Ruchen Wen
Hidden Complexities in the Computational Modeling of Proportionality for Robotic Norm Violation Response
Oct 15, 2022Abstract:Language-capable robots hold unique persuasive power over humans, and thus can help regulate people's behavior and preserve a better moral ecosystem, by rejecting unethical commands and calling out norm violations. However, miscalibrated norm violation responses (when the harshness of a response does not match the actual norm violation severity) may not only decrease the effectiveness of human-robot communication, but may also damage the rapport between humans and robots. Therefore, when robots respond to norm violations, it is crucial that they consider both the moral value of their response (by considering how much positive moral influence their response could exert) and the social value (by considering how much face threat might be imposed by their utterance). In this paper, we present a simple (naive) mathematical model of proportionality which could explain how moral and social considerations should be balanced in multi-agent norm violation response generation. But even more importantly, we use this model to start a discussion about the hidden complexity of modeling proportionality, and use this discussion to identify key research directions that must be explored in order to develop socially and morally competent language-capable robots.
* 5 pages, the AI-HRI Symposium at AAAI Fall Symposium Series (FSS) 2022
Proceedings of the AI-HRI Symposium at AAAI-FSS 2022
Sep 28, 2022Abstract:The Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) Symposium has been a successful venue of discussion and collaboration on AI theory and methods aimed at HRI since 2014. This year, after a review of the achievements of the AI-HRI community over the last decade in 2021, we are focusing on a visionary theme: exploring the future of AI-HRI. Accordingly, we added a Blue Sky Ideas track to foster a forward-thinking discussion on future research at the intersection of AI and HRI. As always, we appreciate all contributions related to any topic on AI/HRI and welcome new researchers who wish to take part in this growing community. With the success of past symposia, AI-HRI impacts a variety of communities and problems, and has pioneered the discussions in recent trends and interests. This year's AI-HRI Fall Symposium aims to bring together researchers and practitioners from around the globe, representing a number of university, government, and industry laboratories. In doing so, we hope to accelerate research in the field, support technology transition and user adoption, and determine future directions for our group and our research.
Human Capabilities as Guiding Lights for the Field of AI-HRI: Insights from Engineering Education
Oct 06, 2021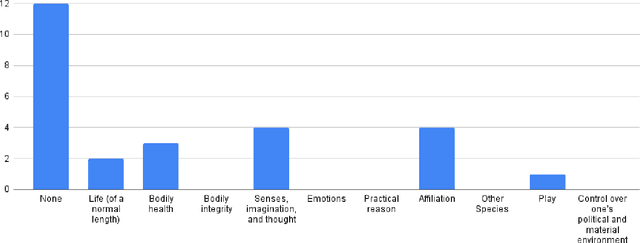
Abstract:Social Justice oriented Engineering Education frameworks have been developed to help guide engineering students' decisions about which projects will genuinely address human needs to create a better and more equitable society. In this paper, we explore the role such theories might play in the field of AI-HRI, consider the extent to which our community is (or is not) aligned with these recommendations, and envision a future in which our research community takes guidance from these theories. In particular, we analyze recent AI-HRI (through analysis of 2020 AI-HRI papers) and consider possible futures of AI-HRI (through a speculative ethics exercise). Both activities are guided through the lens of the Engineering for Social Justice (E4SJ) framework, which centers contextual listening and enhancement of human capabilities. Our analysis suggests that current AI-HRI research is not well aligned with the guiding principles of Engineering for Social Justice, and as such, does not obviously meet the needs of the communities we could be helping most. As such, we suggest that motivating future work through the E4SJ framework could help to ensure that we as researchers are developing technologies that will actually lead to a more equitable world.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge