Yuhao Chen
EvoPrune: Early-Stage Visual Token Pruning for Efficient MLLMs
Mar 04, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have shown strong performance in vision-language tasks, but their inference efficiency is severely limited by the exponential growth of visual tokens in complex scenarios such as high-resolution images and videos. Existing visual token pruning methods mainly operate after visual encoding, overlooking the substantial computational cost incurred during the encoding stage. To address this issue, we propose EvoPrune, an early-stage visual token pruning method for MLLMs that performs pruning directly during visual encoding. Specifically, EvoPrune employs a layer-wise pruning strategy guided by token similarity, diversity, and attention-based importance to retain the most informative visual tokens at selected encoding layers. Extensive experiments on image and video benchmarks validate the effectiveness of EvoPrune. In particular, on the VideoMME dataset, EvoPrune achieves 2$\times$ inference speedup with less than 1% performance degradation, demonstrating its potential for latency-sensitive MLLM deployment.
Implicit-Scale 3D Reconstruction for Multi-Food Volume Estimation from Monocular Images
Feb 13, 2026Abstract:We present Implicit-Scale 3D Reconstruction from Monocular Multi-Food Images, a benchmark dataset designed to advance geometry-based food portion estimation in realistic dining scenarios. Existing dietary assessment methods largely rely on single-image analysis or appearance-based inference, including recent vision-language models, which lack explicit geometric reasoning and are sensitive to scale ambiguity. This benchmark reframes food portion estimation as an implicit-scale 3D reconstruction problem under monocular observations. To reflect real-world conditions, explicit physical references and metric annotations are removed; instead, contextual objects such as plates and utensils are provided, requiring algorithms to infer scale from implicit cues and prior knowledge. The dataset emphasizes multi-food scenes with diverse object geometries, frequent occlusions, and complex spatial arrangements. The benchmark was adopted as a challenge at the MetaFood 2025 Workshop, where multiple teams proposed reconstruction-based solutions. Experimental results show that while strong vision--language baselines achieve competitive performance, geometry-based reconstruction methods provide both improved accuracy and greater robustness, with the top-performing approach achieving 0.21 MAPE in volume estimation and 5.7 L1 Chamfer Distance in geometric accuracy.
RADAR: Benchmarking Vision-Language-Action Generalization via Real-World Dynamics, Spatial-Physical Intelligence, and Autonomous Evaluation
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:VLA models have achieved remarkable progress in embodied intelligence; however, their evaluation remains largely confined to simulations or highly constrained real-world settings. This mismatch creates a substantial reality gap, where strong benchmark performance often masks poor generalization in diverse physical environments. We identify three systemic shortcomings in current benchmarking practices that hinder fair and reliable model comparison. (1) Existing benchmarks fail to model real-world dynamics, overlooking critical factors such as dynamic object configurations, robot initial states, lighting changes, and sensor noise. (2) Current protocols neglect spatial--physical intelligence, reducing evaluation to rote manipulation tasks that do not probe geometric reasoning. (3) The field lacks scalable fully autonomous evaluation, instead relying on simplistic 2D metrics that miss 3D spatial structure or on human-in-the-loop systems that are costly, biased, and unscalable. To address these limitations, we introduce RADAR (Real-world Autonomous Dynamics And Reasoning), a benchmark designed to systematically evaluate VLA generalization under realistic conditions. RADAR integrates three core components: (1) a principled suite of physical dynamics; (2) dedicated tasks that explicitly test spatial reasoning and physical understanding; and (3) a fully autonomous evaluation pipeline based on 3D metrics, eliminating the need for human supervision. We apply RADAR to audit multiple state-of-the-art VLA models and uncover severe fragility beneath their apparent competence. Performance drops precipitously under modest physical dynamics, with the expectation of 3D IoU declining from 0.261 to 0.068 under sensor noise. Moreover, models exhibit limited spatial reasoning capability. These findings position RADAR as a necessary bench toward reliable and generalizable real-world evaluation of VLA models.
Training-Free Text-to-Image Compositional Food Generation via Prompt Grafting
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Real-world meal images often contain multiple food items, making reliable compositional food image generation important for applications such as image-based dietary assessment, where multi-food data augmentation is needed, and recipe visualization. However, modern text-to-image diffusion models struggle to generate accurate multi-food images due to object entanglement, where adjacent foods (e.g., rice and soup) fuse together because many foods do not have clear boundaries. To address this challenge, we introduce Prompt Grafting (PG), a training-free framework that combines explicit spatial cues in text with implicit layout guidance during sampling. PG runs a two-stage process where a layout prompt first establishes distinct regions and the target prompt is grafted once layout formation stabilizes. The framework enables food entanglement control: users can specify which food items should remain separated or be intentionally mixed by editing the arrangement of layouts. Across two food datasets, our method significantly improves the presence of target objects and provides qualitative evidence of controllable separation.
Bridging the Discrete-Continuous Gap: Unified Multimodal Generation via Coupled Manifold Discrete Absorbing Diffusion
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:The bifurcation of generative modeling into autoregressive approaches for discrete data (text) and diffusion approaches for continuous data (images) hinders the development of truly unified multimodal systems. While Masked Language Models (MLMs) offer efficient bidirectional context, they traditionally lack the generative fidelity of autoregressive models and the semantic continuity of diffusion models. Furthermore, extending masked generation to multimodal settings introduces severe alignment challenges and training instability. In this work, we propose \textbf{CoM-DAD} (\textbf{Co}upled \textbf{M}anifold \textbf{D}iscrete \textbf{A}bsorbing \textbf{D}iffusion), a novel probabilistic framework that reformulates multimodal generation as a hierarchical dual-process. CoM-DAD decouples high-level semantic planning from low-level token synthesis. First, we model the semantic manifold via a continuous latent diffusion process; second, we treat token generation as a discrete absorbing diffusion process, regulated by a \textbf{Variable-Rate Noise Schedule}, conditioned on these evolving semantic priors. Crucially, we introduce a \textbf{Stochastic Mixed-Modal Transport} strategy that aligns disparate modalities without requiring heavy contrastive dual-encoders. Our method demonstrates superior stability over standard masked modeling, establishing a new paradigm for scalable, unified text-image generation.
Stable Language Guidance for Vision-Language-Action Models
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have demonstrated impressive capabilities in generalized robotic control; however, they remain notoriously brittle to linguistic perturbations. We identify a critical ``modality collapse'' phenomenon where strong visual priors overwhelm sparse linguistic signals, causing agents to overfit to specific instruction phrasings while ignoring the underlying semantic intent. To address this, we propose \textbf{Residual Semantic Steering (RSS)}, a probabilistic framework that disentangles physical affordance from semantic execution. RSS introduces two theoretical innovations: (1) \textbf{Monte Carlo Syntactic Integration}, which approximates the true semantic posterior via dense, LLM-driven distributional expansion, and (2) \textbf{Residual Affordance Steering}, a dual-stream decoding mechanism that explicitly isolates the causal influence of language by subtracting the visual affordance prior. Theoretical analysis suggests that RSS effectively maximizes the mutual information between action and intent while suppressing visual distractors. Empirical results across diverse manipulation benchmarks demonstrate that RSS achieves state-of-the-art robustness, maintaining performance even under adversarial linguistic perturbations.
Specific Multi-emitter Identification: Theoretical Limits and Low-complexity Design
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Specific emitter identification (SEI) distinguishes emitters by utilizing hardware-induced signal imperfections. However, conventional SEI techniques are primarily designed for single-emitter scenarios. This poses a fundamental limitation in distributed wireless networks, where simultaneous transmissions from multiple emitters result in overlapping signals that conventional single-emitter identification methods cannot effectively handle. To overcome this limitation, we present a specific multi-emitter identification (SMEI) framework via multi-label learning, treating identification as a problem of directly decoding emitter states from overlapping signals. Theoretically, we establish performance bounds using Fano's inequality. Methodologically, the multi-label formulation reduces output dimensionality from exponential to linear scale, thereby substantially decreasing computational complexity. Additionally, we propose an improved SMEI (I-SMEI), which incorporates multi-head attention to effectively capture features in correlated signal combinations. Experimental results demonstrate that SMEI achieves high identification accuracy with a linear computational complexity. Furthermore, the proposed I-SMEI scheme significantly improves identification accuracy across various overlapping scenarios compared to the proposed SMEI and other advanced methods.
Avatar4D: Synthesizing Domain-Specific 4D Humans for Real-World Pose Estimation
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:We present Avatar4D, a real-world transferable pipeline for generating customizable synthetic human motion datasets tailored to domain-specific applications. Unlike prior works, which focus on general, everyday motions and offer limited flexibility, our approach provides fine-grained control over body pose, appearance, camera viewpoint, and environmental context, without requiring any manual annotations. To validate the impact of Avatar4D, we focus on sports, where domain-specific human actions and movement patterns pose unique challenges for motion understanding. In this setting, we introduce Syn2Sport, a large-scale synthetic dataset spanning sports, including baseball and ice hockey. Avatar4D features high-fidelity 4D (3D geometry over time) human motion sequences with varying player appearances rendered in diverse environments. We benchmark several state-of-the-art pose estimation models on Syn2Sport and demonstrate their effectiveness for supervised learning, zero-shot transfer to real-world data, and generalization across sports. Furthermore, we evaluate how closely the generated synthetic data aligns with real-world datasets in feature space. Our results highlight the potential of such systems to generate scalable, controllable, and transferable human datasets for diverse domain-specific tasks without relying on domain-specific real data.
Composite Classifier-Free Guidance for Multi-Modal Conditioning in Wind Dynamics Super-Resolution
Dec 13, 2025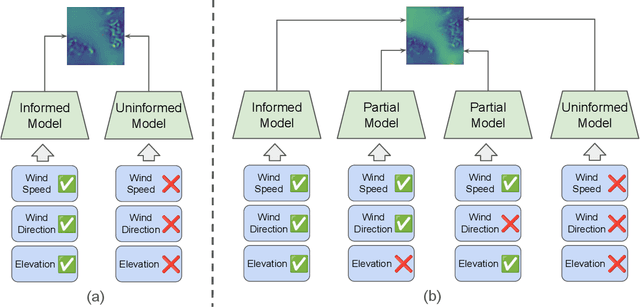
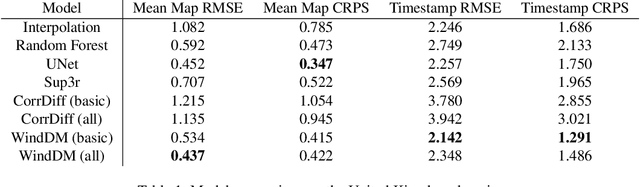
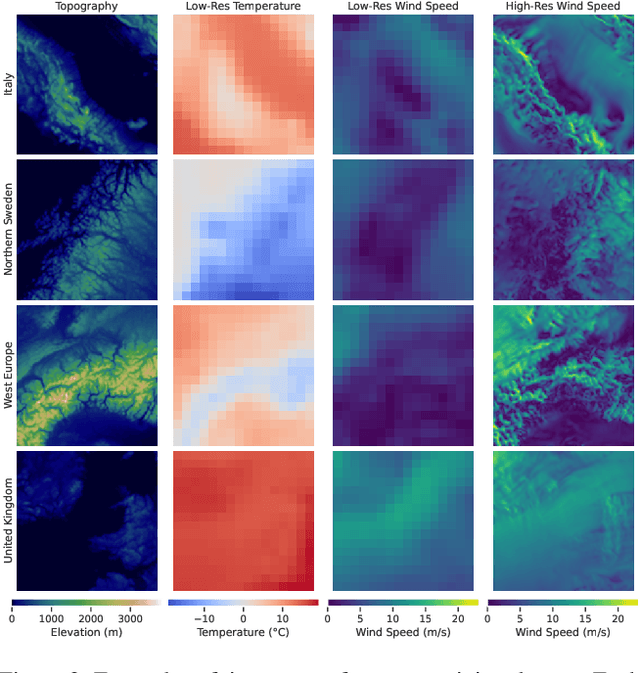
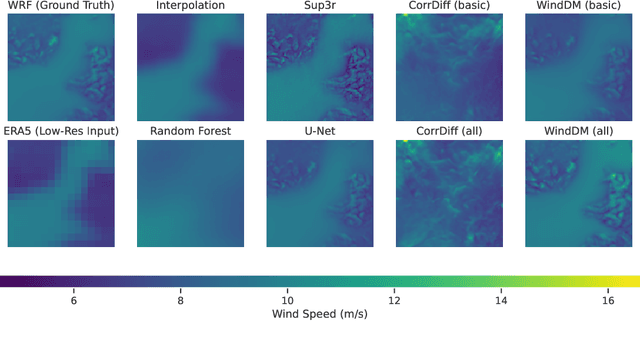
Abstract:Various weather modelling problems (e.g., weather forecasting, optimizing turbine placements, etc.) require ample access to high-resolution, highly accurate wind data. Acquiring such high-resolution wind data, however, remains a challenging and expensive endeavour. Traditional reconstruction approaches are typically either cost-effective or accurate, but not both. Deep learning methods, including diffusion models, have been proposed to resolve this trade-off by leveraging advances in natural image super-resolution. Wind data, however, is distinct from natural images, and wind super-resolvers often use upwards of 10 input channels, significantly more than the usual 3-channel RGB inputs in natural images. To better leverage a large number of conditioning variables in diffusion models, we present a generalization of classifier-free guidance (CFG) to multiple conditioning inputs. Our novel composite classifier-free guidance (CCFG) can be dropped into any pre-trained diffusion model trained with standard CFG dropout. We demonstrate that CCFG outputs are higher-fidelity than those from CFG on wind super-resolution tasks. We present WindDM, a diffusion model trained for industrial-scale wind dynamics reconstruction and leveraging CCFG. WindDM achieves state-of-the-art reconstruction quality among deep learning models and costs up to $1000\times$ less than classical methods.
Food Image Generation on Multi-Noun Categories
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Generating realistic food images for categories with multiple nouns is surprisingly challenging. For instance, the prompt "egg noodle" may result in images that incorrectly contain both eggs and noodles as separate entities. Multi-noun food categories are common in real-world datasets and account for a large portion of entries in benchmarks such as UEC-256. These compound names often cause generative models to misinterpret the semantics, producing unintended ingredients or objects. This is due to insufficient multi-noun category related knowledge in the text encoder and misinterpretation of multi-noun relationships, leading to incorrect spatial layouts. To overcome these challenges, we propose FoCULR (Food Category Understanding and Layout Refinement) which incorporates food domain knowledge and introduces core concepts early in the generation process. Experimental results demonstrate that the integration of these techniques improves image generation performance in the food domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge