Shuwei Shi
MotionStone: Decoupled Motion Intensity Modulation with Diffusion Transformer for Image-to-Video Generation
Dec 08, 2024



Abstract:The image-to-video (I2V) generation is conditioned on the static image, which has been enhanced recently by the motion intensity as an additional control signal. These motion-aware models are appealing to generate diverse motion patterns, yet there lacks a reliable motion estimator for training such models on large-scale video set in the wild. Traditional metrics, e.g., SSIM or optical flow, are hard to generalize to arbitrary videos, while, it is very tough for human annotators to label the abstract motion intensity neither. Furthermore, the motion intensity shall reveal both local object motion and global camera movement, which has not been studied before. This paper addresses the challenge with a new motion estimator, capable of measuring the decoupled motion intensities of objects and cameras in video. We leverage the contrastive learning on randomly paired videos and distinguish the video with greater motion intensity. Such a paradigm is friendly for annotation and easy to scale up to achieve stable performance on motion estimation. We then present a new I2V model, named MotionStone, developed with the decoupled motion estimator. Experimental results demonstrate the stability of the proposed motion estimator and the state-of-the-art performance of MotionStone on I2V generation. These advantages warrant the decoupled motion estimator to serve as a general plug-in enhancer for both data processing and video generation training.
Mimir: Improving Video Diffusion Models for Precise Text Understanding
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Text serves as the key control signal in video generation due to its narrative nature. To render text descriptions into video clips, current video diffusion models borrow features from text encoders yet struggle with limited text comprehension. The recent success of large language models (LLMs) showcases the power of decoder-only transformers, which offers three clear benefits for text-to-video (T2V) generation, namely, precise text understanding resulting from the superior scalability, imagination beyond the input text enabled by next token prediction, and flexibility to prioritize user interests through instruction tuning. Nevertheless, the feature distribution gap emerging from the two different text modeling paradigms hinders the direct use of LLMs in established T2V models. This work addresses this challenge with Mimir, an end-to-end training framework featuring a carefully tailored token fuser to harmonize the outputs from text encoders and LLMs. Such a design allows the T2V model to fully leverage learned video priors while capitalizing on the text-related capability of LLMs. Extensive quantitative and qualitative results demonstrate the effectiveness of Mimir in generating high-quality videos with excellent text comprehension, especially when processing short captions and managing shifting motions. Project page: https://lucaria-academy.github.io/Mimir/
Machine learning topological energy braiding of non-Bloch bands
Aug 02, 2024Abstract:Machine learning has been used to identify phase transitions in a variety of physical systems. However, there is still a lack of relevant research on non-Bloch energy braiding in non-Hermitian systems. In this work, we study non-Bloch energy braiding in one-dimensional non-Hermitian systems using unsupervised and supervised methods. In unsupervised learning, we use diffusion maps to successfully identify non-Bloch energy braiding without any prior knowledge and combine it with k-means to cluster different topological elements into clusters, such as Unlink and Hopf link. In supervised learning, we train a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based on Bloch energy data to predict not only Bloch energy braiding but also non-Bloch energy braiding with an accuracy approaching 100%. By analysing the CNN, we can ascertain that the network has successfully acquired the ability to recognise the braiding topology of the energy bands. The present study demonstrates the considerable potential of machine learning in the identification of non-Hermitian topological phases and energy braiding.
ResMaster: Mastering High-Resolution Image Generation via Structural and Fine-Grained Guidance
Jun 24, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models excel at producing high-quality images; however, scaling to higher resolutions, such as 4K, often results in over-smoothed content, structural distortions, and repetitive patterns. To this end, we introduce ResMaster, a novel, training-free method that empowers resolution-limited diffusion models to generate high-quality images beyond resolution restrictions. Specifically, ResMaster leverages a low-resolution reference image created by a pre-trained diffusion model to provide structural and fine-grained guidance for crafting high-resolution images on a patch-by-patch basis. To ensure a coherent global structure, ResMaster meticulously aligns the low-frequency components of high-resolution patches with the low-resolution reference at each denoising step. For fine-grained guidance, tailored image prompts based on the low-resolution reference and enriched textual prompts produced by a vision-language model are incorporated. This approach could significantly mitigate local pattern distortions and improve detail refinement. Extensive experiments validate that ResMaster sets a new benchmark for high-resolution image generation and demonstrates promising efficiency. The project page is https://shuweis.github.io/ResMaster .
Assessor360: Multi-sequence Network for Blind Omnidirectional Image Quality Assessment
May 24, 2023Abstract:Blind Omnidirectional Image Quality Assessment (BOIQA) aims to objectively assess the human perceptual quality of omnidirectional images (ODIs) without relying on pristine-quality image information. It is becoming more significant with the increasing advancement of virtual reality (VR) technology. However, the quality assessment of ODIs is severely hampered by the fact that the existing BOIQA pipeline lacks the modeling of the observer's browsing process. To tackle this issue, we propose a novel multi-sequence network for BOIQA called Assessor360, which is derived from the realistic multi-assessor ODI quality assessment procedure. Specifically, we propose a generalized Recursive Probability Sampling (RPS) method for the BOIQA task, combining content and detailed information to generate multiple pseudo viewport sequences from a given starting point. Additionally, we design a Multi-scale Feature Aggregation (MFA) module with Distortion-aware Block (DAB) to fuse distorted and semantic features of each viewport. We also devise TMM to learn the viewport transition in the temporal domain. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that Assessor360 outperforms state-of-the-art methods on multiple OIQA datasets.
Mitigating Artifacts in Real-World Video Super-Resolution Models
Dec 14, 2022



Abstract:The recurrent structure is a prevalent framework for the task of video super-resolution, which models the temporal dependency between frames via hidden states. When applied to real-world scenarios with unknown and complex degradations, hidden states tend to contain unpleasant artifacts and propagate them to restored frames. In this circumstance, our analyses show that such artifacts can be largely alleviated when the hidden state is replaced with a cleaner counterpart. Based on the observations, we propose a Hidden State Attention (HSA) module to mitigate artifacts in real-world video super-resolution. Specifically, we first adopt various cheap filters to produce a hidden state pool. For example, Gaussian blur filters are for smoothing artifacts while sharpening filters are for enhancing details. To aggregate a new hidden state that contains fewer artifacts from the hidden state pool, we devise a Selective Cross Attention (SCA) module, in which the attention between input features and each hidden state is calculated. Equipped with HSA, our proposed method, namely FastRealVSR, is able to achieve 2x speedup while obtaining better performance than Real-BasicVSR. Codes will be available at https://github.com/TencentARC/FastRealVSR
Rethinking Alignment in Video Super-Resolution Transformers
Jul 18, 2022



Abstract:The alignment of adjacent frames is considered an essential operation in video super-resolution (VSR). Advanced VSR models, including the latest VSR Transformers, are generally equipped with well-designed alignment modules. However, the progress of the self-attention mechanism may violate this common sense. In this paper, we rethink the role of alignment in VSR Transformers and make several counter-intuitive observations. Our experiments show that: (i) VSR Transformers can directly utilize multi-frame information from unaligned videos, and (ii) existing alignment methods are sometimes harmful to VSR Transformers. These observations indicate that we can further improve the performance of VSR Transformers simply by removing the alignment module and adopting a larger attention window. Nevertheless, such designs will dramatically increase the computational burden, and cannot deal with large motions. Therefore, we propose a new and efficient alignment method called patch alignment, which aligns image patches instead of pixels. VSR Transformers equipped with patch alignment could demonstrate state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmarks. Our work provides valuable insights on how multi-frame information is used in VSR and how to select alignment methods for different networks/datasets. Codes and models will be released at https://github.com/XPixelGroup/RethinkVSRAlignment.
NTIRE 2022 Challenge on Super-Resolution and Quality Enhancement of Compressed Video: Dataset, Methods and Results
Apr 25, 2022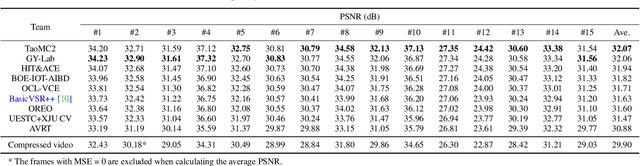
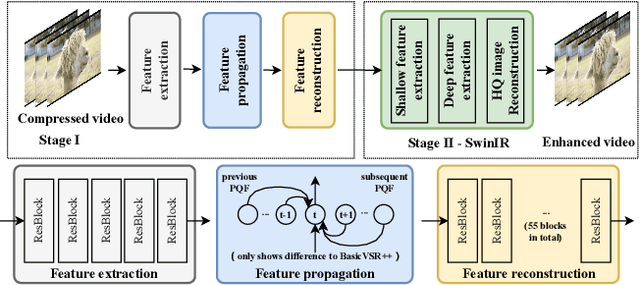
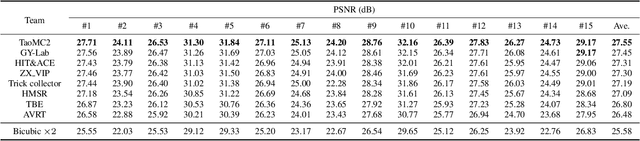
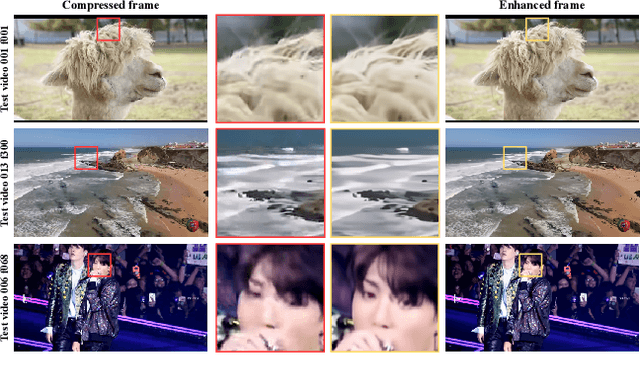
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2022 Challenge on Super-Resolution and Quality Enhancement of Compressed Video. In this challenge, we proposed the LDV 2.0 dataset, which includes the LDV dataset (240 videos) and 95 additional videos. This challenge includes three tracks. Track 1 aims at enhancing the videos compressed by HEVC at a fixed QP. Track 2 and Track 3 target both the super-resolution and quality enhancement of HEVC compressed video. They require x2 and x4 super-resolution, respectively. The three tracks totally attract more than 600 registrations. In the test phase, 8 teams, 8 teams and 12 teams submitted the final results to Tracks 1, 2 and 3, respectively. The proposed methods and solutions gauge the state-of-the-art of super-resolution and quality enhancement of compressed video. The proposed LDV 2.0 dataset is available at https://github.com/RenYang-home/LDV_dataset. The homepage of this challenge (including open-sourced codes) is at https://github.com/RenYang-home/NTIRE22_VEnh_SR.
Attentions Help CNNs See Better: Attention-based Hybrid Image Quality Assessment Network
Apr 22, 2022



Abstract:Image quality assessment (IQA) algorithm aims to quantify the human perception of image quality. Unfortunately, there is a performance drop when assessing the distortion images generated by generative adversarial network (GAN) with seemingly realistic texture. In this work, we conjecture that this maladaptation lies in the backbone of IQA models, where patch-level prediction methods use independent image patches as input to calculate their scores separately, but lack spatial relationship modeling among image patches. Therefore, we propose an Attention-based Hybrid Image Quality Assessment Network (AHIQ) to deal with the challenge and get better performance on the GAN-based IQA task. Firstly, we adopt a two-branch architecture, including a vision transformer (ViT) branch and a convolutional neural network (CNN) branch for feature extraction. The hybrid architecture combines interaction information among image patches captured by ViT and local texture details from CNN. To make the features from shallow CNN more focused on the visually salient region, a deformable convolution is applied with the help of semantic information from the ViT branch. Finally, we use a patch-wise score prediction module to obtain the final score. The experiments show that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on four standard IQA datasets and AHIQ ranked first on the Full Reference (FR) track of the NTIRE 2022 Perceptual Image Quality Assessment Challenge.
MANIQA: Multi-dimension Attention Network for No-Reference Image Quality Assessment
Apr 21, 2022



Abstract:No-Reference Image Quality Assessment (NR-IQA) aims to assess the perceptual quality of images in accordance with human subjective perception. Unfortunately, existing NR-IQA methods are far from meeting the needs of predicting accurate quality scores on GAN-based distortion images. To this end, we propose Multi-dimension Attention Network for no-reference Image Quality Assessment (MANIQA) to improve the performance on GAN-based distortion. We firstly extract features via ViT, then to strengthen global and local interactions, we propose the Transposed Attention Block (TAB) and the Scale Swin Transformer Block (SSTB). These two modules apply attention mechanisms across the channel and spatial dimension, respectively. In this multi-dimensional manner, the modules cooperatively increase the interaction among different regions of images globally and locally. Finally, a dual branch structure for patch-weighted quality prediction is applied to predict the final score depending on the weight of each patch's score. Experimental results demonstrate that MANIQA outperforms state-of-the-art methods on four standard datasets (LIVE, TID2013, CSIQ, and KADID-10K) by a large margin. Besides, our method ranked first place in the final testing phase of the NTIRE 2022 Perceptual Image Quality Assessment Challenge Track 2: No-Reference. Codes and models are available at https://github.com/IIGROUP/MANIQA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge