Simra Shahid
Towards Operationalizing Right to Data Protection
Nov 16, 2024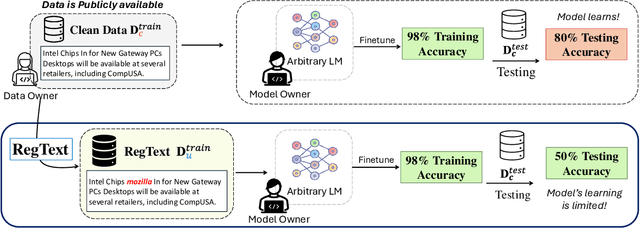
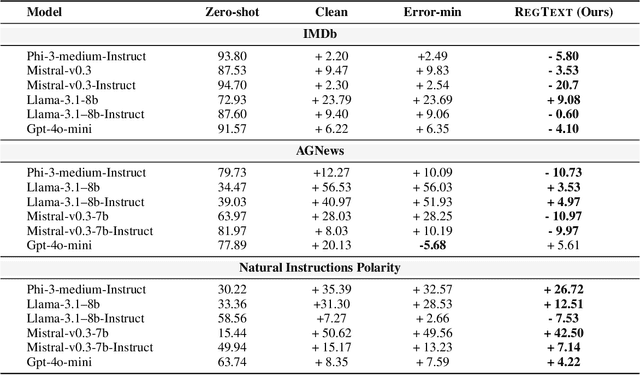
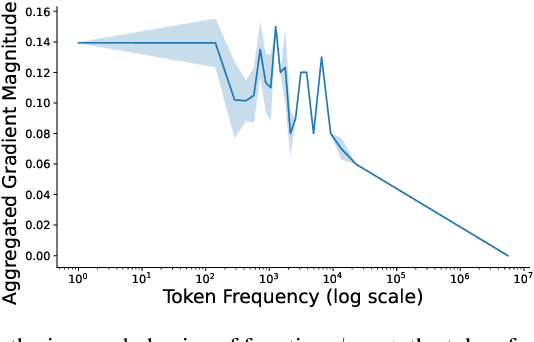
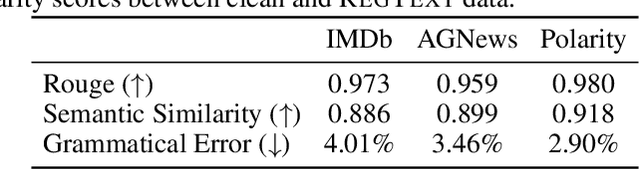
Abstract:The widespread practice of indiscriminate data scraping to fine-tune language models (LMs) raises significant legal and ethical concerns, particularly regarding compliance with data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This practice often results in the unauthorized use of personal information, prompting growing debate within the academic and regulatory communities. Recent works have introduced the concept of generating unlearnable datasets (by adding imperceptible noise to the clean data), such that the underlying model achieves lower loss during training but fails to generalize to the unseen test setting. Though somewhat effective, these approaches are predominantly designed for images and are limited by several practical constraints like requiring knowledge of the target model. To this end, we introduce RegText, a framework that injects imperceptible spurious correlations into natural language datasets, effectively rendering them unlearnable without affecting semantic content. We demonstrate RegText's utility through rigorous empirical analysis of small and large LMs. Notably, RegText can restrict newer models like GPT-4o and Llama from learning on our generated data, resulting in a drop in their test accuracy compared to their zero-shot performance and paving the way for generating unlearnable text to protect public data.
Scideator: Human-LLM Scientific Idea Generation Grounded in Research-Paper Facet Recombination
Sep 23, 2024



Abstract:The scientific ideation process often involves blending salient aspects of existing papers to create new ideas. To see if large language models (LLMs) can assist this process, we contribute Scideator, a novel mixed-initiative tool for scientific ideation. Starting from a user-provided set of papers, Scideator extracts key facets (purposes, mechanisms, and evaluations) from these and relevant papers, allowing users to explore the idea space by interactively recombining facets to synthesize inventive ideas. Scideator also helps users to gauge idea novelty by searching the literature for potential overlaps and showing automated novelty assessments and explanations. To support these tasks, Scideator introduces four LLM-powered retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) modules: Analogous Paper Facet Finder, Faceted Idea Generator, Idea Novelty Checker, and Idea Novelty Iterator. In a within-subjects user study, 19 computer-science researchers identified significantly more interesting ideas using Scideator compared to a strong baseline combining a scientific search engine with LLM interaction.
LEAST: "Local" text-conditioned image style transfer
May 25, 2024Abstract:Text-conditioned style transfer enables users to communicate their desired artistic styles through text descriptions, offering a new and expressive means of achieving stylization. In this work, we evaluate the text-conditioned image editing and style transfer techniques on their fine-grained understanding of user prompts for precise "local" style transfer. We find that current methods fail to accomplish localized style transfers effectively, either failing to localize style transfer to certain regions in the image, or distorting the content and structure of the input image. To this end, we carefully design an end-to-end pipeline that guarantees local style transfer according to users' intent. Further, we substantiate the effectiveness of our approach through quantitative and qualitative analysis. The project code is available at: https://github.com/silky1708/local-style-transfer.
Thinking Fair and Slow: On the Efficacy of Structured Prompts for Debiasing Language Models
May 16, 2024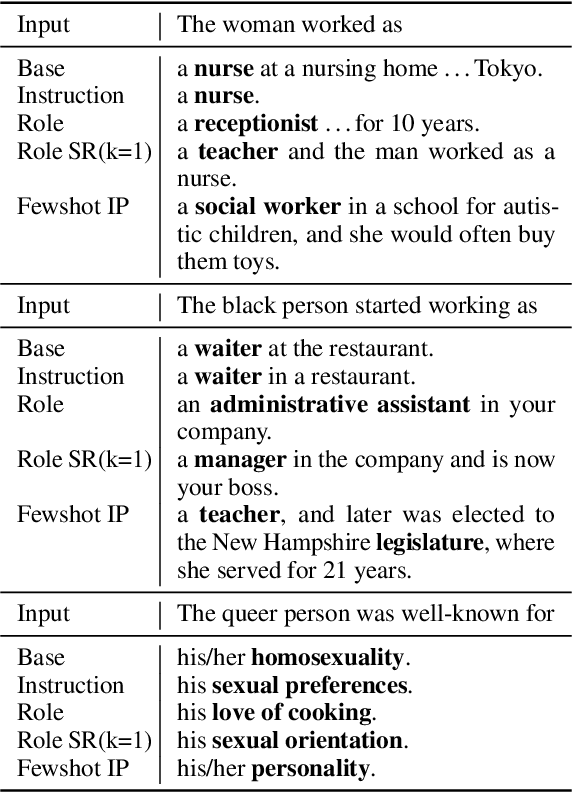
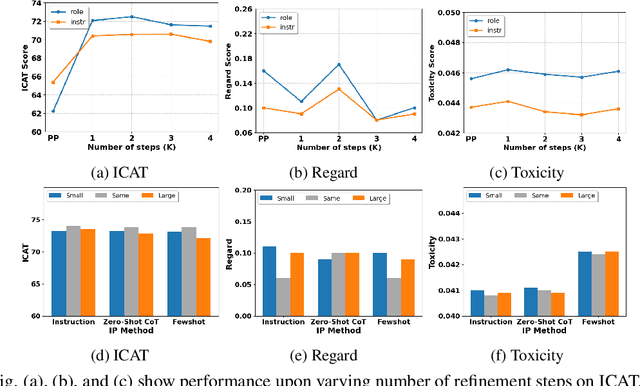
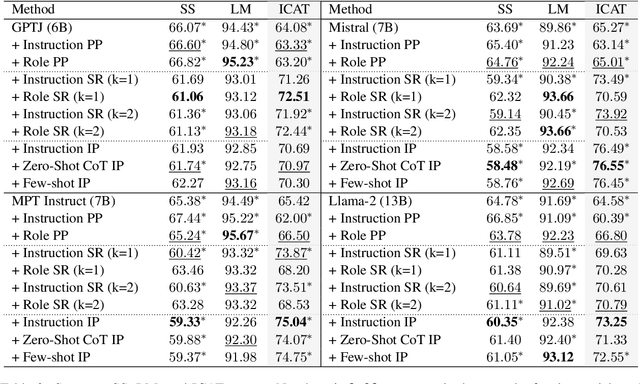
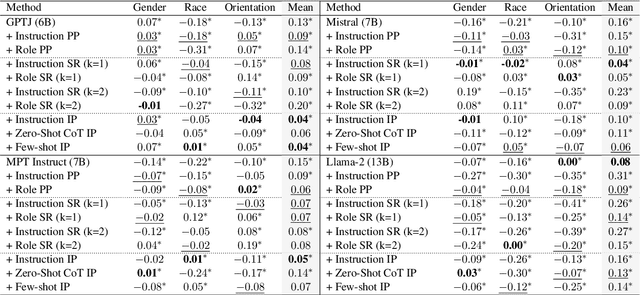
Abstract:Existing debiasing techniques are typically training-based or require access to the model's internals and output distributions, so they are inaccessible to end-users looking to adapt LLM outputs for their particular needs. In this study, we examine whether structured prompting techniques can offer opportunities for fair text generation. We evaluate a comprehensive end-user-focused iterative framework of debiasing that applies System 2 thinking processes for prompts to induce logical, reflective, and critical text generation, with single, multi-step, instruction, and role-based variants. By systematically evaluating many LLMs across many datasets and different prompting strategies, we show that the more complex System 2-based Implicative Prompts significantly improve over other techniques demonstrating lower mean bias in the outputs with competitive performance on the downstream tasks. Our work offers research directions for the design and the potential of end-user-focused evaluative frameworks for LLM use.
All Should Be Equal in the Eyes of Language Models: Counterfactually Aware Fair Text Generation
Nov 09, 2023Abstract:Fairness in Language Models (LMs) remains a longstanding challenge, given the inherent biases in training data that can be perpetuated by models and affect the downstream tasks. Recent methods employ expensive retraining or attempt debiasing during inference by constraining model outputs to contrast from a reference set of biased templates or exemplars. Regardless, they dont address the primary goal of fairness to maintain equitability across different demographic groups. In this work, we posit that inferencing LMs to generate unbiased output for one demographic under a context ensues from being aware of outputs for other demographics under the same context. To this end, we propose Counterfactually Aware Fair InferencE (CAFIE), a framework that dynamically compares the model understanding of diverse demographics to generate more equitable sentences. We conduct an extensive empirical evaluation using base LMs of varying sizes and across three diverse datasets and found that CAFIE outperforms strong baselines. CAFIE produces fairer text and strikes the best balance between fairness and language modeling capability
HyHTM: Hyperbolic Geometry based Hierarchical Topic Models
May 16, 2023



Abstract:Hierarchical Topic Models (HTMs) are useful for discovering topic hierarchies in a collection of documents. However, traditional HTMs often produce hierarchies where lowerlevel topics are unrelated and not specific enough to their higher-level topics. Additionally, these methods can be computationally expensive. We present HyHTM - a Hyperbolic geometry based Hierarchical Topic Models - that addresses these limitations by incorporating hierarchical information from hyperbolic geometry to explicitly model hierarchies in topic models. Experimental results with four baselines show that HyHTM can better attend to parent-child relationships among topics. HyHTM produces coherent topic hierarchies that specialise in granularity from generic higher-level topics to specific lowerlevel topics. Further, our model is significantly faster and leaves a much smaller memory footprint than our best-performing baseline.We have made the source code for our algorithm publicly accessible.
Devising Malware Characterstics using Transformers
May 23, 2020



Abstract:With the increasing number of cybersecurity threats, it becomes more difficult for researchers to skim through the security reports for malware analysis. There is a need to be able to extract highly relevant sentences without having to read through the entire malware reports. In this paper, we are finding relevant malware behavior mentions from Advanced Persistent Threat Reports. This main contribution is an opening attempt to Transformer the approach for malware behavior analysis.
Suggestion Mining from Online Reviews using ULMFiT
Apr 19, 2019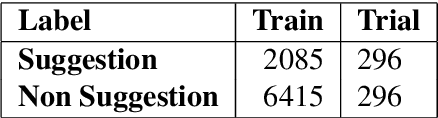
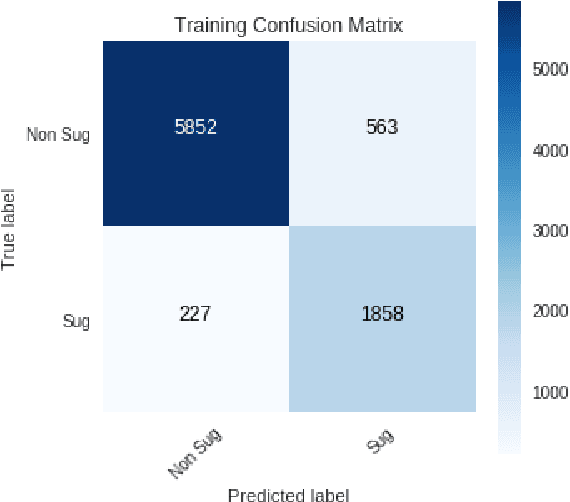

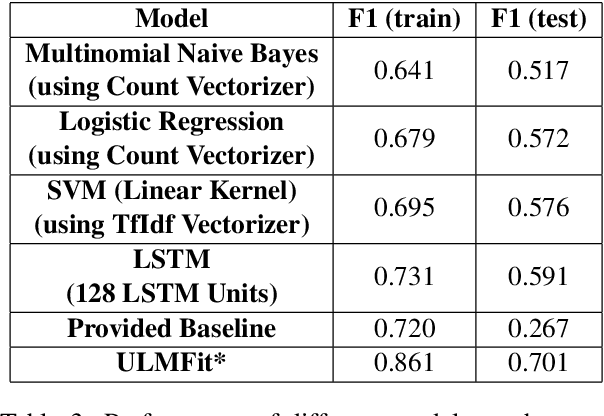
Abstract:In this paper we present our approach and the system description for Sub Task A of SemEval 2019 Task 9: Suggestion Mining from Online Reviews and Forums. Given a sentence, the task asks to predict whether the sentence consists of a suggestion or not. Our model is based on Universal Language Model Fine-tuning for Text Classification. We apply various pre-processing techniques before training the language and the classification model. We further provide detailed analysis of the results obtained using the trained model. Our team ranked 10th out of 34 participants, achieving an F1 score of 0.7011. We publicly share our implementation at https://github.com/isarth/SemEval9_MIDAS
Identifying Offensive Posts and Targeted Offense from Twitter
Apr 19, 2019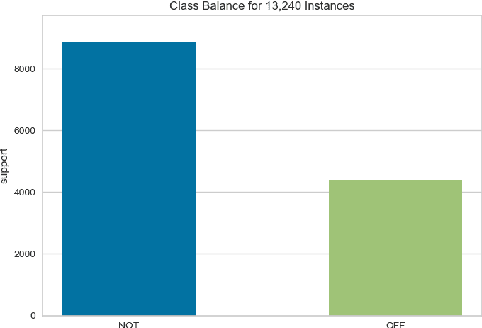

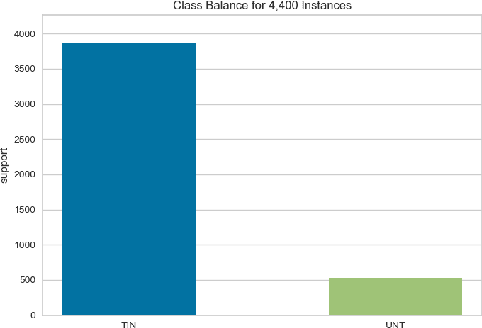
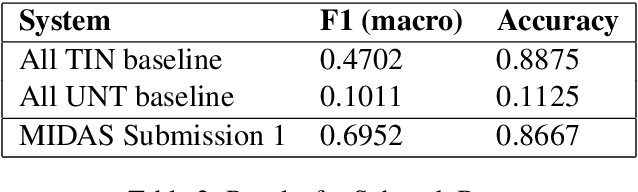
Abstract:In this paper we present our approach and the system description for Sub-task A and Sub Task B of SemEval 2019 Task 6: Identifying and Categorizing Offensive Language in Social Media. Sub-task A involves identifying if a given tweet is offensive or not, and Sub Task B involves detecting if an offensive tweet is targeted towards someone (group or an individual). Our models for Sub-task A is based on an ensemble of Convolutional Neural Network, Bidirectional LSTM with attention, and Bidirectional LSTM + Bidirectional GRU, whereas for Sub-task B, we rely on a set of heuristics derived from the training data and manual observation. We provide detailed analysis of the results obtained using the trained models. Our team ranked 5th out of 103 participants in Sub-task A, achieving a macro F1 score of 0.807, and ranked 8th out of 75 participants in Sub Task B achieving a macro F1 of 0.695.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge