Alexander Capstick
Urinary Tract Infection Detection in Digital Remote Monitoring: Strategies for Managing Participant-Specific Prediction Complexity
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a significant health concern, particularly for people living with dementia (PLWD), as they can lead to severe complications if not detected and treated early. This study builds on previous work that utilised machine learning (ML) to detect UTIs in PLWD by analysing in-home activity and physiological data collected through low-cost, passive sensors. The current research focuses on improving the performance of previous models, particularly by refining the Multilayer Perceptron (MLP), to better handle variations in home environments and improve sex fairness in predictions by making use of concepts from multitask learning. This study implemented three primary model designs: feature clustering, loss-dependent clustering, and participant ID embedding which were compared against a baseline MLP model. The results demonstrated that the loss-dependent MLP achieved the most significant improvements, increasing validation precision from 48.92% to 72.60% and sensitivity from 27.44% to 70.52%, while also enhancing model fairness across sexes. These findings suggest that the refined models offer a more reliable and equitable approach to early UTI detection in PLWD, addressing participant-specific data variations and enabling clinicians to detect and screen for UTI risks more effectively, thereby facilitating earlier and more accurate treatment decisions.
Two-Stage Representation Learning for Analyzing Movement Behavior Dynamics in People Living with Dementia
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:In remote healthcare monitoring, time series representation learning reveals critical patient behavior patterns from high-frequency data. This study analyzes home activity data from individuals living with dementia by proposing a two-stage, self-supervised learning approach tailored to uncover low-rank structures. The first stage converts time-series activities into text sequences encoded by a pre-trained language model, providing a rich, high-dimensional latent state space using a PageRank-based method. This PageRank vector captures latent state transitions, effectively compressing complex behaviour data into a succinct form that enhances interpretability. This low-rank representation not only enhances model interpretability but also facilitates clustering and transition analysis, revealing key behavioral patterns correlated with clinicalmetrics such as MMSE and ADAS-COG scores. Our findings demonstrate the framework's potential in supporting cognitive status prediction, personalized care interventions, and large-scale health monitoring.
Evaluating Spoken Language as a Biomarker for Automated Screening of Cognitive Impairment
Jan 30, 2025Abstract:Timely and accurate assessment of cognitive impairment is a major unmet need in populations at risk. Alterations in speech and language can be early predictors of Alzheimer's disease and related dementias (ADRD) before clinical signs of neurodegeneration. Voice biomarkers offer a scalable and non-invasive solution for automated screening. However, the clinical applicability of machine learning (ML) remains limited by challenges in generalisability, interpretability, and access to patient data to train clinically applicable predictive models. Using DementiaBank recordings (N=291, 64% female), we evaluated ML techniques for ADRD screening and severity prediction from spoken language. We validated model generalisability with pilot data collected in-residence from older adults (N=22, 59% female). Risk stratification and linguistic feature importance analysis enhanced the interpretability and clinical utility of predictions. For ADRD classification, a Random Forest applied to lexical features achieved a mean sensitivity of 69.4% (95% confidence interval (CI) = 66.4-72.5) and specificity of 83.3% (78.0-88.7). On real-world pilot data, this model achieved a mean sensitivity of 70.0% (58.0-82.0) and specificity of 52.5% (39.3-65.7). For severity prediction using Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores, a Random Forest Regressor achieved a mean absolute MMSE error of 3.7 (3.7-3.8), with comparable performance of 3.3 (3.1-3.5) on pilot data. Linguistic features associated with higher ADRD risk included increased use of pronouns and adverbs, greater disfluency, reduced analytical thinking, lower lexical diversity and fewer words reflecting a psychological state of completion. Our interpretable predictive modelling offers a novel approach for in-home integration with conversational AI to monitor cognitive health and triage higher-risk individuals, enabling earlier detection and intervention.
Using Large Language Models for Expert Prior Elicitation in Predictive Modelling
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), trained on diverse data effectively acquire a breadth of information across various domains. However, their computational complexity, cost, and lack of transparency hinder their direct application for specialised tasks. In fields such as clinical research, acquiring expert annotations or prior knowledge about predictive models is often costly and time-consuming. This study proposes using LLMs to elicit expert prior distributions for predictive models. This approach also provides an alternative to in-context learning, where language models are tasked with making predictions directly. We compare LLM-elicited and uninformative priors, evaluate whether LLMs truthfully generate parameter distributions, and propose a model selection strategy for in-context learning and prior elicitation. Our findings show that LLM-elicited prior parameter distributions significantly reduce predictive error compared to uninformative priors in low-data settings. Applied to clinical problems, this translates to fewer required biological samples, lowering cost and resources. Prior elicitation also consistently outperforms and proves more reliable than in-context learning at a lower cost, making it a preferred alternative in our setting. We demonstrate the utility of this method across various use cases, including clinical applications. For infection prediction, using LLM-elicited priors reduced the number of required labels to achieve the same accuracy as an uninformative prior by 55%, at 200 days earlier in the study.
Enabling Regional Explainability by Automatic and Model-agnostic Rule Extraction
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:In Explainable AI, rule extraction translates model knowledge into logical rules, such as IF-THEN statements, crucial for understanding patterns learned by black-box models. This could significantly aid in fields like disease diagnosis, disease progression estimation, or drug discovery. However, such application domains often contain imbalanced data, with the class of interest underrepresented. Existing methods inevitably compromise the performance of rules for the minor class to maximise the overall performance. As the first attempt in this field, we propose a model-agnostic approach for extracting rules from specific subgroups of data, featuring automatic rule generation for numerical features. This method enhances the regional explainability of machine learning models and offers wider applicability compared to existing methods. We additionally introduce a new method for selecting features to compose rules, reducing computational costs in high-dimensional spaces. Experiments across various datasets and models demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods.
Representation Learning of Daily Movement Data Using Text Encoders
May 07, 2024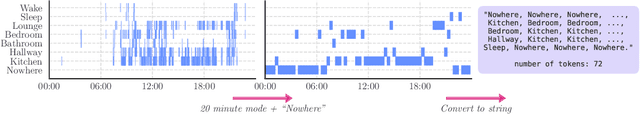
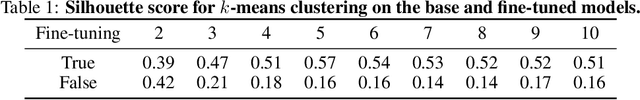


Abstract:Time-series representation learning is a key area of research for remote healthcare monitoring applications. In this work, we focus on a dataset of recordings of in-home activity from people living with Dementia. We design a representation learning method based on converting activity to text strings that can be encoded using a language model fine-tuned to transform data from the same participants within a $30$-day window to similar embeddings in the vector space. This allows for clustering and vector searching over participants and days, and the identification of activity deviations to aid with personalised delivery of care.
* Accepted at ICLR 2024 Workshop on Learning from Time Series For Health: https://openreview.net/forum?id=mmxNNwxvWG
Information Theory Inspired Pattern Analysis for Time-series Data
Feb 22, 2023



Abstract:Current methods for pattern analysis in time series mainly rely on statistical features or probabilistic learning and inference methods to identify patterns and trends in the data. Such methods do not generalize well when applied to multivariate, multi-source, state-varying, and noisy time-series data. To address these issues, we propose a highly generalizable method that uses information theory-based features to identify and learn from patterns in multivariate time-series data. To demonstrate the proposed approach, we analyze pattern changes in human activity data. For applications with stochastic state transitions, features are developed based on Shannon's entropy of Markov chains, entropy rates of Markov chains, entropy production of Markov chains, and von Neumann entropy of Markov chains. For applications where state modeling is not applicable, we utilize five entropy variants, including approximate entropy, increment entropy, dispersion entropy, phase entropy, and slope entropy. The results show the proposed information theory-based features improve the recall rate, F1 score, and accuracy on average by up to 23.01\% compared with the baseline models and a simpler model structure, with an average reduction of 18.75 times in the number of model parameters.
Loss Adapted Plasticity in Deep Neural Networks to Learn from Data with Unreliable Sources
Dec 06, 2022



Abstract:When data is streaming from multiple sources, conventional training methods update model weights often assuming the same level of reliability for each source; that is: a model does not consider data quality of each source during training. In many applications, sources can have varied levels of noise or corruption that has negative effects on the learning of a robust deep learning model. A key issue is that the quality of data or labels for individual sources is often not available during training and could vary over time. Our solution to this problem is to consider the mistakes made while training on data originating from sources and utilise this to create a perceived data quality for each source. This paper demonstrates a straight-forward and novel technique that can be applied to any gradient descent optimiser: Update model weights as a function of the perceived reliability of data sources within a wider data set. The algorithm controls the plasticity of a given model to weight updates based on the history of losses from individual data sources. We show that applying this technique can significantly improve model performance when trained on a mixture of reliable and unreliable data sources, and maintain performance when models are trained on data sources that are all considered reliable. All code to reproduce this work's experiments and implement the algorithm in the reader's own models is made available.
Designing A Clinically Applicable Deep Recurrent Model to Identify Neuropsychiatric Symptoms in People Living with Dementia Using In-Home Monitoring Data
Oct 19, 2021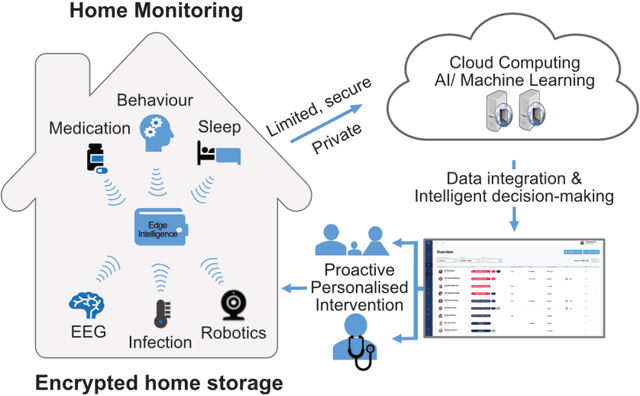
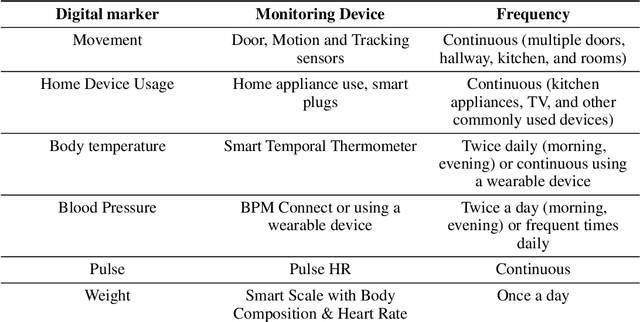
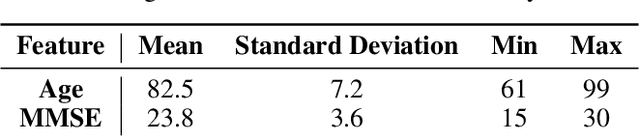
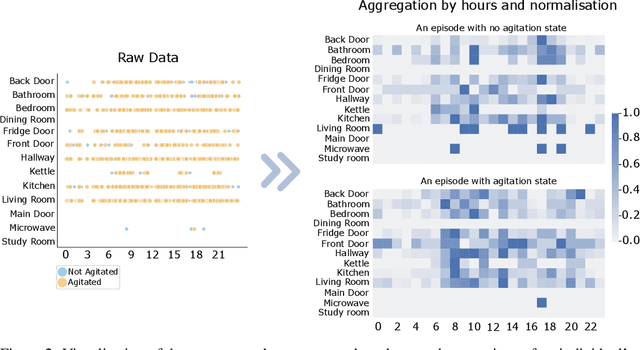
Abstract:Agitation is one of the neuropsychiatric symptoms with high prevalence in dementia which can negatively impact the Activities of Daily Living (ADL) and the independence of individuals. Detecting agitation episodes can assist in providing People Living with Dementia (PLWD) with early and timely interventions. Analysing agitation episodes will also help identify modifiable factors such as ambient temperature and sleep as possible components causing agitation in an individual. This preliminary study presents a supervised learning model to analyse the risk of agitation in PLWD using in-home monitoring data. The in-home monitoring data includes motion sensors, physiological measurements, and the use of kitchen appliances from 46 homes of PLWD between April 2019-June 2021. We apply a recurrent deep learning model to identify agitation episodes validated and recorded by a clinical monitoring team. We present the experiments to assess the efficacy of the proposed model. The proposed model achieves an average of 79.78% recall, 27.66% precision and 37.64% F1 scores when employing the optimal parameters, suggesting a good ability to recognise agitation events. We also discuss using machine learning models for analysing the behavioural patterns using continuous monitoring data and explore clinical applicability and the choices between sensitivity and specificity in-home monitoring applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge