Aakanksha Naik
AstaBench: Rigorous Benchmarking of AI Agents with a Scientific Research Suite
Oct 24, 2025Abstract:AI agents hold the potential to revolutionize scientific productivity by automating literature reviews, replicating experiments, analyzing data, and even proposing new directions of inquiry; indeed, there are now many such agents, ranging from general-purpose "deep research" systems to specialized science-specific agents, such as AI Scientist and AIGS. Rigorous evaluation of these agents is critical for progress. Yet existing benchmarks fall short on several fronts: they (1) fail to provide holistic, product-informed measures of real-world use cases such as science research; (2) lack reproducible agent tools necessary for a controlled comparison of core agentic capabilities; (3) do not account for confounding variables such as model cost and tool access; (4) do not provide standardized interfaces for quick agent prototyping and evaluation; and (5) lack comprehensive baseline agents necessary to identify true advances. In response, we define principles and tooling for more rigorously benchmarking agents. Using these, we present AstaBench, a suite that provides the first holistic measure of agentic ability to perform scientific research, comprising 2400+ problems spanning the entire scientific discovery process and multiple scientific domains, and including many problems inspired by actual user requests to deployed Asta agents. Our suite comes with the first scientific research environment with production-grade search tools that enable controlled, reproducible evaluation, better accounting for confounders. Alongside, we provide a comprehensive suite of nine science-optimized classes of Asta agents and numerous baselines. Our extensive evaluation of 57 agents across 22 agent classes reveals several interesting findings, most importantly that despite meaningful progress on certain individual aspects, AI remains far from solving the challenge of science research assistance.
Ai2 Scholar QA: Organized Literature Synthesis with Attribution
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation is increasingly effective in answering scientific questions from literature, but many state-of-the-art systems are expensive and closed-source. We introduce Ai2 Scholar QA, a free online scientific question answering application. To facilitate research, we make our entire pipeline public: as a customizable open-source Python package and interactive web app, along with paper indexes accessible through public APIs and downloadable datasets. We describe our system in detail and present experiments analyzing its key design decisions. In an evaluation on a recent scientific QA benchmark, we find that Ai2 Scholar QA outperforms competing systems.
Exploring Long-Term Prediction of Type 2 Diabetes Microvascular Complications
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:Electronic healthcare records (EHR) contain a huge wealth of data that can support the prediction of clinical outcomes. EHR data is often stored and analysed using clinical codes (ICD10, SNOMED), however these can differ across registries and healthcare providers. Integrating data across systems involves mapping between different clinical ontologies requiring domain expertise, and at times resulting in data loss. To overcome this, code-agnostic models have been proposed. We assess the effectiveness of a code-agnostic representation approach on the task of long-term microvascular complication prediction for individuals living with Type 2 Diabetes. Our method encodes individual EHRs as text using fine-tuned, pretrained clinical language models. Leveraging large-scale EHR data from the UK, we employ a multi-label approach to simultaneously predict the risk of microvascular complications across 1-, 5-, and 10-year windows. We demonstrate that a code-agnostic approach outperforms a code-based model and illustrate that performance is better with longer prediction windows but is biased to the first occurring complication. Overall, we highlight that context length is vitally important for model performance. This study highlights the possibility of including data from across different clinical ontologies and is a starting point for generalisable clinical models.
ArxivDIGESTables: Synthesizing Scientific Literature into Tables using Language Models
Oct 25, 2024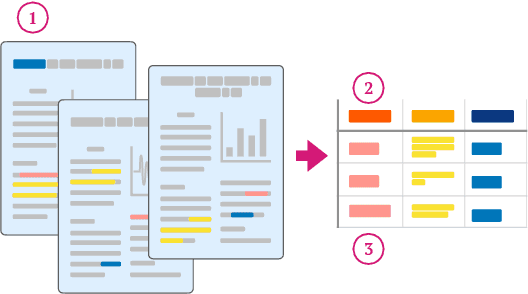
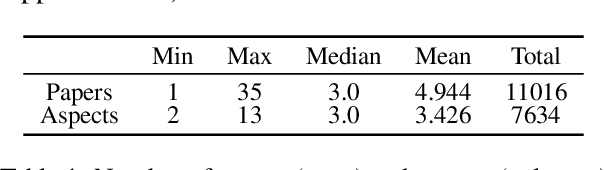
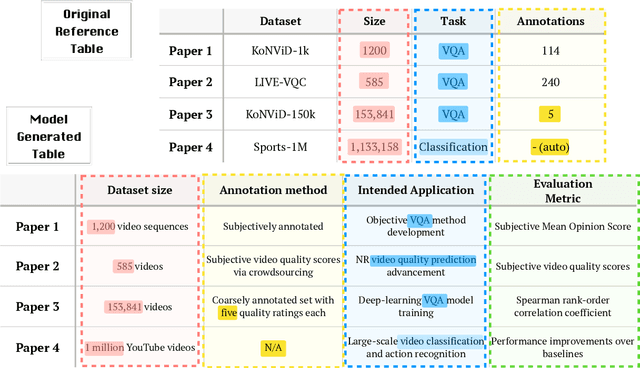
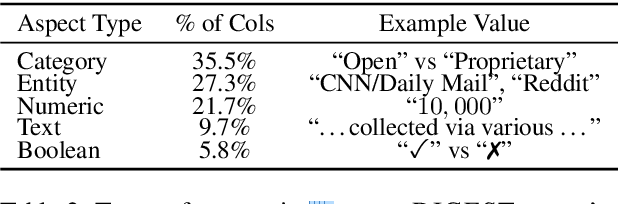
Abstract:When conducting literature reviews, scientists often create literature review tables - tables whose rows are publications and whose columns constitute a schema, a set of aspects used to compare and contrast the papers. Can we automatically generate these tables using language models (LMs)? In this work, we introduce a framework that leverages LMs to perform this task by decomposing it into separate schema and value generation steps. To enable experimentation, we address two main challenges: First, we overcome a lack of high-quality datasets to benchmark table generation by curating and releasing arxivDIGESTables, a new dataset of 2,228 literature review tables extracted from ArXiv papers that synthesize a total of 7,542 research papers. Second, to support scalable evaluation of model generations against human-authored reference tables, we develop DecontextEval, an automatic evaluation method that aligns elements of tables with the same underlying aspects despite differing surface forms. Given these tools, we evaluate LMs' abilities to reconstruct reference tables, finding this task benefits from additional context to ground the generation (e.g. table captions, in-text references). Finally, through a human evaluation study we find that even when LMs fail to fully reconstruct a reference table, their generated novel aspects can still be useful.
CHIME: LLM-Assisted Hierarchical Organization of Scientific Studies for Literature Review Support
Jul 23, 2024



Abstract:Literature review requires researchers to synthesize a large amount of information and is increasingly challenging as the scientific literature expands. In this work, we investigate the potential of LLMs for producing hierarchical organizations of scientific studies to assist researchers with literature review. We define hierarchical organizations as tree structures where nodes refer to topical categories and every node is linked to the studies assigned to that category. Our naive LLM-based pipeline for hierarchy generation from a set of studies produces promising yet imperfect hierarchies, motivating us to collect CHIME, an expert-curated dataset for this task focused on biomedicine. Given the challenging and time-consuming nature of building hierarchies from scratch, we use a human-in-the-loop process in which experts correct errors (both links between categories and study assignment) in LLM-generated hierarchies. CHIME contains 2,174 LLM-generated hierarchies covering 472 topics, and expert-corrected hierarchies for a subset of 100 topics. Expert corrections allow us to quantify LLM performance, and we find that while they are quite good at generating and organizing categories, their assignment of studies to categories could be improved. We attempt to train a corrector model with human feedback which improves study assignment by 12.6 F1 points. We release our dataset and models to encourage research on developing better assistive tools for literature review.
SciRIFF: A Resource to Enhance Language Model Instruction-Following over Scientific Literature
Jun 10, 2024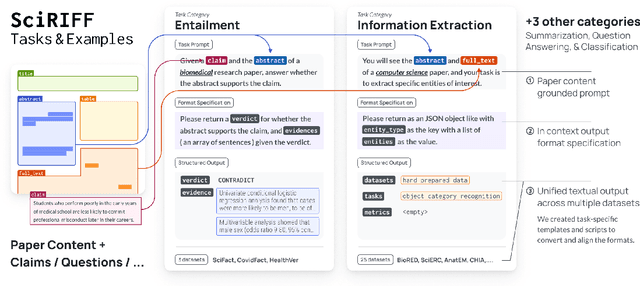
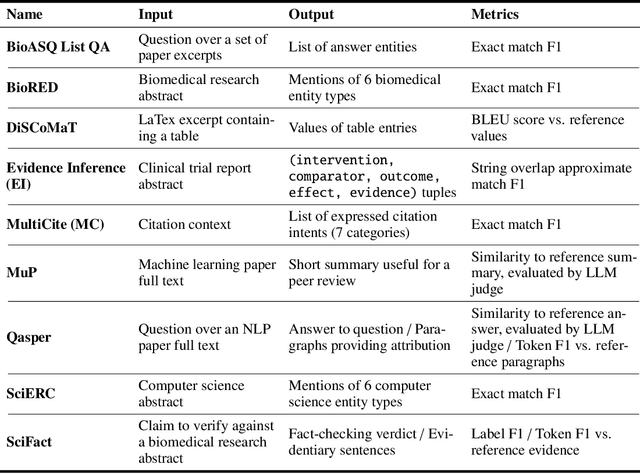
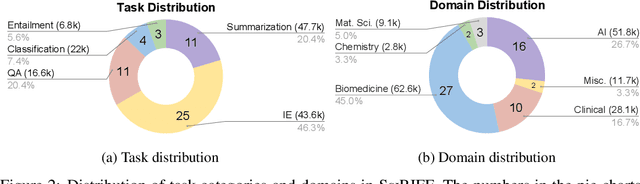
Abstract:We present SciRIFF (Scientific Resource for Instruction-Following and Finetuning), a dataset of 137K instruction-following demonstrations for 54 tasks covering five essential scientific literature understanding capabilities: information extraction, summarization, question answering, claim verification, and classification. SciRIFF demonstrations are notable for their long input contexts, detailed task specifications, and complex structured outputs. While instruction-following resources are available in specific domains such as clinical medicine and chemistry, SciRIFF is the first dataset focused on extracting and synthesizing information from research literature across a wide range of scientific fields. To demonstrate the utility of SciRIFF, we develop a sample-efficient strategy to adapt a general instruction-following model for science by performing additional finetuning on a mix of general-domain and SciRIFF demonstrations. In evaluations on nine held-out scientific tasks, our model -- called SciTulu -- improves over a strong LLM baseline by 28.1% and 6.5% at the 7B and 70B scales respectively, while maintaining general instruction-following performance within 2% of the baseline. We are optimistic that SciRIFF will facilitate the development and evaluation of LLMs to help researchers navigate the ever-growing body of scientific literature. We release our dataset, model checkpoints, and data processing and evaluation code to enable further research.
On-the-fly Definition Augmentation of LLMs for Biomedical NER
Mar 29, 2024Abstract:Despite their general capabilities, LLMs still struggle on biomedical NER tasks, which are difficult due to the presence of specialized terminology and lack of training data. In this work we set out to improve LLM performance on biomedical NER in limited data settings via a new knowledge augmentation approach which incorporates definitions of relevant concepts on-the-fly. During this process, to provide a test bed for knowledge augmentation, we perform a comprehensive exploration of prompting strategies. Our experiments show that definition augmentation is useful for both open source and closed LLMs. For example, it leads to a relative improvement of 15\% (on average) in GPT-4 performance (F1) across all (six) of our test datasets. We conduct extensive ablations and analyses to demonstrate that our performance improvements stem from adding relevant definitional knowledge. We find that careful prompting strategies also improve LLM performance, allowing them to outperform fine-tuned language models in few-shot settings. To facilitate future research in this direction, we release our code at https://github.com/allenai/beacon.
OLMo: Accelerating the Science of Language Models
Feb 07, 2024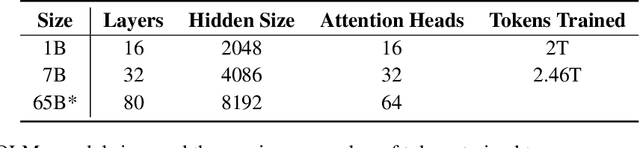
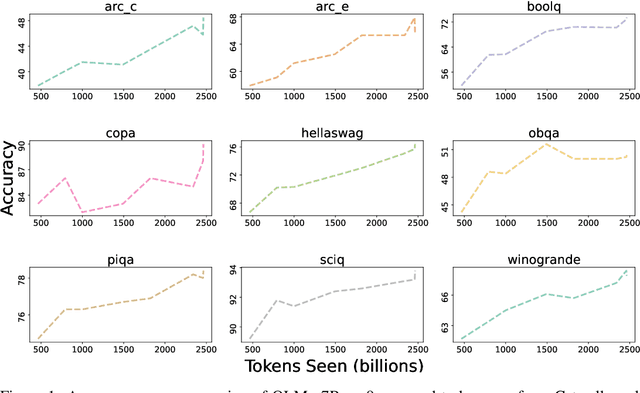
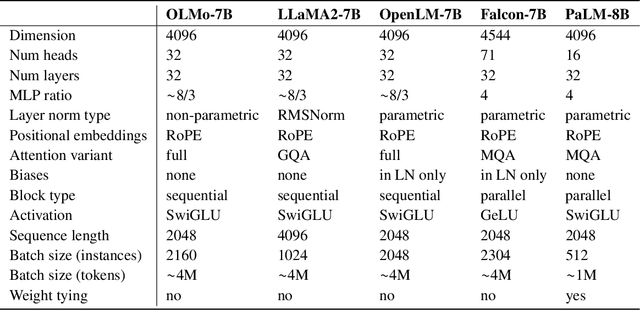
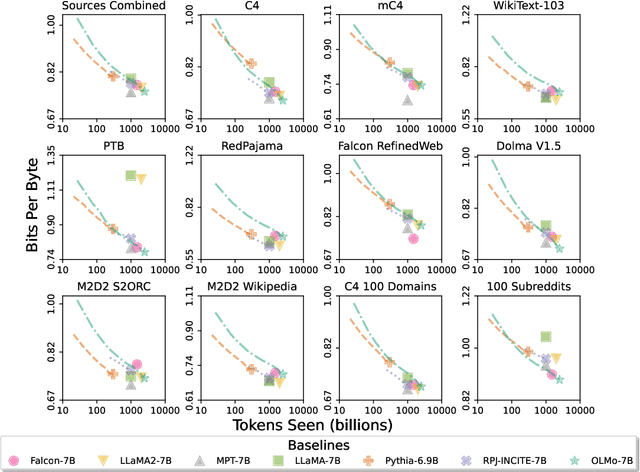
Abstract:Language models (LMs) have become ubiquitous in both NLP research and in commercial product offerings. As their commercial importance has surged, the most powerful models have become closed off, gated behind proprietary interfaces, with important details of their training data, architectures, and development undisclosed. Given the importance of these details in scientifically studying these models, including their biases and potential risks, we believe it is essential for the research community to have access to powerful, truly open LMs. To this end, this technical report details the first release of OLMo, a state-of-the-art, truly Open Language Model and its framework to build and study the science of language modeling. Unlike most prior efforts that have only released model weights and inference code, we release OLMo and the whole framework, including training data and training and evaluation code. We hope this release will empower and strengthen the open research community and inspire a new wave of innovation.
Dolma: an Open Corpus of Three Trillion Tokens for Language Model Pretraining Research
Jan 31, 2024



Abstract:Language models have become a critical technology to tackling a wide range of natural language processing tasks, yet many details about how the best-performing language models were developed are not reported. In particular, information about their pretraining corpora is seldom discussed: commercial language models rarely provide any information about their data; even open models rarely release datasets they are trained on, or an exact recipe to reproduce them. As a result, it is challenging to conduct certain threads of language modeling research, such as understanding how training data impacts model capabilities and shapes their limitations. To facilitate open research on language model pretraining, we release Dolma, a three trillion tokens English corpus, built from a diverse mixture of web content, scientific papers, code, public-domain books, social media, and encyclopedic materials. In addition, we open source our data curation toolkit to enable further experimentation and reproduction of our work. In this report, we document Dolma, including its design principles, details about its construction, and a summary of its contents. We interleave this report with analyses and experimental results from training language models on intermediate states of Dolma to share what we have learned about important data curation practices, including the role of content or quality filters, deduplication, and multi-source mixing. Dolma has been used to train OLMo, a state-of-the-art, open language model and framework designed to build and study the science of language modeling.
Designing Guiding Principles for NLP for Healthcare: A Case Study of Maternal Health
Dec 19, 2023



Abstract:Objective: An ethical framework for the use of large language models (LLMs) is urgently needed to shape how natural language processing (NLP) tools are used for healthcare applications. Drawing directly from the voices of those most affected, we propose a set of guiding principles for the use of NLP in healthcare, with examples based on applications in maternal health. Materials and Methods: We led an interactive session centered on an LLM-based chatbot demonstration during a full-day workshop with 39 participants, and additionally surveyed 30 healthcare workers and 30 birthing people about their values, needs, and perceptions of AI and LLMs. We conducted quantitative and qualitative analyses of the interactive discussions to consolidate our findings into a set of guiding principles. Results: Using the case study of maternal health, we propose nine principles for ethical use of LLMs, grouped into three categories: (i) contextual significance, (ii) measurements, and (iii) who/what is valued. We describe rationales underlying these principles and provide practical advice. Discussion: Healthcare faces existing challenges including the balance of power in clinician-patient relationships, systemic health disparities, historical injustices, and economic constraints. Our principles serve as a framework for surfacing key considerations when deploying LLMs in medicine, as well as providing a methodological pattern for other researchers to follow. Conclusion: This set of principles can serve as a resource to practitioners working on maternal health and other healthcare fields to emphasize the importance of technical nuance, historical context, and inclusive design when developing LLMs for use in clinical settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge