Shide Du
LargeMvC-Net: Anchor-based Deep Unfolding Network for Large-scale Multi-view Clustering
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Deep anchor-based multi-view clustering methods enhance the scalability of neural networks by utilizing representative anchors to reduce the computational complexity of large-scale clustering. Despite their scalability advantages, existing approaches often incorporate anchor structures in a heuristic or task-agnostic manner, either through post-hoc graph construction or as auxiliary components for message passing. Such designs overlook the core structural demands of anchor-based clustering, neglecting key optimization principles. To bridge this gap, we revisit the underlying optimization problem of large-scale anchor-based multi-view clustering and unfold its iterative solution into a novel deep network architecture, termed LargeMvC-Net. The proposed model decomposes the anchor-based clustering process into three modules: RepresentModule, NoiseModule, and AnchorModule, corresponding to representation learning, noise suppression, and anchor indicator estimation. Each module is derived by unfolding a step of the original optimization procedure into a dedicated network component, providing structural clarity and optimization traceability. In addition, an unsupervised reconstruction loss aligns each view with the anchor-induced latent space, encouraging consistent clustering structures across views. Extensive experiments on several large-scale multi-view benchmarks show that LargeMvC-Net consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of both effectiveness and scalability.
Focus on Local: Finding Reliable Discriminative Regions for Visual Place Recognition
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Visual Place Recognition (VPR) is aimed at predicting the location of a query image by referencing a database of geotagged images. For VPR task, often fewer discriminative local regions in an image produce important effects while mundane background regions do not contribute or even cause perceptual aliasing because of easy overlap. However, existing methods lack precisely modeling and full exploitation of these discriminative regions. In this paper, we propose the Focus on Local (FoL) approach to stimulate the performance of image retrieval and re-ranking in VPR simultaneously by mining and exploiting reliable discriminative local regions in images and introducing pseudo-correlation supervision. First, we design two losses, Extraction-Aggregation Spatial Alignment Loss (SAL) and Foreground-Background Contrast Enhancement Loss (CEL), to explicitly model reliable discriminative local regions and use them to guide the generation of global representations and efficient re-ranking. Second, we introduce a weakly-supervised local feature training strategy based on pseudo-correspondences obtained from aggregating global features to alleviate the lack of local correspondences ground truth for the VPR task. Third, we suggest an efficient re-ranking pipeline that is efficiently and precisely based on discriminative region guidance. Finally, experimental results show that our FoL achieves the state-of-the-art on multiple VPR benchmarks in both image retrieval and re-ranking stages and also significantly outperforms existing two-stage VPR methods in terms of computational efficiency. Code and models are available at https://github.com/chenshunpeng/FoL
OpenViewer: Openness-Aware Multi-View Learning
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Multi-view learning methods leverage multiple data sources to enhance perception by mining correlations across views, typically relying on predefined categories. However, deploying these models in real-world scenarios presents two primary openness challenges. 1) Lack of Interpretability: The integration mechanisms of multi-view data in existing black-box models remain poorly explained; 2) Insufficient Generalization: Most models are not adapted to multi-view scenarios involving unknown categories. To address these challenges, we propose OpenViewer, an openness-aware multi-view learning framework with theoretical support. This framework begins with a Pseudo-Unknown Sample Generation Mechanism to efficiently simulate open multi-view environments and previously adapt to potential unknown samples. Subsequently, we introduce an Expression-Enhanced Deep Unfolding Network to intuitively promote interpretability by systematically constructing functional prior-mapping modules and effectively providing a more transparent integration mechanism for multi-view data. Additionally, we establish a Perception-Augmented Open-Set Training Regime to significantly enhance generalization by precisely boosting confidences for known categories and carefully suppressing inappropriate confidences for unknown ones. Experimental results demonstrate that OpenViewer effectively addresses openness challenges while ensuring recognition performance for both known and unknown samples. The code is released at https://github.com/dushide/OpenViewer.
Bridging Trustworthiness and Open-World Learning: An Exploratory Neural Approach for Enhancing Interpretability, Generalization, and Robustness
Aug 07, 2023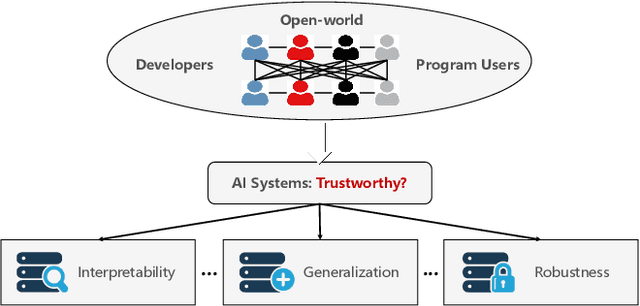
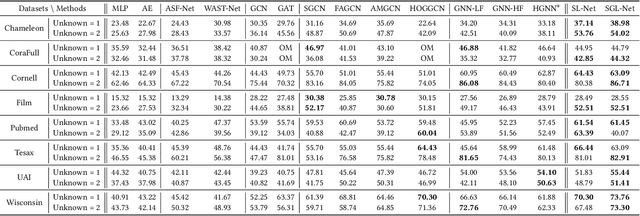
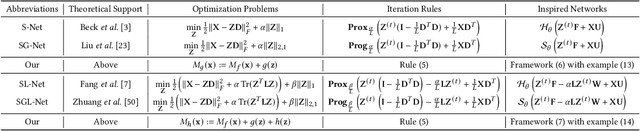
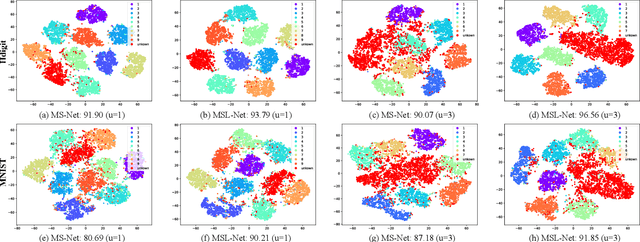
Abstract:As researchers strive to narrow the gap between machine intelligence and human through the development of artificial intelligence technologies, it is imperative that we recognize the critical importance of trustworthiness in open-world, which has become ubiquitous in all aspects of daily life for everyone. However, several challenges may create a crisis of trust in current artificial intelligence systems that need to be bridged: 1) Insufficient explanation of predictive results; 2) Inadequate generalization for learning models; 3) Poor adaptability to uncertain environments. Consequently, we explore a neural program to bridge trustworthiness and open-world learning, extending from single-modal to multi-modal scenarios for readers. 1) To enhance design-level interpretability, we first customize trustworthy networks with specific physical meanings; 2) We then design environmental well-being task-interfaces via flexible learning regularizers for improving the generalization of trustworthy learning; 3) We propose to increase the robustness of trustworthy learning by integrating open-world recognition losses with agent mechanisms. Eventually, we enhance various trustworthy properties through the establishment of design-level explainability, environmental well-being task-interfaces and open-world recognition programs. These designed open-world protocols are applicable across a wide range of surroundings, under open-world multimedia recognition scenarios with significant performance improvements observed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge