Xiyu Wang
ICH-Qwen: A Large Language Model Towards Chinese Intangible Cultural Heritage
May 28, 2025Abstract:The intangible cultural heritage (ICH) of China, a cultural asset transmitted across generations by various ethnic groups, serves as a significant testament to the evolution of human civilization and holds irreplaceable value for the preservation of historical lineage and the enhancement of cultural self-confidence. However, the rapid pace of modernization poses formidable challenges to ICH, including threats damage, disappearance and discontinuity of inheritance. China has the highest number of items on the UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage List, which is indicative of the nation's abundant cultural resources and emphasises the pressing need for ICH preservation. In recent years, the rapid advancements in large language modelling have provided a novel technological approach for the preservation and dissemination of ICH. This study utilises a substantial corpus of open-source Chinese ICH data to develop a large language model, ICH-Qwen, for the ICH domain. The model employs natural language understanding and knowledge reasoning capabilities of large language models, augmented with synthetic data and fine-tuning techniques. The experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of ICH-Qwen in executing tasks specific to the ICH domain. It is anticipated that the model will provide intelligent solutions for the protection, inheritance and dissemination of intangible cultural heritage, as well as new theoretical and practical references for the sustainable development of intangible cultural heritage. Furthermore, it is expected that the study will open up new paths for digital humanities research.
Multi-User Beamforming with Deep Reinforcement Learning in Sensing-Aided Communication
May 09, 2025Abstract:Mobile users are prone to experience beam failure due to beam drifting in millimeter wave (mmWave) communications. Sensing can help alleviate beam drifting with timely beam changes and low overhead since it does not need user feedback. This work studies the problem of optimizing sensing-aided communication by dynamically managing beams allocated to mobile users. A multi-beam scheme is introduced, which allocates multiple beams to the users that need an update on the angle of departure (AoD) estimates and a single beam to the users that have satisfied AoD estimation precision. A deep reinforcement learning (DRL) assisted method is developed to optimize the beam allocation policy, relying only upon the sensing echoes. For comparison, a heuristic AoD-based method using approximated Cram\'er-Rao lower bound (CRLB) for allocation is also presented. Both methods require neither user feedback nor prior state evolution information. Results show that the DRL-assisted method achieves a considerable gain in throughput than the conventional beam sweeping method and the AoD-based method, and it is robust to different user speeds.
Towards Robust and Reliable Concept Representations: Reliability-Enhanced Concept Embedding Model
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs) aim to enhance interpretability by predicting human-understandable concepts as intermediates for decision-making. However, these models often face challenges in ensuring reliable concept representations, which can propagate to downstream tasks and undermine robustness, especially under distribution shifts. Two inherent issues contribute to concept unreliability: sensitivity to concept-irrelevant features (e.g., background variations) and lack of semantic consistency for the same concept across different samples. To address these limitations, we propose the Reliability-Enhanced Concept Embedding Model (RECEM), which introduces a two-fold strategy: Concept-Level Disentanglement to separate irrelevant features from concept-relevant information and a Concept Mixup mechanism to ensure semantic alignment across samples. These mechanisms work together to improve concept reliability, enabling the model to focus on meaningful object attributes and generate faithful concept representations. Experimental results demonstrate that RECEM consistently outperforms existing baselines across multiple datasets, showing superior performance under background and domain shifts. These findings highlight the effectiveness of disentanglement and alignment strategies in enhancing both reliability and robustness in CBMs.
SoftShadow: Leveraging Penumbra-Aware Soft Masks for Shadow Removal
Sep 11, 2024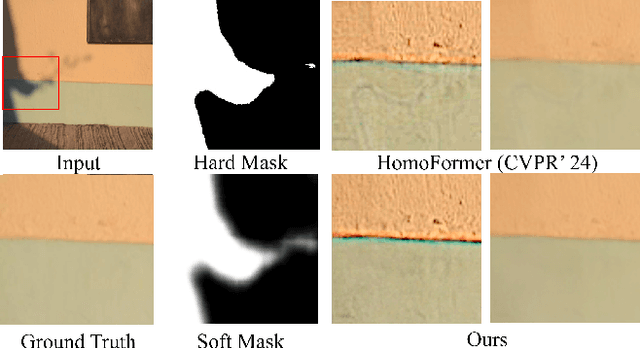
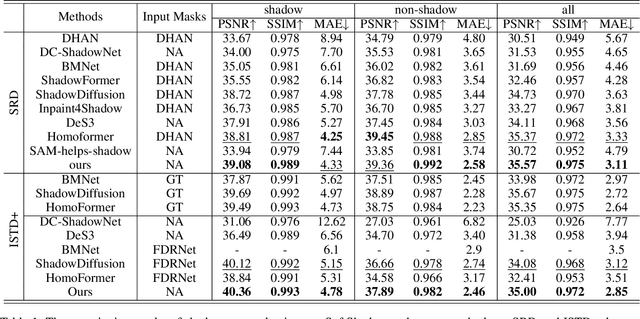
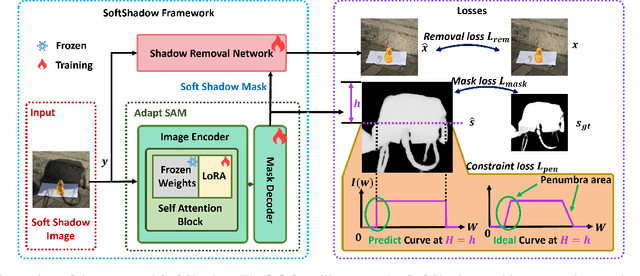
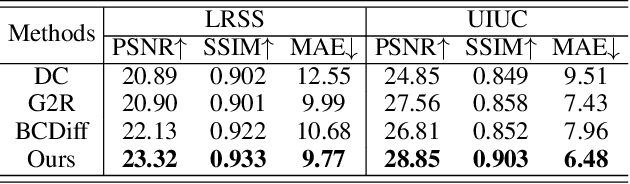
Abstract:Recent advancements in deep learning have yielded promising results for the image shadow removal task. However, most existing methods rely on binary pre-generated shadow masks. The binary nature of such masks could potentially lead to artifacts near the boundary between shadow and non-shadow areas. In view of this, inspired by the physical model of shadow formation, we introduce novel soft shadow masks specifically designed for shadow removal. To achieve such soft masks, we propose a \textit{SoftShadow} framework by leveraging the prior knowledge of pretrained SAM and integrating physical constraints. Specifically, we jointly tune the SAM and the subsequent shadow removal network using penumbra formation constraint loss and shadow removal loss. This framework enables accurate predictions of penumbra (partially shaded regions) and umbra (fully shaded regions) areas while simultaneously facilitating end-to-end shadow removal. Through extensive experiments on popular datasets, we found that our SoftShadow framework, which generates soft masks, can better restore boundary artifacts, achieve state-of-the-art performance, and demonstrate superior generalizability.
Evolving Storytelling: Benchmarks and Methods for New Character Customization with Diffusion Models
May 20, 2024Abstract:Diffusion-based models for story visualization have shown promise in generating content-coherent images for storytelling tasks. However, how to effectively integrate new characters into existing narratives while maintaining character consistency remains an open problem, particularly with limited data. Two major limitations hinder the progress: (1) the absence of a suitable benchmark due to potential character leakage and inconsistent text labeling, and (2) the challenge of distinguishing between new and old characters, leading to ambiguous results. To address these challenges, we introduce the NewEpisode benchmark, comprising refined datasets designed to evaluate generative models' adaptability in generating new stories with fresh characters using just a single example story. The refined dataset involves refined text prompts and eliminates character leakage. Additionally, to mitigate the character confusion of generated results, we propose EpicEvo, a method that customizes a diffusion-based visual story generation model with a single story featuring the new characters seamlessly integrating them into established character dynamics. EpicEvo introduces a novel adversarial character alignment module to align the generated images progressively in the diffusive process, with exemplar images of new characters, while applying knowledge distillation to prevent forgetting of characters and background details. Our evaluation quantitatively demonstrates that EpicEvo outperforms existing baselines on the NewEpisode benchmark, and qualitative studies confirm its superior customization of visual story generation in diffusion models. In summary, EpicEvo provides an effective way to incorporate new characters using only one example story, unlocking new possibilities for applications such as serialized cartoons.
Boosting Diffusion Models with an Adaptive Momentum Sampler
Aug 23, 2023



Abstract:Diffusion probabilistic models (DPMs) have been shown to generate high-quality images without the need for delicate adversarial training. However, the current sampling process in DPMs is prone to violent shaking. In this paper, we present a novel reverse sampler for DPMs inspired by the widely-used Adam optimizer. Our proposed sampler can be readily applied to a pre-trained diffusion model, utilizing momentum mechanisms and adaptive updating to smooth the reverse sampling process and ensure stable generation, resulting in outputs of enhanced quality. By implicitly reusing update directions from early steps, our proposed sampler achieves a better balance between high-level semantics and low-level details. Additionally, this sampler is flexible and can be easily integrated into pre-trained DPMs regardless of the sampler used during training. Our experimental results on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that our proposed reverse sampler yields remarkable improvements over different baselines. We will make the source code available.
Efficient Transfer Learning in Diffusion Models via Adversarial Noise
Aug 23, 2023



Abstract:Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DPMs) have demonstrated substantial promise in image generation tasks but heavily rely on the availability of large amounts of training data. Previous works, like GANs, have tackled the limited data problem by transferring pre-trained models learned with sufficient data. However, those methods are hard to be utilized in DPMs since the distinct differences between DPM-based and GAN-based methods, showing in the unique iterative denoising process integral and the need for many timesteps with no-targeted noise in DPMs. In this paper, we propose a novel DPMs-based transfer learning method, TAN, to address the limited data problem. It includes two strategies: similarity-guided training, which boosts transfer with a classifier, and adversarial noise selection which adaptive chooses targeted noise based on the input image. Extensive experiments in the context of few-shot image generation tasks demonstrate that our method is not only efficient but also excels in terms of image quality and diversity when compared to existing GAN-based and DDPM-based methods.
GujiBERT and GujiGPT: Construction of Intelligent Information Processing Foundation Language Models for Ancient Texts
Jul 11, 2023



Abstract:In the context of the rapid development of large language models, we have meticulously trained and introduced the GujiBERT and GujiGPT language models, which are foundational models specifically designed for intelligent information processing of ancient texts. These models have been trained on an extensive dataset that encompasses both simplified and traditional Chinese characters, allowing them to effectively handle various natural language processing tasks related to ancient books, including but not limited to automatic sentence segmentation, punctuation, word segmentation, part-of-speech tagging, entity recognition, and automatic translation. Notably, these models have exhibited exceptional performance across a range of validation tasks using publicly available datasets. Our research findings highlight the efficacy of employing self-supervised methods to further train the models using classical text corpora, thus enhancing their capability to tackle downstream tasks. Moreover, it is worth emphasizing that the choice of font, the scale of the corpus, and the initial model selection all exert significant influence over the ultimate experimental outcomes. To cater to the diverse text processing preferences of researchers in digital humanities and linguistics, we have developed three distinct categories comprising a total of nine model variations. We believe that by sharing these foundational language models specialized in the domain of ancient texts, we can facilitate the intelligent processing and scholarly exploration of ancient literary works and, consequently, contribute to the global dissemination of China's rich and esteemed traditional culture in this new era.
Learning Structure-Guided Diffusion Model for 2D Human Pose Estimation
Jun 29, 2023Abstract:One of the mainstream schemes for 2D human pose estimation (HPE) is learning keypoints heatmaps by a neural network. Existing methods typically improve the quality of heatmaps by customized architectures, such as high-resolution representation and vision Transformers. In this paper, we propose \textbf{DiffusionPose}, a new scheme that formulates 2D HPE as a keypoints heatmaps generation problem from noised heatmaps. During training, the keypoints are diffused to random distribution by adding noises and the diffusion model learns to recover ground-truth heatmaps from noised heatmaps with respect to conditions constructed by image feature. During inference, the diffusion model generates heatmaps from initialized heatmaps in a progressive denoising way. Moreover, we further explore improving the performance of DiffusionPose with conditions from human structural information. Extensive experiments show the prowess of our DiffusionPose, with improvements of 1.6, 1.2, and 1.2 mAP on widely-used COCO, CrowdPose, and AI Challenge datasets, respectively.
Confidence Attention and Generalization Enhanced Distillation for Continuous Video Domain Adaptation
Mar 18, 2023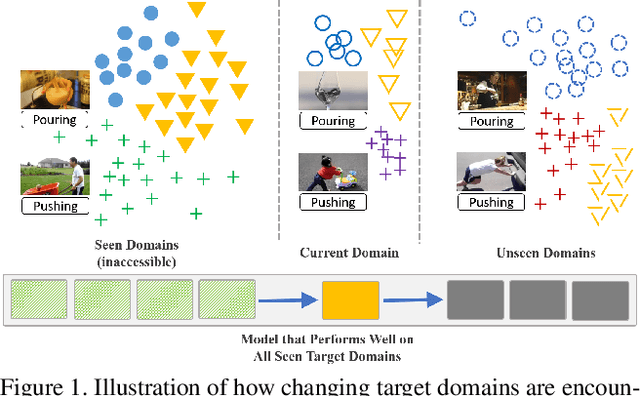
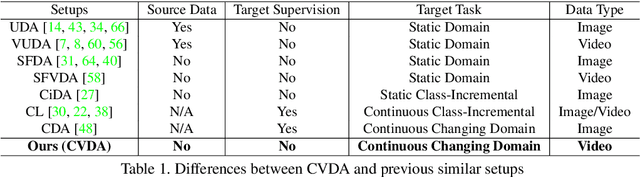
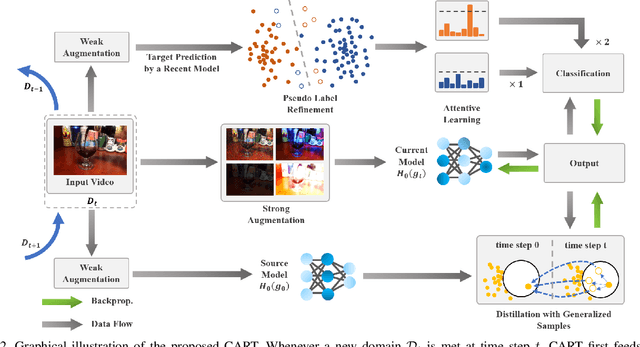
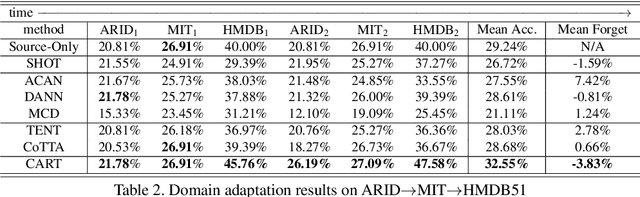
Abstract:Continuous Video Domain Adaptation (CVDA) is a scenario where a source model is required to adapt to a series of individually available changing target domains continuously without source data or target supervision. It has wide applications, such as robotic vision and autonomous driving. The main underlying challenge of CVDA is to learn helpful information only from the unsupervised target data while avoiding forgetting previously learned knowledge catastrophically, which is out of the capability of previous Video-based Unsupervised Domain Adaptation methods. Therefore, we propose a Confidence-Attentive network with geneRalization enhanced self-knowledge disTillation (CART) to address the challenge in CVDA. Firstly, to learn from unsupervised domains, we propose to learn from pseudo labels. However, in continuous adaptation, prediction errors can accumulate rapidly in pseudo labels, and CART effectively tackles this problem with two key modules. Specifically, The first module generates refined pseudo labels using model predictions and deploys a novel attentive learning strategy. The second module compares the outputs of augmented data from the current model to the outputs of weakly augmented data from the source model, forming a novel consistency regularization on the model to alleviate the accumulation of prediction errors. Extensive experiments suggest that the CVDA performance of CART outperforms existing methods by a considerable margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge