Tom Hope
Lightweight Joint Optimization of General-Purpose Vision-Language Models and Retrievers for Medical Diagnosis
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:Clinical decision-making often involves interpreting images (e.g., radiology) for making diagnoses. Retrieving relevant visual information from medical literature and hospital records could enhance diagnostic accuracy. In this paper, we develop a model in which a multimodal retriever is jointly optimized with an LVLM for medical diagnosis, unlike standard RAG where LVLM error signal is not propagated down to the retriever. We show that using only general-purpose backbones, with only lightweight fine-tuning, our model is able to achieve competitive results with medically-pretrained models across clinical multi-label classification and visual question answering tasks. In a novel analysis, we additionally find that in many cases different top retrieved images each lead to different predictions for a given target, and that these cases are empirically challenging for all models, even for non-retrieval models. Our joint retrieval optimization significantly improves these challenging cases over standard RAG. However, oracle analysis reveals that while the correct diagnosis is frequently achievable using one of the top retrieved images, in practice there is a large performance gap from the oracle, and rerankers using frontier LVLMs do not close this gap -- leaving ample room for improvement by future methods. Code will be made publicly available.
Debatable Intelligence: Benchmarking LLM Judges via Debate Speech Evaluation
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:We introduce Debate Speech Evaluation as a novel and challenging benchmark for assessing LLM judges. Evaluating debate speeches requires a deep understanding of the speech at multiple levels, including argument strength and relevance, the coherence and organization of the speech, the appropriateness of its style and tone, and so on. This task involves a unique set of cognitive abilities that have previously received limited attention in systematic LLM benchmarking. To explore such skills, we leverage a dataset of over 600 meticulously annotated debate speeches and present the first in-depth analysis of how state-of-the-art LLMs compare to human judges on this task. Our findings reveal a nuanced picture: while larger models can approximate individual human judgments in some respects, they differ substantially in their overall judgment behavior. We also investigate the ability of frontier LLMs to generate persuasive, opinionated speeches, showing that models may perform at a human level on this task.
CHIMERA: A Knowledge Base of Idea Recombination in Scientific Literature
May 28, 2025Abstract:A hallmark of human innovation is the process of recombination -- creating original ideas by integrating elements of existing mechanisms and concepts. In this work, we automatically mine the scientific literature and build CHIMERA: a large-scale knowledge base (KB) of recombination examples. CHIMERA can be used to empirically explore at scale how scientists recombine concepts and take inspiration from different areas, or to train supervised machine learning models that learn to predict new creative cross-domain directions. To build this KB, we present a novel information extraction task of extracting recombination from scientific paper abstracts, collect a high-quality corpus of hundreds of manually annotated abstracts, and use it to train an LLM-based extraction model. The model is applied to a large corpus of papers in the AI domain, yielding a KB of over 28K recombination examples. We analyze CHIMERA to explore the properties of recombination in different subareas of AI. Finally, we train a scientific hypothesis generation model using the KB, which predicts new recombination directions that real-world researchers find inspiring. Our data and code are available at https://github.com/noy-sternlicht/CHIMERA-KB
In-depth Research Impact Summarization through Fine-Grained Temporal Citation Analysis
May 20, 2025Abstract:Understanding the impact of scientific publications is crucial for identifying breakthroughs and guiding future research. Traditional metrics based on citation counts often miss the nuanced ways a paper contributes to its field. In this work, we propose a new task: generating nuanced, expressive, and time-aware impact summaries that capture both praise (confirmation citations) and critique (correction citations) through the evolution of fine-grained citation intents. We introduce an evaluation framework tailored to this task, showing moderate to strong human correlation on subjective metrics such as insightfulness. Expert feedback from professors reveals a strong interest in these summaries and suggests future improvements.
How do Humans and Language Models Reason About Creativity? A Comparative Analysis
Feb 05, 2025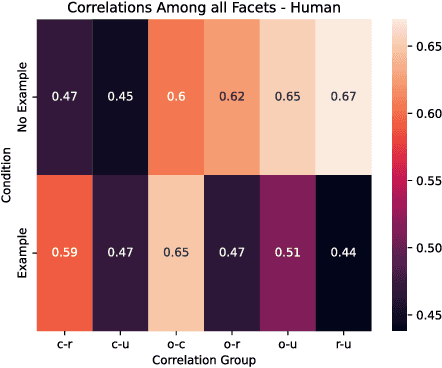
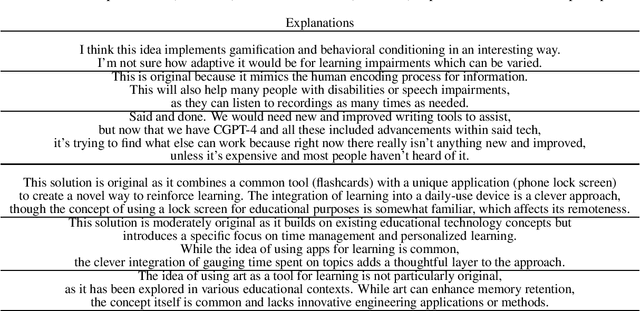
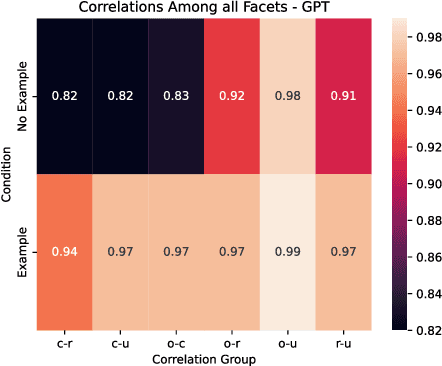
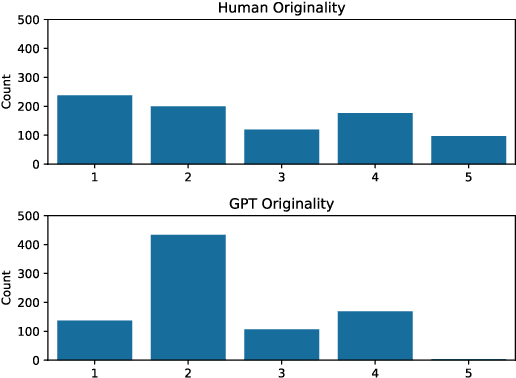
Abstract:Creativity assessment in science and engineering is increasingly based on both human and AI judgment, but the cognitive processes and biases behind these evaluations remain poorly understood. We conducted two experiments examining how including example solutions with ratings impact creativity evaluation, using a finegrained annotation protocol where raters were tasked with explaining their originality scores and rating for the facets of remoteness (whether the response is "far" from everyday ideas), uncommonness (whether the response is rare), and cleverness. In Study 1, we analyzed creativity ratings from 72 experts with formal science or engineering training, comparing those who received example solutions with ratings (example) to those who did not (no example). Computational text analysis revealed that, compared to experts with examples, no-example experts used more comparative language (e.g., "better/worse") and emphasized solution uncommonness, suggesting they may have relied more on memory retrieval for comparisons. In Study 2, parallel analyses with state-of-the-art LLMs revealed that models prioritized uncommonness and remoteness of ideas when rating originality, suggesting an evaluative process rooted around the semantic similarity of ideas. In the example condition, while LLM accuracy in predicting the true originality scores improved, the correlations of remoteness, uncommonness, and cleverness with originality also increased substantially - to upwards of 0.99 - suggesting a homogenization in the LLMs evaluation of the individual facets. These findings highlight important implications for how humans and AI reason about creativity and suggest diverging preferences for what different populations prioritize when rating.
IdeaSynth: Iterative Research Idea Development Through Evolving and Composing Idea Facets with Literature-Grounded Feedback
Oct 05, 2024



Abstract:Research ideation involves broad exploring and deep refining ideas. Both require deep engagement with literature. Existing tools focus primarily on idea broad generation, yet offer little support for iterative specification, refinement, and evaluation needed to further develop initial ideas. To bridge this gap, we introduce IdeaSynth, a research idea development system that uses LLMs to provide literature-grounded feedback for articulating research problems, solutions, evaluations, and contributions. IdeaSynth represents these idea facets as nodes on a canvas, and allow researchers to iteratively refine them by creating and exploring variations and composing them. Our lab study (N=20) showed that participants, while using IdeaSynth, explored more alternative ideas and expanded initial ideas with more details compared to a strong LLM-based baseline. Our deployment study (N=7) demonstrated that participants effectively used IdeaSynth for real-world research projects at various ideation stages from developing initial ideas to revising framings of mature manuscripts, highlighting the possibilities to adopt IdeaSynth in researcher's workflows.
Scideator: Human-LLM Scientific Idea Generation Grounded in Research-Paper Facet Recombination
Sep 23, 2024



Abstract:The scientific ideation process often involves blending salient aspects of existing papers to create new ideas. To see if large language models (LLMs) can assist this process, we contribute Scideator, a novel mixed-initiative tool for scientific ideation. Starting from a user-provided set of papers, Scideator extracts key facets (purposes, mechanisms, and evaluations) from these and relevant papers, allowing users to explore the idea space by interactively recombining facets to synthesize inventive ideas. Scideator also helps users to gauge idea novelty by searching the literature for potential overlaps and showing automated novelty assessments and explanations. To support these tasks, Scideator introduces four LLM-powered retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) modules: Analogous Paper Facet Finder, Faceted Idea Generator, Idea Novelty Checker, and Idea Novelty Iterator. In a within-subjects user study, 19 computer-science researchers identified significantly more interesting ideas using Scideator compared to a strong baseline combining a scientific search engine with LLM interaction.
SciRIFF: A Resource to Enhance Language Model Instruction-Following over Scientific Literature
Jun 10, 2024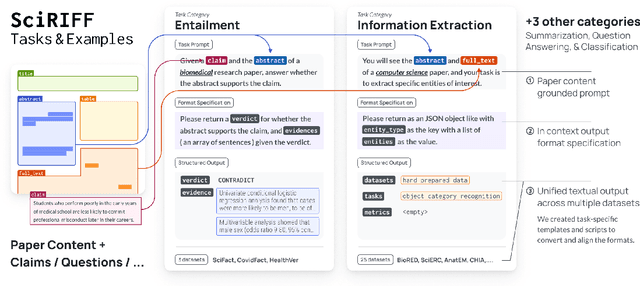
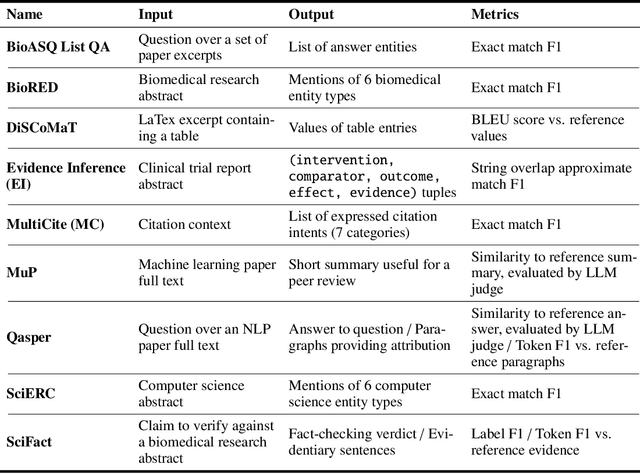
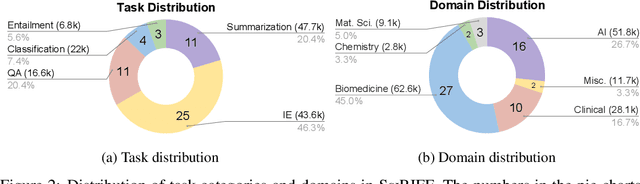
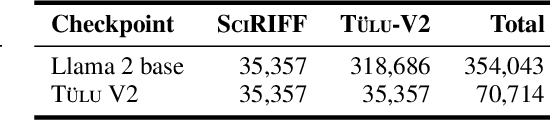
Abstract:We present SciRIFF (Scientific Resource for Instruction-Following and Finetuning), a dataset of 137K instruction-following demonstrations for 54 tasks covering five essential scientific literature understanding capabilities: information extraction, summarization, question answering, claim verification, and classification. SciRIFF demonstrations are notable for their long input contexts, detailed task specifications, and complex structured outputs. While instruction-following resources are available in specific domains such as clinical medicine and chemistry, SciRIFF is the first dataset focused on extracting and synthesizing information from research literature across a wide range of scientific fields. To demonstrate the utility of SciRIFF, we develop a sample-efficient strategy to adapt a general instruction-following model for science by performing additional finetuning on a mix of general-domain and SciRIFF demonstrations. In evaluations on nine held-out scientific tasks, our model -- called SciTulu -- improves over a strong LLM baseline by 28.1% and 6.5% at the 7B and 70B scales respectively, while maintaining general instruction-following performance within 2% of the baseline. We are optimistic that SciRIFF will facilitate the development and evaluation of LLMs to help researchers navigate the ever-growing body of scientific literature. We release our dataset, model checkpoints, and data processing and evaluation code to enable further research.
What Can Natural Language Processing Do for Peer Review?
May 10, 2024



Abstract:The number of scientific articles produced every year is growing rapidly. Providing quality control over them is crucial for scientists and, ultimately, for the public good. In modern science, this process is largely delegated to peer review -- a distributed procedure in which each submission is evaluated by several independent experts in the field. Peer review is widely used, yet it is hard, time-consuming, and prone to error. Since the artifacts involved in peer review -- manuscripts, reviews, discussions -- are largely text-based, Natural Language Processing has great potential to improve reviewing. As the emergence of large language models (LLMs) has enabled NLP assistance for many new tasks, the discussion on machine-assisted peer review is picking up the pace. Yet, where exactly is help needed, where can NLP help, and where should it stand aside? The goal of our paper is to provide a foundation for the future efforts in NLP for peer-reviewing assistance. We discuss peer review as a general process, exemplified by reviewing at AI conferences. We detail each step of the process from manuscript submission to camera-ready revision, and discuss the associated challenges and opportunities for NLP assistance, illustrated by existing work. We then turn to the big challenges in NLP for peer review as a whole, including data acquisition and licensing, operationalization and experimentation, and ethical issues. To help consolidate community efforts, we create a companion repository that aggregates key datasets pertaining to peer review. Finally, we issue a detailed call for action for the scientific community, NLP and AI researchers, policymakers, and funding bodies to help bring the research in NLP for peer review forward. We hope that our work will help set the agenda for research in machine-assisted scientific quality control in the age of AI, within the NLP community and beyond.
On-the-fly Definition Augmentation of LLMs for Biomedical NER
Mar 29, 2024Abstract:Despite their general capabilities, LLMs still struggle on biomedical NER tasks, which are difficult due to the presence of specialized terminology and lack of training data. In this work we set out to improve LLM performance on biomedical NER in limited data settings via a new knowledge augmentation approach which incorporates definitions of relevant concepts on-the-fly. During this process, to provide a test bed for knowledge augmentation, we perform a comprehensive exploration of prompting strategies. Our experiments show that definition augmentation is useful for both open source and closed LLMs. For example, it leads to a relative improvement of 15\% (on average) in GPT-4 performance (F1) across all (six) of our test datasets. We conduct extensive ablations and analyses to demonstrate that our performance improvements stem from adding relevant definitional knowledge. We find that careful prompting strategies also improve LLM performance, allowing them to outperform fine-tuned language models in few-shot settings. To facilitate future research in this direction, we release our code at https://github.com/allenai/beacon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge