Xu Ma
Stephen
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Segmentation-Driven Monocular Shape from Polarization based on Physical Model
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Monocular shape-from-polarization (SfP) leverages the intrinsic relationship between light polarization properties and surface geometry to recover surface normals from single-view polarized images, providing a compact and robust approach for three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction. Despite its potential, existing monocular SfP methods suffer from azimuth angle ambiguity, an inherent limitation of polarization analysis, that severely compromises reconstruction accuracy and stability. This paper introduces a novel segmentation-driven monocular SfP (SMSfP) framework that reformulates global shape recovery into a set of local reconstructions over adaptively segmented convex sub-regions. Specifically, a polarization-aided adaptive region growing (PARG) segmentation strategy is proposed to decompose the global convexity assumption into locally convex regions, effectively suppressing azimuth ambiguities and preserving surface continuity. Furthermore, a multi-scale fusion convexity prior (MFCP) constraint is developed to ensure local surface consistency and enhance the recovery of fine textural and structural details. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets validate the proposed approach, showing significant improvements in disambiguation accuracy and geometric fidelity compared with existing physics-based monocular SfP techniques.
WiFi-based Global Localization in Large-Scale Environments Leveraging Structural Priors from osmAG
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:Global localization is essential for autonomous robotics, especially in indoor environments where the GPS signal is denied. We propose a novel WiFi-based localization framework that leverages ubiquitous wireless infrastructure and the OpenStreetMap Area Graph (osmAG) for large-scale indoor environments. Our approach integrates signal propagation modeling with osmAG's geometric and topological priors. In the offline phase, an iterative optimization algorithm localizes WiFi Access Points (APs) by modeling wall attenuation, achieving a mean localization error of 3.79 m (35.3\% improvement over trilateration). In the online phase, real-time robot localization uses the augmented osmAG map, yielding a mean error of 3.12 m in fingerprinted areas (8.77\% improvement over KNN fingerprinting) and 3.83 m in non-fingerprinted areas (81.05\% improvement). Comparison with a fingerprint-based method shows that our approach is much more space efficient and achieves superior localization accuracy, especially for positions where no fingerprint data are available. Validated across a complex 11,025 &m^2& multi-floor environment, this framework offers a scalable, cost-effective solution for indoor robotic localization, solving the kidnapped robot problem. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/XuMa369/osmag-wifi-localization.
Token-Shuffle: Towards High-Resolution Image Generation with Autoregressive Models
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) models, long dominant in language generation, are increasingly applied to image synthesis but are often considered less competitive than Diffusion-based models. A primary limitation is the substantial number of image tokens required for AR models, which constrains both training and inference efficiency, as well as image resolution. To address this, we present Token-Shuffle, a novel yet simple method that reduces the number of image tokens in Transformer. Our key insight is the dimensional redundancy of visual vocabularies in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), where low-dimensional visual codes from visual encoder are directly mapped to high-dimensional language vocabularies. Leveraging this, we consider two key operations: token-shuffle, which merges spatially local tokens along channel dimension to decrease the input token number, and token-unshuffle, which untangles the inferred tokens after Transformer blocks to restore the spatial arrangement for output. Jointly training with textual prompts, our strategy requires no additional pretrained text-encoder and enables MLLMs to support extremely high-resolution image synthesis in a unified next-token prediction way while maintaining efficient training and inference. For the first time, we push the boundary of AR text-to-image generation to a resolution of 2048x2048 with gratifying generation performance. In GenAI-benchmark, our 2.7B model achieves 0.77 overall score on hard prompts, outperforming AR models LlamaGen by 0.18 and diffusion models LDM by 0.15. Exhaustive large-scale human evaluations also demonstrate our prominent image generation ability in terms of text-alignment, visual flaw, and visual appearance. We hope that Token-Shuffle can serve as a foundational design for efficient high-resolution image generation within MLLMs.
GmNet: Revisiting Gating Mechanisms From A Frequency View
Mar 28, 2025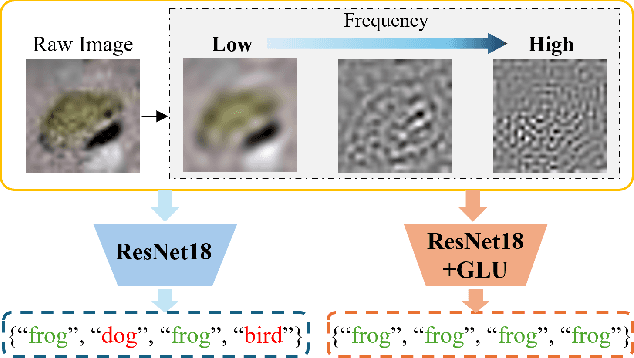
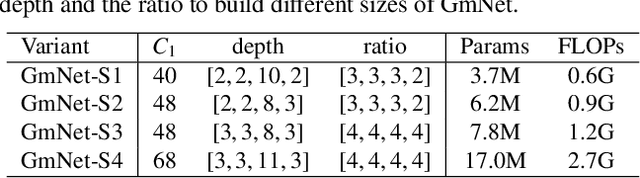
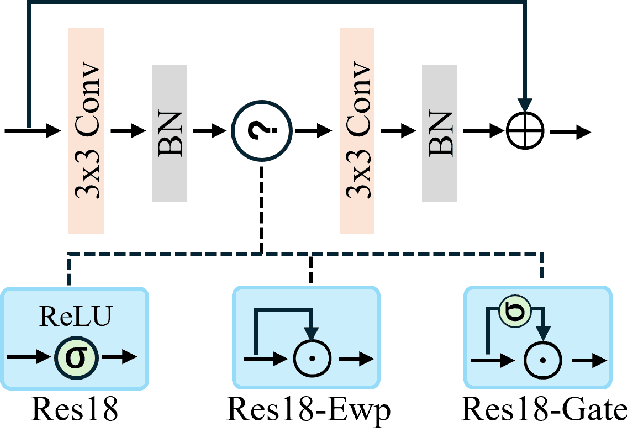
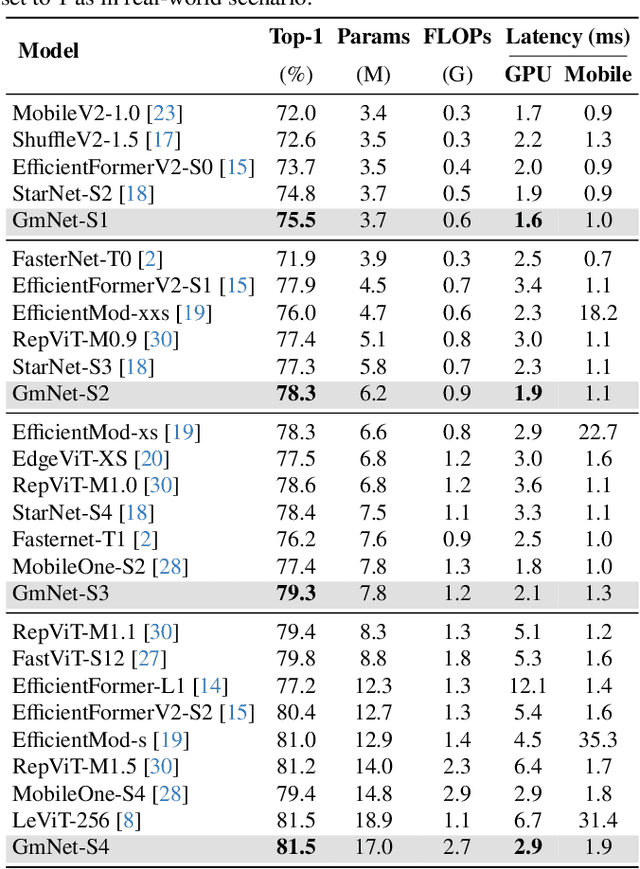
Abstract:Gating mechanisms have emerged as an effective strategy integrated into model designs beyond recurrent neural networks for addressing long-range dependency problems. In a broad understanding, it provides adaptive control over the information flow while maintaining computational efficiency. However, there is a lack of theoretical analysis on how the gating mechanism works in neural networks. In this paper, inspired by the {convolution theorem}, we systematically explore the effect of gating mechanisms on the training dynamics of neural networks from a frequency perspective. We investigate the interact between the element-wise product and activation functions in managing the responses to different frequency components. Leveraging these insights, we propose a Gating Mechanism Network (GmNet), a lightweight model designed to efficiently utilize the information of various frequency components. It minimizes the low-frequency bias present in existing lightweight models. GmNet achieves impressive performance in terms of both effectiveness and efficiency in the image classification task.
PARF-Net: integrating pixel-wise adaptive receptive fields into hybrid Transformer-CNN network for medical image segmentation
Jan 06, 2025



Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) excel in local feature extraction while Transformers are superior in processing global semantic information. By leveraging the strengths of both, hybrid Transformer-CNN networks have become the major architectures in medical image segmentation tasks. However, existing hybrid methods still suffer deficient learning of local semantic features due to the fixed receptive fields of convolutions, and also fall short in effectively integrating local and long-range dependencies. To address these issues, we develop a new method PARF-Net to integrate convolutions of Pixel-wise Adaptive Receptive Fields (Conv-PARF) into hybrid Network for medical image segmentation. The Conv-PARF is introduced to cope with inter-pixel semantic differences and dynamically adjust convolutional receptive fields for each pixel, thus providing distinguishable features to disentangle the lesions with varying shapes and scales from the background. The features derived from the Conv-PARF layers are further processed using hybrid Transformer-CNN blocks under a lightweight manner, to effectively capture local and long-range dependencies, thus boosting the segmentation performance. By assessing PARF-Net on four widely used medical image datasets including MoNuSeg, GlaS, DSB2018 and multi-organ Synapse, we showcase the advantages of our method over the state-of-the-arts. For instance, PARF-Net achieves 84.27% mean Dice on the Synapse dataset, surpassing existing methods by a large margin.
A Backdoor Attack Scheme with Invisible Triggers Based on Model Architecture Modification
Dec 22, 2024Abstract:Machine learning systems are vulnerable to backdoor attacks, where attackers manipulate model behavior through data tampering or architectural modifications. Traditional backdoor attacks involve injecting malicious samples with specific triggers into the training data, causing the model to produce targeted incorrect outputs in the presence of the corresponding triggers. More sophisticated attacks modify the model's architecture directly, embedding backdoors that are harder to detect as they evade traditional data-based detection methods. However, the drawback of the architectural modification based backdoor attacks is that the trigger must be visible in order to activate the backdoor. To further strengthen the invisibility of the backdoor attacks, a novel backdoor attack method is presented in the paper. To be more specific, this method embeds the backdoor within the model's architecture and has the capability to generate inconspicuous and stealthy triggers. The attack is implemented by modifying pre-trained models, which are then redistributed, thereby posing a potential threat to unsuspecting users. Comprehensive experiments conducted on standard computer vision benchmarks validate the effectiveness of this attack and highlight the stealthiness of its triggers, which remain undetectable through both manual visual inspection and advanced detection tools.
Slicing Vision Transformer for Flexible Inference
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViT) is known for its scalability. In this work, we target to scale down a ViT to fit in an environment with dynamic-changing resource constraints. We observe that smaller ViTs are intrinsically the sub-networks of a larger ViT with different widths. Thus, we propose a general framework, named Scala, to enable a single network to represent multiple smaller ViTs with flexible inference capability, which aligns with the inherent design of ViT to vary from widths. Concretely, Scala activates several subnets during training, introduces Isolated Activation to disentangle the smallest sub-network from other subnets, and leverages Scale Coordination to ensure each sub-network receives simplified, steady, and accurate learning objectives. Comprehensive empirical validations on different tasks demonstrate that with only one-shot training, Scala learns slimmable representation without modifying the original ViT structure and matches the performance of Separate Training. Compared with the prior art, Scala achieves an average improvement of 1.6% on ImageNet-1K with fewer parameters.
Accessing Vision Foundation Models at ImageNet-level Costs
Jul 15, 2024



Abstract:Vision foundation models are renowned for their generalization ability due to massive training data. Nevertheless, they demand tremendous training resources, and the training data is often inaccessible, e.g., CLIP, DINOv2, posing great challenges to developing derivatives that could advance research in this field. In this work, we offer a very simple and general solution, named Proteus, to distill foundation models into smaller equivalents on ImageNet-1K without access to the original training data. Specifically, we remove the designs from conventional knowledge distillation settings that result in dataset bias and present three levels of training objectives, i.e., token, patch, and feature, to maximize the efficacy of knowledge transfer. In this manner, Proteus is trained at ImageNet-level costs with surprising ability, facilitating the accessibility of training foundation models for the broader research community. Leveraging DINOv2-g/14 as the teacher, Proteus-L/14 matches the performance of the Oracle method DINOv2-L/14 (142M training data) across 15 benchmarks and outperforms other vision foundation models including CLIP-L/14 (400M), OpenCLIP-L/14 (400M/2B) and SynCLR-L/14 (600M).
Efficient Modulation for Vision Networks
Mar 29, 2024Abstract:In this work, we present efficient modulation, a novel design for efficient vision networks. We revisit the modulation mechanism, which operates input through convolutional context modeling and feature projection layers, and fuses features via element-wise multiplication and an MLP block. We demonstrate that the modulation mechanism is particularly well suited for efficient networks and further tailor the modulation design by proposing the efficient modulation (EfficientMod) block, which is considered the essential building block for our networks. Benefiting from the prominent representational ability of modulation mechanism and the proposed efficient design, our network can accomplish better trade-offs between accuracy and efficiency and set new state-of-the-art performance in the zoo of efficient networks. When integrating EfficientMod with the vanilla self-attention block, we obtain the hybrid architecture which further improves the performance without loss of efficiency. We carry out comprehensive experiments to verify EfficientMod's performance. With fewer parameters, our EfficientMod-s performs 0.6 top-1 accuracy better than EfficientFormerV2-s2 and is 25% faster on GPU, and 2.9 better than MobileViTv2-1.0 at the same GPU latency. Additionally, our method presents a notable improvement in downstream tasks, outperforming EfficientFormerV2-s by 3.6 mIoU on the ADE20K benchmark. Code and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/ma-xu/EfficientMod.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge