Jiankun Li
ADRS-CNet: An adaptive models of dimensionality reduction methods for DNA storage clustering algorithms
Aug 22, 2024



Abstract:DNA storage technology, with its high density, long-term preservation capability, low maintenance requirements, and compact physical size, is emerging as a promising option for large-scale data storage. However, extracting features from DNA sequences of varying lengths can lead to the problem of dimensionality, which needs to be addressed. Techniques such as PCA, UMAP, and t-SNE are commonly used to project high-dimensional data into a lower-dimensional space, but their effectiveness varies across different datasets. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a model based on a multilayer perceptron (MLP) that classifies DNA sequence features and intelligently selects the optimal dimensionality reduction method, thereby enhancing subsequent clustering performance. Experimental results, tested on open-source datasets and compared with multiple benchmark methods, demonstrate that our model not only excels in classification performance but also significantly improves clustering accuracy, indicating that this approach effectively mitigates the challenges posed by high-dimensional features in clustering models.
Exploring the Causality of End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Jul 09, 2024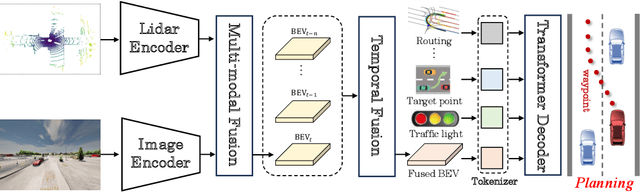
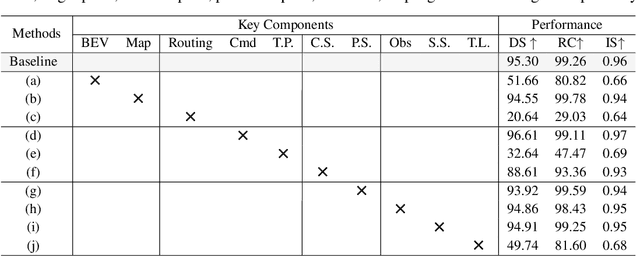
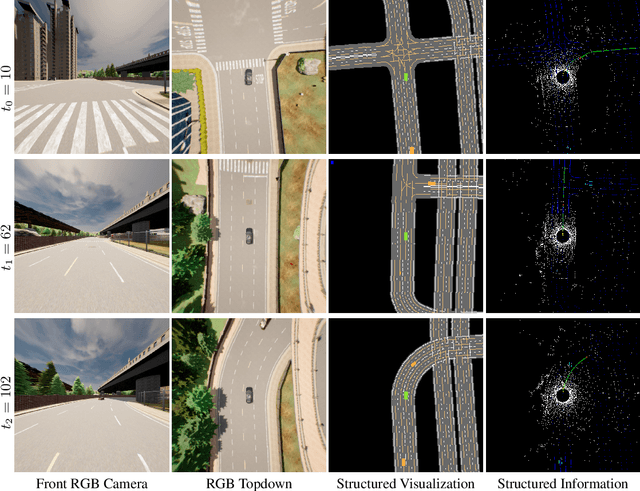
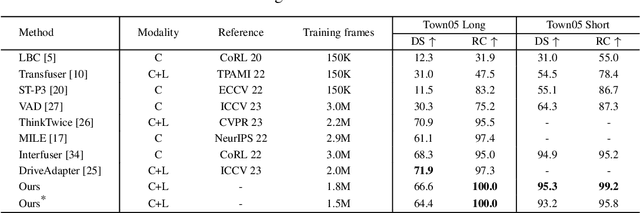
Abstract:Deep learning-based models are widely deployed in autonomous driving areas, especially the increasingly noticed end-to-end solutions. However, the black-box property of these models raises concerns about their trustworthiness and safety for autonomous driving, and how to debug the causality has become a pressing concern. Despite some existing research on the explainability of autonomous driving, there is currently no systematic solution to help researchers debug and identify the key factors that lead to the final predicted action of end-to-end autonomous driving. In this work, we propose a comprehensive approach to explore and analyze the causality of end-to-end autonomous driving. First, we validate the essential information that the final planning depends on by using controlled variables and counterfactual interventions for qualitative analysis. Then, we quantitatively assess the factors influencing model decisions by visualizing and statistically analyzing the response of key model inputs. Finally, based on the comprehensive study of the multi-factorial end-to-end autonomous driving system, we have developed a strong baseline and a tool for exploring causality in the close-loop simulator CARLA. It leverages the essential input sources to obtain a well-designed model, resulting in highly competitive capabilities. As far as we know, our work is the first to unveil the mystery of end-to-end autonomous driving and turn the black box into a white one. Thorough close-loop experiments demonstrate that our method can be applied to end-to-end autonomous driving solutions for causality debugging. Code will be available at https://github.com/bdvisl/DriveInsight.
CLIP-GS: CLIP-Informed Gaussian Splatting for Real-time and View-consistent 3D Semantic Understanding
Apr 22, 2024



Abstract:The recent 3D Gaussian Splatting (GS) exhibits high-quality and real-time synthesis of novel views in 3D scenes. Currently, it primarily focuses on geometry and appearance modeling, while lacking the semantic understanding of scenes. To bridge this gap, we present CLIP-GS, which integrates semantics from Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP) into Gaussian Splatting to efficiently comprehend 3D environments without annotated semantic data. In specific, rather than straightforwardly learning and rendering high-dimensional semantic features of 3D Gaussians, which significantly diminishes the efficiency, we propose a Semantic Attribute Compactness (SAC) approach. SAC exploits the inherent unified semantics within objects to learn compact yet effective semantic representations of 3D Gaussians, enabling highly efficient rendering (>100 FPS). Additionally, to address the semantic ambiguity, caused by utilizing view-inconsistent 2D CLIP semantics to supervise Gaussians, we introduce a 3D Coherent Self-training (3DCS) strategy, resorting to the multi-view consistency originated from the 3D model. 3DCS imposes cross-view semantic consistency constraints by leveraging refined, self-predicted pseudo-labels derived from the trained 3D Gaussian model, thereby enhancing precise and view-consistent segmentation results. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method remarkably outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches, achieving improvements of 17.29% and 20.81% in mIoU metric on Replica and ScanNet datasets, respectively, while maintaining real-time rendering speed. Furthermore, our approach exhibits superior performance even with sparse input data, verifying the robustness of our method.
Uncertainty Guided Adaptive Warping for Robust and Efficient Stereo Matching
Jul 26, 2023Abstract:Correlation based stereo matching has achieved outstanding performance, which pursues cost volume between two feature maps. Unfortunately, current methods with a fixed model do not work uniformly well across various datasets, greatly limiting their real-world applicability. To tackle this issue, this paper proposes a new perspective to dynamically calculate correlation for robust stereo matching. A novel Uncertainty Guided Adaptive Correlation (UGAC) module is introduced to robustly adapt the same model for different scenarios. Specifically, a variance-based uncertainty estimation is employed to adaptively adjust the sampling area during warping operation. Additionally, we improve the traditional non-parametric warping with learnable parameters, such that the position-specific weights can be learned. We show that by empowering the recurrent network with the UGAC module, stereo matching can be exploited more robustly and effectively. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance over the ETH3D, KITTI, and Middlebury datasets when employing the same fixed model over these datasets without any retraining procedure. To target real-time applications, we further design a lightweight model based on UGAC, which also outperforms other methods over KITTI benchmarks with only 0.6 M parameters.
DIP: Deep Inverse Patchmatch for High-Resolution Optical Flow
Apr 01, 2022



Abstract:Recently, the dense correlation volume method achieves state-of-the-art performance in optical flow. However, the correlation volume computation requires a lot of memory, which makes prediction difficult on high-resolution images. In this paper, we propose a novel Patchmatch-based framework to work on high-resolution optical flow estimation. Specifically, we introduce the first end-to-end Patchmatch based deep learning optical flow. It can get high-precision results with lower memory benefiting from propagation and local search of Patchmatch. Furthermore, a new inverse propagation is proposed to decouple the complex operations of propagation, which can significantly reduce calculations in multiple iterations. At the time of submission, our method ranks first on all the metrics on the popular KITTI2015 benchmark, and ranks second on EPE on the Sintel clean benchmark among published optical flow methods. Experiment shows our method has a strong cross-dataset generalization ability that the F1-all achieves 13.73%, reducing 21% from the best published result 17.4% on KITTI2015. What's more, our method shows a good details preserving result on the high-resolution dataset DAVIS and consumes 2x less memory than RAFT.
Practical Stereo Matching via Cascaded Recurrent Network with Adaptive Correlation
Mar 22, 2022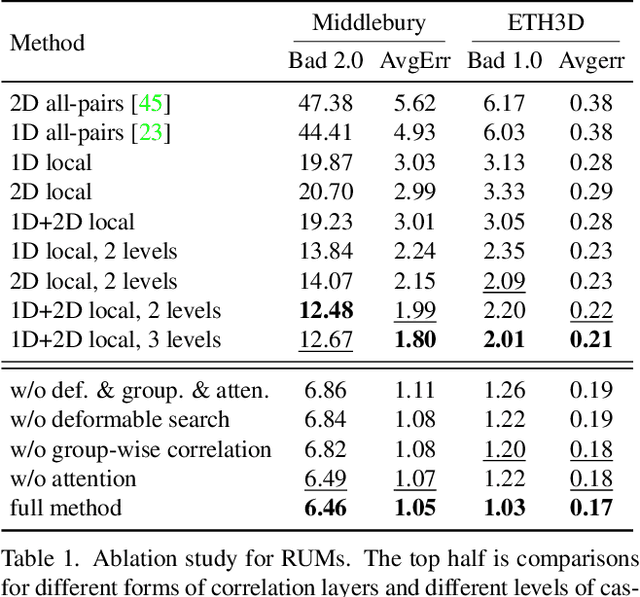
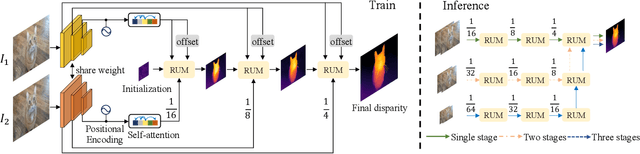
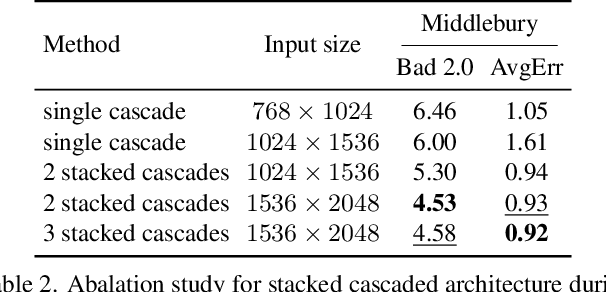
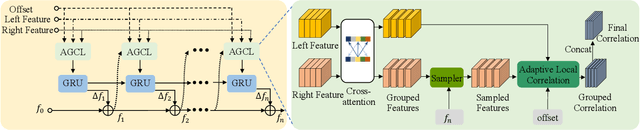
Abstract:With the advent of convolutional neural networks, stereo matching algorithms have recently gained tremendous progress. However, it remains a great challenge to accurately extract disparities from real-world image pairs taken by consumer-level devices like smartphones, due to practical complicating factors such as thin structures, non-ideal rectification, camera module inconsistencies and various hard-case scenes. In this paper, we propose a set of innovative designs to tackle the problem of practical stereo matching: 1) to better recover fine depth details, we design a hierarchical network with recurrent refinement to update disparities in a coarse-to-fine manner, as well as a stacked cascaded architecture for inference; 2) we propose an adaptive group correlation layer to mitigate the impact of erroneous rectification; 3) we introduce a new synthetic dataset with special attention to difficult cases for better generalizing to real-world scenes. Our results not only rank 1st on both Middlebury and ETH3D benchmarks, outperforming existing state-of-the-art methods by a notable margin, but also exhibit high-quality details for real-life photos, which clearly demonstrates the efficacy of our contributions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge