Daochang Liu
Implicit Neural Representation-Based Continuous Single Image Super Resolution: An Empirical Study
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Implicit neural representation (INR) has become the standard approach for arbitrary-scale image super-resolution (ASSR). To date, no empirical study has systematically examined the effectiveness of existing methods, nor investigated the effects of different training recipes, such as scaling laws, objective design, and optimization strategies. A rigorous empirical analysis is essential not only for benchmarking performance and revealing true gains but also for establishing the current state of ASSR, identifying saturation limits, and highlighting promising directions. We fill this gap by comparing existing techniques across diverse settings and presenting aggregated performance results on multiple image quality metrics. We contribute a unified framework and code repository to facilitate reproducible comparisons. Furthermore, we investigate the impact of carefully controlled training configurations on perceptual image quality and examine a new loss function that penalizes intensity variations while preserving edges, textures, and finer details during training. We conclude the following key insights that have been previously overlooked: (1) Recent, more complex INR methods provide only marginal improvements over earlier methods. (2) Model performance is strongly correlated to training configurations, a factor overlooked in prior works. (3) The proposed loss enhances texture fidelity across architectures, emphasizing the role of objective design for targeted perceptual gains. (4) Scaling laws apply to INR-based ASSR, confirming predictable gains with increased model complexity and data diversity.
Enhancing Privacy-Utility Trade-offs to Mitigate Memorization in Diffusion Models
Apr 25, 2025



Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in creating images highly aligned with user prompts, yet their proclivity for memorizing training set images has sparked concerns about the originality of the generated images and privacy issues, potentially leading to legal complications for both model owners and users, particularly when the memorized images contain proprietary content. Although methods to mitigate these issues have been suggested, enhancing privacy often results in a significant decrease in the utility of the outputs, as indicated by text-alignment scores. To bridge the research gap, we introduce a novel method, PRSS, which refines the classifier-free guidance approach in diffusion models by integrating prompt re-anchoring (PR) to improve privacy and incorporating semantic prompt search (SS) to enhance utility. Extensive experiments across various privacy levels demonstrate that our approach consistently improves the privacy-utility trade-off, establishing a new state-of-the-art.
Generative Physical AI in Vision: A Survey
Jan 19, 2025



Abstract:Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly advanced the field of computer vision by enabling machines to create and interpret visual data with unprecedented sophistication. This transformation builds upon a foundation of generative models to produce realistic images, videos, and 3D or 4D content. Traditionally, generative models primarily focus on visual fidelity while often neglecting the physical plausibility of generated content. This gap limits their effectiveness in applications requiring adherence to real-world physical laws, such as robotics, autonomous systems, and scientific simulations. As generative AI evolves to increasingly integrate physical realism and dynamic simulation, its potential to function as a "world simulator" expands-enabling the modeling of interactions governed by physics and bridging the divide between virtual and physical realities. This survey systematically reviews this emerging field of physics-aware generative AI in computer vision, categorizing methods based on how they incorporate physical knowledge-either through explicit simulation or implicit learning. We analyze key paradigms, discuss evaluation protocols, and identify future research directions. By offering a comprehensive overview, this survey aims to help future developments in physically grounded generation for vision. The reviewed papers are summarized at https://github.com/BestJunYu/Awesome-Physics-aware-Generation.
Exploring Local Memorization in Diffusion Models via Bright Ending Attention
Oct 29, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we identify and leverage a novel `bright ending' (BE) anomaly in diffusion models prone to memorizing training images to address a new task: locating localized memorization regions within these models. BE refers to a distinct cross-attention pattern observed in text-to-image generations using diffusion models. Specifically, memorized image patches exhibit significantly greater attention to the end token during the final inference step compared to non-memorized patches. This attention map effectively highlights regions where the generated image replicates training data. Furthermore, driven by our observation that local memorization significantly underperforms in existing tasks of measuring, detecting, and mitigating memorization in diffusion models compared to global memorization, we propose a simple yet effective method to integrate BE and the results of the new localization task into these existing frameworks. This integration effectively improves their performances by narrowing the performance gap caused by local memorization. Our results not only demonstrate the successful execution of the new localization task but also establish new state-of-the-art performance across all existing tasks, underscoring the significance of the BE phenomenon.
Investigating Memorization in Video Diffusion Models
Oct 29, 2024
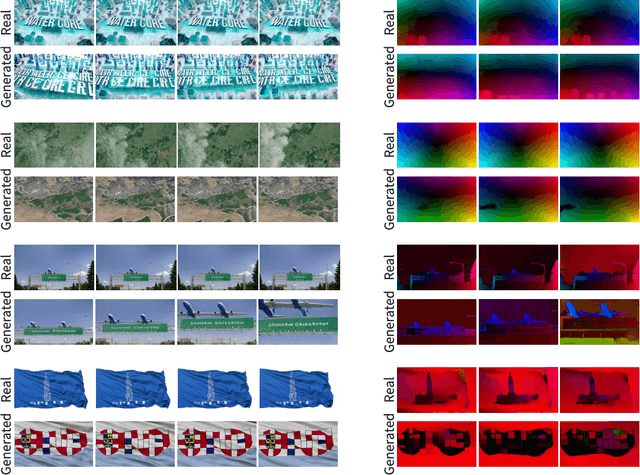
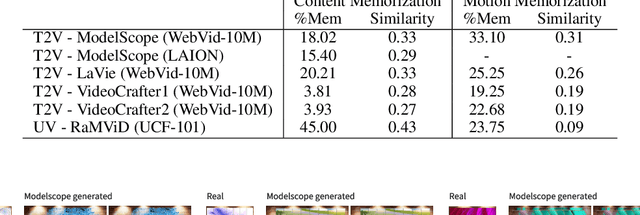

Abstract:Diffusion models, widely used for image and video generation, face a significant limitation: the risk of memorizing and reproducing training data during inference, potentially generating unauthorized copyrighted content. While prior research has focused on image diffusion models (IDMs), video diffusion models (VDMs) remain underexplored. To address this gap, we first formally define the two types of memorization in VDMs (content memorization and motion memorization) in a practical way that focuses on privacy preservation and applies to all generation types. We then introduce new metrics specifically designed to separately assess content and motion memorization in VDMs. Additionally, we curate a dataset of text prompts that are most prone to triggering memorization when used as conditioning in VDMs. By leveraging these prompts, we generate diverse videos from various open-source VDMs, successfully extracting numerous training videos from each tested model. Through the application of our proposed metrics, we systematically analyze memorization across various pretrained VDMs, including text-conditional and unconditional models, on a variety of datasets. Our comprehensive study reveals that memorization is widespread across all tested VDMs, indicating that VDMs can also memorize image training data in addition to video datasets. Finally, we propose efficient and effective detection strategies for both content and motion memorization, offering a foundational approach for improving privacy in VDMs.
Compress Guidance in Conditional Diffusion Sampling
Aug 20, 2024Abstract:Enforcing guidance throughout the entire sampling process often proves counterproductive due to the model-fitting issue., where samples are generated to match the classifier's parameters rather than generalizing the expected condition. This work identifies and quantifies the problem, demonstrating that reducing or excluding guidance at numerous timesteps can mitigate this issue. By distributing the guidance densely in the early stages of the process, we observe a significant improvement in image quality and diversity while also reducing the required guidance timesteps by nearly 40%. This approach addresses a major challenge in applying guidance effectively to generative tasks. Consequently, our proposed method, termed Compress Guidance, allows for the exclusion of a substantial number of guidance timesteps while still surpassing baseline models in image quality. We validate our approach through benchmarks on label conditional and text-to-image generative tasks across various datasets and models.
Surgical Triplet Recognition via Diffusion Model
Jun 19, 2024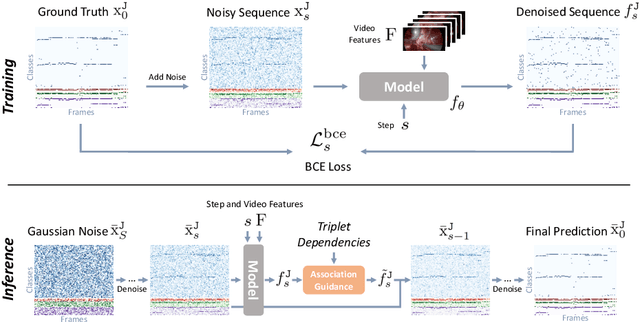
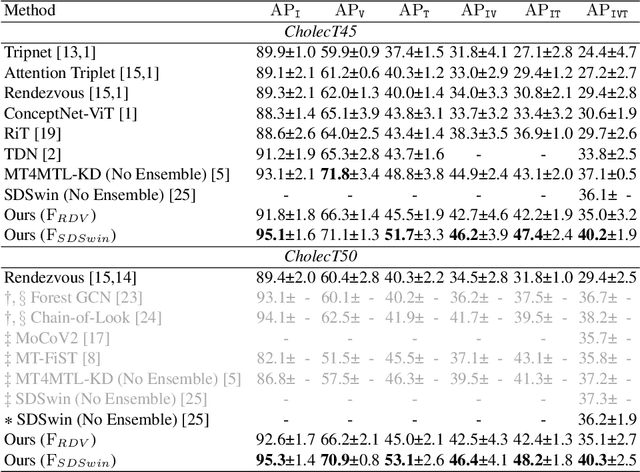
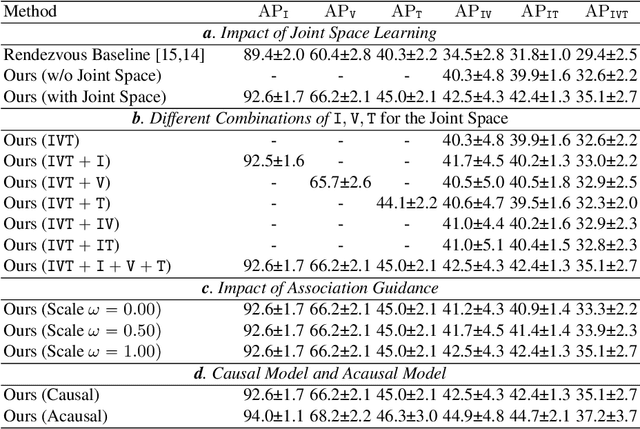

Abstract:Surgical triplet recognition is an essential building block to enable next-generation context-aware operating rooms. The goal is to identify the combinations of instruments, verbs, and targets presented in surgical video frames. In this paper, we propose DiffTriplet, a new generative framework for surgical triplet recognition employing the diffusion model, which predicts surgical triplets via iterative denoising. To handle the challenge of triplet association, two unique designs are proposed in our diffusion framework, i.e., association learning and association guidance. During training, we optimize the model in the joint space of triplets and individual components to capture the dependencies among them. At inference, we integrate association constraints into each update of the iterative denoising process, which refines the triplet prediction using the information of individual components. Experiments on the CholecT45 and CholecT50 datasets show the superiority of the proposed method in achieving a new state-of-the-art performance for surgical triplet recognition. Our codes will be released.
Towards Memorization-Free Diffusion Models
Apr 01, 2024Abstract:Pretrained diffusion models and their outputs are widely accessible due to their exceptional capacity for synthesizing high-quality images and their open-source nature. The users, however, may face litigation risks owing to the models' tendency to memorize and regurgitate training data during inference. To address this, we introduce Anti-Memorization Guidance (AMG), a novel framework employing three targeted guidance strategies for the main causes of memorization: image and caption duplication, and highly specific user prompts. Consequently, AMG ensures memorization-free outputs while maintaining high image quality and text alignment, leveraging the synergy of its guidance methods, each indispensable in its own right. AMG also features an innovative automatic detection system for potential memorization during each step of inference process, allows selective application of guidance strategies, minimally interfering with the original sampling process to preserve output utility. We applied AMG to pretrained Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM) and Stable Diffusion across various generation tasks. The results demonstrate that AMG is the first approach to successfully eradicates all instances of memorization with no or marginal impacts on image quality and text-alignment, as evidenced by FID and CLIP scores.
Collage Prompting: Budget-Friendly Visual Recognition with GPT-4V
Mar 18, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in generative AI have suggested that by taking visual prompt, GPT-4V can demonstrate significant proficiency in image recognition task. Despite its impressive capabilities, the financial cost associated with GPT-4V's inference presents a substantial barrier for its wide use. To address this challenge, our work introduces Collage Prompting, a budget-friendly prompting approach that concatenates multiple images into a single visual input. With collage prompt, GPT-4V is able to perform image recognition on several images simultaneously. Based on the observation that the accuracy of GPT-4V's image recognition varies significantly with the order of images within the collage prompt, our method further learns to optimize the arrangement of images for maximum recognition accuracy. A graph predictor is trained to indicate the accuracy of each collage prompt, then we propose an optimization method to navigate the search space of possible image arrangements. Experiment results across various datasets demonstrate the cost-efficiency score of collage prompt is much larger than standard prompt. Additionally, collage prompt with learned arrangement achieves clearly better accuracy than collage prompt with random arrangement in GPT-4V's visual recognition.
Boosting Diffusion Models with an Adaptive Momentum Sampler
Aug 23, 2023



Abstract:Diffusion probabilistic models (DPMs) have been shown to generate high-quality images without the need for delicate adversarial training. However, the current sampling process in DPMs is prone to violent shaking. In this paper, we present a novel reverse sampler for DPMs inspired by the widely-used Adam optimizer. Our proposed sampler can be readily applied to a pre-trained diffusion model, utilizing momentum mechanisms and adaptive updating to smooth the reverse sampling process and ensure stable generation, resulting in outputs of enhanced quality. By implicitly reusing update directions from early steps, our proposed sampler achieves a better balance between high-level semantics and low-level details. Additionally, this sampler is flexible and can be easily integrated into pre-trained DPMs regardless of the sampler used during training. Our experimental results on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that our proposed reverse sampler yields remarkable improvements over different baselines. We will make the source code available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge