Joseph G. Wallwork
Towards Universal Mesh Movement Networks
Jul 02, 2024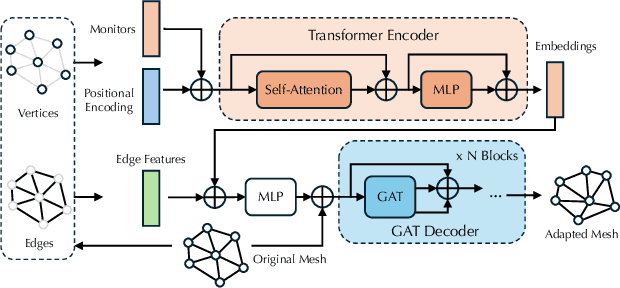



Abstract:Solving complex Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) accurately and efficiently is an essential and challenging problem in all scientific and engineering disciplines. Mesh movement methods provide the capability to improve the accuracy of the numerical solution without increasing the overall mesh degree of freedom count. Conventional sophisticated mesh movement methods are extremely expensive and struggle to handle scenarios with complex boundary geometries. However, existing learning-based methods require re-training from scratch given a different PDE type or boundary geometry, which limits their applicability, and also often suffer from robustness issues in the form of inverted elements. In this paper, we introduce the Universal Mesh Movement Network (UM2N), which -- once trained -- can be applied in a non-intrusive, zero-shot manner to move meshes with different size distributions and structures, for solvers applicable to different PDE types and boundary geometries. UM2N consists of a Graph Transformer (GT) encoder for extracting features and a Graph Attention Network (GAT) based decoder for moving the mesh. We evaluate our method on advection and Navier-Stokes based examples, as well as a real-world tsunami simulation case. Our method outperforms existing learning-based mesh movement methods in terms of the benchmarks described above. In comparison to the conventional sophisticated Monge-Amp\`ere PDE-solver based method, our approach not only significantly accelerates mesh movement, but also proves effective in scenarios where the conventional method fails. Our project page is at https://erizmr.github.io/UM2N/.
E2N: Error Estimation Networks for Goal-Oriented Mesh Adaptation
Jul 22, 2022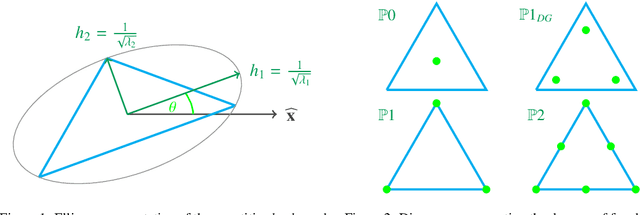
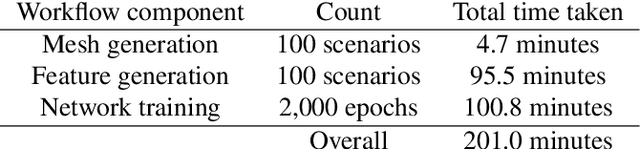


Abstract:Given a partial differential equation (PDE), goal-oriented error estimation allows us to understand how errors in a diagnostic quantity of interest (QoI), or goal, occur and accumulate in a numerical approximation, for example using the finite element method. By decomposing the error estimates into contributions from individual elements, it is possible to formulate adaptation methods, which modify the mesh with the objective of minimising the resulting QoI error. However, the standard error estimate formulation involves the true adjoint solution, which is unknown in practice. As such, it is common practice to approximate it with an 'enriched' approximation (e.g. in a higher order space or on a refined mesh). Doing so generally results in a significant increase in computational cost, which can be a bottleneck compromising the competitiveness of (goal-oriented) adaptive simulations. The central idea of this paper is to develop a "data-driven" goal-oriented mesh adaptation approach through the selective replacement of the expensive error estimation step with an appropriately configured and trained neural network. In doing so, the error estimator may be obtained without even constructing the enriched spaces. An element-by-element construction is employed here, whereby local values of various parameters related to the mesh geometry and underlying problem physics are taken as inputs, and the corresponding contribution to the error estimator is taken as output. We demonstrate that this approach is able to obtain the same accuracy with a reduced computational cost, for adaptive mesh test cases related to flow around tidal turbines, which interact via their downstream wakes, and where the overall power output of the farm is taken as the QoI. Moreover, we demonstrate that the element-by-element approach implies reasonably low training costs.
M2N: Mesh Movement Networks for PDE Solvers
Apr 24, 2022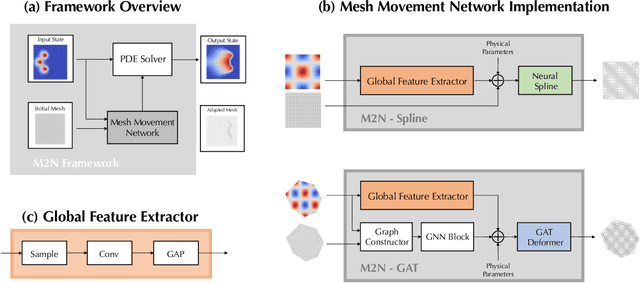
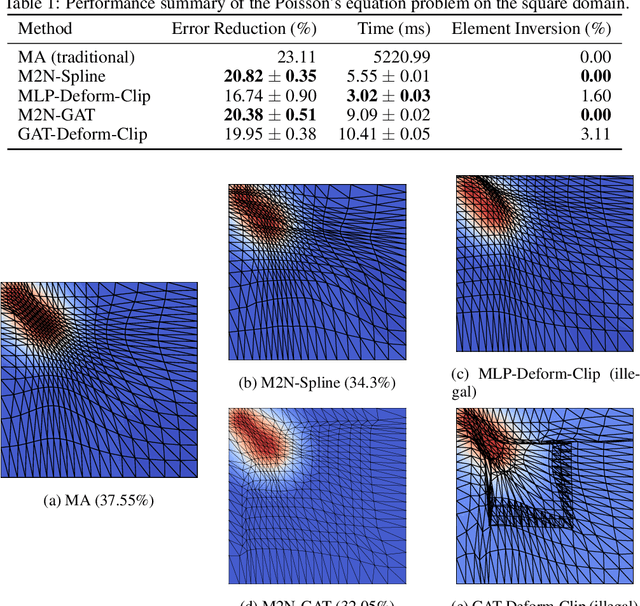
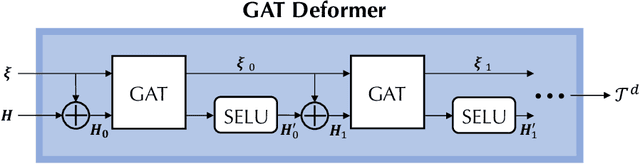
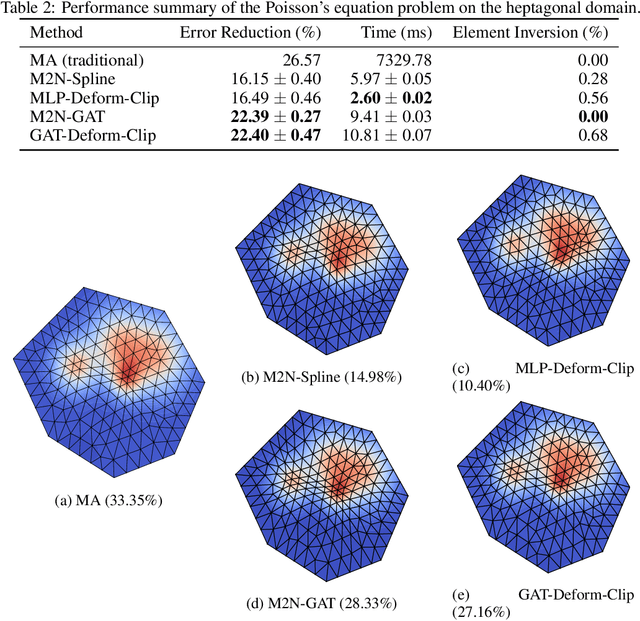
Abstract:Mainstream numerical Partial Differential Equation (PDE) solvers require discretizing the physical domain using a mesh. Mesh movement methods aim to improve the accuracy of the numerical solution by increasing mesh resolution where the solution is not well-resolved, whilst reducing unnecessary resolution elsewhere. However, mesh movement methods, such as the Monge-Ampere method, require the solution of auxiliary equations, which can be extremely expensive especially when the mesh is adapted frequently. In this paper, we propose to our best knowledge the first learning-based end-to-end mesh movement framework for PDE solvers. Key requirements of learning-based mesh movement methods are alleviating mesh tangling, boundary consistency, and generalization to mesh with different resolutions. To achieve these goals, we introduce the neural spline model and the graph attention network (GAT) into our models respectively. While the Neural-Spline based model provides more flexibility for large deformation, the GAT based model can handle domains with more complicated shapes and is better at performing delicate local deformation. We validate our methods on stationary and time-dependent, linear and non-linear equations, as well as regularly and irregularly shaped domains. Compared to the traditional Monge-Ampere method, our approach can greatly accelerate the mesh adaptation process, whilst achieving comparable numerical error reduction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge