the challenges of decentralized multi-concept customization, including concept conflicts resulting from existing single-client LoRA tuning and identity loss during model fusion. Mix-of-Show adopts an embedding-decomposed LoRA (ED-LoRA) for single-client tuning and gradient fusion for the center node to preserve the in-domain essence of single concepts and support theoretically limitless concept fusion. Additionally, we introduce regionally controllable sampling, which extends spatially controllable sampling (e.g., ControlNet and T2I-Adaptor) to address attribute binding and missing object problems in multi-concept sampling. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Mix-of-Show is capable of composing multiple customized concepts with high fidelity, including characters, objects, and scenes.
Learning with Fantasy: Semantic-Aware Virtual Contrastive Constraint for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Apr 02, 2023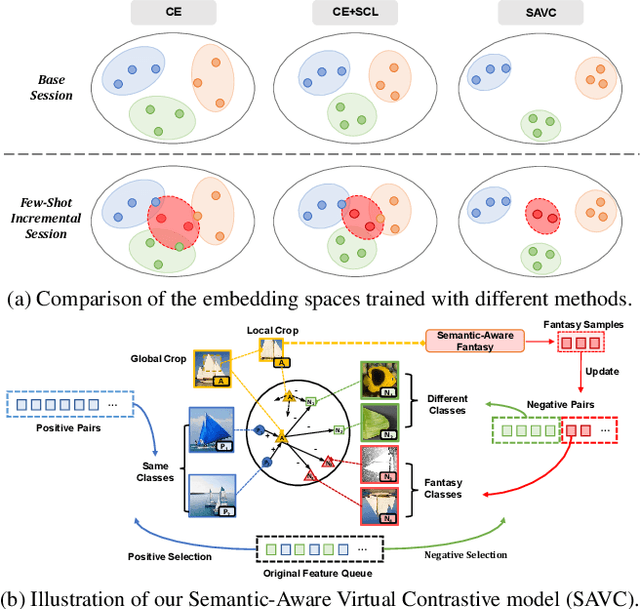
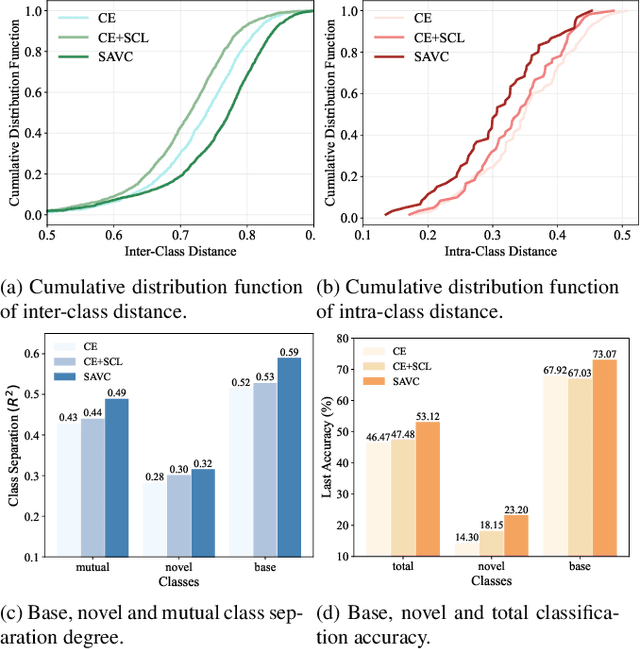
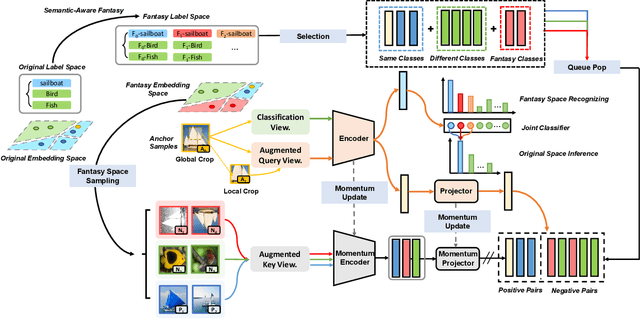
Abstract:Few-shot class-incremental learning (FSCIL) aims at learning to classify new classes continually from limited samples without forgetting the old classes. The mainstream framework tackling FSCIL is first to adopt the cross-entropy (CE) loss for training at the base session, then freeze the feature extractor to adapt to new classes. However, in this work, we find that the CE loss is not ideal for the base session training as it suffers poor class separation in terms of representations, which further degrades generalization to novel classes. One tempting method to mitigate this problem is to apply an additional naive supervised contrastive learning (SCL) in the base session. Unfortunately, we find that although SCL can create a slightly better representation separation among different base classes, it still struggles to separate base classes and new classes. Inspired by the observations made, we propose Semantic-Aware Virtual Contrastive model (SAVC), a novel method that facilitates separation between new classes and base classes by introducing virtual classes to SCL. These virtual classes, which are generated via pre-defined transformations, not only act as placeholders for unseen classes in the representation space, but also provide diverse semantic information. By learning to recognize and contrast in the fantasy space fostered by virtual classes, our SAVC significantly boosts base class separation and novel class generalization, achieving new state-of-the-art performance on the three widely-used FSCIL benchmark datasets. Code is available at: https://github.com/zysong0113/SAVC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge