Maja Matarić
HRIBench: Benchmarking Vision-Language Models for Real-Time Human Perception in Human-Robot Interaction
Jun 25, 2025Abstract:Real-time human perception is crucial for effective human-robot interaction (HRI). Large vision-language models (VLMs) offer promising generalizable perceptual capabilities but often suffer from high latency, which negatively impacts user experience and limits VLM applicability in real-world scenarios. To systematically study VLM capabilities in human perception for HRI and performance-latency trade-offs, we introduce HRIBench, a visual question-answering (VQA) benchmark designed to evaluate VLMs across a diverse set of human perceptual tasks critical for HRI. HRIBench covers five key domains: (1) non-verbal cue understanding, (2) verbal instruction understanding, (3) human-robot object relationship understanding, (4) social navigation, and (5) person identification. To construct HRIBench, we collected data from real-world HRI environments to curate questions for non-verbal cue understanding, and leveraged publicly available datasets for the remaining four domains. We curated 200 VQA questions for each domain, resulting in a total of 1000 questions for HRIBench. We then conducted a comprehensive evaluation of both state-of-the-art closed-source and open-source VLMs (N=11) on HRIBench. Our results show that, despite their generalizability, current VLMs still struggle with core perceptual capabilities essential for HRI. Moreover, none of the models within our experiments demonstrated a satisfactory performance-latency trade-off suitable for real-time deployment, underscoring the need for future research on developing smaller, low-latency VLMs with improved human perception capabilities. HRIBench and our results can be found in this Github repository: https://github.com/interaction-lab/HRIBench.
Modeling Personalized Difficulty of Rehabilitation Exercises Using Causal Trees
May 07, 2025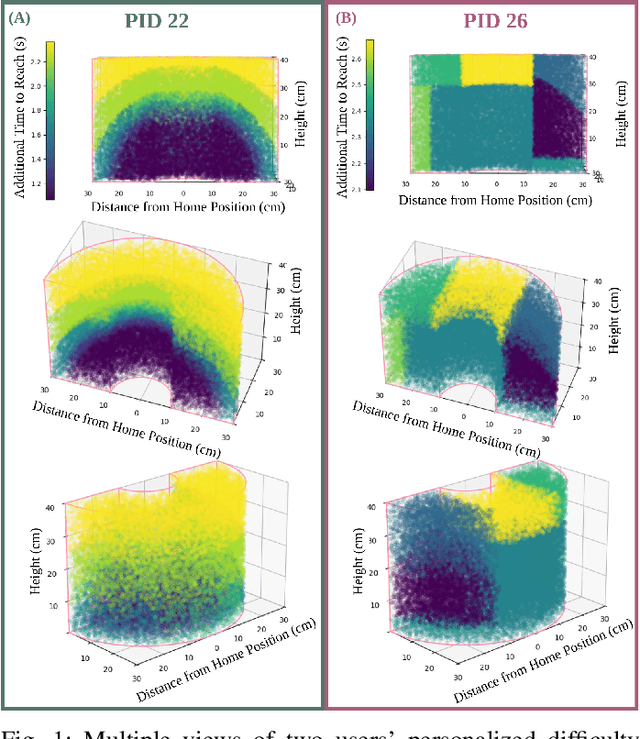
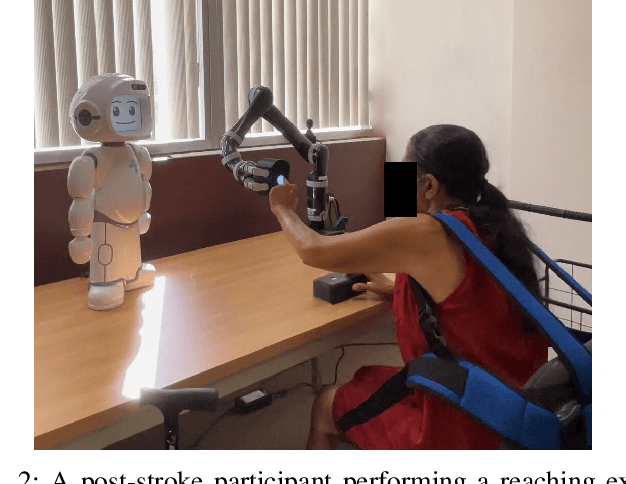

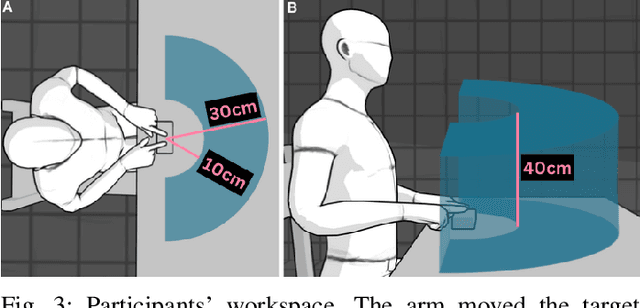
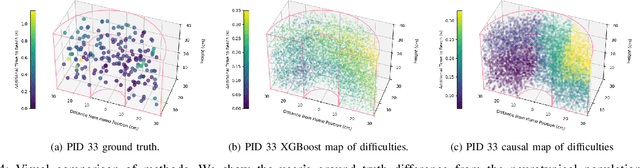
Abstract:Rehabilitation robots are often used in game-like interactions for rehabilitation to increase a person's motivation to complete rehabilitation exercises. By adjusting exercise difficulty for a specific user throughout the exercise interaction, robots can maximize both the user's rehabilitation outcomes and the their motivation throughout the exercise. Previous approaches have assumed exercises have generic difficulty values that apply to all users equally, however, we identified that stroke survivors have varied and unique perceptions of exercise difficulty. For example, some stroke survivors found reaching vertically more difficult than reaching farther but lower while others found reaching farther more challenging than reaching vertically. In this paper, we formulate a causal tree-based method to calculate exercise difficulty based on the user's performance. We find that this approach accurately models exercise difficulty and provides a readily interpretable model of why that exercise is difficult for both users and caretakers.
Toward Anxiety-Reducing Pocket Robots for Children
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:A common denominator for most therapy treatments for children who suffer from an anxiety disorder is daily practice routines to learn techniques needed to overcome anxiety. However, applying those techniques while experiencing anxiety can be highly challenging. This paper presents the design, implementation, and pilot study of a tactile hand-held pocket robot AffectaPocket, designed to work alongside therapy as a focus object to facilitate coping during an anxiety attack. The robot does not require daily practice to be used, has a small form factor, and has been designed for children 7 to 12 years old. The pocket robot works by sensing when it is being held and attempts to shift the child's focus by presenting them with a simple three-note rhythm-matching game. We conducted a pilot study of the pocket robot involving four children aged 7 to 10 years, and then a main study with 18 children aged 6 to 8 years; neither study involved children with anxiety. Both studies aimed to assess the reliability of the robot's sensor configuration, its design, and the effectiveness of the user tutorial. The results indicate that the morphology and sensor setup performed adequately and the tutorial process enabled the children to use the robot with little practice. This work demonstrates that the presented pocket robot could represent a step toward developing low-cost accessible technologies to help children suffering from anxiety disorders.
* 8 pages
Conversational Planning for Personal Plans
Feb 26, 2025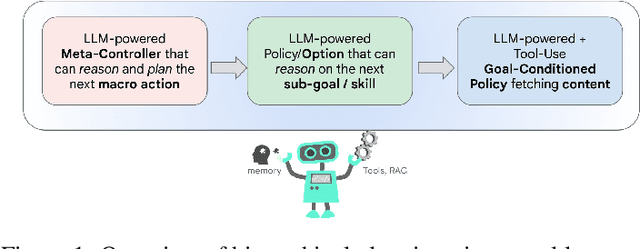
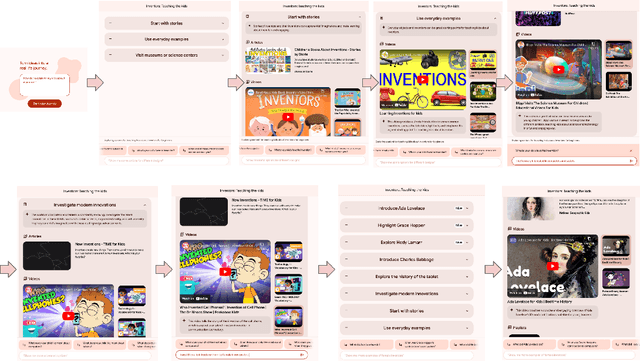
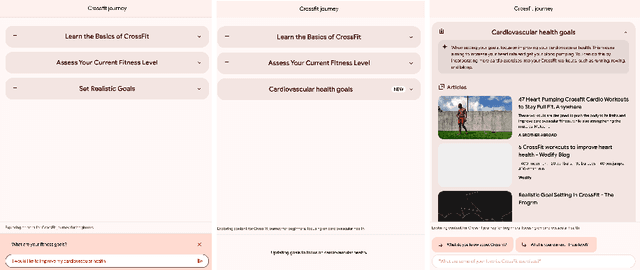
Abstract:The language generation and reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) have enabled conversational systems with impressive performance in a variety of tasks, from code generation, to composing essays, to passing STEM and legal exams, to a new paradigm for knowledge search. Besides those short-term use applications, LLMs are increasingly used to help with real-life goals or tasks that take a long time to complete, involving multiple sessions across days, weeks, months, or even years. Thus to enable conversational systems for long term interactions and tasks, we need language-based agents that can plan for long horizons. Traditionally, such capabilities were addressed by reinforcement learning agents with hierarchical planning capabilities. In this work, we explore a novel architecture where the LLM acts as the meta-controller deciding the agent's next macro-action, and tool use augmented LLM-based option policies execute the selected macro-action. We instantiate this framework for a specific set of macro-actions enabling adaptive planning for users' personal plans through conversation and follow-up questions collecting user feedback. We show how this paradigm can be applicable in scenarios ranging from tutoring for academic and non-academic tasks to conversational coaching for personal health plans.
Sleepless Nights, Sugary Days: Creating Synthetic Users with Health Conditions for Realistic Coaching Agent Interactions
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:We present an end-to-end framework for generating synthetic users for evaluating interactive agents designed to encourage positive behavior changes, such as in health and lifestyle coaching. The synthetic users are grounded in health and lifestyle conditions, specifically sleep and diabetes management in this study, to ensure realistic interactions with the health coaching agent. Synthetic users are created in two stages: first, structured data are generated grounded in real-world health and lifestyle factors in addition to basic demographics and behavioral attributes; second, full profiles of the synthetic users are developed conditioned on the structured data. Interactions between synthetic users and the coaching agent are simulated using generative agent-based models such as Concordia, or directly by prompting a language model. Using two independently-developed agents for sleep and diabetes coaching as case studies, the validity of this framework is demonstrated by analyzing the coaching agent's understanding of the synthetic users' needs and challenges. Finally, through multiple blinded evaluations of user-coach interactions by human experts, we demonstrate that our synthetic users with health and behavioral attributes more accurately portray real human users with the same attributes, compared to generic synthetic users not grounded in such attributes. The proposed framework lays the foundation for efficient development of conversational agents through extensive, realistic, and grounded simulated interactions.
Evaluating Spoken Language as a Biomarker for Automated Screening of Cognitive Impairment
Jan 30, 2025Abstract:Timely and accurate assessment of cognitive impairment is a major unmet need in populations at risk. Alterations in speech and language can be early predictors of Alzheimer's disease and related dementias (ADRD) before clinical signs of neurodegeneration. Voice biomarkers offer a scalable and non-invasive solution for automated screening. However, the clinical applicability of machine learning (ML) remains limited by challenges in generalisability, interpretability, and access to patient data to train clinically applicable predictive models. Using DementiaBank recordings (N=291, 64% female), we evaluated ML techniques for ADRD screening and severity prediction from spoken language. We validated model generalisability with pilot data collected in-residence from older adults (N=22, 59% female). Risk stratification and linguistic feature importance analysis enhanced the interpretability and clinical utility of predictions. For ADRD classification, a Random Forest applied to lexical features achieved a mean sensitivity of 69.4% (95% confidence interval (CI) = 66.4-72.5) and specificity of 83.3% (78.0-88.7). On real-world pilot data, this model achieved a mean sensitivity of 70.0% (58.0-82.0) and specificity of 52.5% (39.3-65.7). For severity prediction using Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores, a Random Forest Regressor achieved a mean absolute MMSE error of 3.7 (3.7-3.8), with comparable performance of 3.3 (3.1-3.5) on pilot data. Linguistic features associated with higher ADRD risk included increased use of pronouns and adverbs, greater disfluency, reduced analytical thinking, lower lexical diversity and fewer words reflecting a psychological state of completion. Our interpretable predictive modelling offers a novel approach for in-home integration with conversational AI to monitor cognitive health and triage higher-risk individuals, enabling earlier detection and intervention.
Soft and Compliant Contact-Rich Hair Manipulation and Care
Jan 05, 2025



Abstract:Hair care robots can help address labor shortages in elderly care while enabling those with limited mobility to maintain their hair-related identity. We present MOE-Hair, a soft robot system that performs three hair-care tasks: head patting, finger combing, and hair grasping. The system features a tendon-driven soft robot end-effector (MOE) with a wrist-mounted RGBD camera, leveraging both mechanical compliance for safety and visual force sensing through deformation. In testing with a force-sensorized mannequin head, MOE achieved comparable hair-grasping effectiveness while applying significantly less force than rigid grippers. Our novel force estimation method combines visual deformation data and tendon tensions from actuators to infer applied forces, reducing sensing errors by up to 60.1% and 20.3% compared to actuator current load-only and depth image-only baselines, respectively. A user study with 12 participants demonstrated statistically significant preferences for MOE-Hair over a baseline system in terms of comfort, effectiveness, and appropriate force application. These results demonstrate the unique advantages of soft robots in contact-rich hair-care tasks, while highlighting the importance of precise force control despite the inherent compliance of the system.
Contrastive Learning from Exploratory Actions: Leveraging Natural Interactions for Preference Elicitation
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:People have a variety of preferences for how robots behave. To understand and reason about these preferences, robots aim to learn a reward function that describes how aligned robot behaviors are with a user's preferences. Good representations of a robot's behavior can significantly reduce the time and effort required for a user to teach the robot their preferences. Specifying these representations -- what "features" of the robot's behavior matter to users -- remains a difficult problem; Features learned from raw data lack semantic meaning and features learned from user data require users to engage in tedious labeling processes. Our key insight is that users tasked with customizing a robot are intrinsically motivated to produce labels through exploratory search; they explore behaviors that they find interesting and ignore behaviors that are irrelevant. To harness this novel data source of exploratory actions, we propose contrastive learning from exploratory actions (CLEA) to learn trajectory features that are aligned with features that users care about. We learned CLEA features from exploratory actions users performed in an open-ended signal design activity (N=25) with a Kuri robot, and evaluated CLEA features through a second user study with a different set of users (N=42). CLEA features outperformed self-supervised features when eliciting user preferences over four metrics: completeness, simplicity, minimality, and explainability.
Improving User Experience in Preference-Based Optimization of Reward Functions for Assistive Robots
Nov 17, 2024



Abstract:Assistive robots interact with humans and must adapt to different users' preferences to be effective. An easy and effective technique to learn non-expert users' preferences is through rankings of robot behaviors, for example, robot movement trajectories or gestures. Existing techniques focus on generating trajectories for users to rank that maximize the outcome of the preference learning process. However, the generated trajectories do not appear to reflect the user's preference over repeated interactions. In this work, we design an algorithm to generate trajectories for users to rank that we call Covariance Matrix Adaptation Evolution Strategies with Information Gain (CMA-ES-IG). CMA-ES-IG prioritizes the user's experience of the preference learning process. We show that users find our algorithm more intuitive and easier to use than previous approaches across both physical and social robot tasks. This project's code is hosted at github.com/interaction-lab/CMA-ES-IG
Agents Thinking Fast and Slow: A Talker-Reasoner Architecture
Oct 10, 2024Abstract:Large language models have enabled agents of all kinds to interact with users through natural conversation. Consequently, agents now have two jobs: conversing and planning/reasoning. Their conversational responses must be informed by all available information, and their actions must help to achieve goals. This dichotomy between conversing with the user and doing multi-step reasoning and planning can be seen as analogous to the human systems of "thinking fast and slow" as introduced by Kahneman. Our approach is comprised of a "Talker" agent (System 1) that is fast and intuitive, and tasked with synthesizing the conversational response; and a "Reasoner" agent (System 2) that is slower, more deliberative, and more logical, and is tasked with multi-step reasoning and planning, calling tools, performing actions in the world, and thereby producing the new agent state. We describe the new Talker-Reasoner architecture and discuss its advantages, including modularity and decreased latency. We ground the discussion in the context of a sleep coaching agent, in order to demonstrate real-world relevance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge