Shiping Wang
LargeMvC-Net: Anchor-based Deep Unfolding Network for Large-scale Multi-view Clustering
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Deep anchor-based multi-view clustering methods enhance the scalability of neural networks by utilizing representative anchors to reduce the computational complexity of large-scale clustering. Despite their scalability advantages, existing approaches often incorporate anchor structures in a heuristic or task-agnostic manner, either through post-hoc graph construction or as auxiliary components for message passing. Such designs overlook the core structural demands of anchor-based clustering, neglecting key optimization principles. To bridge this gap, we revisit the underlying optimization problem of large-scale anchor-based multi-view clustering and unfold its iterative solution into a novel deep network architecture, termed LargeMvC-Net. The proposed model decomposes the anchor-based clustering process into three modules: RepresentModule, NoiseModule, and AnchorModule, corresponding to representation learning, noise suppression, and anchor indicator estimation. Each module is derived by unfolding a step of the original optimization procedure into a dedicated network component, providing structural clarity and optimization traceability. In addition, an unsupervised reconstruction loss aligns each view with the anchor-induced latent space, encouraging consistent clustering structures across views. Extensive experiments on several large-scale multi-view benchmarks show that LargeMvC-Net consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of both effectiveness and scalability.
Simplifying Graph Convolutional Networks with Redundancy-Free Neighbors
Apr 21, 2025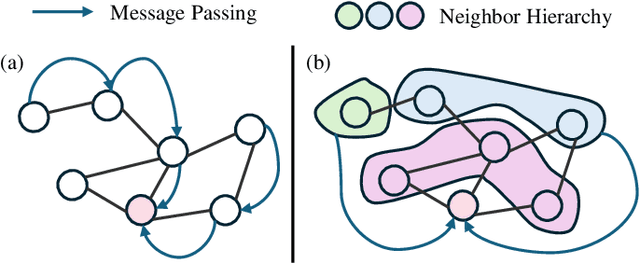
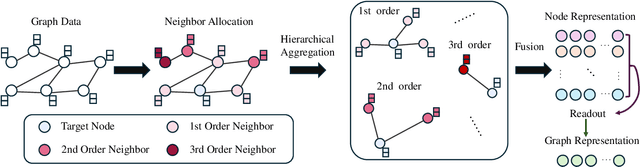
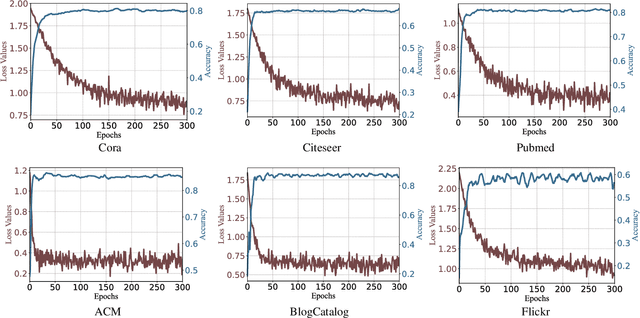
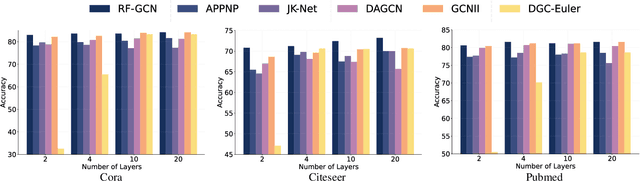
Abstract:In recent years, Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) have gained popularity for their exceptional ability to process graph-structured data. Existing GCN-based approaches typically employ a shallow model architecture due to the over-smoothing phenomenon. Current approaches to mitigating over-smoothing primarily involve adding supplementary components to GCN architectures, such as residual connections and random edge-dropping strategies. However, these improvements toward deep GCNs have achieved only limited success. In this work, we analyze the intrinsic message passing mechanism of GCNs and identify a critical issue: messages originating from high-order neighbors must traverse through low-order neighbors to reach the target node. This repeated reliance on low-order neighbors leads to redundant information aggregation, a phenomenon we term over-aggregation. Our analysis demonstrates that over-aggregation not only introduces significant redundancy but also serves as the fundamental cause of over-smoothing in GCNs.
Multi-View Incremental Learning with Structured Hebbian Plasticity for Enhanced Fusion Efficiency
Dec 17, 2024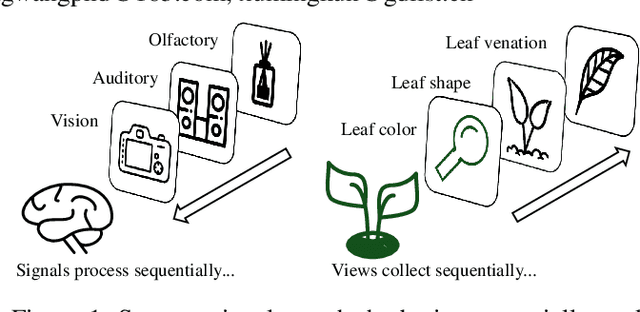

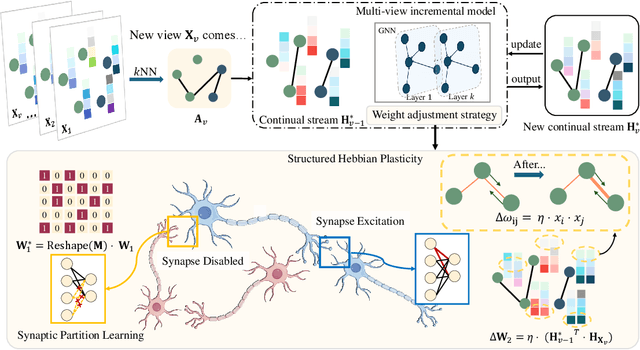

Abstract:The rapid evolution of multimedia technology has revolutionized human perception, paving the way for multi-view learning. However, traditional multi-view learning approaches are tailored for scenarios with fixed data views, falling short of emulating the intricate cognitive procedures of the human brain processing signals sequentially. Our cerebral architecture seamlessly integrates sequential data through intricate feed-forward and feedback mechanisms. In stark contrast, traditional methods struggle to generalize effectively when confronted with data spanning diverse domains, highlighting the need for innovative strategies that can mimic the brain's adaptability and dynamic integration capabilities. In this paper, we propose a bio-neurologically inspired multi-view incremental framework named MVIL aimed at emulating the brain's fine-grained fusion of sequentially arriving views. MVIL lies two fundamental modules: structured Hebbian plasticity and synaptic partition learning. The structured Hebbian plasticity reshapes the structure of weights to express the high correlation between view representations, facilitating a fine-grained fusion of view representations. Moreover, synaptic partition learning is efficient in alleviating drastic changes in weights and also retaining old knowledge by inhibiting partial synapses. These modules bionically play a central role in reinforcing crucial associations between newly acquired information and existing knowledge repositories, thereby enhancing the network's capacity for generalization. Experimental results on six benchmark datasets show MVIL's effectiveness over state-of-the-art methods.
OpenViewer: Openness-Aware Multi-View Learning
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Multi-view learning methods leverage multiple data sources to enhance perception by mining correlations across views, typically relying on predefined categories. However, deploying these models in real-world scenarios presents two primary openness challenges. 1) Lack of Interpretability: The integration mechanisms of multi-view data in existing black-box models remain poorly explained; 2) Insufficient Generalization: Most models are not adapted to multi-view scenarios involving unknown categories. To address these challenges, we propose OpenViewer, an openness-aware multi-view learning framework with theoretical support. This framework begins with a Pseudo-Unknown Sample Generation Mechanism to efficiently simulate open multi-view environments and previously adapt to potential unknown samples. Subsequently, we introduce an Expression-Enhanced Deep Unfolding Network to intuitively promote interpretability by systematically constructing functional prior-mapping modules and effectively providing a more transparent integration mechanism for multi-view data. Additionally, we establish a Perception-Augmented Open-Set Training Regime to significantly enhance generalization by precisely boosting confidences for known categories and carefully suppressing inappropriate confidences for unknown ones. Experimental results demonstrate that OpenViewer effectively addresses openness challenges while ensuring recognition performance for both known and unknown samples. The code is released at https://github.com/dushide/OpenViewer.
ADEdgeDrop: Adversarial Edge Dropping for Robust Graph Neural Networks
Mar 14, 2024
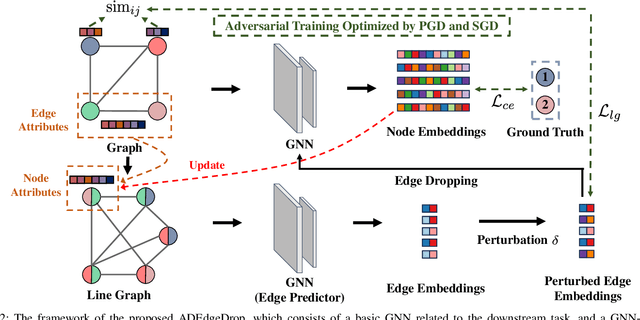

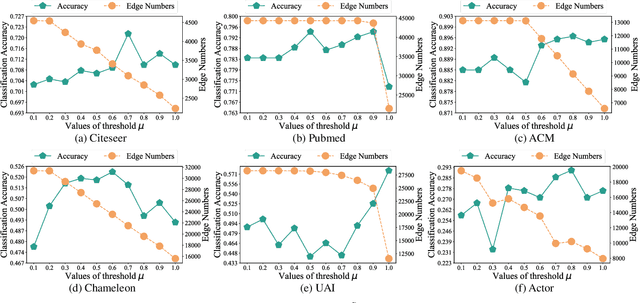
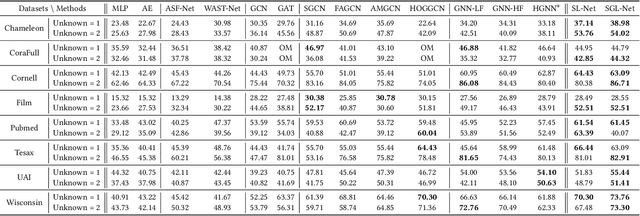
Abstract:Although Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have exhibited the powerful ability to gather graph-structured information from neighborhood nodes via various message-passing mechanisms, the performance of GNNs is limited by poor generalization and fragile robustness caused by noisy and redundant graph data. As a prominent solution, Graph Augmentation Learning (GAL) has recently received increasing attention. Among prior GAL approaches, edge-dropping methods that randomly remove edges from a graph during training are effective techniques to improve the robustness of GNNs. However, randomly dropping edges often results in bypassing critical edges, consequently weakening the effectiveness of message passing. In this paper, we propose a novel adversarial edge-dropping method (ADEdgeDrop) that leverages an adversarial edge predictor guiding the removal of edges, which can be flexibly incorporated into diverse GNN backbones. Employing an adversarial training framework, the edge predictor utilizes the line graph transformed from the original graph to estimate the edges to be dropped, which improves the interpretability of the edge-dropping method. The proposed ADEdgeDrop is optimized alternately by stochastic gradient descent and projected gradient descent. Comprehensive experiments on six graph benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed ADEdgeDrop outperforms state-of-the-art baselines across various GNN backbones, demonstrating improved generalization and robustness.
MuseGraph: Graph-oriented Instruction Tuning of Large Language Models for Generic Graph Mining
Mar 13, 2024Abstract:Graphs with abundant attributes are essential in modeling interconnected entities and improving predictions in various real-world applications. Traditional Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), which are commonly used for modeling attributed graphs, need to be re-trained every time when applied to different graph tasks and datasets. Although the emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has introduced a new paradigm in natural language processing, the generative potential of LLMs in graph mining remains largely under-explored. To this end, we propose a novel framework MuseGraph, which seamlessly integrates the strengths of GNNs and LLMs and facilitates a more effective and generic approach for graph mining across different tasks and datasets. Specifically, we first introduce a compact graph description via the proposed adaptive input generation to encapsulate key information from the graph under the constraints of language token limitations. Then, we propose a diverse instruction generation mechanism, which distills the reasoning capabilities from LLMs (e.g., GPT-4) to create task-specific Chain-of-Thought-based instruction packages for different graph tasks. Finally, we propose a graph-aware instruction tuning with a dynamic instruction package allocation strategy across tasks and datasets, ensuring the effectiveness and generalization of the training process. Our experimental results demonstrate significant improvements in different graph tasks, showcasing the potential of our MuseGraph in enhancing the accuracy of graph-oriented downstream tasks while keeping the generation powers of LLMs.
BCLNet: Bilateral Consensus Learning for Two-View Correspondence Pruning
Jan 07, 2024Abstract:Correspondence pruning aims to establish reliable correspondences between two related images and recover relative camera motion. Existing approaches often employ a progressive strategy to handle the local and global contexts, with a prominent emphasis on transitioning from local to global, resulting in the neglect of interactions between different contexts. To tackle this issue, we propose a parallel context learning strategy that involves acquiring bilateral consensus for the two-view correspondence pruning task. In our approach, we design a distinctive self-attention block to capture global context and parallel process it with the established local context learning module, which enables us to simultaneously capture both local and global consensuses. By combining these local and global consensuses, we derive the required bilateral consensus. We also design a recalibration block, reducing the influence of erroneous consensus information and enhancing the robustness of the model. The culmination of our efforts is the Bilateral Consensus Learning Network (BCLNet), which efficiently estimates camera pose and identifies inliers (true correspondences). Extensive experiments results demonstrate that our network not only surpasses state-of-the-art methods on benchmark datasets but also showcases robust generalization abilities across various feature extraction techniques. Noteworthily, BCLNet obtains 3.98\% mAP5$^{\circ}$ gains over the second best method on unknown outdoor dataset, and obviously accelerates model training speed. The source code will be available at: https://github.com/guobaoxiao/BCLNet.
Graph Context Transformation Learning for Progressive Correspondence Pruning
Dec 26, 2023
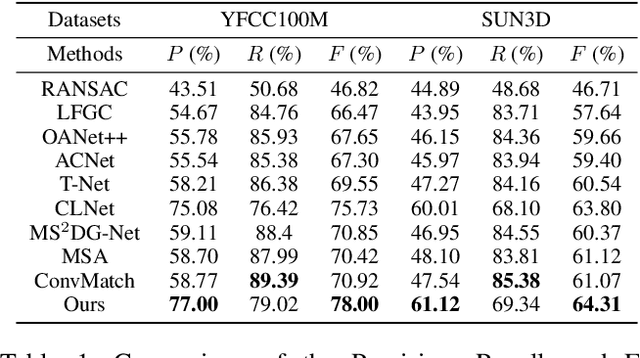
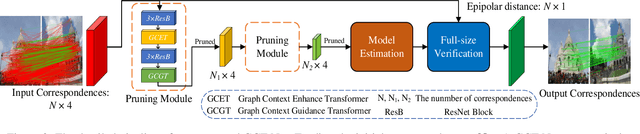
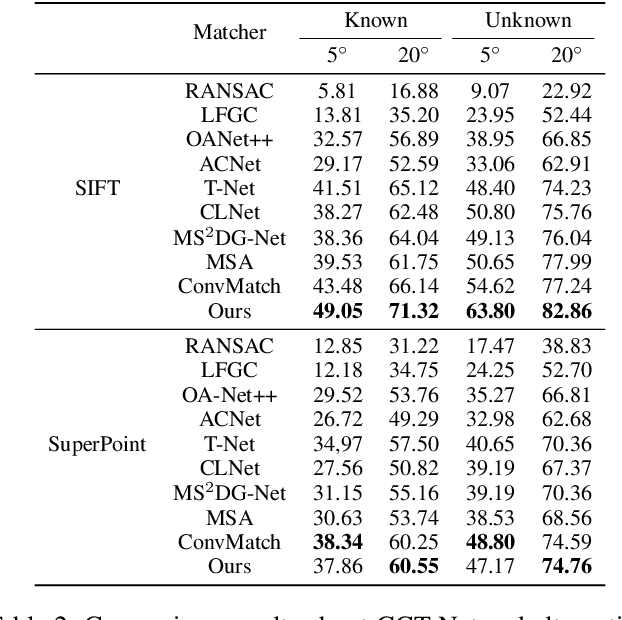
Abstract:Most of existing correspondence pruning methods only concentrate on gathering the context information as much as possible while neglecting effective ways to utilize such information. In order to tackle this dilemma, in this paper we propose Graph Context Transformation Network (GCT-Net) enhancing context information to conduct consensus guidance for progressive correspondence pruning. Specifically, we design the Graph Context Enhance Transformer which first generates the graph network and then transforms it into multi-branch graph contexts. Moreover, it employs self-attention and cross-attention to magnify characteristics of each graph context for emphasizing the unique as well as shared essential information. To further apply the recalibrated graph contexts to the global domain, we propose the Graph Context Guidance Transformer. This module adopts a confident-based sampling strategy to temporarily screen high-confidence vertices for guiding accurate classification by searching global consensus between screened vertices and remaining ones. The extensive experimental results on outlier removal and relative pose estimation clearly demonstrate the superior performance of GCT-Net compared to state-of-the-art methods across outdoor and indoor datasets. The source code will be available at: https://github.com/guobaoxiao/GCT-Net/.
Bridging Trustworthiness and Open-World Learning: An Exploratory Neural Approach for Enhancing Interpretability, Generalization, and Robustness
Aug 07, 2023
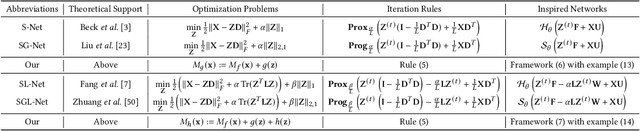
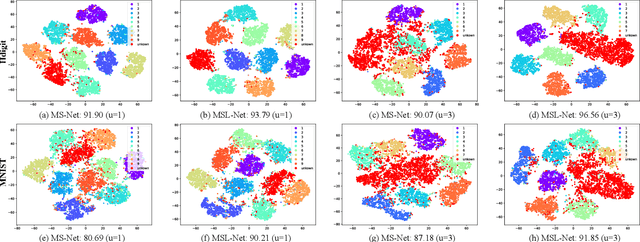
Abstract:As researchers strive to narrow the gap between machine intelligence and human through the development of artificial intelligence technologies, it is imperative that we recognize the critical importance of trustworthiness in open-world, which has become ubiquitous in all aspects of daily life for everyone. However, several challenges may create a crisis of trust in current artificial intelligence systems that need to be bridged: 1) Insufficient explanation of predictive results; 2) Inadequate generalization for learning models; 3) Poor adaptability to uncertain environments. Consequently, we explore a neural program to bridge trustworthiness and open-world learning, extending from single-modal to multi-modal scenarios for readers. 1) To enhance design-level interpretability, we first customize trustworthy networks with specific physical meanings; 2) We then design environmental well-being task-interfaces via flexible learning regularizers for improving the generalization of trustworthy learning; 3) We propose to increase the robustness of trustworthy learning by integrating open-world recognition losses with agent mechanisms. Eventually, we enhance various trustworthy properties through the establishment of design-level explainability, environmental well-being task-interfaces and open-world recognition programs. These designed open-world protocols are applicable across a wide range of surroundings, under open-world multimedia recognition scenarios with significant performance improvements observed.
Attributed Multi-order Graph Convolutional Network for Heterogeneous Graphs
Apr 18, 2023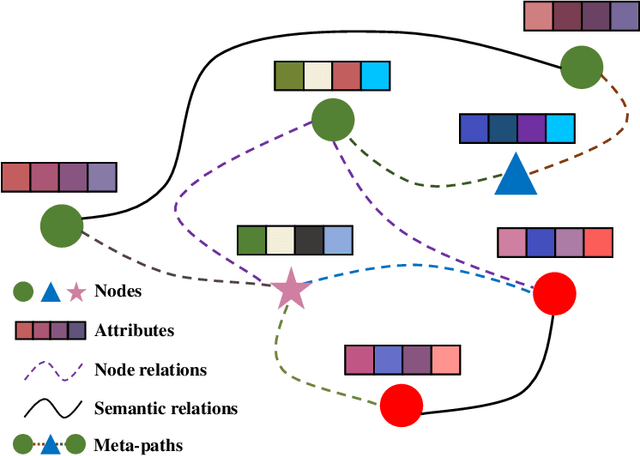
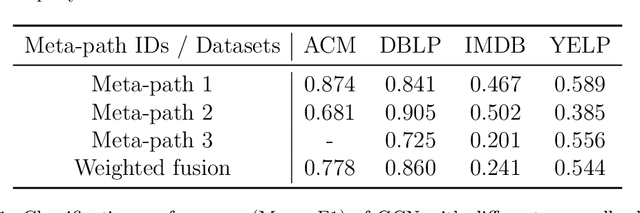
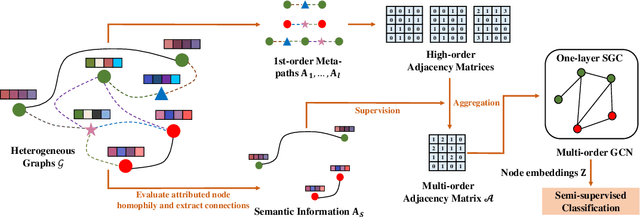
Abstract:Heterogeneous graph neural networks aim to discover discriminative node embeddings and relations from multi-relational networks.One challenge of heterogeneous graph learning is the design of learnable meta-paths, which significantly influences the quality of learned embeddings.Thus, in this paper, we propose an Attributed Multi-Order Graph Convolutional Network (AMOGCN), which automatically studies meta-paths containing multi-hop neighbors from an adaptive aggregation of multi-order adjacency matrices. The proposed model first builds different orders of adjacency matrices from manually designed node connections. After that, an intact multi-order adjacency matrix is attached from the automatic fusion of various orders of adjacency matrices. This process is supervised by the node semantic information, which is extracted from the node homophily evaluated by attributes. Eventually, we utilize a one-layer simplifying graph convolutional network with the learned multi-order adjacency matrix, which is equivalent to the cross-hop node information propagation with multi-layer graph neural networks. Substantial experiments reveal that AMOGCN gains superior semi-supervised classification performance compared with state-of-the-art competitors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge