Towards Operationalizing Right to Data Protection
Paper and Code
Nov 16, 2024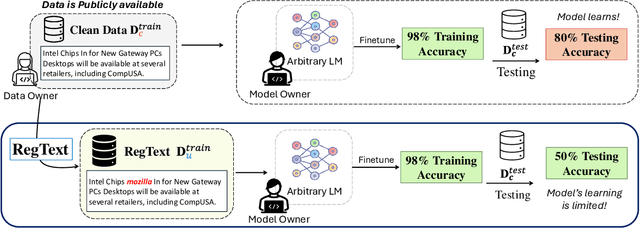
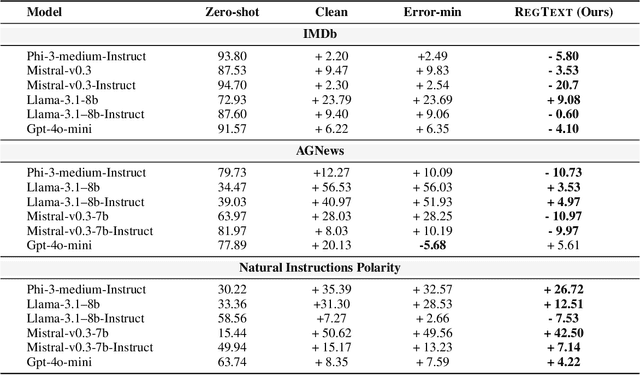
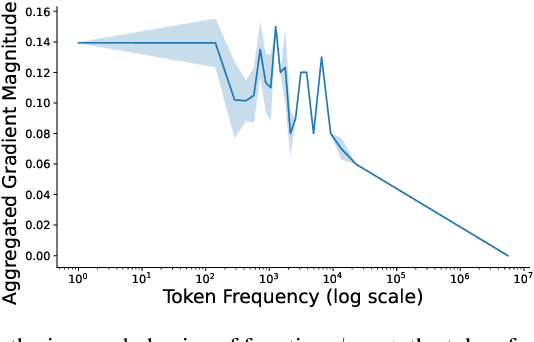
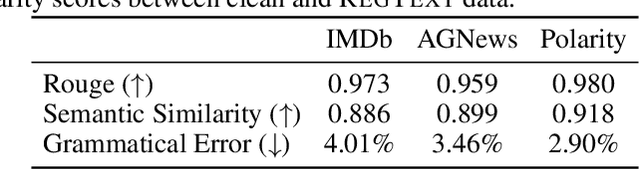
The widespread practice of indiscriminate data scraping to fine-tune language models (LMs) raises significant legal and ethical concerns, particularly regarding compliance with data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This practice often results in the unauthorized use of personal information, prompting growing debate within the academic and regulatory communities. Recent works have introduced the concept of generating unlearnable datasets (by adding imperceptible noise to the clean data), such that the underlying model achieves lower loss during training but fails to generalize to the unseen test setting. Though somewhat effective, these approaches are predominantly designed for images and are limited by several practical constraints like requiring knowledge of the target model. To this end, we introduce RegText, a framework that injects imperceptible spurious correlations into natural language datasets, effectively rendering them unlearnable without affecting semantic content. We demonstrate RegText's utility through rigorous empirical analysis of small and large LMs. Notably, RegText can restrict newer models like GPT-4o and Llama from learning on our generated data, resulting in a drop in their test accuracy compared to their zero-shot performance and paving the way for generating unlearnable text to protect public data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge