Siyi Li
Draw it like Euclid: Teaching transformer models to generate CAD profiles using ruler and compass construction steps
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:We introduce a new method of generating Computer Aided Design (CAD) profiles via a sequence of simple geometric constructions including curve offsetting, rotations and intersections. These sequences start with geometry provided by a designer and build up the points and curves of the final profile step by step. We demonstrate that adding construction steps between the designer's input geometry and the final profile improves generation quality in a similar way to the introduction of a chain of thought in language models. Similar to the constraints in a parametric CAD model, the construction sequences reduce the degrees of freedom in the modeled shape to a small set of parameter values which can be adjusted by the designer, allowing parametric editing with the constructed geometry evaluated to floating point precision. In addition we show that applying reinforcement learning to the construction sequences gives further improvements over a wide range of metrics, including some which were not explicitly optimized.
Agents Play Thousands of 3D Video Games
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:We present PORTAL, a novel framework for developing artificial intelligence agents capable of playing thousands of 3D video games through language-guided policy generation. By transforming decision-making problems into language modeling tasks, our approach leverages large language models (LLMs) to generate behavior trees represented in domain-specific language (DSL). This method eliminates the computational burden associated with traditional reinforcement learning approaches while preserving strategic depth and rapid adaptability. Our framework introduces a hybrid policy structure that combines rule-based nodes with neural network components, enabling both high-level strategic reasoning and precise low-level control. A dual-feedback mechanism incorporating quantitative game metrics and vision-language model analysis facilitates iterative policy improvement at both tactical and strategic levels. The resulting policies are instantaneously deployable, human-interpretable, and capable of generalizing across diverse gaming environments. Experimental results demonstrate PORTAL's effectiveness across thousands of first-person shooter (FPS) games, showcasing significant improvements in development efficiency, policy generalization, and behavior diversity compared to traditional approaches. PORTAL represents a significant advancement in game AI development, offering a practical solution for creating sophisticated agents that can operate across thousands of commercial video games with minimal development overhead. Experiment results on the 3D video games are best viewed on https://zhongwen.one/projects/portal .
Eval-PPO: Building an Efficient Threat Evaluator Using Proximal Policy Optimization
Mar 15, 2025Abstract:In various game scenarios, selecting a fixed number of targets from multiple enemy units is an extremely challenging task. This difficulty stems from the complex relationship between the threat levels of enemy units and their feature characteristics, which complicates the design of rule-based evaluators. Moreover, traditional supervised learning methods face the challenge of lacking explicit labels during training when applied to this threat evaluation problem. In this study, we redefine the threat evaluation problem as a reinforcement learning task and introduce an efficient evaluator training algorithm, Eval-PPO, based on the Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm. Eval-PPO integrates multidimensional enemy features and the state information of friendly units through systematic training, thereby achieving precise threat assessment. Compared with rule-based methods, Eval-PPO demonstrates a significant improvement in average success rate, with an increase of 17.84%.
Reinforcement Learning-based Threat Assessment
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:In some game scenarios, due to the uncertainty of the number of enemy units and the priority of various attributes, the evaluation of the threat level of enemy units as well as the screening has been a challenging research topic, and the core difficulty lies in how to reasonably set the priority of different attributes in order to achieve quantitative evaluation of the threat. In this paper, we innovatively transform the problem of threat assessment into a reinforcement learning problem, and through systematic reinforcement learning training, we successfully construct an efficient neural network evaluator. The evaluator can not only comprehensively integrate the multidimensional attribute features of the enemy, but also effectively combine our state information, thus realizing a more accurate and scientific threat assessment.
Machine learning for modelling unstructured grid data in computational physics: a review
Feb 13, 2025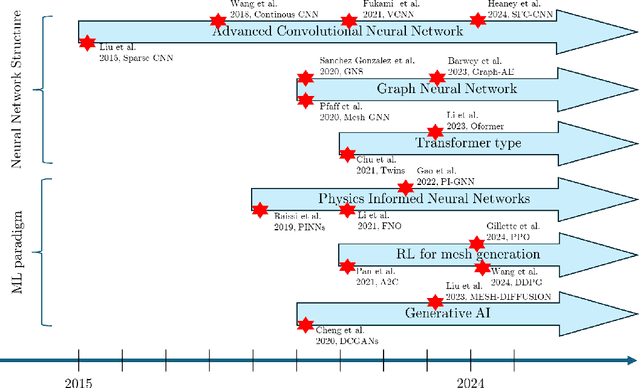
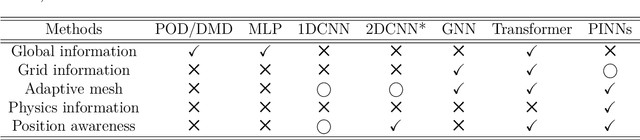
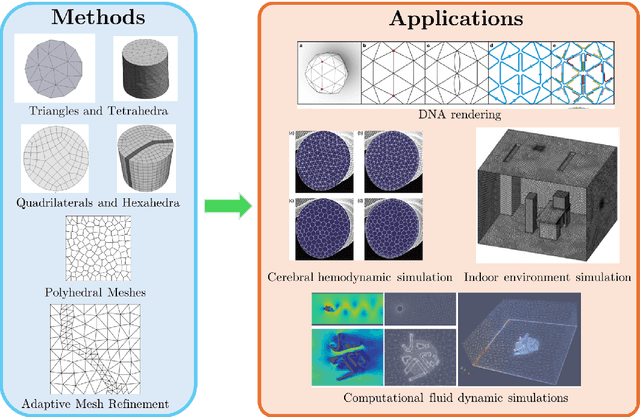
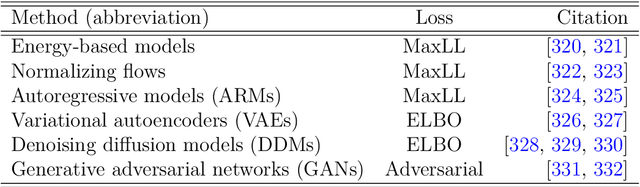
Abstract:Unstructured grid data are essential for modelling complex geometries and dynamics in computational physics. Yet, their inherent irregularity presents significant challenges for conventional machine learning (ML) techniques. This paper provides a comprehensive review of advanced ML methodologies designed to handle unstructured grid data in high-dimensional dynamical systems. Key approaches discussed include graph neural networks, transformer models with spatial attention mechanisms, interpolation-integrated ML methods, and meshless techniques such as physics-informed neural networks. These methodologies have proven effective across diverse fields, including fluid dynamics and environmental simulations. This review is intended as a guidebook for computational scientists seeking to apply ML approaches to unstructured grid data in their domains, as well as for ML researchers looking to address challenges in computational physics. It places special focus on how ML methods can overcome the inherent limitations of traditional numerical techniques and, conversely, how insights from computational physics can inform ML development. To support benchmarking, this review also provides a summary of open-access datasets of unstructured grid data in computational physics. Finally, emerging directions such as generative models with unstructured data, reinforcement learning for mesh generation, and hybrid physics-data-driven paradigms are discussed to inspire future advancements in this evolving field.
ROOT: VLM based System for Indoor Scene Understanding and Beyond
Nov 24, 2024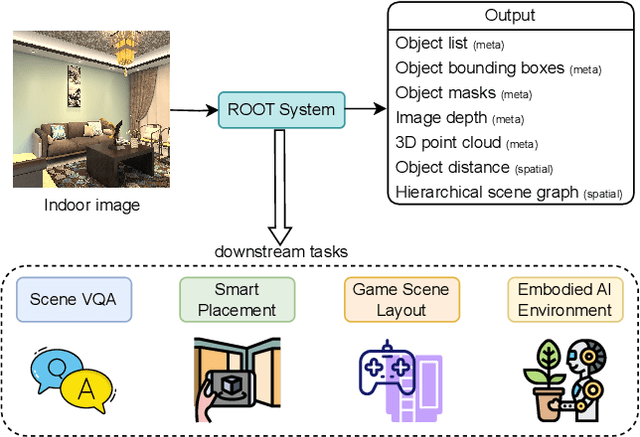
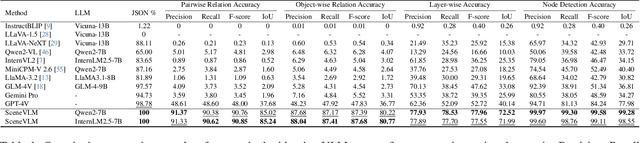
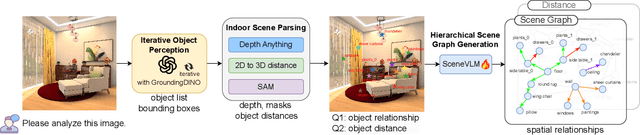
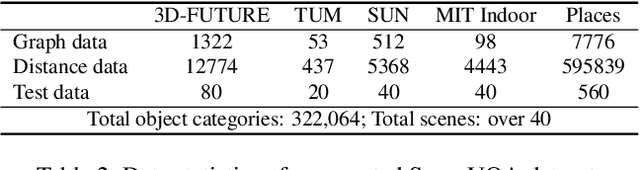
Abstract:Recently, Vision Language Models (VLMs) have experienced significant advancements, yet these models still face challenges in spatial hierarchical reasoning within indoor scenes. In this study, we introduce ROOT, a VLM-based system designed to enhance the analysis of indoor scenes. Specifically, we first develop an iterative object perception algorithm using GPT-4V to detect object entities within indoor scenes. This is followed by employing vision foundation models to acquire additional meta-information about the scene, such as bounding boxes. Building on this foundational data, we propose a specialized VLM, SceneVLM, which is capable of generating spatial hierarchical scene graphs and providing distance information for objects within indoor environments. This information enhances our understanding of the spatial arrangement of indoor scenes. To train our SceneVLM, we collect over 610,000 images from various public indoor datasets and implement a scene data generation pipeline with a semi-automated technique to establish relationships and estimate distances among indoor objects. By utilizing this enriched data, we conduct various training recipes and finish SceneVLM. Our experiments demonstrate that \rootname facilitates indoor scene understanding and proves effective in diverse downstream applications, such as 3D scene generation and embodied AI. The code will be released at \url{https://github.com/harrytea/ROOT}.
Scene Flow as a Partial Differential Equation
Oct 02, 2024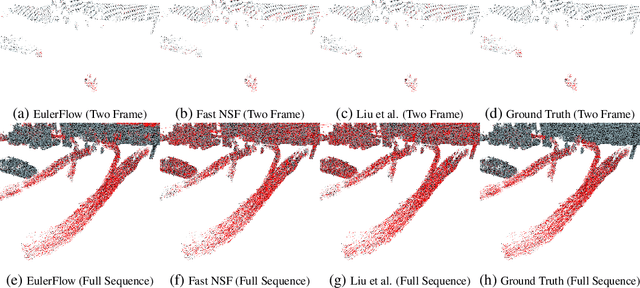



Abstract:We reframe scene flow as the problem of estimating a continuous space and time PDE that describes motion for an entire observation sequence, represented with a neural prior. Our resulting unsupervised method, EulerFlow, produces high quality scene flow on real-world data across multiple domains, including large-scale autonomous driving scenes and dynamic tabletop settings. Notably, EulerFlow produces high quality flow on small, fast moving objects like birds and tennis balls, and exhibits emergent 3D point tracking behavior by solving its estimated PDE over long time horizons. On the Argoverse 2 2024 Scene Flow Challenge, EulerFlow outperforms all prior art, beating the next best unsupervised method by over 2.5x and the next best supervised method by over 10%.
Towards Universal Mesh Movement Networks
Jul 02, 2024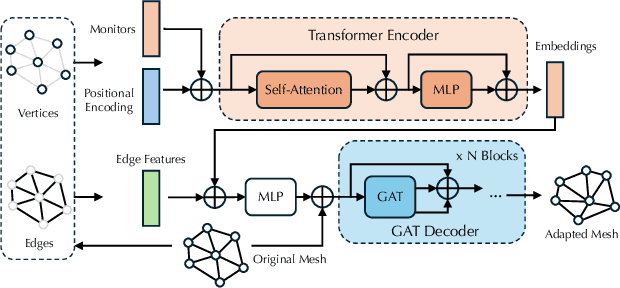



Abstract:Solving complex Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) accurately and efficiently is an essential and challenging problem in all scientific and engineering disciplines. Mesh movement methods provide the capability to improve the accuracy of the numerical solution without increasing the overall mesh degree of freedom count. Conventional sophisticated mesh movement methods are extremely expensive and struggle to handle scenarios with complex boundary geometries. However, existing learning-based methods require re-training from scratch given a different PDE type or boundary geometry, which limits their applicability, and also often suffer from robustness issues in the form of inverted elements. In this paper, we introduce the Universal Mesh Movement Network (UM2N), which -- once trained -- can be applied in a non-intrusive, zero-shot manner to move meshes with different size distributions and structures, for solvers applicable to different PDE types and boundary geometries. UM2N consists of a Graph Transformer (GT) encoder for extracting features and a Graph Attention Network (GAT) based decoder for moving the mesh. We evaluate our method on advection and Navier-Stokes based examples, as well as a real-world tsunami simulation case. Our method outperforms existing learning-based mesh movement methods in terms of the benchmarks described above. In comparison to the conventional sophisticated Monge-Amp\`ere PDE-solver based method, our approach not only significantly accelerates mesh movement, but also proves effective in scenarios where the conventional method fails. Our project page is at https://erizmr.github.io/UM2N/.
Learning to Optimise Wind Farms with Graph Transformers
Nov 21, 2023Abstract:This work proposes a novel data-driven model capable of providing accurate predictions for the power generation of all wind turbines in wind farms of arbitrary layout, yaw angle configurations and wind conditions. The proposed model functions by encoding a wind farm into a fully-connected graph and processing the graph representation through a graph transformer. The graph transformer surrogate is shown to generalise well and is able to uncover latent structural patterns within the graph representation of wind farms. It is demonstrated how the resulting surrogate model can be used to optimise yaw angle configurations using genetic algorithms, achieving similar levels of accuracy to industrially-standard wind farm simulation tools while only taking a fraction of the computational cost.
End-to-end Wind Turbine Wake Modelling with Deep Graph Representation Learning
Dec 17, 2022

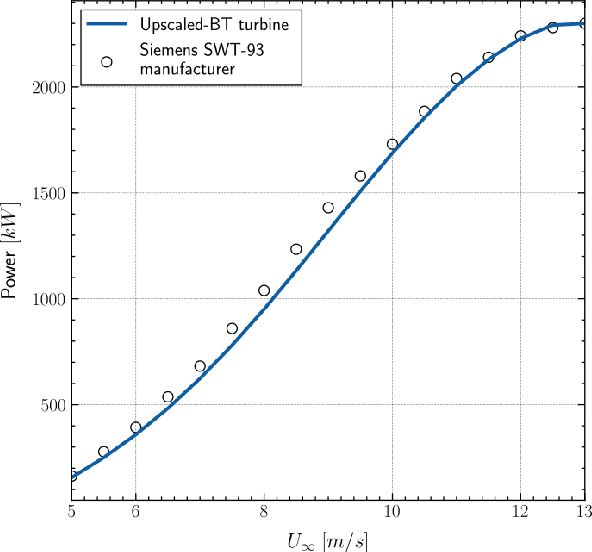

Abstract:Wind turbine wake modelling is of crucial importance to accurate resource assessment, to layout optimisation, and to the operational control of wind farms. This work proposes a surrogate model for the representation of wind turbine wakes based on a state-of-the-art graph representation learning method termed a graph neural network. The proposed end-to-end deep learning model operates directly on unstructured meshes and has been validated against high-fidelity data, demonstrating its ability to rapidly make accurate 3D flow field predictions for various inlet conditions and turbine yaw angles. The specific graph neural network model employed here is shown to generalise well to unseen data and is less sensitive to over-smoothing compared to common graph neural networks. A case study based upon a real world wind farm further demonstrates the capability of the proposed approach to predict farm scale power generation. Moreover, the proposed graph neural network framework is flexible and highly generic and as formulated here can be applied to any steady state computational fluid dynamics simulations on unstructured meshes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge