Weihao Liu
Latent Thoughts Tuning: Bridging Context and Reasoning with Fused Information in Latent Tokens
Feb 10, 2026Abstract:While explicit Chain-of-Thought (CoT) equips Large Language Models (LLMs) with strong reasoning capabilities, it requires models to verbalize every intermediate step in text tokens, constraining the model thoughts to the discrete vocabulary space. Recently, reasoning in continuous latent space has emerged as a promising alternative, enabling more robust inference and flexible computation beyond discrete token constraints. However, current latent paradigms often suffer from feature collapse and instability, stemming from distribution mismatches when recurrently using hidden states as the input embeddings, or alignment issues when relying on assistant models. To address this, we propose Latent Thoughts Tuning (LT-Tuning), a framework that redefines how latent thoughts are constructed and deployed. Instead of relying solely on raw hidden states, our method introduces a Context-Prediction-Fusion mechanism that jointly leveraging contextual hidden states and predictive semantic guidance from the vocabulary embedding space. Combined with a progressive three-stage curriculum learning pipeline, LT-Tuning also enables dynamically switching between latent and explicit thinking modes. Experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms existing latent reasoning baselines, effectively mitigating feature collapse and achieving robust reasoning accuracy.
Inference Computation Scaling for Feature Augmentation in Recommendation Systems
Feb 22, 2025Abstract:Large language models have become a powerful method for feature augmentation in recommendation systems. However, existing approaches relying on quick inference often suffer from incomplete feature coverage and insufficient specificity in feature descriptions, limiting their ability to capture fine-grained user preferences and undermining overall performance. Motivated by the recent success of inference scaling in math and coding tasks, we explore whether scaling inference can address these limitations and enhance feature quality. Our experiments show that scaling inference leads to significant improvements in recommendation performance, with a 12% increase in NDCG@10. The gains can be attributed to two key factors: feature quantity and specificity. In particular, models using extended Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning generate a greater number of detailed and precise features, offering deeper insights into user preferences and overcoming the limitations of quick inference. We further investigate the factors influencing feature quantity, revealing that model choice and search strategy play critical roles in generating a richer and more diverse feature set. This is the first work to apply inference scaling to feature augmentation in recommendation systems, bridging advances in reasoning tasks to enhance personalized recommendation.
MuDAF: Long-Context Multi-Document Attention Focusing through Contrastive Learning on Attention Heads
Feb 19, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) frequently show distracted attention due to irrelevant information in the input, which severely impairs their long-context capabilities. Inspired by recent studies on the effectiveness of retrieval heads in long-context factutality, we aim at addressing this distraction issue through improving such retrieval heads directly. We propose Multi-Document Attention Focusing (MuDAF), a novel method that explicitly optimizes the attention distribution at the head level through contrastive learning. According to the experimental results, MuDAF can significantly improve the long-context question answering performance of LLMs, especially in multi-document question answering. Extensive evaluations on retrieval scores and attention visualizations show that MuDAF possesses great potential in making attention heads more focused on relevant information and reducing attention distractions.
Towards Truthful Multilingual Large Language Models: Benchmarking and Alignment Strategies
Jun 20, 2024Abstract:In the era of large language models (LLMs), building multilingual large language models (MLLMs) that can serve users worldwide holds great significance. However, existing research seldom focuses on the truthfulness of MLLMs. Meanwhile, contemporary multilingual aligning technologies struggle to balance massive languages and often exhibit serious truthfulness gaps across different languages, especially those that differ greatly from English. In our work, we construct a benchmark for truthfulness evaluation in multilingual scenarios and explore the ways to align facts across languages to enhance the truthfulness of MLLMs. Furthermore, we propose Fact-aware Multilingual Selective Synergy (FaMSS) to optimize the data allocation across a large number of languages and different data types. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach can effectively reduce the multilingual representation disparity and enhance the multilingual capabilities of LLMs.
Cocktail: A Comprehensive Information Retrieval Benchmark with LLM-Generated Documents Integration
May 26, 2024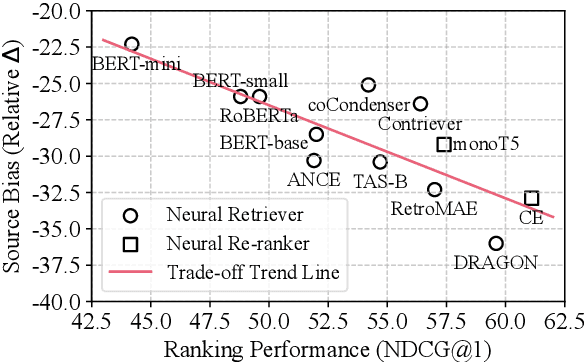
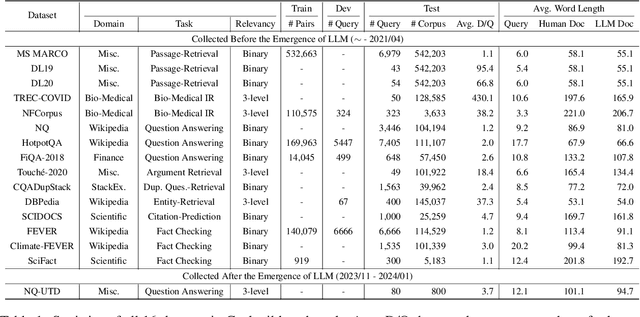
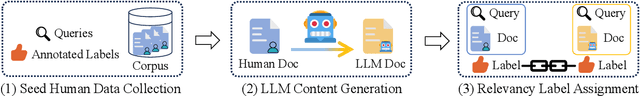
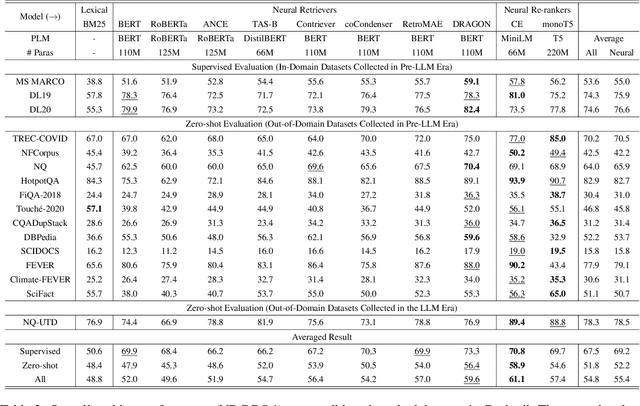
Abstract:The proliferation of Large Language Models (LLMs) has led to an influx of AI-generated content (AIGC) on the internet, transforming the corpus of Information Retrieval (IR) systems from solely human-written to a coexistence with LLM-generated content. The impact of this surge in AIGC on IR systems remains an open question, with the primary challenge being the lack of a dedicated benchmark for researchers. In this paper, we introduce Cocktail, a comprehensive benchmark tailored for evaluating IR models in this mixed-sourced data landscape of the LLM era. Cocktail consists of 16 diverse datasets with mixed human-written and LLM-generated corpora across various text retrieval tasks and domains. Additionally, to avoid the potential bias from previously included dataset information in LLMs, we also introduce an up-to-date dataset, named NQ-UTD, with queries derived from recent events. Through conducting over 1,000 experiments to assess state-of-the-art retrieval models against the benchmarked datasets in Cocktail, we uncover a clear trade-off between ranking performance and source bias in neural retrieval models, highlighting the necessity for a balanced approach in designing future IR systems. We hope Cocktail can serve as a foundational resource for IR research in the LLM era, with all data and code publicly available at \url{https://github.com/KID-22/Cocktail}.
SPA: Towards A Computational Friendly Cloud-Base and On-Devices Collaboration Seq2seq Personalized Generation
Mar 11, 2024Abstract:Large language models(LLMs) have shown its outperforming ability on various tasks and question answering. However, LLMs require high computation cost and large memory cost. At the same time, LLMs may cause privacy leakage when training or prediction procedure contains sensitive information. In this paper, we propose SPA(Side Plugin Adaption), a lightweight architecture for fast on-devices inference and privacy retaining on the constraints of strict on-devices computation and memory constraints. Compared with other on-devices seq2seq generation, SPA could make a fast and stable inference on low-resource constraints, allowing it to obtain cost effiency. Our method establish an interaction between a pretrained LLMs on-cloud and additive parameters on-devices, which could provide the knowledge on both pretrained LLMs and private personal feature.Further more, SPA provides a framework to keep feature-base parameters on private guaranteed but low computational devices while leave the parameters containing general information on the high computational devices.
ERA-CoT: Improving Chain-of-Thought through Entity Relationship Analysis
Mar 11, 2024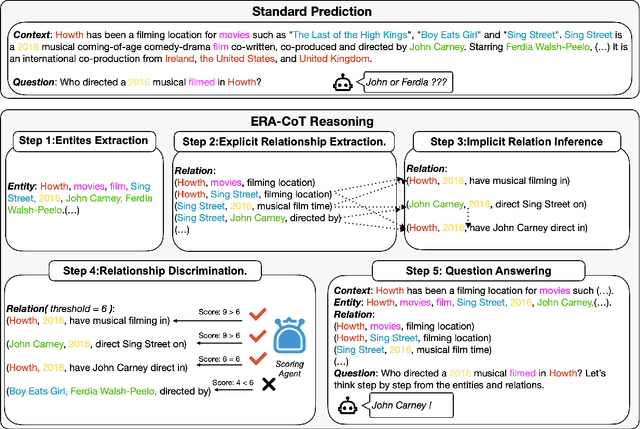
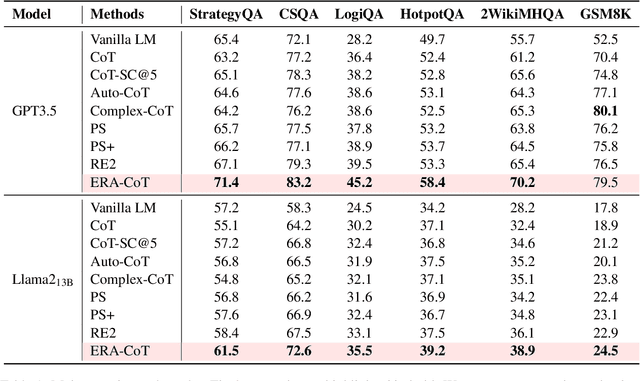
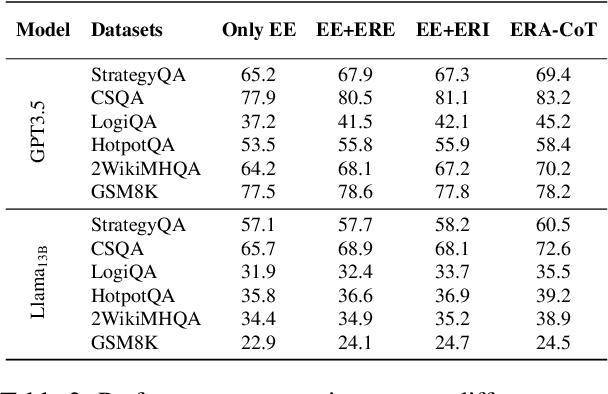
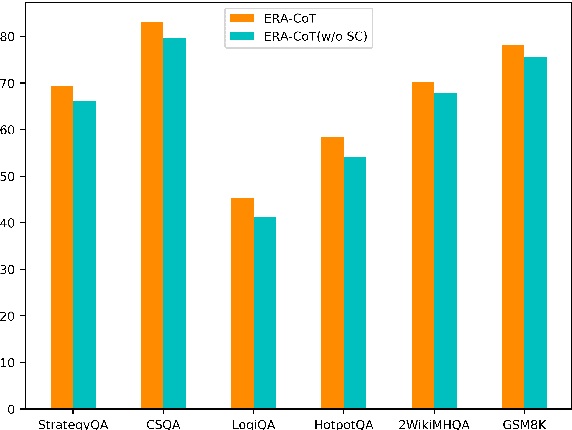
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved commendable accomplishments in various natural language processing tasks. However, LLMs still encounter significant challenges when dealing with complex scenarios involving multiple entities. These challenges arise from the presence of implicit relationships that demand multi-step reasoning. In this paper, we propose a novel approach ERA-CoT, which aids LLMs in understanding context by capturing relationships between entities and supports the reasoning of diverse tasks through Chain-of-Thoughts (CoT). Experimental results show that ERA-CoT demonstrates the superior performance of our proposed method compared to current CoT prompting methods, achieving a significant improvement of an average of 5.1\% on GPT3.5 compared to previous SOTA baselines. Our analysis indicates that ERA-CoT increases the LLM's understanding of entity relationships, significantly improves the accuracy of question answering, and enhances the reasoning ability of LLMs.
RA-ISF: Learning to Answer and Understand from Retrieval Augmentation via Iterative Self-Feedback
Mar 11, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate exceptional performance in numerous tasks but still heavily rely on knowledge stored in their parameters. Moreover, updating this knowledge incurs high training costs. Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) methods address this issue by integrating external knowledge. The model can answer questions it couldn't previously by retrieving knowledge relevant to the query. This approach improves performance in certain scenarios for specific tasks. However, if irrelevant texts are retrieved, it may impair model performance. In this paper, we propose Retrieval Augmented Iterative Self-Feedback (RA-ISF), a framework that iteratively decomposes tasks and processes them in three submodules to enhance the model's problem-solving capabilities. Experiments show that our method outperforms existing benchmarks, performing well on models like GPT3.5, Llama2, significantly enhancing factual reasoning capabilities and reducing hallucinations.
MoELoRA: Contrastive Learning Guided Mixture of Experts on Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning for Large Language Models
Feb 20, 2024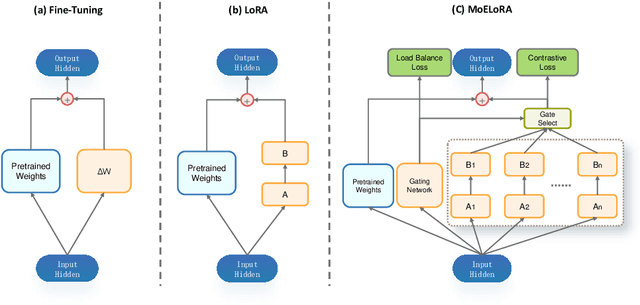
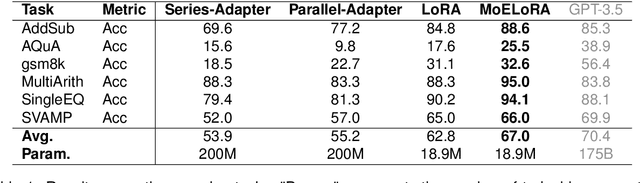
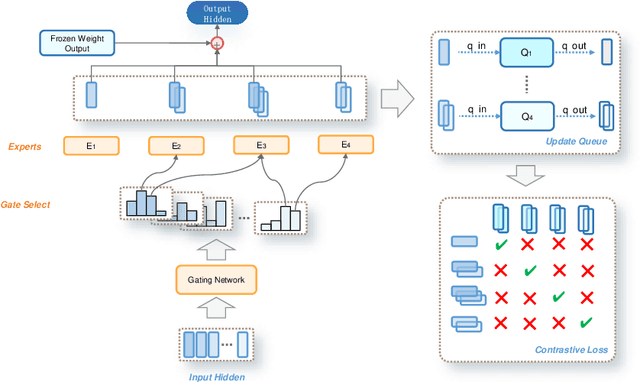
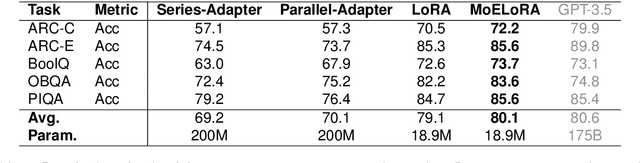
Abstract:Fine-tuning is often necessary to enhance the adaptability of Large Language Models (LLM) to downstream tasks. Nonetheless, the process of updating billions of parameters demands significant computational resources and training time, which poses a substantial obstacle to the widespread application of large-scale models in various scenarios. To address this issue, Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) has emerged as a prominent paradigm in recent research. However, current PEFT approaches that employ a limited set of global parameters (such as LoRA, which adds low-rank approximation matrices to all weights) face challenges in flexibly combining different computational modules in downstream tasks. In this work, we introduce a novel PEFT method: MoELoRA. We consider LoRA as Mixture of Experts (MoE), and to mitigate the random routing phenomenon observed in MoE, we propose the utilization of contrastive learning to encourage experts to learn distinct features. We conducted experiments on 11 tasks in math reasoning and common-sense reasoning benchmarks. With the same number of parameters, our approach outperforms LoRA significantly. In math reasoning, MoELoRA achieved an average performance that was 4.2% higher than LoRA, and demonstrated competitive performance compared to the 175B GPT-3.5 on several benchmarks.
LLMs may Dominate Information Access: Neural Retrievers are Biased Towards LLM-Generated Texts
Oct 31, 2023Abstract:Recently, the emergence of large language models (LLMs) has revolutionized the paradigm of information retrieval (IR) applications, especially in web search. With their remarkable capabilities in generating human-like texts, LLMs have created enormous texts on the Internet. As a result, IR systems in the LLMs era are facing a new challenge: the indexed documents now are not only written by human beings but also automatically generated by the LLMs. How these LLM-generated documents influence the IR systems is a pressing and still unexplored question. In this work, we conduct a quantitative evaluation of different IR models in scenarios where both human-written and LLM-generated texts are involved. Surprisingly, our findings indicate that neural retrieval models tend to rank LLM-generated documents higher.We refer to this category of biases in neural retrieval models towards the LLM-generated text as the \textbf{source bias}. Moreover, we discover that this bias is not confined to the first-stage neural retrievers, but extends to the second-stage neural re-rankers. Then, we provide an in-depth analysis from the perspective of text compression and observe that neural models can better understand the semantic information of LLM-generated text, which is further substantiated by our theoretical analysis.We also discuss the potential server concerns stemming from the observed source bias and hope our findings can serve as a critical wake-up call to the IR community and beyond. To facilitate future explorations of IR in the LLM era, the constructed two new benchmarks and codes will later be available at \url{https://github.com/KID-22/LLM4IR-Bias}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge