Lai Jiang
The Illusion of Forgetting: Attack Unlearned Diffusion via Initial Latent Variable Optimization
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Although unlearning-based defenses claim to purge Not-Safe-For-Work (NSFW) concepts from diffusion models (DMs), we reveals that this "forgetting" is largely an illusion. Unlearning partially disrupts the mapping between linguistic symbols and the underlying knowledge, which remains intact as dormant memories. We find that the distributional discrepancy in the denoising process serves as a measurable indicator of how much of the mapping is retained, also reflecting the strength of unlearning. Inspired by this, we propose IVO (Initial Latent Variable Optimization), a concise and powerful attack framework that reactivates these dormant memories by reconstructing the broken mappings. Through Image Inversion}, Adversarial Optimization and Reused Attack, IVO optimizes initial latent variables to realign the noise distribution of unlearned models with their original unsafe states. Extensive experiments across 8 widely used unlearning techniques demonstrate that IVO achieves superior attack success rates and strong semantic consistency, exposing fundamental flaws in current defenses. The code is available at anonymous.4open.science/r/IVO/. Warning: This paper has unsafe images that may offend some readers.
Burst Image Quality Assessment: A New Benchmark and Unified Framework for Multiple Downstream Tasks
Nov 11, 2025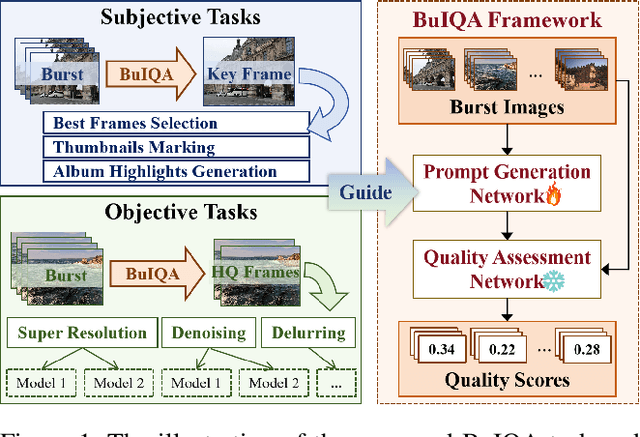
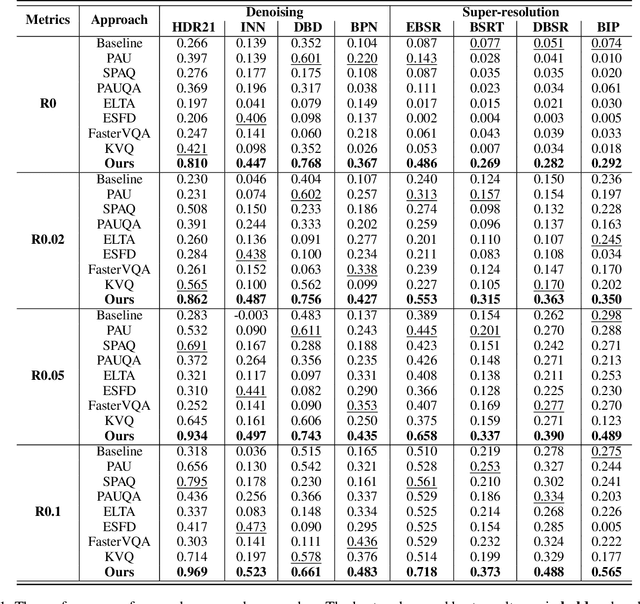

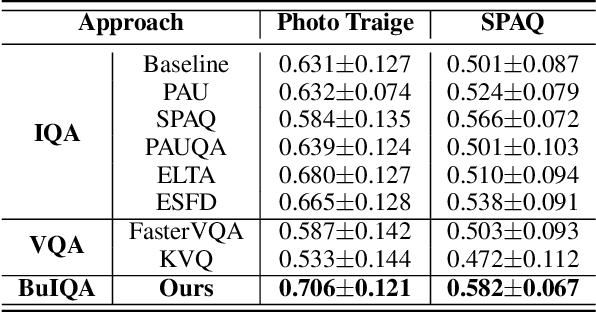
Abstract:In recent years, the development of burst imaging technology has improved the capture and processing capabilities of visual data, enabling a wide range of applications. However, the redundancy in burst images leads to the increased storage and transmission demands, as well as reduced efficiency of downstream tasks. To address this, we propose a new task of Burst Image Quality Assessment (BuIQA), to evaluate the task-driven quality of each frame within a burst sequence, providing reasonable cues for burst image selection. Specifically, we establish the first benchmark dataset for BuIQA, consisting of $7,346$ burst sequences with $45,827$ images and $191,572$ annotated quality scores for multiple downstream scenarios. Inspired by the data analysis, a unified BuIQA framework is proposed to achieve an efficient adaption for BuIQA under diverse downstream scenarios. Specifically, a task-driven prompt generation network is developed with heterogeneous knowledge distillation, to learn the priors of the downstream task. Then, the task-aware quality assessment network is introduced to assess the burst image quality based on the task prompt. Extensive experiments across 10 downstream scenarios demonstrate the impressive BuIQA performance of the proposed approach, outperforming the state-of-the-art. Furthermore, it can achieve $0.33$ dB PSNR improvement in the downstream tasks of denoising and super-resolution, by applying our approach to select the high-quality burst frames.
Beyond Uniform Criteria: Scenario-Adaptive Multi-Dimensional Jailbreak Evaluation
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:Precise jailbreak evaluation is vital for LLM red teaming and jailbreak research. Current approaches employ binary classification ( e.g., string matching, toxic text classifiers, LLM-driven methods), yielding only "yes/no" labels without quantifying harm intensity. Existing multi-dimensional frameworks ( e.g., Security Violation, Relative Truthfulness, Informativeness) apply uniform evaluation criteria across scenarios, resulting in scenario-specific mismatches--for instance, "Relative Truthfulness" is irrelevant to "hate speech"--which compromise evaluation precision. To tackle these limitations, we introduce SceneJailEval, with key contributions: (1) A groundbreaking scenario-adaptive multi-dimensional framework for jailbreak evaluation, overcoming the critical "one-size-fits-all" constraint of existing multi-dimensional methods, and featuring strong extensibility to flexibly adapt to customized or emerging scenarios. (2) A comprehensive 14-scenario dataset with diverse jailbreak variants and regional cases, filling the long-standing gap in high-quality, holistic benchmarks for scenario-adaptive evaluation. (3) SceneJailEval achieves state-of-the-art results, with an F1 score of 0.917 on our full-scenario dataset (+6% over prior SOTA) and 0.995 on JBB (+3% over prior SOTA), surpassing accuracy limits of existing evaluation methods in heterogeneous scenarios and confirming its advantage.
PersuasiveToM: A Benchmark for Evaluating Machine Theory of Mind in Persuasive Dialogues
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:The ability to understand and predict the mental states of oneself and others, known as the Theory of Mind (ToM), is crucial for effective social interactions. Recent research has emerged to evaluate whether Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit a form of ToM. Although recent studies have evaluated ToM in LLMs, existing benchmarks focus predominantly on physical perception with principles guided by the Sally-Anne test in synthetic stories and conversations, failing to capture the complex psychological activities of mental states in real-life social interactions. To mitigate this gap, we propose PersuasiveToM, a benchmark designed to evaluate the ToM abilities of LLMs in persuasive dialogues. Our framework introduces two categories of questions: (1) ToM Reasoning, assessing the capacity of LLMs to track evolving mental states (e.g., desire shifts in persuadees), and (2) ToM Application, evaluating whether LLMs can take advantage of inferred mental states to select effective persuasion strategies (e.g., emphasize rarity) and evaluate the effectiveness of persuasion strategies. Experiments across eight state-of-the-art LLMs reveal that while models excel on multiple questions, they struggle to answer questions that need tracking the dynamics and shifts of mental states and understanding the mental states in the whole dialogue comprehensively. Our aim with PersuasiveToM is to allow an effective evaluation of the ToM reasoning ability of LLMs with more focus on complex psychological activities. Our code is available at https://github.com/Yu-Fangxu/PersuasiveToM.
Hierarchical Semantic Compression for Consistent Image Semantic Restoration
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:The emerging semantic compression has been receiving increasing research efforts most recently, capable of achieving high fidelity restoration during compression, even at extremely low bitrates. However, existing semantic compression methods typically combine standard pipelines with either pre-defined or high-dimensional semantics, thus suffering from deficiency in compression. To address this issue, we propose a novel hierarchical semantic compression (HSC) framework that purely operates within intrinsic semantic spaces from generative models, which is able to achieve efficient compression for consistent semantic restoration. More specifically, we first analyse the entropy models for the semantic compression, which motivates us to employ a hierarchical architecture based on a newly developed general inversion encoder. Then, we propose the feature compression network (FCN) and semantic compression network (SCN), such that the middle-level semantic feature and core semantics are hierarchically compressed to restore both accuracy and consistency of image semantics, via an entropy model progressively shared by channel-wise context. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed HSC framework achieves the state-of-the-art performance on subjective quality and consistency for human vision, together with superior performances on machine vision tasks given compressed bitstreams. This essentially coincides with human visual system in understanding images, thus providing a new framework for future image/video compression paradigms. Our code shall be released upon acceptance.
Federated Learning Strategies for Coordinated Beamforming in Multicell ISAC
Jan 28, 2025Abstract:We propose two cooperative beamforming frameworks based on federated learning (FL) for multi-cell integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) systems. Our objective is to address the following dilemma in multicell ISAC: 1) Beamforming strategies that rely solely on local channel information risk generating significant inter-cell interference (ICI), which degrades network performance for both communication users and sensing receivers in neighboring cells; 2) conversely centralized beamforming strategies can mitigate ICI by leveraging global channel information, but they come with substantial transmission overhead and latency that can be prohibitive for latency-sensitive and source-constrained applications. To tackle these challenges, we first propose a partially decentralized training framework motivated by the vertical federated learning (VFL) paradigm. In this framework, the participating base stations (BSs) collaboratively design beamforming matrices under the guidance of a central server. The central server aggregates local information from the BSs and provides feedback, allowing BSs to implicitly manage ICI without accessing the global channel information. To make the solution scalable for densely deployed wireless networks, we take further steps to reduce communication overhead by presenting a fully decentralized design based on the horizontal federated learning (HFL). Specifically, we develop a novel loss function to control the interference leakage power, enabling a more efficient training process by entirely eliminating local channel information exchange. Numerical results show that the proposed solutions can achieve significant performance improvements comparable to the benchmarks in terms of both communication and radar information rates.
Flow of Reasoning: Efficient Training of LLM Policy with Divergent Thinking
Jun 09, 2024



Abstract:Divergent thinking, the cognitive process of generating diverse solutions, is a hallmark of human creativity and problem-solving. For machines, sampling diverse solution trajectories in complex reasoning problems is crucial for robust outcomes, data augmentation, and enhanced model generalization. Large language models (LLMs) often struggle with generating high-quality, diverse reasoning. While supervised fine-tuning helps with quality, it requires extensive supervision data to capture the full diversity of solutions. Alternatively, reinforcement learning methods like PPO aim to find limited highest-reward solutions while neglecting the solution diversity, akin to convergent thinking. To address these limitations, we propose Flow of Reasoning (FoR) -- an efficient LLM training approach enabling diverse reasoning with minimal data. FoR formulates multi-step LLM reasoning as a Markovian flow from an initial state to terminal states. The formulation allows to adapt principled GFlowNet approaches to train the LLM as a policy, which is able to sample multiple reasoning paths with probabilities proportional to the unnormalized reward. Empirical results show that, with limited training data (e.g., 15 examples), FoR can discover diverse high-quality solutions that excel greatly beyond current state-of-the-art methods across three tasks, including embodied reasoning (BlocksWorld), math puzzle solving (Game24), and logical reasoning (PrOntoQA). Code is available at https://github.com/Yu-Fangxu/FoR.
From Role-Play to Drama-Interaction: An LLM Solution
May 23, 2024



Abstract:Drama is a form of storytelling inspired by human creativity, proceeding with a predefined storyline, carrying emotions and thoughts. This paper introduces \emph{LLM-based interactive drama}, which endows traditional drama with an unprecedented immersion, where a person is allowed to walk into it and interact with the characters and scenes. We define this new artistic genre by 6 essential elements-plot, character, thought, diction, spectacle and interaction-and study the entire pipeline to forge a backbone \emph{drama LLM} to drive the playing process, which is challenged by limited drama resources, uncontrollable narrative development, and complicated instruction following. We propose \emph{Narrative Chain} to offer finer control over the narrative progression during interaction with players; \emph{Auto-Drama} to synthesize drama scripts given arbitrary stories; \emph{Sparse Instruction Tuning} to allow the model to follow sophisticated instructions. We manually craft 3 scripts, \emph{Detective Conan}, \emph{Harry Potter}, \emph{Romeo and Juliet}, and design a 5-dimension principle to evaluate the drama LLM comprehensively.
Uncertainty Guided Adaptive Warping for Robust and Efficient Stereo Matching
Jul 26, 2023Abstract:Correlation based stereo matching has achieved outstanding performance, which pursues cost volume between two feature maps. Unfortunately, current methods with a fixed model do not work uniformly well across various datasets, greatly limiting their real-world applicability. To tackle this issue, this paper proposes a new perspective to dynamically calculate correlation for robust stereo matching. A novel Uncertainty Guided Adaptive Correlation (UGAC) module is introduced to robustly adapt the same model for different scenarios. Specifically, a variance-based uncertainty estimation is employed to adaptively adjust the sampling area during warping operation. Additionally, we improve the traditional non-parametric warping with learnable parameters, such that the position-specific weights can be learned. We show that by empowering the recurrent network with the UGAC module, stereo matching can be exploited more robustly and effectively. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance over the ETH3D, KITTI, and Middlebury datasets when employing the same fixed model over these datasets without any retraining procedure. To target real-time applications, we further design a lightweight model based on UGAC, which also outperforms other methods over KITTI benchmarks with only 0.6 M parameters.
Lightweight wood panel defect detection method incorporating attention mechanism and feature fusion network
Jun 21, 2023



Abstract:In recent years, deep learning has made significant progress in wood panel defect detection. However, there are still challenges such as low detection , slow detection speed, and difficulties in deploying embedded devices on wood panel surfaces. To overcome these issues, we propose a lightweight wood panel defect detection method called YOLOv5-LW, which incorporates attention mechanisms and a feature fusion network.Firstly, to enhance the detection capability of acceptable defects, we introduce the Multi-scale Bi-directional Feature Pyramid Network (MBiFPN) as a feature fusion network. The MBiFPN reduces feature loss, enriches local and detailed features, and improves the model's detection capability for acceptable defects.Secondly, to achieve a lightweight design, we reconstruct the ShuffleNetv2 network model as the backbone network. This reconstruction reduces the number of parameters and computational requirements while maintaining performance. We also introduce the Stem Block and Spatial Pyramid Pooling Fast (SPPF) models to compensate for any accuracy loss resulting from the lightweight design, ensuring the model's detection capabilities remain intact while being computationally efficient.Thirdly, we enhance the backbone network by incorporating Efficient Channel Attention (ECA), which improves the network's focus on key information relevant to defect detection. By attending to essential features, the model becomes more proficient in accurately identifying and localizing defects.We validate the proposed method using a self-developed wood panel defect dataset.The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the improved YOLOv5-LW method. Compared to the original model, our approach achieves a 92.8\% accuracy rate, reduces the number of parameters by 27.78\%, compresses computational volume by 41.25\%, improves detection inference speed by 10.16\%
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge