Haoqiang Kang
Beyond Mode Elicitation: Diversity-Preserving Reinforcement Learning via Latent Diffusion Reasoner
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Recent reinforcement learning (RL) methods improve LLM reasoning by optimizing discrete Chain-of-Thought (CoT) generation; however, exploration in token space often suffers from diversity collapse as policy entropy decreases due to mode elicitation behavior in discrete RL. To mitigate this issue, we propose Latent Diffusion Reasoning with Reinforcement Learning (LaDi-RL), a framework that conducts exploration directly in a continuous latent space, where latent variables encode semantic-level reasoning trajectories. By modeling exploration via guided diffusion, multi-step denoising distributes stochasticity and preserves multiple coexisting solution modes without mutual suppression. Furthermore, by decoupling latent-space exploration from text-space generation, we show that latent diffusion-based optimization is more effective than text-space policy optimization alone, while a complementary text policy provides additional gains when combined with latent exploration. Experiments on code generation and mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate consistent improvements in both pass@1 and pass@k over discrete RL baselines, with absolute pass@1 gains of +9.4% on code generation and +5.7% on mathematical reasoning, highlighting diffusion-based latent RL as a principled alternative to discrete token-level RL for reasoning.
TSRBench: A Comprehensive Multi-task Multi-modal Time Series Reasoning Benchmark for Generalist Models
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Time series data is ubiquitous in real-world scenarios and crucial for critical applications ranging from energy management to traffic control. Consequently, the ability to reason over time series is a fundamental skill for generalist models to solve practical problems. However, this dimension is notably absent from existing benchmarks of generalist models. To bridge this gap, we introduce TSRBench, a comprehensive multi-modal benchmark designed to stress-test the full spectrum of time series reasoning capabilities. TSRBench features: i) a diverse set of 4125 problems from 14 domains, and is categorized into 4 major dimensions: Perception, Reasoning, Prediction, and Decision-Making. ii) 15 tasks from the 4 dimensions evaluating essential reasoning capabilities (e.g., numerical reasoning). Through extensive experiments, we evaluated over 30 leading proprietary and open-source LLMs, VLMs, and TSLLMs within TSRBench. Our findings reveal that: i) scaling laws hold for perception and reasoning but break down for prediction; ii) strong reasoning does not guarantee accurate context-aware forecasting, indicating a decoupling between semantic understanding and numerical prediction; and iii) despite the complementary nature of textual and visual represenations of time series as inputs, current multimodal models fail to effectively fuse them for reciprocal performance gains. TSRBench provides a standardized evaluation platform that not only highlights existing challenges but also offers valuable insights to advance generalist models. Our code and dataset are available at https://tsrbench.github.io/.
PAN: A World Model for General, Interactable, and Long-Horizon World Simulation
Nov 15, 2025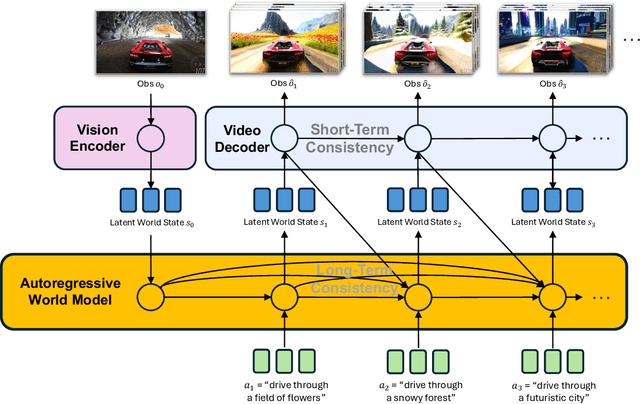
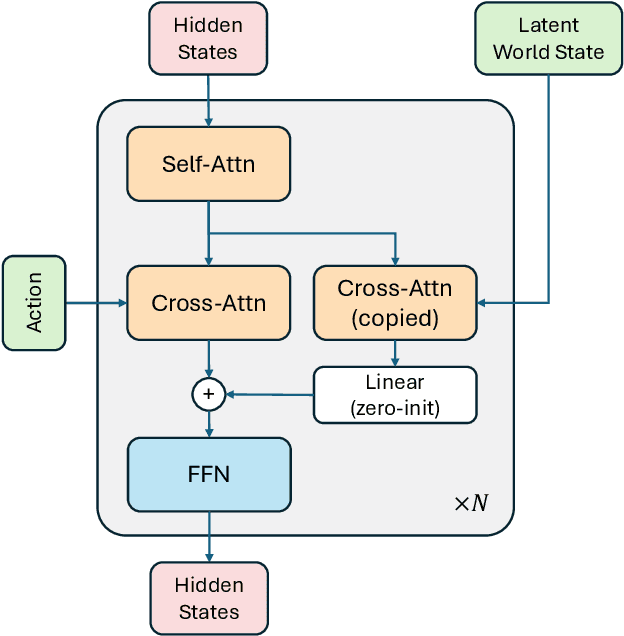
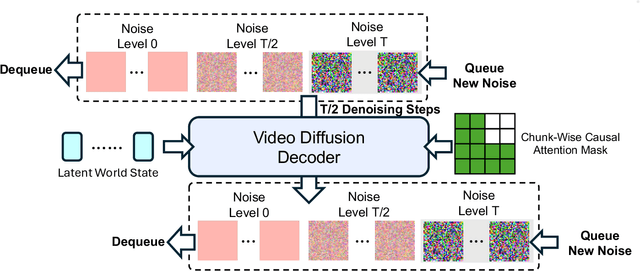
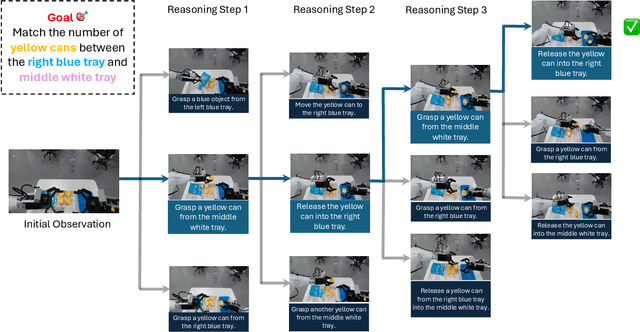
Abstract:A world model enables an intelligent agent to imagine, predict, and reason about how the world evolves in response to its actions, and accordingly to plan and strategize. While recent video generation models produce realistic visual sequences, they typically operate in the prompt-to-full-video manner without causal control, interactivity, or long-horizon consistency required for purposeful reasoning. Existing world modeling efforts, on the other hand, often focus on restricted domains (e.g., physical, game, or 3D-scene dynamics) with limited depth and controllability, and struggle to generalize across diverse environments and interaction formats. In this work, we introduce PAN, a general, interactable, and long-horizon world model that predicts future world states through high-quality video simulation conditioned on history and natural language actions. PAN employs the Generative Latent Prediction (GLP) architecture that combines an autoregressive latent dynamics backbone based on a large language model (LLM), which grounds simulation in extensive text-based knowledge and enables conditioning on language-specified actions, with a video diffusion decoder that reconstructs perceptually detailed and temporally coherent visual observations, to achieve a unification between latent space reasoning (imagination) and realizable world dynamics (reality). Trained on large-scale video-action pairs spanning diverse domains, PAN supports open-domain, action-conditioned simulation with coherent, long-term dynamics. Extensive experiments show that PAN achieves strong performance in action-conditioned world simulation, long-horizon forecasting, and simulative reasoning compared to other video generators and world models, taking a step towards general world models that enable predictive simulation of future world states for reasoning and acting.
LaDiR: Latent Diffusion Enhances LLMs for Text Reasoning
Oct 06, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate their reasoning ability through chain-of-thought (CoT) generation. However, LLM's autoregressive decoding may limit the ability to revisit and refine earlier tokens in a holistic manner, which can also lead to inefficient exploration for diverse solutions. In this paper, we propose LaDiR (Latent Diffusion Reasoner), a novel reasoning framework that unifies the expressiveness of continuous latent representation with the iterative refinement capabilities of latent diffusion models for an existing LLM. We first construct a structured latent reasoning space using a Variational Autoencoder (VAE) that encodes text reasoning steps into blocks of thought tokens, preserving semantic information and interpretability while offering compact but expressive representations. Subsequently, we utilize a latent diffusion model that learns to denoise a block of latent thought tokens with a blockwise bidirectional attention mask, enabling longer horizon and iterative refinement with adaptive test-time compute. This design allows efficient parallel generation of diverse reasoning trajectories, allowing the model to plan and revise the reasoning process holistically. We conduct evaluations on a suite of mathematical reasoning and planning benchmarks. Empirical results show that LaDiR consistently improves accuracy, diversity, and interpretability over existing autoregressive, diffusion-based, and latent reasoning methods, revealing a new paradigm for text reasoning with latent diffusion.
GFlowVLM: Enhancing Multi-step Reasoning in Vision-Language Models with Generative Flow Networks
Mar 09, 2025



Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have recently shown promising advancements in sequential decision-making tasks through task-specific fine-tuning. However, common fine-tuning methods, such as Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and Reinforcement Learning (RL) techniques like Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), present notable limitations: SFT assumes Independent and Identically Distributed (IID) data, while PPO focuses on maximizing cumulative rewards. These limitations often restrict solution diversity and hinder generalization in multi-step reasoning tasks. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel framework, GFlowVLM, a framework that fine-tune VLMs using Generative Flow Networks (GFlowNets) to promote generation of diverse solutions for complex reasoning tasks. GFlowVLM models the environment as a non-Markovian decision process, allowing it to capture long-term dependencies essential for real-world applications. It takes observations and task descriptions as inputs to prompt chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning which subsequently guides action selection. We use task based rewards to fine-tune VLM with GFlowNets. This approach enables VLMs to outperform prior fine-tuning methods, including SFT and RL. Empirical results demonstrate the effectiveness of GFlowVLM on complex tasks such as card games (NumberLine, BlackJack) and embodied planning tasks (ALFWorld), showing enhanced training efficiency, solution diversity, and stronger generalization capabilities across both in-distribution and out-of-distribution scenarios.
Flow of Reasoning: Efficient Training of LLM Policy with Divergent Thinking
Jun 09, 2024



Abstract:Divergent thinking, the cognitive process of generating diverse solutions, is a hallmark of human creativity and problem-solving. For machines, sampling diverse solution trajectories in complex reasoning problems is crucial for robust outcomes, data augmentation, and enhanced model generalization. Large language models (LLMs) often struggle with generating high-quality, diverse reasoning. While supervised fine-tuning helps with quality, it requires extensive supervision data to capture the full diversity of solutions. Alternatively, reinforcement learning methods like PPO aim to find limited highest-reward solutions while neglecting the solution diversity, akin to convergent thinking. To address these limitations, we propose Flow of Reasoning (FoR) -- an efficient LLM training approach enabling diverse reasoning with minimal data. FoR formulates multi-step LLM reasoning as a Markovian flow from an initial state to terminal states. The formulation allows to adapt principled GFlowNet approaches to train the LLM as a policy, which is able to sample multiple reasoning paths with probabilities proportional to the unnormalized reward. Empirical results show that, with limited training data (e.g., 15 examples), FoR can discover diverse high-quality solutions that excel greatly beyond current state-of-the-art methods across three tasks, including embodied reasoning (BlocksWorld), math puzzle solving (Game24), and logical reasoning (PrOntoQA). Code is available at https://github.com/Yu-Fangxu/FoR.
The FinBen: An Holistic Financial Benchmark for Large Language Models
Feb 20, 2024



Abstract:LLMs have transformed NLP and shown promise in various fields, yet their potential in finance is underexplored due to a lack of thorough evaluations and the complexity of financial tasks. This along with the rapid development of LLMs, highlights the urgent need for a systematic financial evaluation benchmark for LLMs. In this paper, we introduce FinBen, the first comprehensive open-sourced evaluation benchmark, specifically designed to thoroughly assess the capabilities of LLMs in the financial domain. FinBen encompasses 35 datasets across 23 financial tasks, organized into three spectrums of difficulty inspired by the Cattell-Horn-Carroll theory, to evaluate LLMs' cognitive abilities in inductive reasoning, associative memory, quantitative reasoning, crystallized intelligence, and more. Our evaluation of 15 representative LLMs, including GPT-4, ChatGPT, and the latest Gemini, reveals insights into their strengths and limitations within the financial domain. The findings indicate that GPT-4 leads in quantification, extraction, numerical reasoning, and stock trading, while Gemini shines in generation and forecasting; however, both struggle with complex extraction and forecasting, showing a clear need for targeted enhancements. Instruction tuning boosts simple task performance but falls short in improving complex reasoning and forecasting abilities. FinBen seeks to continuously evaluate LLMs in finance, fostering AI development with regular updates of tasks and models.
Comparing Hallucination Detection Metrics for Multilingual Generation
Feb 16, 2024Abstract:While many automatic hallucination detection techniques have been proposed for English texts, their effectiveness in multilingual contexts remains unexplored. This paper aims to bridge the gap in understanding how these hallucination detection metrics perform on non-English languages. We evaluate the efficacy of various detection metrics, including lexical metrics like ROUGE and Named Entity Overlap and Natural Language Inference (NLI)-based metrics, at detecting hallucinations in biographical summaries in many languages; we also evaluate how correlated these different metrics are to gauge whether they measure the same phenomena. Our empirical analysis reveals that while lexical metrics show limited effectiveness, NLI-based metrics perform well in high-resource languages at the sentence level. In contrast, NLI-based metrics often fail to detect atomic fact hallucinations. Our findings highlight existing gaps in multilingual hallucination detection and motivate future research to develop more robust detection methods for LLM hallucination in other languages.
Deficiency of Large Language Models in Finance: An Empirical Examination of Hallucination
Nov 27, 2023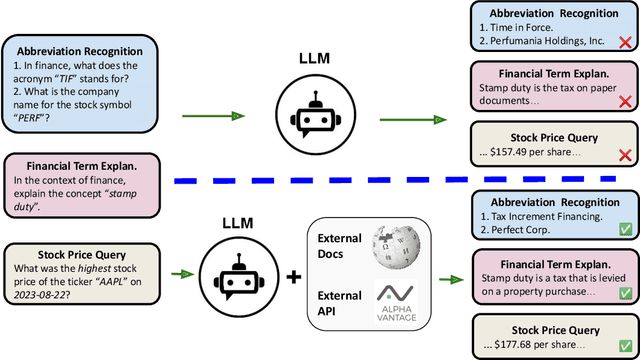
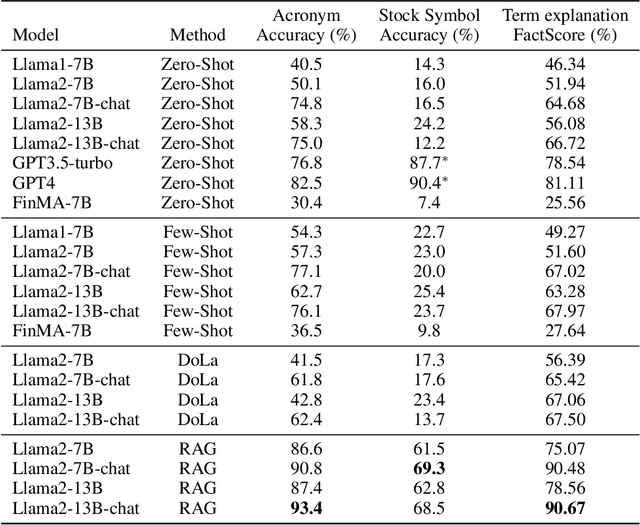
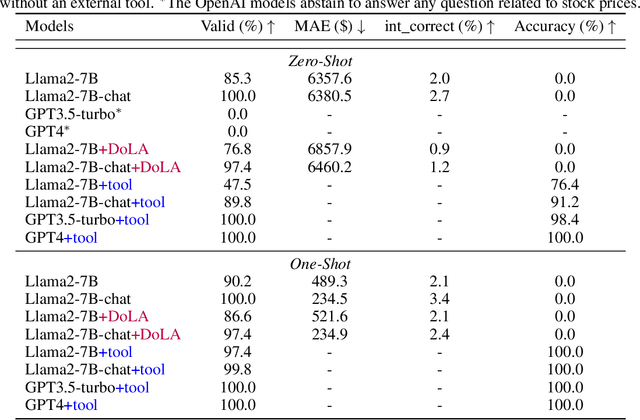

Abstract:The hallucination issue is recognized as a fundamental deficiency of large language models (LLMs), especially when applied to fields such as finance, education, and law. Despite the growing concerns, there has been a lack of empirical investigation. In this paper, we provide an empirical examination of LLMs' hallucination behaviors in financial tasks. First, we empirically investigate LLM model's ability of explaining financial concepts and terminologies. Second, we assess LLM models' capacity of querying historical stock prices. Third, to alleviate the hallucination issue, we evaluate the efficacy of four practical methods, including few-shot learning, Decoding by Contrasting Layers (DoLa), the Retrieval Augmentation Generation (RAG) method and the prompt-based tool learning method for a function to generate a query command. Finally, our major finding is that off-the-shelf LLMs experience serious hallucination behaviors in financial tasks. Therefore, there is an urgent need to call for research efforts in mitigating LLMs' hallucination.
Ever: Mitigating Hallucination in Large Language Models through Real-Time Verification and Rectification
Nov 15, 2023



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable proficiency in generating fluent text. However, they often encounter the challenge of generating inaccurate or hallucinated content. This issue is common in both non-retrieval-based generation and retrieval-augmented generation approaches, and existing post-hoc rectification methods may not address the accumulated hallucination errors that may be caused by the "snowballing" issue, especially in reasoning tasks. To tackle these challenges, we introduce a novel approach called Real-time Verification and Rectification (Ever). Instead of waiting until the end of the generation process to rectify hallucinations, Ever employs a real-time, step-wise generation and hallucination rectification strategy. The primary objective is to detect and rectify hallucinations as they occur during the text generation process. When compared to both retrieval-based and non-retrieval-based baselines, Ever demonstrates a significant improvement in generating trustworthy and factually accurate text across a diverse range of tasks, including short-form QA, biography generation, and multi-hop reasoning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge