Mingkun Xu
BMAM: Brain-inspired Multi-Agent Memory Framework
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Language-model-based agents operating over extended interaction horizons face persistent challenges in preserving temporally grounded information and maintaining behavioral consistency across sessions, a failure mode we term soul erosion. We present BMAM (Brain-inspired Multi-Agent Memory), a general-purpose memory architecture that models agent memory as a set of functionally specialized subsystems rather than a single unstructured store. Inspired by cognitive memory systems, BMAM decomposes memory into episodic, semantic, salience-aware, and control-oriented components that operate at complementary time scales. To support long-horizon reasoning, BMAM organizes episodic memories along explicit timelines and retrieves evidence by fusing multiple complementary signals. Experiments on the LoCoMo benchmark show that BMAM achieves 78.45 percent accuracy under the standard long-horizon evaluation setting, and ablation analyses confirm that the hippocampus-inspired episodic memory subsystem plays a critical role in temporal reasoning.
MMPG: MoE-based Adaptive Multi-Perspective Graph Fusion for Protein Representation Learning
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have been widely adopted for Protein Representation Learning (PRL), as residue interaction networks can be naturally represented as graphs. Current GNN-based PRL methods typically rely on single-perspective graph construction strategies, which capture partial properties of residue interactions, resulting in incomplete protein representations. To address this limitation, we propose MMPG, a framework that constructs protein graphs from multiple perspectives and adaptively fuses them via Mixture of Experts (MoE) for PRL. MMPG constructs graphs from physical, chemical, and geometric perspectives to characterize different properties of residue interactions. To capture both perspective-specific features and their synergies, we develop an MoE module, which dynamically routes perspectives to specialized experts, where experts learn intrinsic features and cross-perspective interactions. We quantitatively verify that MoE automatically specializes experts in modeling distinct levels of interaction from individual representations, to pairwise inter-perspective synergies, and ultimately to a global consensus across all perspectives. Through integrating this multi-level information, MMPG produces superior protein representations and achieves advanced performance on four different downstream protein tasks.
CogniSNN: Enabling Neuron-Expandability, Pathway-Reusability, and Dynamic-Configurability with Random Graph Architectures in Spiking Neural Networks
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Spiking neural networks (SNNs), regarded as the third generation of artificial neural networks, are expected to bridge the gap between artificial intelligence and computational neuroscience. However, most mainstream SNN research directly adopts the rigid, chain-like hierarchical architecture of traditional artificial neural networks (ANNs), ignoring key structural characteristics of the brain. Biological neurons are stochastically interconnected, forming complex neural pathways that exhibit Neuron-Expandability, Pathway-Reusability, and Dynamic-Configurability. In this paper, we introduce a new SNN paradigm, named Cognition-aware SNN (CogniSNN), by incorporating Random Graph Architecture (RGA). Furthermore, we address the issues of network degradation and dimensional mismatch in deep pathways by introducing an improved pure spiking residual mechanism alongside an adaptive pooling strategy. Then, we design a Key Pathway-based Learning without Forgetting (KP-LwF) approach, which selectively reuses critical neural pathways while retaining historical knowledge, enabling efficient multi-task transfer. Finally, we propose a Dynamic Growth Learning (DGL) algorithm that allows neurons and synapses to grow dynamically along the internal temporal dimension. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CogniSNN achieves performance comparable to, or even surpassing, current state-of-the-art SNNs on neuromorphic datasets and Tiny-ImageNet. The Pathway-Reusability enhances the network's continuous learning capability across different scenarios, while the dynamic growth algorithm improves robustness against interference and mitigates the fixed-timestep constraints during neuromorphic chip deployment. This work demonstrates the potential of SNNs with random graph structures in advancing brain-inspired intelligence and lays the foundation for their practical application on neuromorphic hardware.
Self-Calibrated Consistency can Fight Back for Adversarial Robustness in Vision-Language Models
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) such as CLIP have demonstrated strong zero-shot capabilities across diverse domains, yet remain highly vulnerable to adversarial perturbations that disrupt image-text alignment and compromise reliability. Existing defenses typically rely on adversarial fine-tuning with labeled data, limiting their applicability in zero-shot settings. In this work, we identify two key weaknesses of current CLIP adversarial attacks -- lack of semantic guidance and vulnerability to view variations -- collectively termed semantic and viewpoint fragility. To address these challenges, we propose Self-Calibrated Consistency (SCC), an effective test-time defense. SCC consists of two complementary modules: Semantic consistency, which leverages soft pseudo-labels from counterattack warm-up and multi-view predictions to regularize cross-modal alignment and separate the target embedding from confusable negatives; and Spatial consistency, aligning perturbed visual predictions via augmented views to stabilize inference under adversarial perturbations. Together, these modules form a plug-and-play inference strategy. Extensive experiments on 22 benchmarks under diverse attack settings show that SCC consistently improves the zero-shot robustness of CLIP while maintaining accuracy, and can be seamlessly integrated with other VLMs for further gains. These findings highlight the great potential of establishing an adversarially robust paradigm from CLIP, with implications extending to broader vision-language domains such as BioMedCLIP.
Modest-Align: Data-Efficient Alignment for Vision-Language Models
Oct 24, 2025Abstract:Cross-modal alignment aims to map heterogeneous modalities into a shared latent space, as exemplified by models like CLIP, which benefit from large-scale image-text pretraining for strong recognition capabilities. However, when operating in resource-constrained settings with limited or low-quality data, these models often suffer from overconfidence and degraded performance due to the prevalence of ambiguous or weakly correlated image-text pairs. Current contrastive learning approaches, which rely on single positive pairs, further exacerbate this issue by reinforcing overconfidence on uncertain samples. To address these challenges, we propose Modest-Align, a lightweight alignment framework designed for robustness and efficiency. Our approach leverages two complementary strategies -- Random Perturbation, which introduces controlled noise to simulate uncertainty, and Embedding Smoothing, which calibrates similarity distributions in the embedding space. These mechanisms collectively reduce overconfidence and improve performance on noisy or weakly aligned samples. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that Modest-Align outperforms state-of-the-art methods in retrieval tasks, achieving competitive results with over 100x less training data and 600x less GPU time than CLIP. Our method offers a practical and scalable solution for cross-modal alignment in real-world, low-resource scenarios.
Beyond Classification Accuracy: Neural-MedBench and the Need for Deeper Reasoning Benchmarks
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in vision-language models (VLMs) have achieved remarkable performance on standard medical benchmarks, yet their true clinical reasoning ability remains unclear. Existing datasets predominantly emphasize classification accuracy, creating an evaluation illusion in which models appear proficient while still failing at high-stakes diagnostic reasoning. We introduce Neural-MedBench, a compact yet reasoning-intensive benchmark specifically designed to probe the limits of multimodal clinical reasoning in neurology. Neural-MedBench integrates multi-sequence MRI scans, structured electronic health records, and clinical notes, and encompasses three core task families: differential diagnosis, lesion recognition, and rationale generation. To ensure reliable evaluation, we develop a hybrid scoring pipeline that combines LLM-based graders, clinician validation, and semantic similarity metrics. Through systematic evaluation of state-of-the-art VLMs, including GPT-4o, Claude-4, and MedGemma, we observe a sharp performance drop compared to conventional datasets. Error analysis shows that reasoning failures, rather than perceptual errors, dominate model shortcomings. Our findings highlight the necessity of a Two-Axis Evaluation Framework: breadth-oriented large datasets for statistical generalization, and depth-oriented, compact benchmarks such as Neural-MedBench for reasoning fidelity. We release Neural-MedBench at https://neuromedbench.github.io/ as an open and extensible diagnostic testbed, which guides the expansion of future benchmarks and enables rigorous yet cost-effective assessment of clinically trustworthy AI.
CogniSNN: A First Exploration to Random Graph Architecture based Spiking Neural Networks with Enhanced Expandability and Neuroplasticity
May 09, 2025



Abstract:Despite advances in spiking neural networks (SNNs) in numerous tasks, their architectures remain highly similar to traditional artificial neural networks (ANNs), restricting their ability to mimic natural connections between biological neurons. This paper develops a new modeling paradigm for SNN with random graph architecture (RGA), termed Cognition-aware SNN (CogniSNN). Furthermore, we improve the expandability and neuroplasticity of CogniSNN by introducing a modified spiking residual neural node (ResNode) to counteract network degradation in deeper graph pathways, as well as a critical path-based algorithm that enables CogniSNN to perform continual learning on new tasks leveraging the features of the data and the RGA learned in the old task. Experiments show that CogniSNN with re-designed ResNode performs outstandingly in neuromorphic datasets with fewer parameters, achieving 95.5% precision in the DVS-Gesture dataset with only 5 timesteps. The critical path-based approach decreases 3% to 5% forgetting while maintaining expected performance in learning new tasks that are similar to or distinct from the old ones. This study showcases the potential of RGA-based SNN and paves a new path for biologically inspired networks based on graph theory.
An Integrated AI-Enabled System Using One Class Twin Cross Learning (OCT-X) for Early Gastric Cancer Detection
Mar 31, 2025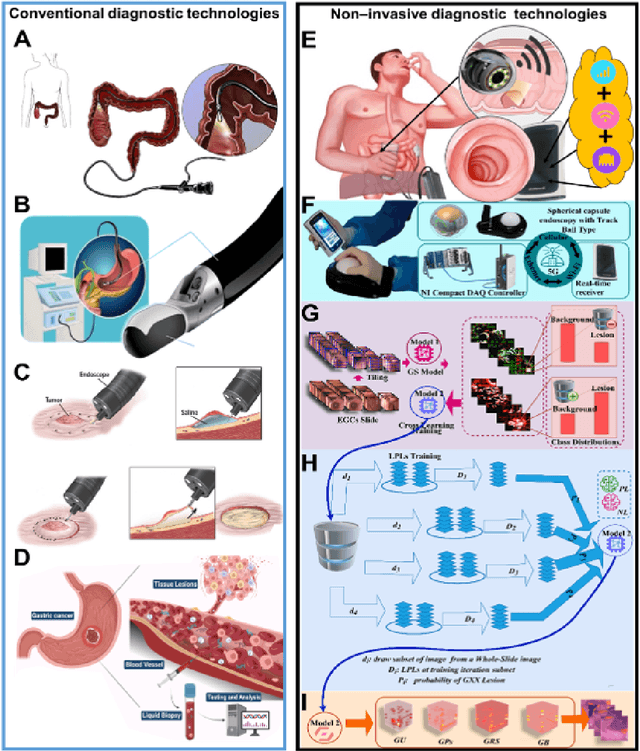
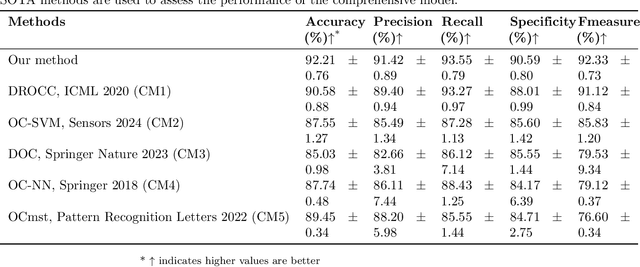
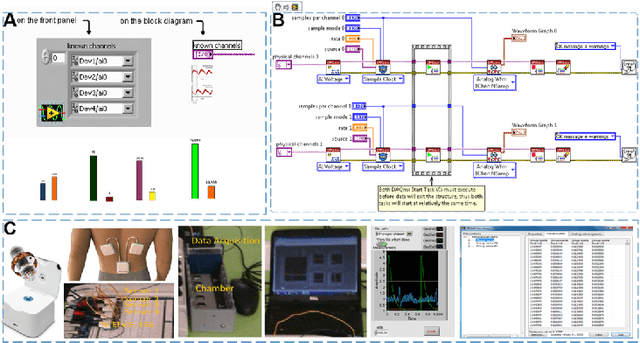
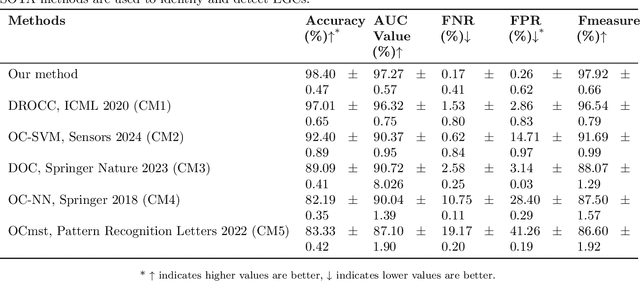
Abstract:Early detection of gastric cancer, a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, remains hampered by the limitations of current diagnostic technologies, leading to high rates of misdiagnosis and missed diagnoses. To address these challenges, we propose an integrated system that synergizes advanced hardware and software technologies to balance speed-accuracy. Our study introduces the One Class Twin Cross Learning (OCT-X) algorithm. Leveraging a novel fast double-threshold grid search strategy (FDT-GS) and a patch-based deep fully convolutional network, OCT-X maximizes diagnostic accuracy through real-time data processing and seamless lesion surveillance. The hardware component includes an all-in-one point-of-care testing (POCT) device with high-resolution imaging sensors, real-time data processing, and wireless connectivity, facilitated by the NI CompactDAQ and LabVIEW software. Our integrated system achieved an unprecedented diagnostic accuracy of 99.70%, significantly outperforming existing models by up to 4.47%, and demonstrated a 10% improvement in multirate adaptability. These findings underscore the potential of OCT-X as well as the integrated system in clinical diagnostics, offering a path toward more accurate, efficient, and less invasive early gastric cancer detection. Future research will explore broader applications, further advancing oncological diagnostics. Code is available at https://github.com/liu37972/Multirate-Location-on-OCT-X-Learning.git.
Interpretable Droplet Digital PCR Assay for Trustworthy Molecular Diagnostics
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:Accurate molecular quantification is essential for advancing research and diagnostics in fields such as infectious diseases, cancer biology, and genetic disorders. Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) has emerged as a gold standard for achieving absolute quantification. While computational ddPCR technologies have advanced significantly, achieving automatic interpretation and consistent adaptability across diverse operational environments remains a challenge. To address these limitations, we introduce the intelligent interpretable droplet digital PCR (I2ddPCR) assay, a comprehensive framework integrating front-end predictive models (for droplet segmentation and classification) with GPT-4o multimodal large language model (MLLM, for context-aware explanations and recommendations) to automate and enhance ddPCR image analysis. This approach surpasses the state-of-the-art models, affording 99.05% accuracy in processing complex ddPCR images containing over 300 droplets per image with varying signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs). By combining specialized neural networks and large language models, the I2ddPCR assay offers a robust and adaptable solution for absolute molecular quantification, achieving a sensitivity capable of detecting low-abundance targets as low as 90.32 copies/{\mu}L. Furthermore, it improves model's transparency through detailed explanation and troubleshooting guidance, empowering users to make informed decisions. This innovative framework has the potential to benefit molecular diagnostics, disease research, and clinical applications, especially in resource-constrained settings.
Multi-View Incremental Learning with Structured Hebbian Plasticity for Enhanced Fusion Efficiency
Dec 17, 2024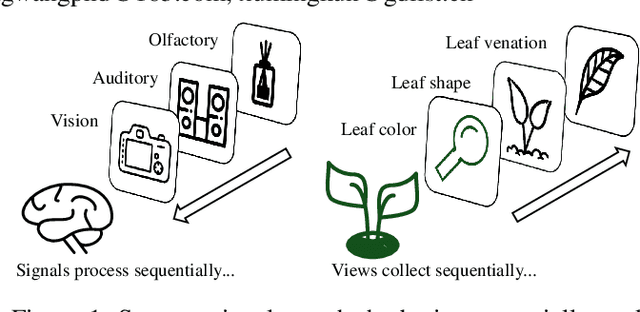

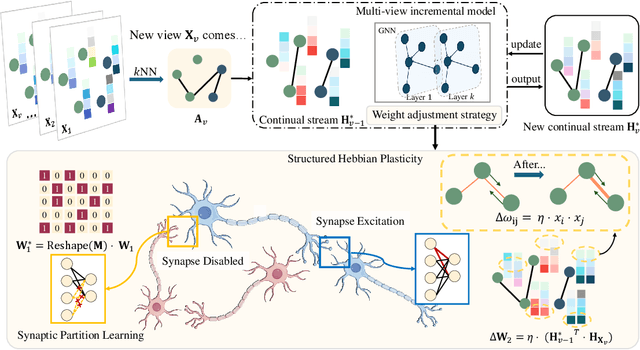

Abstract:The rapid evolution of multimedia technology has revolutionized human perception, paving the way for multi-view learning. However, traditional multi-view learning approaches are tailored for scenarios with fixed data views, falling short of emulating the intricate cognitive procedures of the human brain processing signals sequentially. Our cerebral architecture seamlessly integrates sequential data through intricate feed-forward and feedback mechanisms. In stark contrast, traditional methods struggle to generalize effectively when confronted with data spanning diverse domains, highlighting the need for innovative strategies that can mimic the brain's adaptability and dynamic integration capabilities. In this paper, we propose a bio-neurologically inspired multi-view incremental framework named MVIL aimed at emulating the brain's fine-grained fusion of sequentially arriving views. MVIL lies two fundamental modules: structured Hebbian plasticity and synaptic partition learning. The structured Hebbian plasticity reshapes the structure of weights to express the high correlation between view representations, facilitating a fine-grained fusion of view representations. Moreover, synaptic partition learning is efficient in alleviating drastic changes in weights and also retaining old knowledge by inhibiting partial synapses. These modules bionically play a central role in reinforcing crucial associations between newly acquired information and existing knowledge repositories, thereby enhancing the network's capacity for generalization. Experimental results on six benchmark datasets show MVIL's effectiveness over state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge