Ross Mead
Dialogue with Robots: Proposals for Broadening Participation and Research in the SLIVAR Community
Apr 01, 2024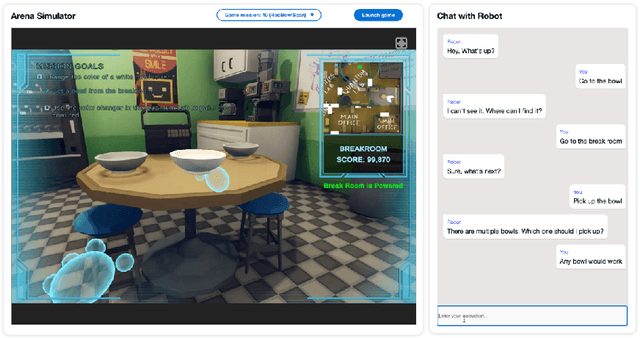
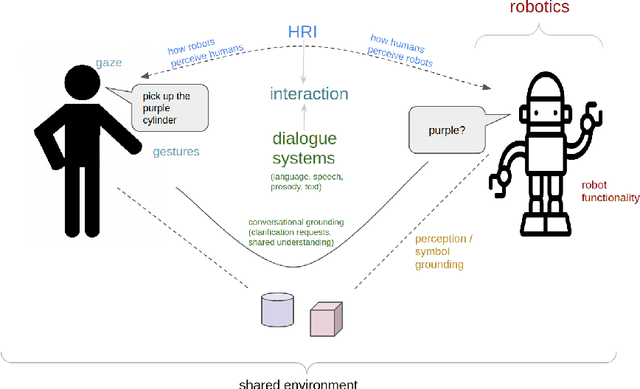
Abstract:The ability to interact with machines using natural human language is becoming not just commonplace, but expected. The next step is not just text interfaces, but speech interfaces and not just with computers, but with all machines including robots. In this paper, we chronicle the recent history of this growing field of spoken dialogue with robots and offer the community three proposals, the first focused on education, the second on benchmarks, and the third on the modeling of language when it comes to spoken interaction with robots. The three proposals should act as white papers for any researcher to take and build upon.
End-User Development for Human-Robot Interaction
Feb 27, 2024Abstract:End-user development (EUD) represents a key step towards making robotics accessible for experts and nonexperts alike. Within academia, researchers investigate novel ways that EUD tools can capture, represent, visualize, analyze, and test developer intent. At the same time, industry researchers increasingly build and ship programming tools that enable customers to interact with their robots. However, despite this growing interest, the role of EUD within HRI is not well defined. EUD struggles to situate itself within a growing array of alternative approaches to application development, such as robot learning and teleoperation. EUD further struggles due to the wide range of individuals who can be considered end users, such as independent third-party application developers, consumers, hobbyists, or even employees of the robot manufacturer. Key questions remain such as how EUD is justified over alternate approaches to application development, which contexts EUD is most suited for, who the target users of an EUD system are, and where interaction between a human and a robot takes place, amongst many other questions. We seek to address these challenges and questions by organizing the first End-User Development for Human-Robot Interaction (EUD4HRI) workshop at the 2024 International Conference of Human-Robot Interaction. The workshop will bring together researchers with a wide range of expertise across academia and industry, spanning perspectives from multiple subfields of robotics, with the primary goal being a consensus of perspectives about the role that EUD must play within human-robot interaction.
Proceedings of the AI-HRI Symposium at AAAI-FSS 2022
Sep 28, 2022Abstract:The Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) Symposium has been a successful venue of discussion and collaboration on AI theory and methods aimed at HRI since 2014. This year, after a review of the achievements of the AI-HRI community over the last decade in 2021, we are focusing on a visionary theme: exploring the future of AI-HRI. Accordingly, we added a Blue Sky Ideas track to foster a forward-thinking discussion on future research at the intersection of AI and HRI. As always, we appreciate all contributions related to any topic on AI/HRI and welcome new researchers who wish to take part in this growing community. With the success of past symposia, AI-HRI impacts a variety of communities and problems, and has pioneered the discussions in recent trends and interests. This year's AI-HRI Fall Symposium aims to bring together researchers and practitioners from around the globe, representing a number of university, government, and industry laboratories. In doing so, we hope to accelerate research in the field, support technology transition and user adoption, and determine future directions for our group and our research.
AI-HRI 2021 Proceedings
Sep 23, 2021Abstract:The Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) Symposium has been a successful venue of discussion and collaboration since 2014. During that time, these symposia provided a fertile ground for numerous collaborations and pioneered many discussions revolving trust in HRI, XAI for HRI, service robots, interactive learning, and more. This year, we aim to review the achievements of the AI-HRI community in the last decade, identify the challenges facing ahead, and welcome new researchers who wish to take part in this growing community. Taking this wide perspective, this year there will be no single theme to lead the symposium and we encourage AI-HRI submissions from across disciplines and research interests. Moreover, with the rising interest in AR and VR as part of an interaction and following the difficulties in running physical experiments during the pandemic, this year we specifically encourage researchers to submit works that do not include a physical robot in their evaluation, but promote HRI research in general. In addition, acknowledging that ethics is an inherent part of the human-robot interaction, we encourage submissions of works on ethics for HRI. Over the course of the two-day meeting, we will host a collaborative forum for discussion of current efforts in AI-HRI, with additional talks focused on the topics of ethics in HRI and ubiquitous HRI.
Quori: A Community-Informed Design of a Socially Interactive Humanoid Robot
Sep 02, 2021
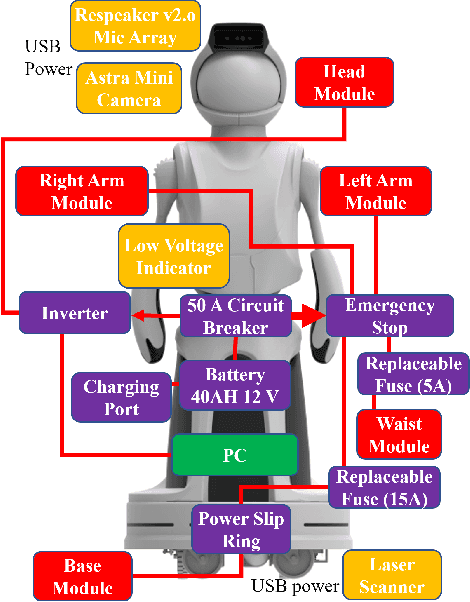
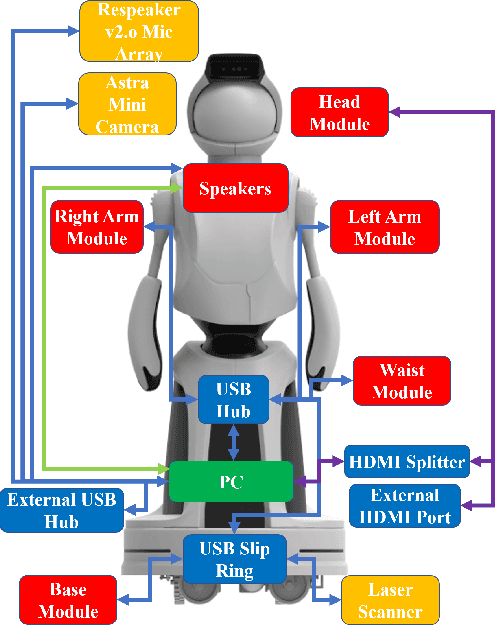
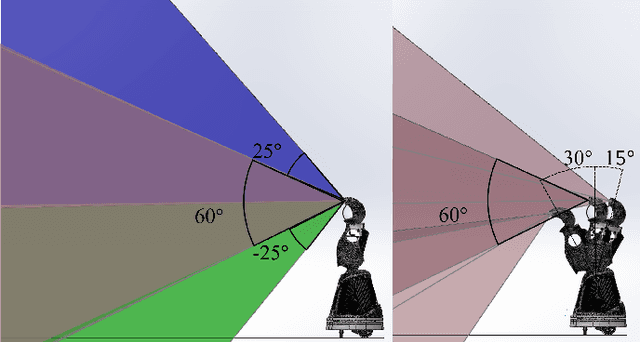
Abstract:Hardware platforms for socially interactive robotics can be limited by cost or lack of functionality. This paper presents the overall system -- design, hardware, and software -- for Quori, a novel, affordable, socially interactive humanoid robot platform for facilitating non-contact human-robot interaction (HRI) research. The design of the system is motivated by feedback sampled from the HRI research community. The overall design maintains a balance of affordability and functionality. Initial Quori testing and a six-month deployment are presented. Ten Quori platforms have been awarded to a diverse group of researchers from across the United States to facilitate HRI research to build a community database from a common platform.
Proceedings of the AI-HRI Symposium at AAAI-FSS 2020
Nov 11, 2020Abstract:The Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) Symposium has been a successful venue of discussion and collaboration since 2014. In that time, the related topic of trust in robotics has been rapidly growing, with major research efforts at universities and laboratories across the world. Indeed, many of the past participants in AI-HRI have been or are now involved with research into trust in HRI. While trust has no consensus definition, it is regularly associated with predictability, reliability, inciting confidence, and meeting expectations. Furthermore, it is generally believed that trust is crucial for adoption of both AI and robotics, particularly when transitioning technologies from the lab to industrial, social, and consumer applications. However, how does trust apply to the specific situations we encounter in the AI-HRI sphere? Is the notion of trust in AI the same as that in HRI? We see a growing need for research that lives directly at the intersection of AI and HRI that is serviced by this symposium. Over the course of the two-day meeting, we propose to create a collaborative forum for discussion of current efforts in trust for AI-HRI, with a sub-session focused on the related topic of explainable AI (XAI) for HRI.
Proceedings of the AI-HRI Symposium at AAAI-FSS 2019
Sep 19, 2019Abstract:The past few years have seen rapid progress in the development of service robots. Universities and companies alike have launched major research efforts toward the deployment of ambitious systems designed to aid human operators performing a variety of tasks. These robots are intended to make those who may otherwise need to live in assisted care facilities more independent, to help workers perform their jobs, or simply to make life more convenient. Service robots provide a powerful platform on which to study Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) in the real world. Research sitting at the intersection of AI and HRI is crucial to the success of service robots if they are to fulfill their mission. This symposium seeks to highlight research enabling robots to effectively interact with people autonomously while modeling, planning, and reasoning about the environment that the robot operates in and the tasks that it must perform. AI-HRI deals with the challenge of interacting with humans in environments that are relatively unstructured or which are structured around people rather than machines, as well as the possibility that the robot may need to interact naturally with people rather than through teach pendants, programming, or similar interfaces.
Proceedings of the AI-HRI Symposium at AAAI-FSS 2018
Sep 18, 2018Abstract:The goal of the Interactive Learning for Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) symposium is to bring together the large community of researchers working on interactive learning scenarios for interactive robotics. While current HRI research involves investigating ways for robots to effectively interact with people, HRI's overarching goal is to develop robots that are autonomous while intelligently modeling and learning from humans. These goals greatly overlap with some central goals of AI and interactive machine learning, such that HRI is an extremely challenging problem domain for interactive learning and will elicit fresh problem areas for robotics research. Present-day AI research still does not widely consider situations for interacting directly with humans and within human-populated environments, which present inherent uncertainty in dynamics, structure, and interaction. We believe that the HRI community already offers a rich set of principles and observations that can be used to structure new models of interaction. The human-aware AI initiative has primarily been approached through human-in-the-loop methods that use people's data and feedback to improve refinement and performance of the algorithms, learned functions, and personalization. We thus believe that HRI is an important component to furthering AI and robotics research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge